Exam 2 evolution terms
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Homeotic
Genes that regulate spatial and temporal patterning
Homeotic loci
Genes of large effect
Homeotic gene complexes
Code for transcription factors that regulate expression of other genes
Colinearity
the linear arrangement of genes on a chromosome, where the order of nucleotides in a gene directly corresponds to the order of amino acids in the protein it encodes
What are the three parts of the tetrapod limbs
Stylopod, zeugopod, autopod
What was the first organism to show signs of terrestrial limbs?
Panderichthyidae
Apical extodermal ridge (AER)
A structure that forms from ectodermal cells at the distal end of the limb bud, acting as a signaling center during limb development
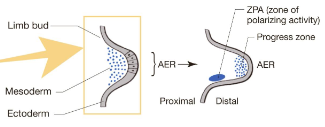
Zone of polarizing activity (ZPA)
a specific region in the limb bud that acts as a signaling center along the anteroposterior axis of the limb
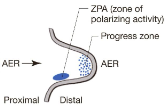
What regulates ZPA?
Sonic hedgehog (shh)
What regulates AER?
Fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF-2)
What are the assumptions of Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium?
No selection, mutation, migration, genetic drift. There is also random mating and diploid and sexual reproduction
Selection against recessive
Gene frequencies change rapidly at first but as the recessive becomes rare and masked in the heterozygote, rate of evaluation slows
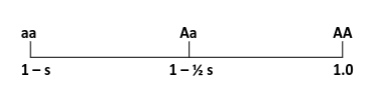
Complete dominance
Heterozygote fitness equal to that of homozygous dominant

No dominance
Heterozygote intermediate to that of either homozygote
Overdominance
Heterozygote superiority
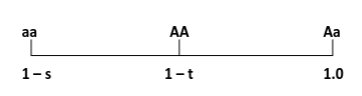
Underdominance
Selection against heterozygote

Mutation-selection balance
Removal by selection offsets recurrent mutations
Migration
Movements of individuals among population
Gene flow
Movement of alleles
Effective population size (Ne)
Number of individuals in a population that reproduce
Genetic drift
Chance fluctuations in gene frequencies between generations
Panmictic population
Large randomly mating population
Inbreeding
Indivduals may choose to mate with genetic relatives
Hypothesis testing
The most direct method for discerning among multiple possible explanations for a phenomenon
What are the limits on adaptations
Time lags, genetic constraints, developmental constraints, functional constraints, and trade offs