Biology - Unit 4
1/98
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Pearson Edexcel International Advanced Subsidiary/Advanced Level in Biology Topic 5 and 6
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
photosynthesis
requiring energy from light to split apart the strong bonds in water molecules, storing the hydrogen in a fuel (glucose) by combining it with carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen into the atmosphere
photophosphorylation of ADP
requires energy and the hydrolysis of ATP provides an immediate supply of energy for biological reasons
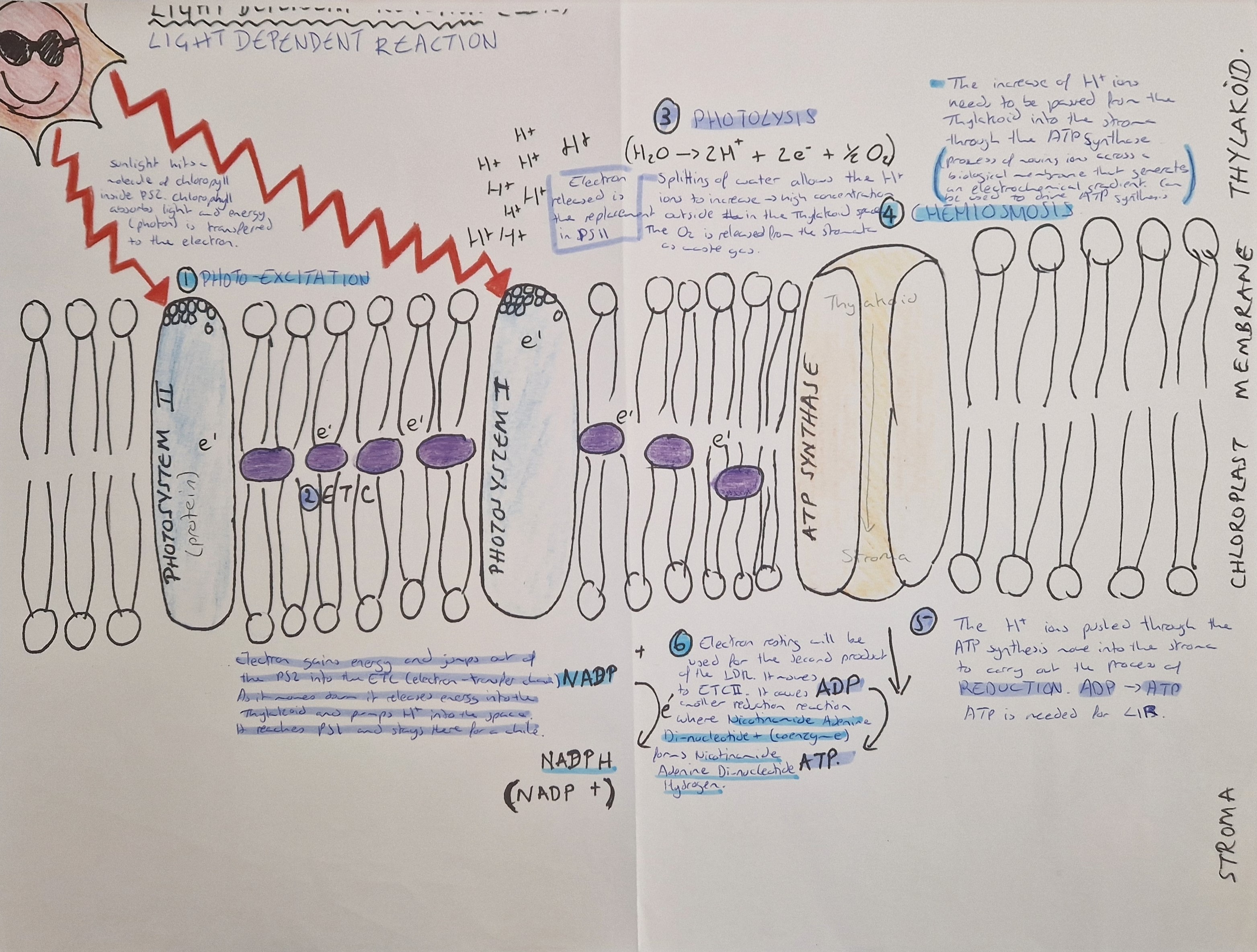
light-dependent reaction
light energy is trapped by exciting electrons in chlorophyll, which jump from PSII to PSI via ETC. Photolysis happens and the hydrogen concentration increases (oxygen is released as waste gas). Chemiosmosis is the increase of H+ ions that create a pH and concentration gradient. The H+ ions are passed through the ATP Synthase, which starts reduction (ADP+Pi→ATP). The H+ ions start another reduction reaction (NADP++H+→NADPH+e-). The extra electron is sent back to PSII for the reaction to start again.
light-independent reaction
Calvin Cycle: fixation of carbon dioxide using the products of the LDR.
C02+RuBP with the enzyme RUBISCO → two molecules of 3GP. ATP is added and 3GP is activated. NADPH is added and it’s reduced into G3P.
Two G3P are needed to form glucose but out of the 6 products 5 are used to replace RuBP. Two cycles are needed to synthesise new biological molecules.
Chloroplasts
Thylakoid
Grana
Photosystems
Stroma
Lamellae
Absorption spectrum
used to determine the wavelengths absorbed by specific pigments, showing the percentage of light absorbed at each wavelength
Action spectrum
helps to show the relationship between the rate of photosynthesis for a given wavelength
NPP = GPP - R
NPP - net primary productivity, gpp - the rate of energy loss to metabolism and mantainance
GPP - gross primary productivity, the amount of chemical energy created from light energy at a specific time
R - respiration
Population
all the members of one species in a habitat at one time
Community
all the organisms in a particular habitat at one time
Habitat
geographical area occupied by an ecosystem
Ecosystem
all biotic and abiotic factors in a particular area, which interact and are interdependent. They make up a self-contained system which is self-supporting in terms of energy flow
numbers and distribution of organisms in a habitat
controlled by biotic (predators) and abiotic factors (temperature)
Niche
role of a species within an ecosystem
Primary succession
area previously inhabited → pioneer community (lichens, mosses and weeds) will colonise it (little diversity, low biomass and simple food web) → over time nutrient-rich soil will form and other plants will be able to grow → Intermediate communities (grasses and shrubs) will give way to more complex plants (more biomass, more diversity and a bigger food web) → climax community will develop with a stable and complex ecosystem
records of carbon dioxide levels
CO2 levels have been rising for all of history, but had a significant increase after the Industrial Revolution.
We know CO2 is a greenhouse gas, and the records see a correlation between high CO2 levels and increasing temperatures.
pollen in peat bogs
Made of partly decomposed plant material, mainly mosses. They’re acidic, cool and anaerobic, which helps peat preserve pollen grains, moss spores and even plant tissue.
As it builds in layers, we can determine the type of vegetation growing around that specific time.
Some mosses indicate wet conditions, and some dry; warmer and cooler, etc.
temperature records
Scientists drill down into the Antarctic and Greenlandic ice cores and analyse the air trapped in them.
Oxygen isotope ratios show the temperature of the air when the ice formed.
CO2 can also be analysed to measure its levels.
dendrochronology
The dating of past events using tree ring growth can tell us about the climate past. Large cells in spring and small cells in autumn give the illusion of rings.
The growth depends on many factors, which can help determining changes in the climate.
anthropogenic climate change
humans have increased the release of greenhouse gasses significantly since the Industrial Revolution, and this has enhanced the greenhouse effect.
The release of CO2, methane and the burning of fossil fuels
Carbon cycle
There are carbon sinks in nature, through which carbon fluctuates and ragulates naturally.
Humans have altered this balance by burning fossil fuels.
Planting more trees, or limiting industries would be some solutions
Climate change models
scientists use data to create reliable models to predict how climate change will affect the future
Climat change models limitations
models can’t perfectly predict everything as there will be sudden changes and events that have no warning
trends in society can also affect the climate and those can’t be predicted either
effects of climate change
warm season become longer and cold ones shorter as temperatures increase
precipitation patterns will change, extreme precipitation events will increase in serverity and frequency, blizzards will be worse
the atmosphere will hold onto more moisture
more extreme heat waves and cold
effects of climate change on animals
breeding seasons/coming out of hibernation is earlier
mismatched prey-predator habits
less food
surviving young decrease
some species will have no food/shelter and will disappear
temperature
warmer temperatures mean higher enzyme rate but also more chances of them denaturing
if it rises too much they might stop working and the organisms would die
temperature coefficient
Q10 = (R2/R1)10/ (T2-T1)
Evolution
Natural selection → Individuals with a specific characteristic are the only ones to reproduce
Genetic mutation → some individuals have better chances of survival because of a mutation fitted for their life
Speciation
a group within a species separates from other members of its species and develops its own unique characteristics. The demands of a different environment or the characteristics of the members of the new group will differentiate the new species from their ancestors.
Allopatric speciation
geographical speciation. The difference in environmental factors causes the change in allopatric speciation.
Sympatric speciation
evolution of new species takes place from a single ancestral species without geographical interference
how decisions about controversial things (climate change) can have different results depending on who takes it
politicians usually make these decisions and can be influenced by groups
many look at short term benefit
the action needed can negatively affect many of those who are in charge of deciding
Human needs and conservation
a middle ground is needed:
reforestation
biofuels
limiting certain industries
sustainable resources
Thylakoid
flattened discs that have small internal volume to maximise the hydrogen gradient
Grana
thylakoid arranged into stacks to increase SA:Vol of the membrane
Photosystems
pigments are organised to maximise light absorption
Stroma
central cavity with appropriate enzymes and pH for the reactions to take place
Lamellae
connects and separates grana, maximising photosynthetic efficiency
pioneer community
(lichens, mosses and weeds)
Intermediate communities
(grasses and shrubs)
climax community
Oaks
photosynthesis equation
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
aseptic technique
when an organism is grown, we must avoid cross-contaminating. Methods of handling sterile equipment and microorganisms are used so cultures are made without unwanted organisms
aseptic method 1
sterilise the inoculating loop in a blue flame
dip the loop in the suspension of the bacteria
streak the loop across the agar dish’s surface
replace the lid, tape it close and turn in upside down
aseptic method 2
sterilise the inoculating loop in a blue flame
dip the inoculating loop across the agar dish or wherever the culture is
swirl the loop in the serialised liquid medium in a conical flask
remove the loop and seal the flask with a sterilised cotton wool
methods of measuring the growth of microorganisms
cell counts
dilution plating
mass
optical methods (turbidity)
phases of bacterial growth curve
lag (time it takes for bacteria to reach a state where they can grow and divide quickly)
exponential/log (when cells divide by binary fission and the doubling of each generation creates the exponential growth)
stationary (time where population size is constant following the log phase due to limiting factors like a lack of available nutrients)
death (decrease in the number of bacteria caused by the depletion of nutrients or other unfavourable conditions)
bacteria
living organisms
bigger
single cell organism
can reproduce outside host
microscopic
limited to a part of the body
pneumonia, tuberculosis, tetanus, food poisoning
types of bacteria
spherical - cocci
rod-shaped - bacilli
spiral - spirilla
virus
not living organisms
smaller
can only reproduce in host (dormant otherwise)
submicroscopic
infection is systemic
influenza, measles, polio, aids, covid-19
lytic cycle
viral replication cycle
virus takes over a host cell’s genetic material and uses the cell’s structure to replicate until the cell bursts
lysogenic (latency) cycle
viral replication cycle
virus’ nucleic acid is integrated into host cell’s chromosomes, a provirus is formed and replicates everytime the cell reproduces, cell survives until the virus is activated and the cycle begins
ebola virus
severe and often fatal fever
unexplained bleeding
fatigue
vomiting and diarrhea
headaches
transferred through bodily fluids
genetic material - RNA
tobacco mosaic virus (TMV)
plant virus → affects the chloroplasts
turns leaves yellow/white forming a mosaic pattern
spread naturally or through contact from farmers
reduces surface area and ability to photosynthesise
lytic virus
genetic material → RNA
human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
targets T-helper cells
once they are activated the virus replicates and bursts the cell
causes a weakened immune system and leads to AIDs
AIDs is when the body can’t defend itself against basic infections
symptoms → weight loss, diarrhoea, dementia, cancers and oportunistic infections (TB)
latent virus (lysogenic)
gentic material - RNA
lambda phage
bacteriophage - infects bacterial cells
lambda phage infects E. coli
found in intestines, normally harmless but can cause food poisoning
head, tail, tail fibres
can alternate between life cycles
genetic material → DNA
tuberculosis (TB)
bacterial disease (Mycobacterium tuberculosis)
infects phagocytes in the lungs
first infection is symptomless as the infected phagocyted are sealed in tubercules as a result of inflamatory response
bacteria lie dormant in the tubercules as they are covered by a thick waxy layer that protects them
activated when the immune system is weak
symptoms → breathing problems, coughing (blood), weight loss, fever, fatigue
genetic material → DNA
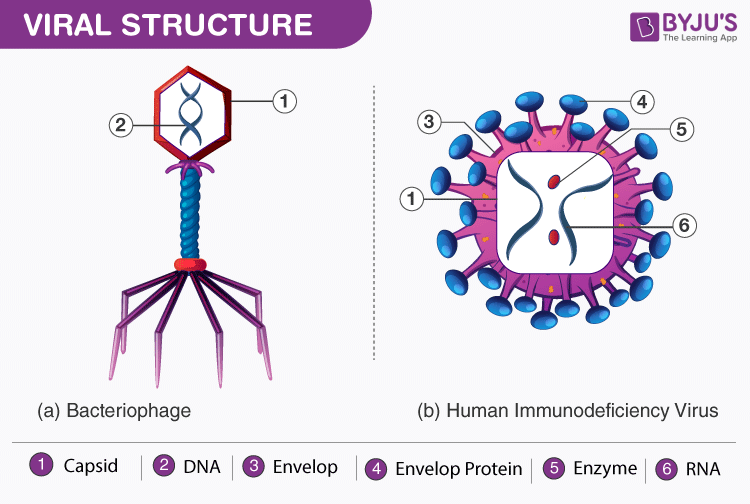
virus structure
protein capsid
lipid envelope
spikes
genome (RNA)
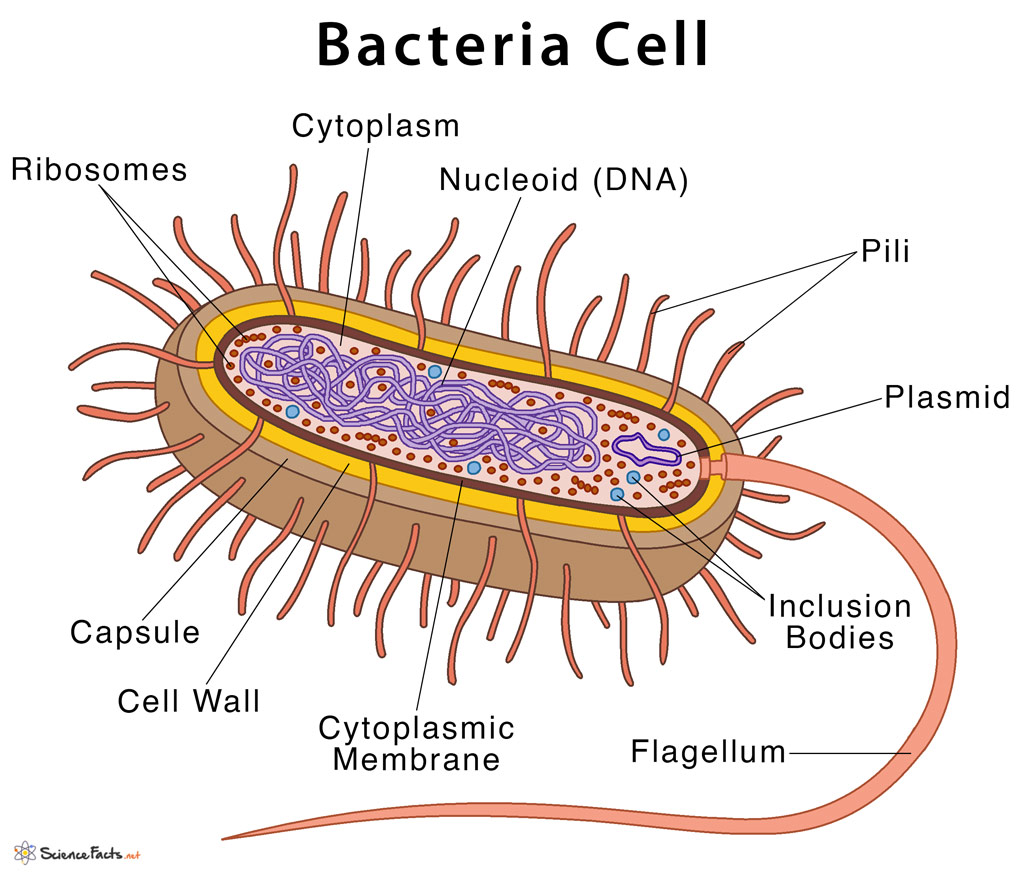
bacteria structure
flagellum
plasmid
cell wall
nucleoid (DNA)
cytoplasm
ribosomes
cell membrane
major routes pathogens take
inhalation - coughing, sneezing and talking
ingestion - contaminated food
direct contact - skin to skin or bodily fluids
vector - organisms that carry the pathogen
fomites - inanimate objects that carry the pathogen
physical and chemical barriers
skin
stomach acid
gut and skin flora
cough reflex
mucus
skin
physical
epidermal cells
keratinised cells
strong barrier
stomach acid
chemical
gastrointestinal tract
low pH kills the pathogens
quick change in pH guarantees no pathogen has survived
gut and skin flora
chemical
skin - sebum is produced
gut - they compete with the pathogens for food and space
mucus
physical
produced in the goblet cells
mucus traps the pathogens and the cilia pushes them back out of the system
non-specific immune response (innate)
inflammation
lysozyme
interferon
phagocytosis
fever
inflammation
tissue gets damaged
platelets and basophils release histamine
histamine causes blood vasodilation and the increased permeability of blood vessels
result; more blood flow to that area (looks red) and more antibodies, white blood cells and plasma are leaked out into the damaged tissue
lysozyme
enzyme found in secretions like tears and mucus which kills bacteria by damaging their cell walls
interferon
produced by the infected cell
anti-viral protein
they stimulate inflammation
inhibit translation of viral proteins
activate T-killer cells
phagocytosis
process through which a white blood cell called a phagocyte engulfs the pathogen
pathogen is in a phagocytic vessel in which lysosomes release lysozyme
the pathogen is digested
digested pathogen will be removed through exocytosis
some antigen molecules will be kept and presented on the surface of their cells
types of white blood cells
Neutrophil - first responders
Lymphocytes - adaptive immunity
Monocyte - antigen presentation
Eosinophil - multicellular parasites
Basophil - inflammatory response
specific response
after the pathogen is digested some molecules are presented on the outside of the phagocyte’s cell wall
it becomes an antigen-presenting cell (macrophage)
macrophages activate other types of immune systems
B cells
T cell
T lymphocytes
white blood cells with specific receptors on their cell surface
when it binds to its complementary antigen (macrophage/pathogen) it’s activated (clonal selection)
when activated it divides by mitosis (clonal expansion)
T helper cells
T killer cells
T memory cells
T helper cells
activate B lymphocytes
activate T killer cells
T killer cells
destroy any cells that have been infected by the pathogen
memory cells
kept in low levels in the bloodstream
if activated they replicate to create an immune response
when there is another infection the response is much quicker
allow for longterm immunity
B lymphocytes
white blood cells with specific antibodies (membrane-bound) on their cell surface
activate when T helper cells release chemicals or when a complimentary antigen binds to it
when activated they divide by mitosis and differentiate
B effector cells (plasma cells) - secrete antibodies
B memory cells
can also digest the pathogen, present its antigen and activate T cells
B effector cell / plasma cell
produce complementary antibodies for the antigen
antibodies
structure
four polypeptide chains held together by disulphide bridges
variable site (specific) → antigen-binding site
constant region (non-specific) → binding site for the immune system
hinge region → flexibility
functioning
agglutination - antibodies bind to two pathogens simultaneously so they are clumped together
neutralising →bind to toxins released to neutralise their effects
blocking access to human cells
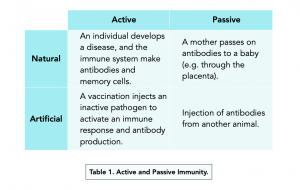
how do individuals develop immunity
ways
natural
artificial
types
active
passive
natural
active → individual has an infection and develops the antibodies for it
passive → mother passes on antibodies to their baby/foetus via body fluids (placenta, breast milk)
artificial
active → vaccine
passive → injected antibodies from another organism
evolution of pathogens
bacteria and viruses replicate very quickly
this allows them to quickly develop adaptations to evade the immune system
this means new infections may need new responses as memory cells don’t recognise it
advantageous alleles are passed on quickly, creating a resisting strain
antibiotics
chemicals that are used to fight infection
bactericidal
bacteriostatic
bactericidal
kill the bacteria by bursting open their cell walls
bacteriostatic
inhibit the growth of bacteria by stopping protein synthesis and production of nucleic acid so they can’t divide
pathogens and evolution
they evolve to evade the immune system
high mutation rate means every infection needs a new primary immune response; eg. HIV
memory cells from previous responses don’t recognise the new antigen
evolution could make them resistant to antibiotics
resistant strain
bacteria that have had mutations that make them immune to antibiotics as they are a selection pressure
those with a resistant mutation will survive and reproduce passing on the advantageous allele
this could happen very quickly as viruses and bacteria reproduce fast
nosocomial infections
resistance to antibiotics can cause infections in hospitals
there are some guidelines to stop this from happening
preventing nosocomial infections
new patients are screened, isolated and treated if it’s an infectious disease
antibiotics are only used when needed and their course if completed so no resistant strains form
staff must follow the code of practice
strict hygiene
washing hands with alcohol-based gels
wearing suitable clothing
energy units
kJ m-2 year-1
microorganisms in decomposition and recycling of carbon
break down tissue, forming gas and decomp. fluid, which leaves through orifices
inorganic ions are returned to the soil → assimilated by plants
carbon → taken in by microorganisms and released into the atmosphere when they respire
CO2 is taken in through photosynthesis → turned into biomass → die
decomposition cycle begins again
decomposition
autolysis → body’s own enzymes digest and break down tissue
putrefaction → microorganisms (bacteria/fungi) break down the remaining dead tissue
estimating time of death (ToD)
stage of succession
body temperature
degree of muscle contraction
forensic entomology
extent of decomposition
stage of succession
fresh
putrefaction
fermentation
dry decay
skeletonization
each stage attracts different organisms and happen during different periods in a specific order
body temperature
decreases in a sigmoid curve over the first 24 hours
1.5 - 2ºC per hour
stops when it reaches ambient temperature
factors that affect it: weather, body fat, body size, clothes, water, air movement, cover
degree of muscle contraction
rigor mortis is the process where ethe body muscles contract after death
4-6 hours muscles will stiffen
no oxygen → anaerobic respiration → accumulation of lactic acid
lactic acid has a low pH so enzymes denature
ATP can’t be used to unbind muscle proteins (actin and myosin) which causes the muscles to stiffen
smaller muscles → bigger muscles → bigger muscles → smaller muscles
36 hours post-mortem muscles begin to relax
factors that affect it: muscle development, temperature
forensic entomology
study of insects found in the body
blow flies → flesh flies →beetles (decomposed fats) → pyralid moths (flesh and clothes —better if natural fibers) → cheese skippers (digested and remaining food) → burying beetles (dead flesh)
they lay eggs in warm and moist places (orifices)
identifying the species can help understand the extent of the decomposition as they have different life cycles and times of appearance
letting maggots develop to identify which species it is is sometimes needed
extent of decomposition
appearance of the body
up to a few days → skin turns green
few days to few weeks → body becomes bloated, skin falls off
after several weeks → tissues liquefy and seep out of the body
few months to a few years → all tissues are broken down and only bones remain
after several decades → bones disintegrate