CPH EXAM Definitions
1/498
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
499 Terms
Attributable risk
Rate of disease in exposed individuals that can be attributed to the exposure. Or the proportion of all cases that can be attributed to a particular exposure.
Adjusted rate
Effects of differences in composition of pops being compared have been minimized by statistical methods.
ex: regression analysis and strandardization
-often used on rates or relative risks
Ecological Fallacy
Bias that may occur because an association observed between variables or an aggregate level does not represent the association that exists at an individual level
Confidence Interval
95% confident that the true value of a variable is contained within the interval.
-used to account for sampling variability
-it is a point estimate +_ margin of error, where the point estimate is the best estimate of teh unknown parameter and the margin of error is the product of the confidence level and the standard error.
if a 95% CI for the differences in mean does not include 0 (the null value) then there is eveidence of a statistically significant difference at sigma=0.05
Clinical Trial Phases
1. Safety and Pharmacologic profiles
2. pilot efficacy studies
3. extensive clinical trials
4. after the FDA approves, look at specific effects to establish incidence of adverse reactions, etc. longterm use effects.
interpretation of studies
temporality: cause precedes effect
Specificity: important in assessing the possibility of biases.
Consistency: several studies showing similar results. homogeneity statistically.
Confounders
-non-causal association between exposure and outcome as a result of a third variable.
-distortion of effect by other factors
-must be related to exposure AND outcome
-not an intermediate variable on causal pathway
Controlling for confounders
before data collection: random collection, individual matching, frequency matching
After data collection: direct adjustment, indirect adjustment, mantel-haenszel, regression techniques
Quality Assurance vs. Quality Control
QA: ensure quality before data collection
QC: monitor and maintain quality during study
reliability vs. validity
R: precision, reproducibility
V: accuracy, absence of bias
systematic error
(lack of validity) if there's a difference between what is actually being estimated and what is intended to be measured. Increasing sample size doesn't help.
Random Error
(lack of precision) occurs, but increasing sample size helps.
RCT studies
Tests efficacy or effectiveness of healthcare services. random allocation of participants to different treatments. Includes blinding, placebo. gold standard for evidence.
Community Intervention/cluster RCT
community-wide basis or groupwide
Case-Crossover RCT design
-cases serve as their own control
-exposure has transient effect
Cross Sectional Studies
SNAPSHOT! at a single point in time. tells the prevalence and association. causation cannot be implied. a study that examines the relationship between diseases and other variables as they exist in a defined population at one particular time.
Matching
used to make cases and controls as similar as possible to avoid confounding. ex: race, gender, age. +Maybe the only way to control confounding. increases statistical power, straightforward. -requires use of special analytical techniques, residual confounding can occur if you match continuous variables by category.
types of matching
individual matching: case and control matched individually
frequency matching: a group of controls
Minimum Euclidean Distance measure: match to closest person.
Cohort Studies
RISK RATIO, RELATIVE RISK, INCIDENCE RATE, RATE RATIO
-rare exposures
-group of subjects who shared experiences during a particular time. Determines if incidence is related to exposure.
Concurrent/longitudinal cohort studies
starts now (with a baseline exam) and goes into future. expensive and time intensive.
non-concurrent/retrospective cohort studies
assembled in past based on existing records. faster and quicker, but records can be limited or biased. follow up can be hard.
Prevalence of disease
measure of the burden of disease in a community (new and existing cases). the number of events in a given population at a designated time.
-obscures causal relationships
point prevalence
-proportion of pop that is diseased during a single point of time.
-at a specific point in time
number of cases at a particular moment/
number in population at that moment
period prevalence
-proportion of pop that is diseased during a specified duration of time.
-during a specific period of time
number of cases during a specified time period/
number in population at midpoint of period
incidence of disease
measure of risk (new cases)
the rate at which people without a disease develop the disease during a specific period of time.
#of new cases over a period of time/
population @ risk of the disease in that time
incidence rate (also incidence density)
CASES OF DISEASE/PERSON-TIME AT RISK
TIME is important.
-it shows greater accuracy, but is hard to calculate.
-used for causal research
Incidence Proportion
CASES OF DISEASE/PERSONS AT RISK
cumulative risk/average risk
the proportion of a group of people who experience the onset of a health-related event during a specified time interval.
Incidence Odds
CASES OF DISEASE/SURVIVORS
Ratio of people who experience outcome to ratio of people who no not experience outcome.
Rate Ratio
ratio of incidence rate in the exposed group to the non-exposed group
Risk Ratio
-measures the increased risk for developing a disease after being exposed to a risk factor compared to not being exposed to the risk factor.
RR= risk for the exposed/
risk for the unexposed
-often referred to as "relative risk"
Odds Ratio
Ratio of incidence odds in exposed group to non-exposed group.
[p1/(1/p1)]/[p2/(1/p2)]
OR: ad/bc
exposed not exposed
cases a b
controls c d
Information Bias (also observational bias)
systematic error/flaw due to incorrect definition, measurement, or classification that results in reduced quality (accuracy)
Ex: false positives/negatives or errors in death records.
Differential Information Bias
Probability of cases vs. non-cases of misclassification is different.
Non-Differential Information Bias
Probability of cases vs. non-cases of misclassification is NOT different.
Selection Bias
When sample/participants aren't representative. how to avoid: control confounders and choose good comparison group.
power
-the ability to reject the null hypothesis when the null is in fact false.
-probability of detecting a difference if one truly exists. 1-beta= probability of declaring a difference not statistically significant when a difference truly exists.
Type 1 Error
reject the null hypothesis when it is true
alpha or
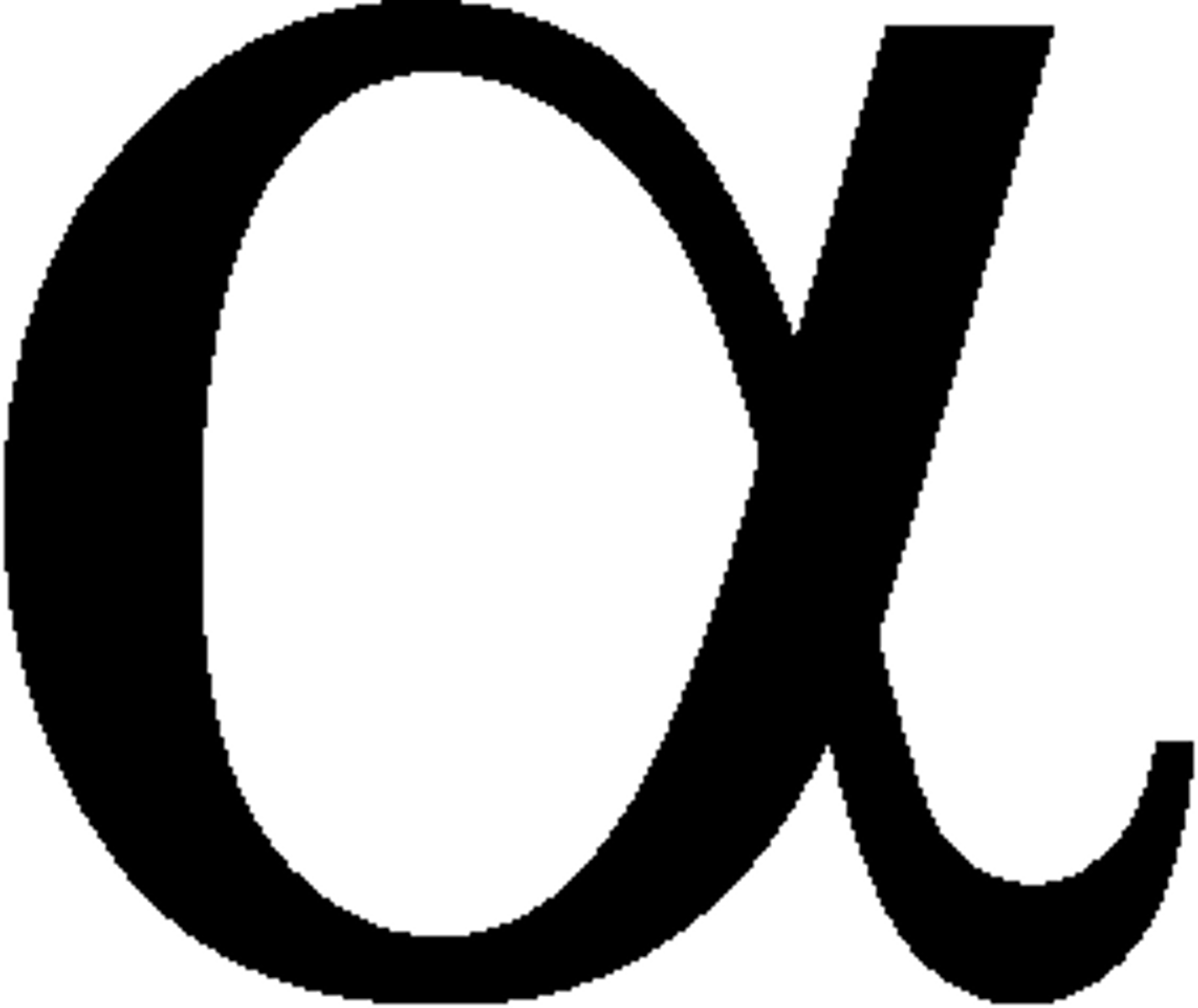
Type 11 Error
fail to reject the null hypothesis when it is false
beta
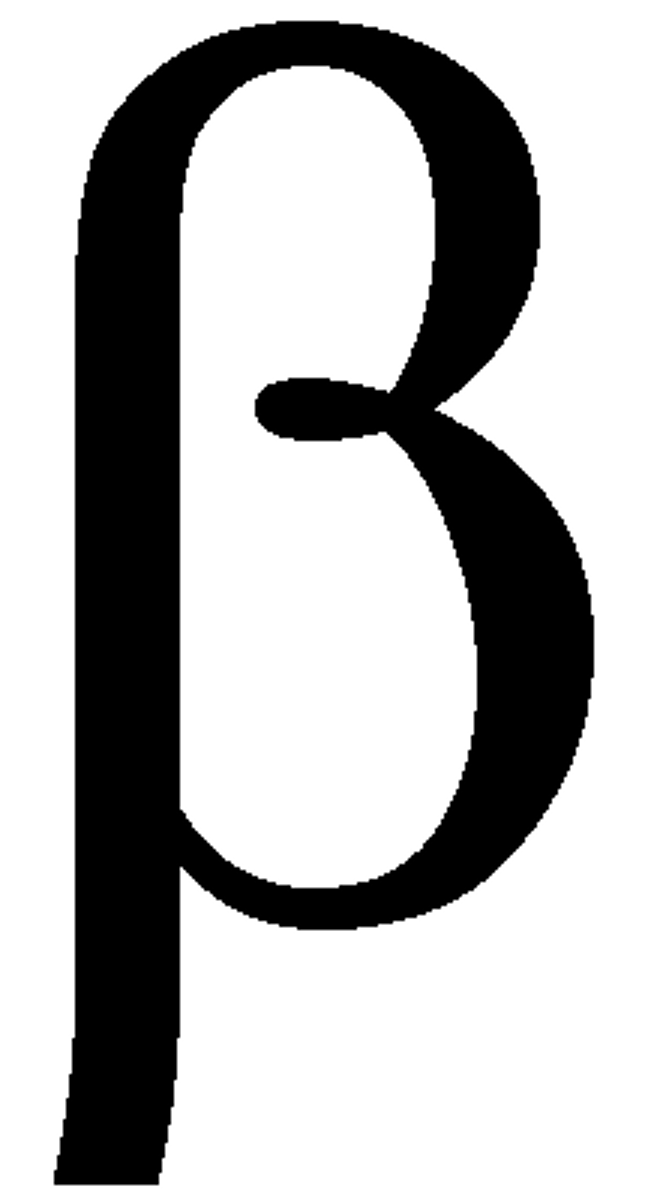
aggregate data
vital stats, data from govt databases, summaries from reporting systems, production and sales data, group-level. COMBINED
individual level data
questionnaires, medical records, national surveys, biological specimens
Stages of disease prevention
Primary, secondary, tertiary
Primary Disease Prevention
Prevent it from occurring (vaccines)
Secondary Disease Prevention
Modify severity (better access to ER)
Tertiary Disease Prevention
Rehabilitation. measures to prevent reoccurrence of disease
Rate of Disease
how fast is the disease occurring in the population
Proportion of Disease
What fraction of the population is affected?
Case Fatality (CF) or Fatality Rate
Measures of the severity of disease.
9 deaths per 10,000/1 year
Within a given year, out of 10,000 people diagnosed with a disease, 9 died.
Secondary Attack Rate (person-to-person spread)
# of persons sick by the primary case/# exposed to primary case
Attack Rate
# of people at risk who develop disease /# of people at risk
Outbreak investigation steps
1. define epidemic
2. look for the time-place interaction of cases
3. look for combination of variables
4. Develop hypothesis
5. Recommend control measures
Common Source Outbreaks
groups of persons exposed to common agent
Propagated Outbreaks
spreads gradually from person to person
Mixed epidemic Outbreaks
both common source and person to person exposure
Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs)
toxic chemicals that persist in the environment for long periods of time. adverse effects on humans and animals. circulates globally.
organophosphates
pesticides that contain phosphorus. short lived. toxic when first applied.
Mutagen
agent that causes a permanent genetic change outside of normal growth.
mutagenicity
capacity to cause permanent genetic change
MRSA
bacterial strains. resistent to antibiotics. benign colonizers of the skin. may cause severe infections.
Morbidity
rate of disease, incidence. HOW MANY PEOPLE ARE SICK
Mortality
death rate. PEOPLE WHO HAVE DIED.
Metabolism
conversion or breakdown of a substance from one form to another by a living organism
metabolites
substance produced by biological processes
metabolomics
use of genomic information to facilitate studies of metabolic processes.
Latency
time from 1st exposure until the appearence of a toxic effect.
IRIS (integrated risk information system)
descriptive, quantitative regulatory information on chemicals. health professionals not experts.
Incidence
# of new cases in a defined population over a specific time period.
hydrophilic
strong affinity for water
hydrophobic
strong aversion for water
helminths
group of parasites that infect humans (Schistosoma haematobium) cestodes: beef and pork tapeworms
HACCP (hazard analysis and critical control points)
production control system for the food industry. identifies potential contamination and then strictly manages and monitors points. designed to prevent rather than catch.
gray (Gy)
international system unit of absorbed dose
exposure-dose reconstruction
method of estimating the amount of past exposures to hazardous substances. computers and approximation methods can be used when info is missing or limited.
EPCRA (emergency planning and community right-to-know act)
requirements for federal, stat and local govts regarding emergency planning and CRTK reporting on hazardous and toxic chemicals.
-triggered by Bhopal, India 2,000 people died by release of methyl isocyanate.
ED50
dose of drug that is pharmacologically effective for 50% of the population.
disease vector
intermediate host for parasites. required for development. delivers parasite to subsequent hosts.
ex: schistosoma
Curie
basic unit to describe the intensity of radioactivity in a sample of material.
cryptosporidium
microbe that is transmitted through water and person-to-person contact. causes acute diarrhea, stomach pain, vomiting, fever.
-milwaukee episode, largest waterborne disease outbreak.
Criteria Pollutants
1970 ammendment to Clean Air Act. required EPA to set standards for 6 pollutants.
ozone, carbon monoxide, total suspended particles, sulfurdioxide, lead, nitrogenoxide.
Comparison value
the calculated concentration of a substance in air, food, or soil that is unlikely to cause harm. used as a screening level during assessment process.
Command and Control
regulates how activities need to be carried out. compliance monitoring and sanctions of trespasses. CONS: inflexibility, not adaptable, no incentive for reaching higher.
CBRNE incidents
deliberate malicious acts with the intention of killing others and disrupting society.
CHEMICAL, BIOLOGICAL, RADIOACTIVE, NUCLEAR, EXPLOSIVE.
Temporality
The cause must precede the effect
Specificity
-the proportion of truly nondiseased persons who are so identified by the screening test.
-Specificity of the effect is important in assessing possibility of biases
true negatives/disease free population
D/B+D
"of those who do not have disease, __% will test negative."
Interaction
This occurs when the incidence of disease in the presence of two or more risk factors differs from the incidence expected to result from their individual effects
Epidemiology's basic ethical principles
1. respect for people
2. Beneficence (do not harm)
3. Justice
Applications of Epidemiology's basic ethical principles
1. informed consent
2. assessment of risk and benefit
3. selection of subjects
Tuskegee Syphilis Experiment
A clinical study conducted between 1932 and 1972 in Tuskegee, Alabama by The U.S. Public Health Service. 399 impoverished African American sharecroppers with syphilis were recruited for research related to the natural progression of the untreated disease. After penicillin was discovered as a cure, researchers continued to deny such treatments to medical participants for another 25 years. Many patients were lied to and given placebo treatments so researchers could observe the progression of the fatal disease. This study led to the 1979 Belmont Report and establishment of the Office for Human Research Protection (OHRP). In 1974, Congress passed the National Research Act and created a commission to study and write regulations governing studies involving human participants.
Accuracy
The degree to which a measurement or an estimate based on measurements represents the true value of the attribute that is being measured.
Acute Disease
a health effect with sudden onset, often brief. sometimes used to mean severe.
adjusted rate
a rate in which the effects of differences in composition of the populations being compared have been minimized by statistical measures.
Association
statistical dependence between two or more events, characteristics or other variables.
attack rate
the cumulative incidence of infection in a group observed over a period during an epidemic.
Crude rate
a summary rate based on the actual number of events in a population over a given time period.
death rate
an estimate of the portion of a population that dies during a specific period.
#of people dying /population
Ecologic study
a study in which the units of analysis are populations or groups of people rather than individuals.
etiology
the science of causes, causality.
Hawthorne Effect
The effect of knowing that you're being studied influences behavior.
healthy worker effect
workers usually exhibit lower overall death rates than the general population because chronically ill are bared from employment.
index case
the first case in a family or other defined group to come to the attention of the investigator
induction period
the period required for a specific cause to produce disease. the interval from the causal action of a factor to the initiation of the disease.