PTE 731: exam 1
1/118
Earn XP
Description and Tags
pathophysiology module 1: chapters 1-4
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
119 Terms
why must physical therapists perform a screening for referral?
treat as specifically as possible by determining the most appropriate plan of care and intervention strategy for each patient
recognize the need for medical referral
what 4 factors empowers a physical therapist for proper decision making processes?
to other health care professions, PTs can:
refer
consult
retain (direct/supervise)
co-manage
list the 7 reasons for screening per the text.
direct therapy access
quicker and sicker patient base
signed prescription
medical specialization
disease progression
patient disclosure
presence of 1 or more yellow or red flags
T or F: a physical therapist shall consult with an approved health care provider after ten visits or 30 days, whichever comes first, before continuing PT if a patient’s condition has improved and the therapist believes that continued PT is reasonable and necessary.
T
health
state of complete and physical, mental, and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease
disease
state of impaired physical, mental, or social functioning
_______ is the study of the transition from “normal” to “abnormal”.
pathophysiology
recovery involves treatments. what are some examples of treatments discussed in class?
diet
active rest
protected physical activity
medications
emotional support
what are the 3 types of prevention?
primary: stop/avoid disease or illness prior to clinical onset
secondary: early disease detection to limit damage; not clinical apparent
tertiary: improve outcomes in those with disease
what are the elements of patient management?
examination: hx, review of systems, tests and measures
evaluation: assessment of data
diagnosis: determined within scope of practice
intervention: coordination, communication, and documentation of plan
outcomes: actual results of plan
methodological screening chart
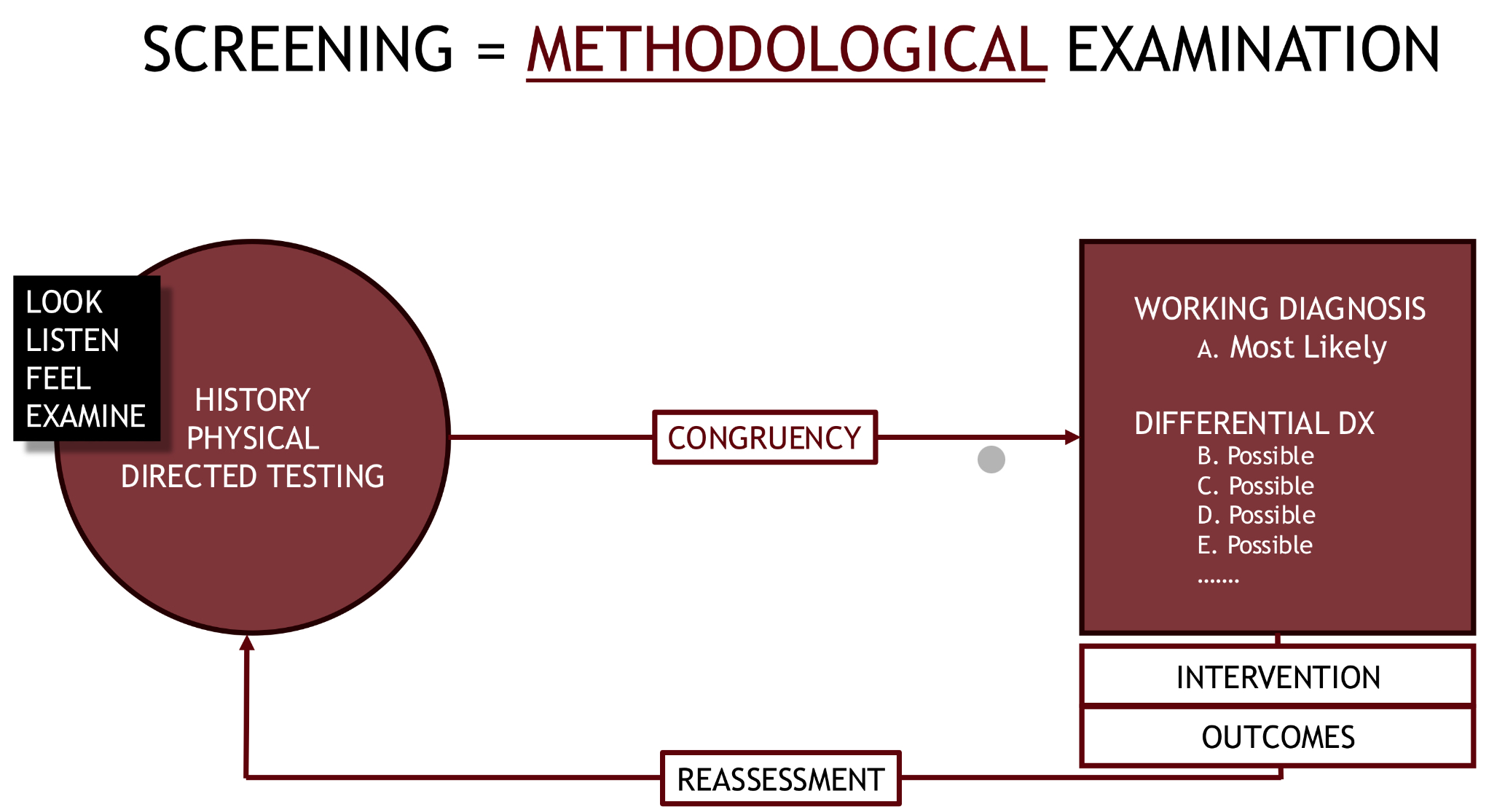
what is possible in the event of incongruence between a patient’s history and a therapist’s working diagnosis?
red or yellow flags
what is considered the number one red flag?
patient has a history of the disease/condition
what characteristics of the patient’s disease are we looking for?
type
onset
intensity
location
duration
progression
modifying factors
what are constitutional symptoms?
a general, systemic indicator of illness that affects a person's overall well-being, rather than a specific organ or localized problem
list the constitutional symptoms.
fever
diaphoresis
episodic sweats
nausea
vomiting
diarrhea
pallor
dizziness/syncope
fatigue
weight loss
what screening list do we perform while collecting subjective information according to Dr. Joe?
chief complaint
history of present illness
past medical and surgical history
medications/ allergies
social history
family medical history
chief complaint
statement of why patient is here
in their own words
give them time to answer
open posture and attitude
history of present illness
pertinent information on the patient’s disease and dis-ease
search for red and yellow flags
include if patient has had this before; if so, what was done and what were the outcomes
past medical history
gathering of historical health info that is seemingly not related to the present illness
past surgical history
any prior surgeries and their outcomes/complications
if it pertains to chief complaint, obtain detailed info
medications/ allergies
any and all current medications (rx, OTC, herbs/spices)
include any allergies- intolerances and reactions
social history
interactions with surroundings and society
think socioeconomic factors
family medical history
similar to past medical history but for family
first degree: mom, dad, brother, sister
second degree: grandparents, uncles, aunts
what are the big 4 medical historical events that are important to obtain during the subjective?
ASCVD (MI/stroke)
hypertension
diabetes
cancer
pain referral patterns
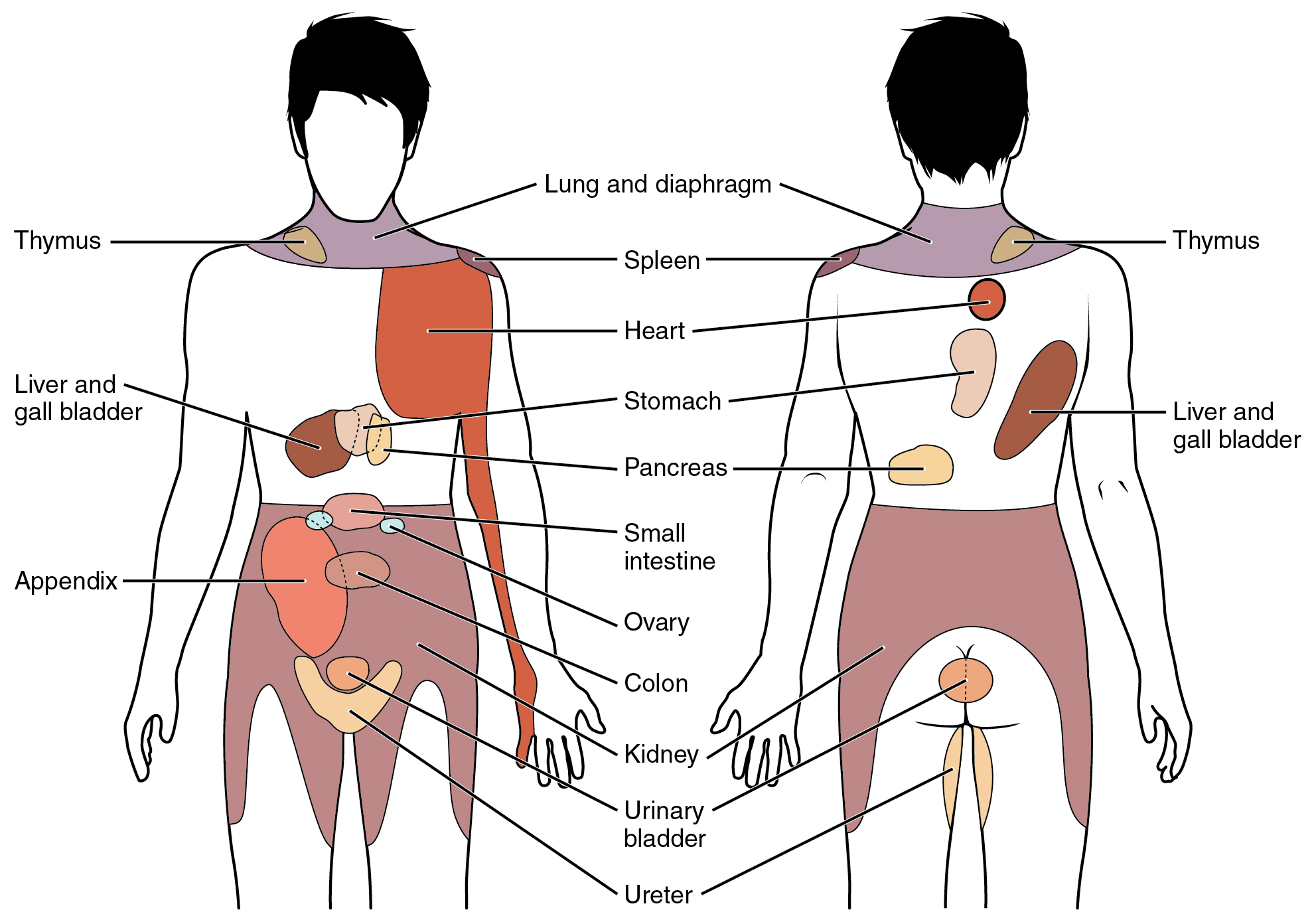
what are the two instances where a therapist will need to refer a patient?
“when no apparent movement dysfunction, causative factors, or syndrome can be identified, and/or the findings are not consistent with the NMS dysfunction.”
reached the limits of your medical knowledge
patient evaluation and referral flow chart
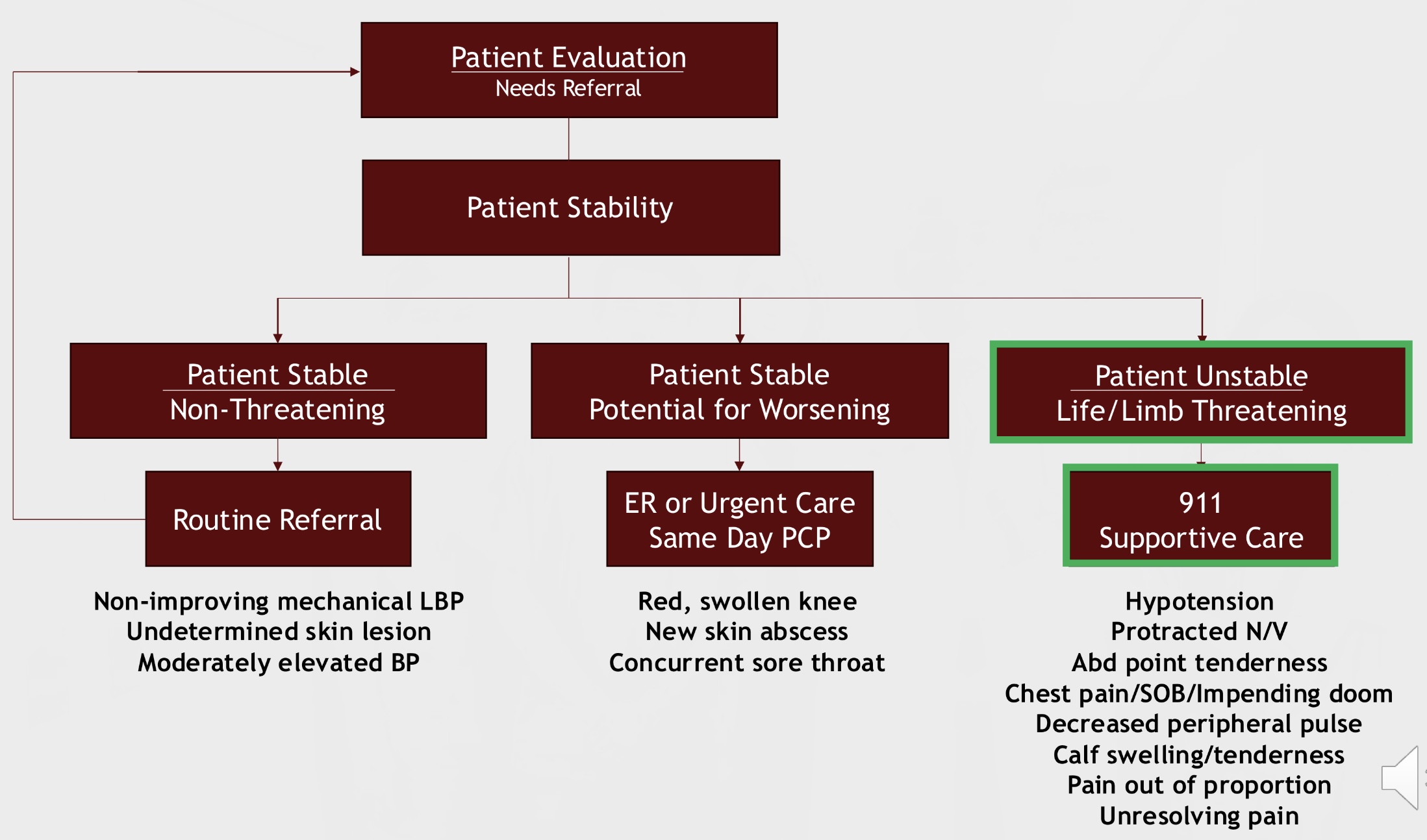
how can a therapist improve his or her nonverbal communication skills when collecting subjective info?
declutter area, sit down, present with an open posture, affirm patient, and maintain neutral expressions
what are the three common errors exhibited by the therapist while collecting the subjective info?
control of conversation
understanding (lack of?)
over assumption
what factors frame an individual’s communication style?
age
gender
ethnic identity
education
religion
what are the therapist traits needed for a good collection of subjective info?
unhurried
empathetic
patient
inviting and accepting
guiding
encouraging
educational
adaptable
what’s the difference between open-ended and close-ended questions according to Dr. Joe?
open-ended: absence of bias; allows patient to state his/her perceived response with out forcefully fitting it to therapist’s agenda (inviting)
close-ended: leading and limits patient’s response (restrictive)
what is the purpose of paraphrasing a patient’s response back to him or her?
it shows/provides validation, clarification, and enhancement
tools/reviews of systems provide these 4 factors to the therapist’s decision making process:
standardization
completeness
relevance
reproducibility
what does the CAGE questionnaire stand for?
pertains to questions related to alcohol use
cut down
annoyed by criticism
guilty about
eye-opener
____ is the most common primary risk factor for disease, illness, and comorbidities.
age
what does CH2OPD2 stand for?
community
home, hobbies
occupation
personal habits
diet, drugs
what factors constitute a fall risk assessment?
impaired balance and/or vision
slower reaction times
decreased strength
limited range of motion
medications/polypharmacy
comorbidities
fear of falling
adverse drug events (ADE)
any harm or injury resulting from the use of a medication
what information is important to gather from a hospitalized patient’s medical record?
age
medical diagnosis
surgery report
physician/nursing notes
associated or additional problems
medications
current precautions or restrictions
lab results
vital signs
what is pain?
an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with, or resembling that of, actual or potential tissue damage
not a vital sign
clinicians should asses pain’s impact on function, context, and patient goals
how are pain and nociception different?
pain is a perception whereas nociception is a “true” neurological experience
what are the three characteristics of pain?
perceptional
personal
learned
pain is a sum of what three functions?
biological
social
psychological
what is the purpose of pain?
to patient: acts as a protective warning system for body
to therapist: an indicator and guide for treatment plan
how is pain perceived?
via a loop response within the body between receptors, neurons, and the cortex
pathway follows along sympathetic pathways
T or F: chronic pain is a learned response
T
nociceptive pain
pain related to damage of somatic or visceral tissue as a result of trauma or inflammation
what are three examples of nociceptive pain cases?
RA and OA
tendonitis/ bursitis
neck and back pain with structural pathology
neuropathic pain
pain related to damage of peripheral or central nerves; an irritated or dying nerve
this type of pain indicates an abnormality of transmission
what are three examples of neuropathic pain cases?
lumbar or cervical radiculopathy
stenosis
PHN
central sensitization
pain without identifiable nerve or tissue damage thought to result form persistent neuronal dysregulation (CNS amplification)
aka nociplastic
what are three examples of central sensitization pain cases?
fibromyalgia
IBS
chronic fatigue syndrome
if a patient presents with mixed pain conditions with multiple pain pathophysiologies (like chronic back pain) what should a therapist do?
identify the predominate type of pain to address first
what are the five sources of pain?
cutaneous
somatic
visceral
neuropathic
referred
T or F: somatic and visceral pain from a deeper source are usually poorly localized.
T
visceral pain patterns are usually experienced in a _______ pattern because the central nervous system has trouble interpreting the input.
dermatomal
what is referred pain?
pain that is perceived at a location different from the actual source of the pain stimulus
list five places referred pain is most likely to be experienced?
chest
back
shoulder
scapula
pelvis
a patient presents with middle and lower back pain. he claims a gradual onset and that his pain does not change when he tries different positions. what source do you suppose his pain is originating from?
visceral diagnosis of abdomen and pelvis area
a patient presents with shoulder pain. she is a collegiate volleyball player, yet the therapist cannot reproduce her pain during testing. what source do you suppose her pain is originating from?
visceral diagnosis of thorax area
the lower thorax and the upper abdomen are visceral pain sources that are hard to differentiate and require careful examination. what are the referral areas associated with each one?
visceral diagnosis of lower thorax: shoulder, mid/upper back, upper abdomen
visceral diagnosis of upper abdomen: lower chest, mid back, shoulder
what are the three mechanisms of referred visceral pain?
embryologic development
multisegmental innervation
direct pressure and shared pathways
how does embryological development play a role in referred pain?
the referred pain pattern is based on the development of tissues and organs from the same embryonic origin
referred pain via ______ _______ describes how viscera (organs) share overlapping spinal segments with somatic structures.
multisegmental innervation
define “pain equivalences”
(painful) symptoms associated with activity while experiencing an underlying visceral issue
example: cardiac issues leads to painful sensations like shortness of breath, fatigue, and nausea
the innervation levels of ______ explain why patients with cardiac issues experience referred pain in various UE and upper trunk regions.
C3 - T4
how do direct pressure and shared pathways play a role in referred pain?
direct pressure: irritation, inflammation, obstruction, or distention of an organ brings it into contact with another, uninvolved organ
shared pathways: nerve signals from the irritated organ travel through ganglions nad nerve plexuses that connect different neural systems and provide local control to organs
describe visceral-organ cross-sensitization
ganglions from each neural system gather and share info through the spinal cord to the plexus
aka pain in one organ results in pain in another, because 2nd order neurons in the CNA have convergent inputs
visceral organs are innervated by the _____ nervous system.
autonomic
visceral pain patterns
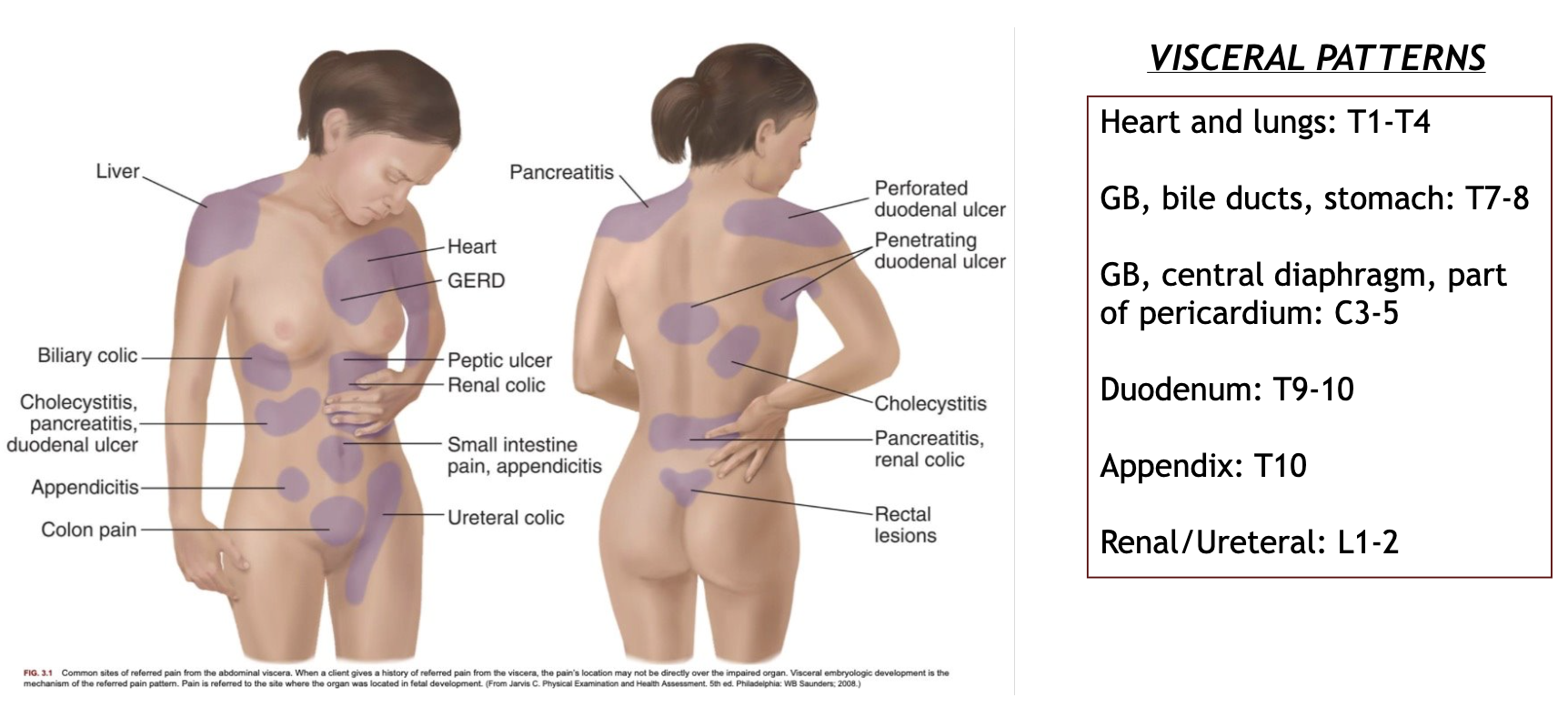
what characteristics of the patient’s pain are we looking for?
type
onset
duration
location
intensity
pattern/behavior
associated signs and symptoms
a patient describes her pain as “aching, sore, and deep.” what source of pain did she just describe?
musculoskeletal
a patient reports “throbbing and sometimes pulsing” pain in his left LE. what source of pain did he just describe?
vascular
a patient “sharp, itching, tingling, and shooting” pain down her right UE. what source of pain did she just describe?
neurogenic
studying for the pathophysiology exam brings on “frightful, agonizing, exhausting, and annoying” pain. what source of pain are you feeling?
emotional :)
T or F: during the screening process, therapists are more interested in separating the musculoskeletal from the non-MSK causes of pain in order to properly identify and refer patients.
T
T or F: cyclical pain is not considered a red flag because it is a natural, reoccurring pain pattern that the patient can deal with.
F; cyclical pain = red flag!
what is the purpose of the physical assessment screen tool?
gather info on the physical condition of the patient in order to identify those who are and are not appropriate for therapy and to arrange appropriate triage in a timely manner for those who are at risk
T or F: a full head to toe physical assessment is always needed.
F; not always needed! if the screening tests are congruent, move on with interventions
what are the four parts of the general survey?
mental status: delirium
nutritional status
odors
vital signs: pulse, temp, RR, SaO2, BP
what are the three parts of the mental status exam?
LOC: awake, aware, responsive
orientation x4: person, place, time, situation
communication: congruent words, actions, and affect
what is delirium?
a temporary often reversible change in mental status that commonly occurs in older patients, especially ~24 hours after hospitalization for serious illness or surgery with general anesthesia
what can lead to a state of delirium?
injury, infection, hypoglycemia, hypoxia, hypotension, and/or medications
the BMI is not the end all, be all for checking nutritional status, but it can still provide healthcare providers with helpful info. what can a classification of over-nutrition and under-nutrition show providers?
over-nutrition: patient may have or be at an increase risk of diabetes, hypertension, MI, stroke, cancer, or dylipidemia
under-nutrition: patient may have or be at an increase risk of poor intake, malabsorption, or hypermetabolic
a patient presents to the clinic with constant fatigue and neck pain/headaches. the therapist notices after a couple weeks that the patient appears more gaunt with noticeable bruising, bagger clothing, and seems disinterested in therapy. what may explain this change?
patient is undernourished
what three smells are common in a patient with diabetes who is not taking care of himself?
pseudomonas
yeasty small
acetone smell
what are considered the primary vital signs according to Dr. Joe?
BP, HR, RR, core temp, and SaO2 (oxygen saturation)
what are considered the secondary vital signs according to Dr. Joe?
pain rating, skin temp, capillary refill, and walking speed
what’s the difference between respiration and ventilation?
respiration: breathing, the physical act of taking in oxygen and expelling carbon dioxide
ventilation: process of bringing fresh, outdoor air into a space while removing stale, indoor air.
normal respiratory rates chart
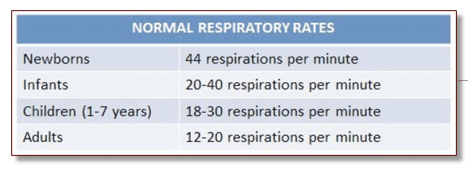
patients with what diseases may experience a low respiratory drive?
TBI, stroke, drug users, and NMD (neuromuscular disease)
where in the cortex is the respiratory drive center located?
pons and medulla oblongata
what is the purpose of the cardiovascular system?
deliver oxygen/nutrients
remove waste
circulate hormones/immune cells
regulate temp, fluid balances, and pH
what is the protocol for measuring an accurate reading of a patient’s blood pressure?
empty bladder
no eating, drinking, or smoking for 30 mins prior
feet flat on floor in quiet environment for 5 mins prior
proper sized cuff
proper patient posture: sitting upright in chair, legs and feet uncrossed, arm resting at heart level, and cuff right above elbow on bare skin
blood pressure chart
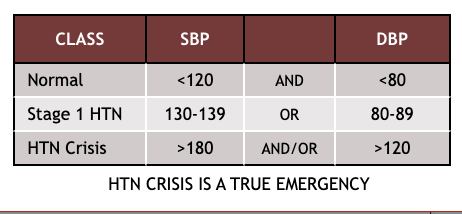
if a blood pressure reading is whack, what should the health care provider do?
wait 5 mins and measure it again (while following proper protocol)
measure it on opposite arm
call/refer out if still whack
a resting SBP > 180 and/or a DBP > 120 are considered a hypertensive crisis, but what’s difference between a hypertensive urgency and emergency?
hypertensive urgency: without signs of organ failure
hypertensive emergency: with signs of organ failure, stroke, heart attack, or dyspnea
a patient who is on vacation in Colorado (high altitude) walked in to a clinic after encountering a bear on a hike. she presents with high stress/anxiety from the incident and states her heart rate hasn’t slowed even after meeting her family for lunch. the health care provider should expect her blood pressure to be ____ than normal.
higher