Final - Economía I UFM
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
1
New cards
Commodity tax
Tax on goods
2
New cards
Excise tax
A tax that is paid directly by suppliers to the government
3
New cards
Sales tax
A tax that is paid directly by consumers to the government.
4
New cards
Economic incidence
The division of a tax burden according to who actually pays the tax.
5
New cards
Legal incidence
The division of a tax burden according to who is required under the law to pay the tax.
6
New cards
What is the main consequence of a tax?
Less quantity exchanged
7
New cards
Label a supply and demand graph with a tax wedge
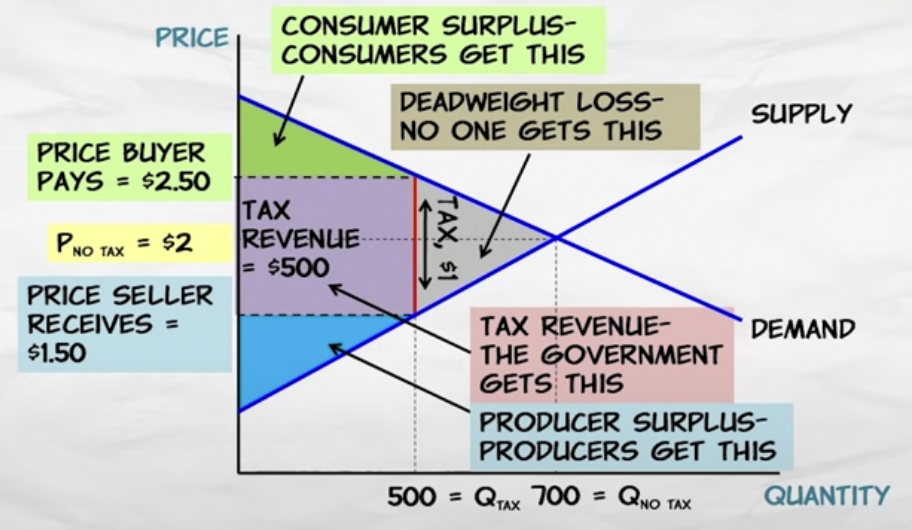
8
New cards
Subsidy
A "negative tax", where the government gives money to consumers or producers.
9
New cards
What is the main consequence of a subsidy?
Creates inefficient increase in trades.
10
New cards
Label a supply and demand curve with a subsidy wedge
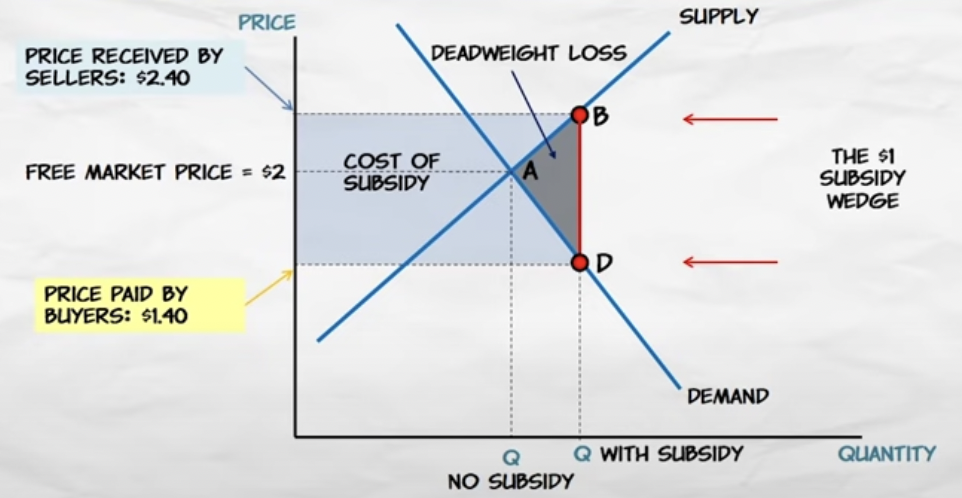
11
New cards
Protectionism
The economic policy of restraining trade through tariffs, quotas o other regulations that burden foreign producers but not domestic producers.
12
New cards
Tariff
A tax on imports
13
New cards
Quota
Restriction on the quantity of goods that can be imported.
14
New cards
Label a supply and demand graph with the impact of a tariff
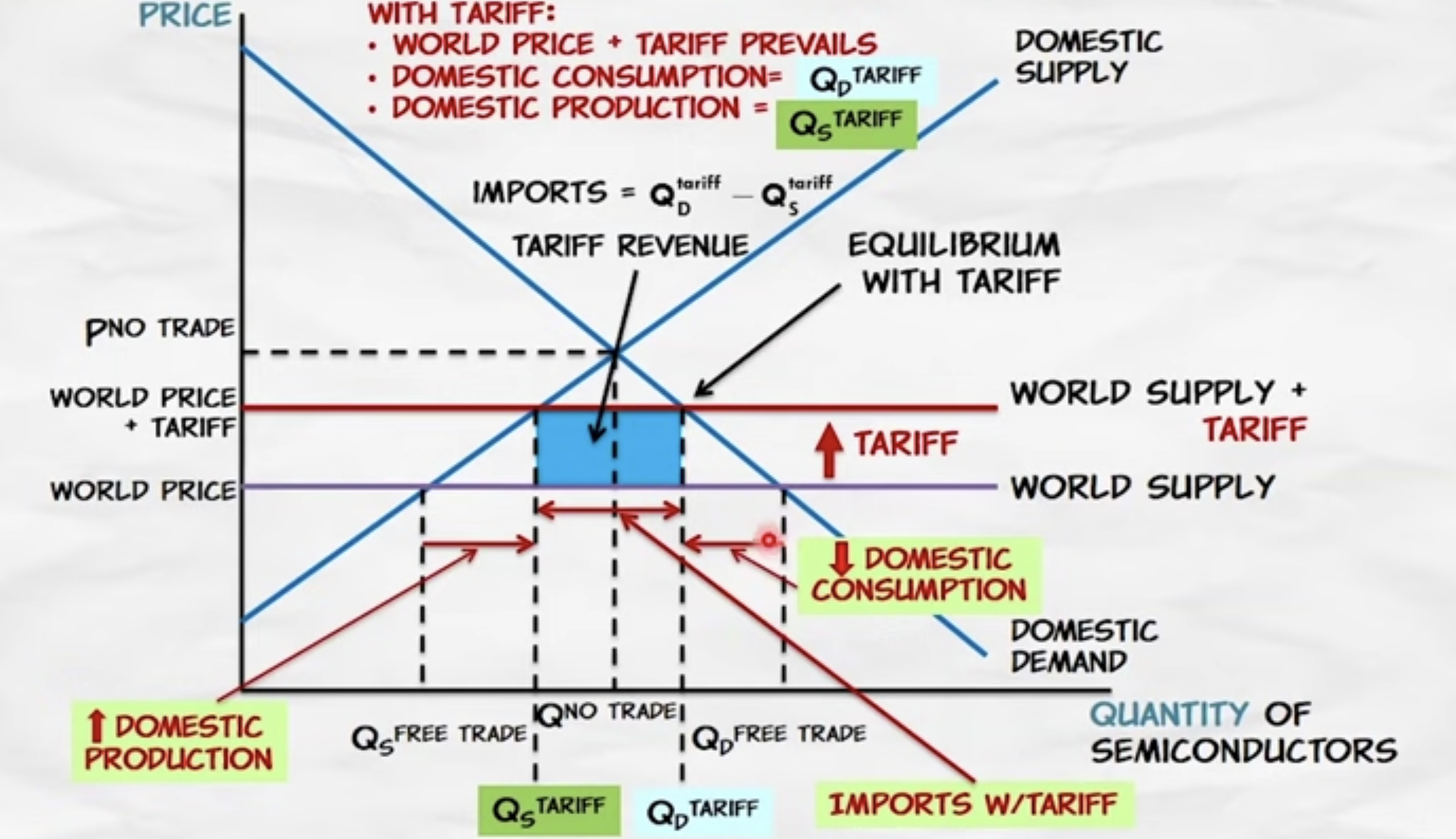
15
New cards
What is the main difference between wage, rent and income, and profit?
Contractual agreements reduce uncertainty.
16
New cards
How do opportunity costs influence an entrepreneur’s decisions?
\
\
Monetary expenses do not capture the total costs of production.
The forgone wage of an entrepreneur might not appear on a ledger, but it will remain in mind and influence choices.
The forgone wage of an entrepreneur might not appear on a ledger, but it will remain in mind and influence choices.
17
New cards
What causes profits to not be reduced to zero by competition?
Uncertainty
18
New cards
What do entrepreneurs do?
They try to reorganize activity to gain profit. They also take the responsibility if it is loss. They are the residual claimant.
19
New cards
Three forms of entrepreneurial driving force
Arbitrage, innovation, imitation
20
New cards
Arbitrage
To buy goods at a low price and sell them at a higher price.
21
New cards
Innovation
Entrepreneurs are always on the lookout for better ways to satisfy consumer demand.
22
New cards
They key to an efficient market process is
Open entry and exit, because comparative advantages change over time.
23
New cards
Speculators help the market by
Coordinating market exchanges through time, they even out the flow of commodities into consumption and diminish price fluctuations over time.
24
New cards
Cost plus markup theory
Business firms calculate their unit costs and add on a percentage markup.
25
New cards
Marginal revenue
The additional revenue expected from an action under consideration.
26
New cards
To maximize net revenue, you need to
Set a price that will enable you to sell all those units, but only those units, for which marginal revenue is expected to be greater than marginal cost.
27
New cards
How are you able to lower the price only to a select group of people?
Price discrimination
28
New cards
Three conditions for successful price discrimination
1. distinguish buyers with different elasticities of demand
2. prevent low-price buyers from reselling to high-price buyers
3. control resentment.
29
New cards
How do price searchers find what they’re looking for?
* estimating the marginal cost and marginal revenue
* determining the level of output that will enable them to sell all those units of output, and only those units for which marginal revenue is greater than marginal cost
* setting their price so that they can just manage to sell the output produced
* determining the level of output that will enable them to sell all those units of output, and only those units for which marginal revenue is greater than marginal cost
* setting their price so that they can just manage to sell the output produced