Study Guide BFI - History Theme 1 : 1930-1945
Key terms :
Depression
Dust Bowl
Alphabet Agencies
Welfare State
Social Security
Keynesian economics
Matignon Agreement
French Popular Front
—> Why the US Democrats became the party of many blacks in America and why the Republican party no longer is
1854 - democrats were pro-slavery and Republicans (come from collapse of Whigs because of division on slavery) were against slavery
Late 1800s - republicans continue to fight for black men rights
In North, Republican appealing to business (wealthy men) = pro business but to get votes in the South, they stop talking about civil rights
19th - rep do well, good economy so good for them but not so good starting in 1929 + Roosevelt (democrat)
50 and 60s - civil rights mvt
1964 - President Lyndon B. Johnson (democrat) signs civil rights act → white people in South leave Democrats (don’t want equality even though they would benefit financially from it)
Blacks convert to democrat (70% today) and S. white men switch to Rep
Great Depression and New Deal
How was the GD a challenge to democracy? —> Economic and social hardship pushes people to radical political changes because they become desperate for change, more prone to put their trust into one person who presents themself the right way. IN THE US: Need to have faith in the system (president, banks, money, etc.) for democracy to work —> People question what American democracy is, if it works.
Causes of the Great Depression (in reality don’t know, just listing everything that went wrong)
Banks close, stocks crash→ 9000 banks closed (middle class lost savings)
Made worse by high interest rate (bad Gov decision)
Loans made economy grow, so no loans, no growth
Structure of US economy frail→ needed more industrial diversity (not just oil, gaz), Middle and lower class weak purchasing power (need to buy for eco but can’t), many bad loans because of credit issue (used badly for stocks), Us less competitive in International trade as EU competed
Hawley- Smoot Tariff of 1930→ hard for Eu to sell goods to US, limited international trade, Eu could not pay back WW1 debts (international debt structure), world market not good
Causes for stock market crash: buying on a margin, the stock market bubble, too many people owned stocks and tried to sell them off to quickly, prices for stocks peaked and then fell quickly, biggest cause→ gov kept interest rates low and allowed companies to borrow money very easily, thus creating large debt
Social + Economic consequences
Social
Hoovervilles→ unregulated and makeshift housing emerged in parts of America
Bread lines, lines of people waiting to receive food provided by charitable organizations or public agencies,
Soup kitchen→ places that would offer free food or low-cost food for people living in shantytowns
Environmental disasters: Dust Bowl→ Farmers had exhausted the sand with overproduction, Drought and winds arrived and very few trees and little grass were left to keep the soil down. The dust would be picked up by the winds and would travel hundreds of miles. The region that was hit the hardest (Kansas, Oklahoma, Texas, New Mexico, and Colorado) became known as the Dust Bowl.
GD tremendous social and psychological impact, people lost their will to survive
Women were also ashamed to reveal their hardships so many were starving to death in cold attics and rooming houses
Poor diets and a lack of money for health care for children
Economic
Manufacturing down 50 %, capitalism broken, 1932→ 270 000 families lost their homes
9000 banks closed( middle class lost savings)
15 million unemployed (⅓ of the workforce)
GDP down 20-30%
Automobile industry down to 1/5 of previous level
—> Why was Hoover unsuccessful in resolving the GD?
Raised taxes to pay government budget, cut money supply
Hawley-Smoot tariff 1930 → deepened depression by limiting trade and profit
“Laissez-faire” economics = Hoover took a cautious approach to the depression, didn’t want to get directly involved in the economy/inject money → asked employers not to cut wages or lay off workers.
Opposed any form of federal welfare, or direct relief to the needy
Hoover did some stuff to help GD but it wasn’t enough, didn’t allow the Fed to take over completely and instead relied on private businesses and local and state governments
The New Deal - FDR elected in 1933
New deal: 1933-1938, program to resolve GD (2 parts, 1 (1933-1934)→ restructuring economy, providing relief, 2(1934-1938) → use nation’s resources, help for farmers, work programs)
Relief, Recovery, Reform
Provide relief for the poor and unemployed
Recover economy to its normal level
Reform financial systems so that it won’t fail next time
Social Programs
Agricultural Adjustment Act AAA : Limited overproduction from farmers’ crop (manipulated market), gave value to the farmers’ crops
National Industrial Recovery Act: Union supposed to be recognised, minimum wage 30 to 40 cents/hour, max work weeks 35-40h (to employ more people), no child labor
Tennessee Valley Authority TVA: Public work projects: dams, flood protection → infrastructure and employment = win win
Civil Works Administration CWA and Civilian Conservation Corps CCC: Employed 4 million people, public infrastructure: roads, parks, schools, national parks, reservoir BUT segregated work
Work Progress Administration WPA: Renovated 110 000 public buildings (schools, post offices, gov offices), built 600 airports, 500 000 miles of road, 100 000 bridges
Federal Housing Administration FHA: Middle class can get a home, insure mortgages for single family properties BUT blacks intentionally omitted
Social Security and welfare 1935:
Retirement → collect it when retire, pay in from income
Payroll tax - automatic pay out of pay-check
Unemployment insurance
Help children and disabled
Economic Reforms (banks)
Emergency Banking Act→ reconstructed banks to salvage bad ones
Middle class protected
Restore people’s faith in banks
Federal gov guaranteed bank deposit
Security and exchange commission (SEC) → policing the banks, anything that would upset economy, banks monitored
Saving banks created→ they could not use the money to invest
Glass-Steagall Act 1933 - curb irresponsible speculation, regulate the banks
Tax rates for the rich in 1930s, 40s, 50s, 60s: Rich had to pay high income taxes, started to get bigger during the 1930s and were very high (marginal tax rate around 90%) during these years
Political Change —> The significance of FDR for defining the Democrats as Big Government and who its voting constituents were
FDR was able to consolidate demographics of the democratic political party with unions, African Americans, and middle class (democrats and republicans arrived during FDR)
Big government→ Keynesian economics: when economy doing poorly, spend money so the economy will have some level of inflation, people will start getting jobs, stop spending money when level of jobs good and pay back debts
FDR – large public work programs, dams, roads, national parks, bridges → interferes with the economy
National minimum wage, so people spend more if less insecure, public housing
Social democracy in US during FDR: unions right to bargain collectively, public works program, high taxes on rich, social security
—> The Two concepts of Liberty
Democrats and FDR “liberty is greater security of the average man” → liberty closer to security versus minimal gov interference
Positive liberty (left) - to be free, you need to be given more than just set free, you need things to flourish (good healthcare, …)
Negative liberty (right) - let me do what I want, freedom from interference
France during the Great Depression
Interwar FR period
1.3 million dead soldiers bc of WW1, especially young men, gueules cassees → no evolution of people, birth rate goes down
Led to melting pot = letting in immigrants to work
Analysis : great power declining
Fear of communism starting in 1917
Women
Not allowed to work anymore, contraception and abortion prohibited, want right to vote with BR giving it
1938 New woman - shorter skirts, makeup, unisex fashion, drank, smoke, rode bycicle and wore pants, became independent, did the same things as men
French Popular Front 1936
Appeared due to the rise of the right in EU and FR
Union of the french leftist parties - socialist + commu + workers
Left won majority in Assembly - great coalition, commu work with socio, unite to fight facism
Leon Blum government - Govern france from 1936 to 1938
The general strike: 2 million workers go on strike to make gov allow Leon Blum to make social reforms. Happens twice 1936, 38 → but delegitimized left gov, socialists start losing votes
June 20, 1936 Matignon agreement - recognizes the right to unionize
40h / week, 2 weeks paid holiday for all employees, wages go up 10%, facist leagues dissolved and driven underground collectives agreements - established wage rates, hours of labor, and working conditions, right to unionize
Blum will step down in 37, economic difficulties, rising unemployment = caused french politics to splinter
Nazi and Soviet Totalitarianism
Fascism: solution to national division and a way to resist socialist revolution, expression of authoritarianism, used democracy to destroy democracy (leadership, electoral system, rallies, marches, political meetings), use of terror as political tool, isolation of individuals to prevent them from grouping against the state (people do not talk to each other because scared), no individual/only the state
Totalitarianism: colonization of self and people by the state → take individual, limit speech, religion, freedom to meet, political parties → replace everything with state, make a “New man”
If do not comply, get killed or sent to prison → Uneasy to control people’s mind
New technologies help totalitarian grow → surveillance used to police, spy, propaganda, revolutions from above → get to power and then influence the people
Terror created the “New communist man” or “New fascist man” —> old obsolete man eliminated by purges, labor camps, abuse
Totalitarian regimes:
Nazi Germany
Communist Russia
Fascist Italy (not as totalitarian, end with M’s death)
Franco’s Spain (not as totalitarian)
Context
Fascism in Italy: (not very totalitarian)
Unstable after WW1, division between north and south economically and industrially, 1918 —> inflation, market speculation, social instability → Mussolini will arrive as strong man to help
1/3 seat go to left wing in Parliament
Red scare: Communist revs start in Ru --> middle and uppers classes scared all over EU --> Right increased --> polarization, some go left, others right, rich landowners align with right cuz not supported by socialists
Pushed for fascism --> working left, middle right
The rise of communism created the conditions for fascism to exist
Benito Mussolini (1883-1945) - Italian Prime Minister 1922-1943
Mussolini --> 1883-1945 “I am Fascism”
Created the “Fasci Italiani di Combattimento” in 1919, an ultranationalist organization, use of paramilitary violence against Socialist Party members. Becomes the National Fascist Party in 1921.
Got attention by fighting socialist in the streets which got them the respect of middle and upper class because of the red scare —> upper class investments allowed them to create a private army
Armed ‘Black Shirts’ militia : 1922 —> marched to Rome and occupied capital, King invites Mussolini to form a cabinet, Mussolini shuts down parliament and rules as a dictator
Makes socialism illegal —> resentment from working class
Head of authoritarian party, eliminates political enemies, controls police, press, academic activity
Winning over the people:
Public work programs, liberal building, paid vacation and social security
Befriends the Pope and brings back Catholicism to get more votes (state religion again, taught in schools)
Ended economic chaos, creates a “new citizen” —> youth camps, exercise the young, encourage people to have kids
Nationalist movement often did parades —> people identify with the greatness of it
Problem: corruption and violation of individual rights
Fascism according to M: statism --> nothing above the state, nothing outside of the state, nothing against the state
Corporation --> union between gov and private business, IT eco based under 22 corporations, each responsible for major enterprise, intended to create corruption
Nationalism --> collective ideology not individualistic
Militarism --> nations that don’t expand would eventually die down (social Darwinism)
German Fascism (totalitarianism):
Hitler: 1889-1945, born in Austria, volunteer in German army during WW1, blamed Marxism and Jews for the WW1 German losses, hated the humiliation of the country by the Treaty of Versailles and the German government for submitting to its terms
Nazi Party: created in 1919 in Munich as the NSDAP,
National Socialist German workers party —> appeal to working class, was socialist, then went right (like Mussolini)
Hitler took over the party from 1920-1922, drew on ideas of socialism and the right at the same time, created the paramilitary wing of the party (Brown Shirts) and the NSDAP’s 25-point plan (1920) —> Antisemitic, wanted corporate order like it, nationalist and expansionist
“German should expand to the east” (imply war with east)
Wanted German classless society based on German ethnicity —> was about RACE
Expansionism —> Lebensraum (living space)
Antisemitism
Nationalism
Anti-Marxist no class market
Represented all people —> working class, veterans, old people all mentioned in the 25 point plan for relief.
Hitler is unknown until 1923, Beerhall Putsch —> marches and tries to do a coup in Munich, gets shot at and arrested, spends 1 y in prison (writes “Mein Kampf”) —> calls for Greater German Reich, German unity, says all Marxist, capitalist and Jews must be banned, wanted to create mass party
Nazi Ideology:
Race and nation --> nation= race=driving force of History (competition and survival of fittest)
Anthropology backed up by science of the day, science based on race, skull size —> Aryan supremacy, eugenics, natural segregation of stronger and weaker
Don’t “breed” w/ Jews because it makes Germany weaker
Germany held back because blood polluted —> need to purify the race
Combination of ideas of Nietzsche (will to power), and social Darwinism (race concepts)
Antisemitism:
Jews have never been able to convert to Christianity, “did not find true religion”, odd one out
Immigrant population —> separated by religious practice, created xenophobia
Scapegoat for everything going wrong in Germany: economic depression, Treaty of Versailles
Aryans: brave, create culture vs Jews: cowards, destroy culture
Holocaust —> warning signs in Mein Kampf, final solution, camps to limit psych effects on Germans
Rise to power:
1925 —> Hitler reestablishes party after made illegal, overturn dem from inside
1928 —> chose swastika as symbol, NSDAP only 3% of vote
GD projects them into the spotlight, need for a new political current because of the massive depression seen as a failure of the government
Appealed to people: negative speeches against the Weimar government, focus on local and regional concerns
Did not preach Aryan race yet, gave people what they wanted first,
Used democratic tools: campaign all the time used film, radio, planes
Created violence in the streets (beat up communists, good for middle and upper class) —> the government could not stop it but the Nazis appeared as saviors, pacifiers because they were able to stop the fighting THEY created
1930 —> Nazi 18 % of vote
1932 —> election year, Hitler loses to Hindenburg for president —> came 2nd against very respectable man, success for him, conservatives join hands with Nazi’s
H. demands for chancellor position —> Hind says no, votes go down
Conservatives make deal with H. that Brown shirts will not integrate military and to get rid of a man, gives H. majority of votes and gets Chancellorship --> Nazis go out and beat up people
1933 —> Hitler becomes chancellor
H chancellor:
Day1 → Jan 31, 1933, will eliminate democracy, socialism and communism = threats
Day 2 → dissolved Reichstag (parliament), rule by Article 48, ends constitutional gov
Day 3 → brown shirts become regular police, targets communist and socialist
Feb 27 —> Reichstag burn and used as symbol for hatred against communists, emergency decree (eliminates civil liberties, imprisonment without trial, bans political parties)
March 23 —> Enabling Act - Hitler assumes dictatorial powers democratically
3rd Reich --> Nazi fascism
Catholic church --> did not try to eliminate, concordat with Vatican in 1933, pope and Nazis do not attack each other
Terror, repression
Gestapo secret police
Banned all political parties
Heavy censorship
Dachau opened in 1933 —> in all camps 225 000 by 1935, 165000 by 1939, end of war 700 000 Germans in camps, in camps: gays, dissidents, political enemies, mentally handicapped, Jews, Romanis
Economy back up —> industrial leaders told to build again, build highways, subways, … country reaches full employment by 1936
Volksgemeinschaft —> people’s community (Volk is natural mankind, state existed to serve the Volk) = the individual is subordinate to the Volk, to the interests of the nation rather than his own (has to be racially unified)
Antisemitism
Nuremberg laws, 1935
Kristallnacht November 9 - 10, 1938 —> all the jewish markets, economy, merchants were destroyed, synagogues too, 30 000 jewish men incarcerated to concentration camps = prelude to the final solution, everything got worse after
Wansee conference, 1942
Indoctrination through propaganda and brainwashing
Rallies, parades, shows of military power —> Joseph Goebbels, Minister of Propaganda
Photos of these events were purposefully staged in a way that put Hitler in the center of crowds of people, of perfectly aligned soldiers, Hitler was always towering over the others to be perceived as a powerful protector
Hitler undertook ambitious architectural projects that showcased his power, especially in Nuremberg where rallies were held
Propaganda posters, films, radio
“Ein Reich, Ein Volk, Ein Führer”
Hitler youth 1936 —> 10 to 18 years old required to be members
The USSR and Stalin
Marxism: exploitation of masses:
Superstructure --> culture above eco conditions, religion, education, media, …
Base --> eco conditions of society, determine the cultural conditions, capitalism, socialism, …
Industrial rev --> changed structure of eco, before all agro no in cities and work, created new middle and lower class, industrial magnets most powerful people, not aristocracy
One day everything would be owned by rich, and poor will have nothing, inequality so big people would revolt,
Flaw --> Marx did not see middle class grew and poor got stuff like PP and benefits, poor not so unhappy
Engine of social change --> economic, but class conflicts stopped this,
Capitalist contradictions --> Lower class would make everything and own nothing
Socialism comes out of capitalism
Historical materialism → “eco conditions driven historical change” → thought this was scientific evidence, truth of history,
Dialectical change → capitalist too powerful and rich but no power under feudalism, so get it and now run by rich → class conflicts
Class consciousness → once lower class realized capitalism can be changed, realize they are oppressed, that their boss takes everything
Capitalism --> private property, wealth in one place, reinvest to make more wealth, huge inequalities, more wealth on long run
Socialism --> public property, wealth redistributed, individual not scared because can be sacrificed for greater good of everyone else, pull-down top to make equality
Liberalism protects capitalism because of private property
Communist Russia: USSR (here socialist=communist)
Communism: reign in EU with Fascism, only FR and BR democratic
1917 → WW1 bad, people revolt, soldiers, working class, liberals create new gov
Tzar abdicates → Lenin arrives and seizes power takes Moscow, imposes socialism, Red vs. Whites
Commands —> heavy industry, banks, agrarian states, communication, transportation all owned by gov
Forced nationalism, land reform chaotic, socialism did not really work
Lenin died 1924 —> how can we complete communism state?
Trotsky —> agree to rev all over the world
Stalin —>
Stalin: secretary of c party → connected to everyone so wins
Support socialism in 1 party --> creates 2 5-year plans → forced industrialization 1928-1938
Plan 1: create and advance industrial state, profit from farmers taken to boost industry
Kulaks (middle class farms) revolt and kill all cows, lost social status, don’t own their own land anymore, made poor
Famine—6 million die → Ukrainian Famine 1932-1933
New serfdom --> yes for agricultural workers, cannot go to city, work for gov, Farmers killed if did not comply
Industrial programs --> millions dependent on state, famine, deaths, Terror, all not acknowledged by press
Plan 2: fast industrialization (fastest in Eu history), engineers of EU and Us come over,
1938 --> farm tractors, railway locomotives
Industrialization achieved through sacrifice, hard work for future, no unemployment, communist state looked like solution to GD
1930s communism provided solution to failures of capitalism
Empire struck back --> RU crushed GR with new artillery, industrial dev helped Axes win WW2
Triumph of communism --> universal suffrage, right to job, racism condemned, liberate yourself
Great terror / great purge: 1934-1938
Stalin paranoid and start killing everyone: communists, worried about purity,
1930-1953 --> 3 778 334 people sentence, 786 098 killed
S. only man in power, remove all rivals, killed off his own army
Higher up in office --> more likely to die, paranoia and fear, atomization of people
T state→take over police, Tv according to state, radio controlled, brainwashing,
Religion: atheist --> state religion, dechristianize, priests killed, forced out of religion
New religion --> communism, bright future, better tmr
Education: Lenin and Marxism new kind of catechism, brainwashing, breakdown down class distinction
Enemies --> capitalist, selfish people, corrupted mentality
In RU: cult of personality individual sacrificed for goal of rev, sacrificed standard of living and consumer industry for heavy, industry, military and power
Human liberation and communist dream?
Hopped for better world,
Women --> got better because of industrialization, better education, divorce and abortion legal in 1920 (not under Stalin because of declining birth rate so made it harder), 1920 beg of women leaders but changed in 1930s, Material changes bring more change than ideals of freedom and divorce laws, Stalin praised family, like H. M., worked for their families, waited in bread lines, men had leisure
Legacy: Communism one of biggest events in 20th century --> challenge to capitalism
Success against capitalist world, eastern Eu annexed to the soviet empire, c spreads
Inspire people around world, cool to be Marxist
1980s: loses moral claims and legitimacy so decline of communism, collapses, goal doesn’t justify the means anymore, can’t kill people for better future
Nazi vs soviet:
Both --> cult of personality, warped versions of 19th century social theories (Stalin= Marxism, Hitler= mix social Darwinism and ideas of Nietzsche), homicidal paranoiacs / extermination campaigns (enslave, deport, exterminate entire categories of people, Stalin= Kulaks, Hitler= Jews, slaves, Romani, …), both rose to power through weak liberal democracies (h. legitimately elected / RUS WW1 crisis), rose through GD, populist appeal, promised utopian future (new men and women for GER, land of fairness and social justice for RUS), claimed to have truth of History (S= class conflict, H.= racial theory), imperialistic, expansionist, indoctrination (teaching in schools), non -democratic, caused fear, terror used as tool, heavily industrialized before, both practiced atomization, youth groups
Differences --> Stalin =class conflict, Hitler=race conflict / Russians rose through redistribution of wealth, ideology different --> both totalitarian but Gr capitalist and RU communist and centralized control of society, extreme right vs extreme left
WW2
How Hitler ignored the Versailles restrictions
Restrictions: No more than 100 000 troops, the manufacture of armored cars, tanks, submarines, airplanes, and poison gas was forbidden; and only a small number of specified factories could make weapons or munitions
1933 - Hitler removed GER from disarmament conference at the League of Nations
FR issued a complaint about GER, they’re going to rearm but NO ONE supported FR —> league of Nations does nothing despite being aware of rearmament
BR allow GER to build Navy ⅓ size of BR —> Betrayal of France
No EU response to any of Hitler’s moves —> this encourages him to keep going
Hitler did not believe western powers would fight him over eastern EU, though west was weak —> Takes CZ because of this, invasion of a free country in March 1939
1935 Airforce 400 planes
New modern planes
German Wehrmacht expanded from 100 000 to 550 000 troops, tanks, special forces
1936 - GER sends troops to Rhineland, supposed to be a demilitarised zone since the Treaty
1938 - Germany invades and annexes Austria - Pan-Germanism
Nazi party had been banned after an attempt to overthrow the government in 1934
Hitler threatens AU - tells AU to restore Nazis because he says that since the Nazi party doesn’t exist, Germans that live in AU are being mistreated so need for invasion, no war just rolling army
Japanese Expansion 1931
Other great powers have already divided world between them→ if Japan tries to take some would be stepping on other countries’ territory
When go into china→ BR, FR, GR, US, SU not happy → china already “sphere of influence”
SEP 1931 —> Invades Manchuria (West of Korea and N. of China), U.S declare “international outlawry” → Sino-Japanese war (1931-1945)
In asian mind→ Japanese like nazi, brutal and feel superior, ≈ 10 thousand dying around empire, millions die in Asia
Significance of Spanish civil war for Germany
1936 - April 1st, 1939 - military revolt against the Republican government of Spain → first military coup failed because of massive popular resistance → country split in half
Socialist Liberals / Republicans / Loyalists / Reds (supported by USSR) vs conservative Catholics / Nationalists/ Facists/ Whites (Nazi supported catholics) → 3 years of bloody fighting and led to authoritarian regime with Franco until 1975
Nazi practice military during this war (airforce, tactics, bombs → bomb cities to test material)
Global opinion seen as a struggle of democracy against Fascism or Christian vs Communists
Western governments signed a non intervention pact and refused to allow Spain to buy arms on the international market → led to ppl rallying with the republic - 2800 Americans traveled to Spain→ Abraham Lincoln brigade
German annexation of the Sudetenland - 1938 to 1939 - If Hitler annexes mountains, Czechs are defenceless, so CZ asks for help, FR and BR mobilise troops —> FR and BR wonder if they're going for world war over a small territory
Appeasement for the Sudetenland and Neville Chamberlain
“Peace in our time”
Western powers give in, agree to give Czechoslovakia, thinking they avoid WW
British PM Neville Chamberlain cuts deal with GER → Hitler promises to not invade Czechoslovakia
Sept 1938 Munich Conference - BR, FR, GER, ITA agree to German territorial demands
Appeasement for the annexation of Czechoslovakia / Poland
Western powers give hitler ultimatum
Scared that Poland is next so FR and BR guarantee POL security and give Hitler ultimatum to not do it
The Reason BR did not go to war
Br believed FR was unreliable bc FR was in 3rd Republic, constantly shifting govs
BR alone → US in isolation, FR unreliable, USSR communist (threat)
WW seemed the greatest evil and enemy
BR took the most reasonable choice at the time
Nazi-Soviet Non-Aggression Pact 1939 and why Stalin did it
Stalin feared GER invasion in RUS→ if holds back, western powers would go to war between each other because they’re greedy capitalists pigs
1935 → hoped to form alliance with capitalist nations against Nazis
1939 → signed Nazi-Soviet non-aggression pact to avoid GER invasion
German Invasion of Poland 1939 (September 1 - October 6)
Planned it w/ Soviet Union —> split Poland between GER and RUS
Hitler happy because has colonial land, Stalin happy because created buffer zone between Russia and Germany
Did it in 2 weeks→ Blitzkrieg→ quick, mechanised war, pushed people forward, speed and penetration
The Phony War
FR / BR declare war but nothing happens, just prepare with arms, both expected the war to be defensive (like WW1)
Summer 1940, GER takes Denmark and Norway while nothing happens
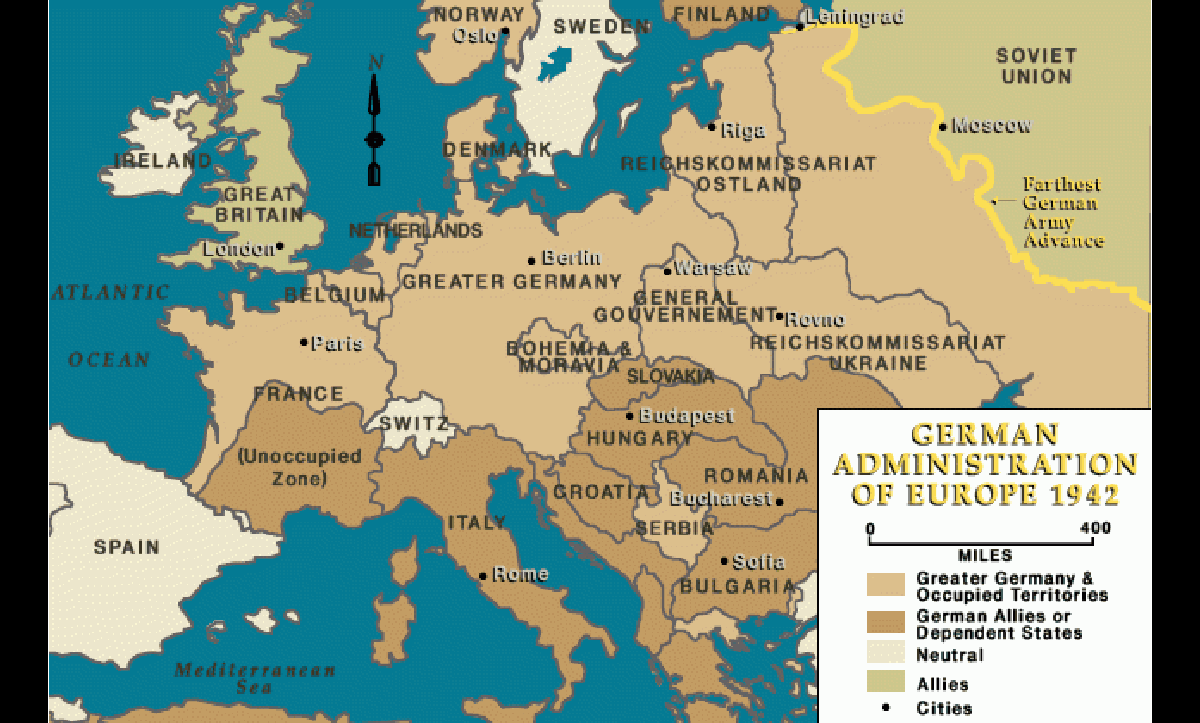
The German invasion of France in May 1940
FR lost in 6 weeks
Vichy regime→ North of FR occupied in June 1940, led by Maréchal Pétain (WW1 hero)
Puppet regime→ authoritarian regime, cooperated with Nazis, collaborationist, conservative (give tributes, men, weapons), sort of part of GER regime
Force labor 600 000 young men work in GER
Anti semitic art shows
FR gathered Jews out of its own initiative, sent 80 000 to camps —> July 16th 1942, Vel d’Hiv Roundup (11 000 French Jews), Internment camp in Drancy
Myth of resistance→ FR free zone occupied 1942, cooperated w/ Nazi racist campaigns, most people did nothing, National Council of the Resistance created in 1943 coordinates all movements of resistance during WW2 in FR (Jean Moulin, Charles de Gaulle)
Triumph of conservatism→ Work / Family / Fatherland
Accommodation - allowed GER to live in their territory, live in their houses, cook for them, les accueillir, ils se sont fait envahir basically
Japan's Southern Strategy
Search for southeast asian ressources (oil) —> US was supplying 80% of Japan's oil
1940 - French Indochina → FR falls and JAP takes it after 1940 for oil
US embargo on oil for JAP to stop them for conquering → reason for Pearl Harbor
Dec 7th 1941 - Pearl Harbor surprise attack, US oil tanks were main target but JAP didn't touch them, just wanted to attack US to take indies 2 months after and conquer East and Southeast Asia —> US enters the war
American Isolationism
Neutrality acts 1935 —> No arm selling to belligerents, no loans
Cash and Carry 1939 —> You can come to US and get your own supply if you had the cash
Too expensive for GER, does not have the means, and hard to go to US
BR control sea so it favors BR
Makes US neutral, anyone could come
US steps towards war before Dec 7, 1941 —> Got scared of JAP, started drafting people, not in war yet but mobilises
Election of 1940→ FDR re elected (3rd time)
“Lend-lease” → allow allies to have stuff for free and pay back later→ hasn’t declared war but subsidising
The Blitz - 1940 to 1941
German bombing campaign on the UK —> initiated with attacks on London in 1940
Aimed to demoralize and destroy British industrial centers and cities
Successful at first
Luftwaffe shifted to night bombings after facing resistance from the RAF —> Liverpool, Hull, Bristol, Cardiff, Birmingham
Over 40,000 civilians were killed but didn't significantly affect British war production
Failure of the German air offensive attributed to a lack of strategic planning and intelligence about British industries.
Battle of Dunkirk summer 1940
As BR sees Fr army failing, tries to retreat to BR but stuck in Dunkirk → Hitler says to stop his army to wait for BR army to catch up
300 000 BR soldiers flee to BR on ships and citizens in BR with boats came to save the army→ very proud moment
The Battle of Britain July-Oct 1940
Right now only BR fighting Nazis in WW2
GER airforce vs BR
Royal air force → Nazis never defeat it, they lost pilots every crash so GER was fighting defense position
Heavy bombing of British cities → kill more civilians with this, want to create fear of massive casualties
Churchill → BR PM, pro-war, famous for keeping up the morale of BR, call to resist through his speeches over radio
Eastern Front
German Invasion (1941):
Operation Barbarossa: German invasion of the Soviet Union on June 22, 1941.
Initial Blitzkrieg: Germans quickly advanced, capturing vast territories and encircling Soviet troops.
Siege of Leningrad: Leningrad (now St. Petersburg) was besieged for over 2 years, resulting in significant civilian casualties.
Battle of Moscow: Germans advanced close to Moscow but were halted by fierce Soviet resistance and harsh winter conditions.
Soviet Counteroffensive (1942-1943) (this is where the tides of the war turn, Germany starts losing):
Battle of Stalingrad: Turning point of the Eastern Front; Soviets encircled and defeated the German 6th Army in early 1943.
Operation Uranus: Soviet counteroffensive at Stalingrad, encircling and trapping German forces.
Battle of Kursk: Largest tank battle in history; Soviets repelled German offensive, marking the end of German offensive capabilities in the East.
Soviet Advance (1944-1945):
Operation Bagration: Soviet offensive in Belarus, resulting in the destruction of German Army Group Centre.
Liberation of Eastern Europe: Soviet forces advanced westward, liberating countries like Poland, Romania, Hungary, and Czechoslovakia.
Battle of Berlin: Soviet capture of Berlin in April-May 1945, leading to the fall of Nazi Germany.
D Day June 6 1944 —> Largest amphibious assault in world history, Normandy
Holocaust
Mass murder, could only be done with effective gov , jews have no identity only # = objectified, dehumanization
6 million jews dead
By 1942 knew they were losing, Einsatzgruppen wasn't working, not efficient enough, dig out all bodies and burn them, the “final solution”
Babi Yar Massacre Sept 1941 - apex of the holocaust by bullets
German forces invaded the SU and took Kyiv (Ukraine) and perpetrated one of the most horrific acts of genocide in history : forced kyiv jewish pop to go to Babi Yar ravine, and forced to walk and undress and shot by the SS and German police
33 771 died during those two days → first european city to lose all of its inhabitants to premeditated murder
American society during WW2
Manhattan project - code name for the American-led effort to develop a functional atomic weapon during ww2
Civilians casualties
40 million civilian deaths
Bombing cities (Dresden)
most people die in Russia 27 millions
War of attrition, holocaust, dont focus too much about tech, blitzkreig only worked with the invasion of france and then WW2 was the failure of it
Guerre totale : goal was to scare everyone so bombing on factories to hurt economy but also civilians
Key terms :
Vichy Regime - collaborationist, led by Petain, anti semitic art show
National Revolution
Collaboration
Accommodation
Conseil National de la Résistance (CNR)
Einsatzgruppen
Holocaust (Shoah)
D Day
Manhattan Project
Key terms
Totalitarianism
Propaganda & Censorship
Police State
Single-Party State
Germany
Aryanism
Volksgemeinschaft
Hitler Youth
Night of the Long Knives (June 30-July 2, 1934)
Reichstag Fire
Enabling Act - voted- 1933
Nuremberg Laws (1935)
Soviet Union:
Communist Youth
Collectivization
Five-Year Plans
Ukrainian Famine
Great Purge
Kulak
Cult of Personality
Reign of Terror