A level psychology
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/306
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 8:37 AM on 10/12/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
307 Terms
1
New cards
classical conditioning
learning through association
2
New cards
operant conditioning
learning through consequences
3
New cards
behaviourist approach
explains behaviour in terms of observation and learning
4
New cards
reinforcement
consequence of behaviour that increases likelihood of that behaviour being repeated (can be positive or negative)
5
New cards
social learning theory
explains behaviour with direct and indirect reinforcement
6
New cards
imitation
copying the behaviour of others
7
New cards
vicarious reinforcement
through observing someone else being reinforced for a behaviour
8
New cards
mediational processes
cognitive factors (thinking) that influence learning - come between stimulus and response
9
New cards
cognitive approach
how our mental processes (thoughts, perceptions, attention) affect behaviour
10
New cards
biological approach
perspective that emphasises importance of physical processes such as genetic inheritance and neural function
11
New cards
genes
sections of DNA that code for specific characteristics
12
New cards
phenotype
characteristics of individual determined by genes and environment
13
New cards
neuron
nerve cells that process and transmit messages through chemical and electrical signals
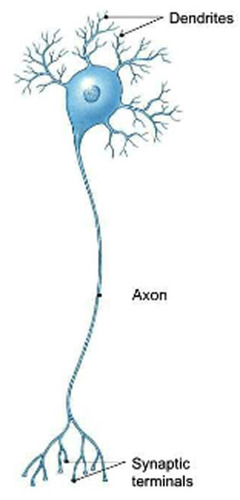
14
New cards
sensory neurons
carry messages from PNS to CNS - long dendrites and short axons
15
New cards
relay neurons
connect sensory neurons to motor or other relay neurons - short dendrites and short axons
16
New cards
motor neurons
connect CNS to effectors (muscles, glands) - short dendrites and long axons
17
New cards
synaptic transmission
when neighbouring neurons communicate with each other by sending chemical messages across the synapse (gap that separates them)
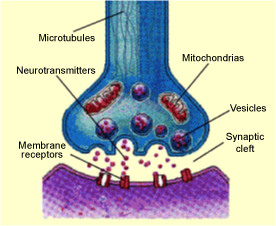
18
New cards
neurotransmitter
chemicals released by synaptic vesicles that carry signals across the synapse
19
New cards
excitation
when a neurotransmitter increases positive charge of the postsynaptic neuron - increases chance that neuron will fire and pass on electrical impulse
20
New cards
inhibition
neurotransmitter (ie serotonin) increases negative charge of postsynaptic neuron - decreases chance of neuron firing and passing on electrical impulse
21
New cards
Statistical infrequency
when an individual has a less common characteristic
22
New cards
Deviation from social norms
Concerns behaviour that is different from the accepted standards of behaviour in a community or society
23
New cards
Failure to function adequately
when someone is unable to cope with ordinary demands of everyday life
24
New cards
Deviation from ideal mental health
when someone does not meet a set of criteria for good mental health
25
New cards
Three examples of Jahodas criteria for good mental health
- no symptoms or distress
- self actualise (reach our potential)
- can successfully work, love and enjoy daily life
- self actualise (reach our potential)
- can successfully work, love and enjoy daily life
26
New cards
Phobia
an irrational fear of an object or situation
27
New cards
Behavioural
ways in which people act
28
New cards
Emotional
Ways in which people feel
29
New cards
Cognitive
process of thinking - knowing, percieving, believing
30
New cards
Behavioural characteristics of phobias
panic, avoidance, endurance
31
New cards
Emotional characteristics of phobias
anxiety
32
New cards
cognitive characteristics of phobias
selective attention, irrational beliefs, cognitive distortions
33
New cards
Depression
mental disorder characterised by low mood and low energy levels
34
New cards
Behavioural characteristics of depression
activity levels, disruption to sleep and eating behaviour, aggression and self harm
35
New cards
Emotional characteristics of depression
lowered mood, anger, lowered self-esteem
36
New cards
Cognitive characteristics of depression
poor concentration, dwelling on the negative, absolutist thinking
37
New cards
Obsessive compulsive disorder
condition characterised by obsessions and/o compulsive behaviour
38
New cards
Behavioural characteristics of OCD
compulsions (repetitive and reduce anxiety), avoidance
39
New cards
Emotional characteristics of OCD
anxiety and distress, accompanying to depression, guilt and disgust
40
New cards
Cognitive characteristics of OCD
obsessive thought, cognitive strategies to cope, insight into excessive anxiety
41
New cards
The two-process model to explaining phobias
phobias are acquired by classical conditioning and maintained by operant conditioning
42
New cards
Systematic desensitisation
behavioural therapy to reduce an unwanted response to a stimulus by using reserved classical conditioning
43
New cards
Flooding
a treatment for phobias in which clients are exposed repeatedly and intensively to a feared object and made to see that it is actually harmless
44
New cards
Becks three parts of cognitive vulnerability to depression
faulty information processing, negative self-schemas, the negative triad
45
New cards
Negative triad
negative views of the self, the world, and the future
46
New cards
ABC model
Ellis proposed that depression occurs when an activating event (A) triggers an irrational belief (B) which in turn produces a consequence (C)
47
New cards
cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT)
method for treating mental disorders based on cognitive and behavioural techniques
48
New cards
Ellis' rational emotive behaviour therapy (REBT)
extends the ABC model to an ABCDE model - D standing for dispute and E standing for effective
49
New cards
Genetic explanations for OCD
candidate genes, OCD is polygenic, different types of OCD
50
New cards
diathesis-stress model
a diagnostic model that proposes that a disorder may develop when an underlying vulnerability is coupled with an event
51
New cards
Neural explanations for OCD
role of serotonin (lower levels = lower mood), decision making systems (not making rational decisions)
52
New cards
Drug therapy for treating OCD
treatment that involves drugs that affect the balance of chemicals within the brain
53
New cards
SSRIs (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors)
antidepressant drug that prevents the reabsorption and breakdown of serotonin which effectively increases the amount of serotonin that reaches the brain
54
New cards
Combining SSRIs with other treatments
SSRIs reduce the patients emotional symptoms which means that they can engage more effectively with CBT
55
New cards
Tricyclics
has the same affect as SSRIs but more severe side effects - tends to be used on patients who dont respond to SSRI treatment
56
New cards
SNRIs (serotonin noradrenaline reuptake inhibitors)
increases levels of serotonin and noradrenaline (hormone that slows heart rate and causes an inhibitatory reaction)
57
New cards
Aim
general statement of what the researcher intends to study/investigate
58
New cards
Hypothesis
clear, precise and testable statement that says the relationship between the variables to be investigated
59
New cards
Directional hypothesis
hypothesis that states the sort of difference that is anticipated between conditions
60
New cards
Non-directional hypothesis
hypothesis that states there is a difference between conditions but doesnt specify
61
New cards
Variables
anything that can change/vary in an experiment
62
New cards
Independant variable
The factor that is manipulated; variable whose effect is being studied
63
New cards
Dependent variable
The outcome factor; the variable that may change in response to manipulations of the independent variable.
64
New cards
Operationalisation
clearly defining variables in terms of how they can be measured
65
New cards
Extraneous variables
any variables (other than the IV) that can have an affect on the DV
66
New cards
Confounding variables
anything that may have already affected the DV, questioning the state of the DV at the beginning of the experiment
67
New cards
Demand characteristics
any cue from the researcher/from the research situation that may be interpreted by the participant as revealing the purpose of the experiment
68
New cards
Investigator effects
any effect of the investigators behaviour on the outcome of the experiment
69
New cards
Randomisation
the use of chance to reduce the researchers influence on the design of the experiment
70
New cards
Experimental design
different ways in which testing of participants can be organised according to experimental conditions
71
New cards
Standardisation
using the exact same procedures for all participants in a research study
72
New cards
Independant group designs
two separate groups of participants experience two different conditions in the experiment
73
New cards
Repeated measures
All participants take part in all conditions of the experiment
74
New cards
Matched pairs design
Participants are matched on key characteristics. One participant does control condition and the other does the experimental condition.
75
New cards
Random allocation
participants are randomly allocated to the different conditions
76
New cards
Counterbalancing
attempt to control for effects of order, half the participants experience the conditions in one order, the other half experience the conditions in another order
77
New cards
Lab experiments
takes place in a controlled environment, researcher manipulates the IV and the DV is measured by the researcher whilst maintaining control of the extraneous variables
78
New cards
Field experiments
takes place in a natural setting, researcher manipulates the IV and measures the DV
79
New cards
Quasi experiments
IV is based on an existing difference (ie age), the DV is measured by the researcher, can be in lab or natural settings
80
New cards
Natural experiments
takes place in controlled environment, IV is not manipulated by the researcher and the DV is measured by the researchers
81
New cards
Population
group of people who are the focus of the researchers interest, from which a small sample is drawn
82
New cards
Sample
group of people who take part in a research investigation, drawn from a population
83
New cards
Sampling techniques
methods used to select people from the population
84
New cards
Bias (sampling)
certain groups can be under/over represented in the sample which limits the extent to which it can be generalised
85
New cards
Generalisation
extent to which findings and conclusions can be applied to the population
86
New cards
Ethical issues with psychological studies
issues that arise when there is conflict between the rights of the participants and the goals of the research to produce authentic, valid and worthwhile data
87
New cards
BPS code of ethics
document produced by the British Psychological Society (BPS) that instructs psychologists in the UK about how to behave when dealing with participants
88
New cards
Four main prinicples of the BPS code of ethics
respect, competence, responsability, integrity
89
New cards
Pilot study
small scale version of an investigation that takes place before the real investigation to check that the procedures/equipment works
90
New cards
Single blind procedure
researcher is aware of the experiment but the participants are unaware
91
New cards
Double blind procedure
researcher and participants are unaware of the experiment
92
New cards
Naturalistic observation
watching and recording behaviour in a setting within which it would normally occur
93
New cards
Controlled observation
watching and recording behaviour in a controlled environment
94
New cards
Covert observation
Participants behaviour is observed and recorded without their knowledge
95
New cards
Overt observation
participants behaviour is watched and recorded with their knowledge
96
New cards
Participant observation
researcher becomes a member of the group being studied
97
New cards
Non-participant observation
researcher remains outside the group being studied
98
New cards
Behavioural categories
target behaviour is broken up into observable/measurable components
99
New cards
Event sampling
target behaviour or event is established then the researcher records this event everytime is occurs
100
New cards
Time sampling
A target individual or group is first established then the researcher records their behaviour in a fixed time frame