IBIO TF slides
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Examples of intrinsic immunity
epithelial barriers, antimicrobial peptides, complement
Type of immunity: pathogen induced but not specific to a microbe.
Innate immunity
PAMPs stand for
pathogen associated molecular patterns
PRRs stand for
pattern recognition receptors
Hallmark of adaptive immunity
pathogen specific memory response
2 types of adaptive immunity
humoral immunity: antibodies
cellular immunity: T cells kill virus infected cells
Immature dendritic cells reside in ________. Dendritic cells then migrate to __________.
peripheral tissues; lymph nodes
What activates naive T cells?
mature DCs
_______ lineage comprises most of cells in the innate immune system?
myeloid
Examples of inflammatory inducers
bacterial lipopolysaccharides (LPS), ATP, urate crystals
Location of macrophages? What do macrophages do
Reside in tissues
Phagocytosis and activation of bactericidal mechanisms, antigen presentation, cytokine production
Have phagocytic receptors that bind to microbes
Location of neutrophils? What do they do
In circulation but go to site of infection
Phagocytosis and activation of bactericidal mechanisms
Location of eosinophils? Why do they do
GI tract
Kill antibody-coated parasites
Location of basophils? What do they do
Circulation
Promote allergic response and augment anti-parasitic immunity
Location of mast cells? What do they do
Barrier sites: skin, gut, respiratory mucosa
Release granules containing histamine and active agents
3 major outcomes of complement?
increased phagocytosis (opsonization via opsonins)
cell lysis (via MACs, membrane attack complex)
increased inflammation (via anaphylatoxin)
3 pathways of complement
classical, alternative, lectin
What steps are the same in all 3 pathways?
Only initiation is different, early/late phase are all the same
C3 convertase: cleaves C3 forming C3a (anaphylatoxin), C3b (opsonizes foreign pathogen), and C4b2a which forms complex w/ C3b to become…….
v
C5 convertase: cleaves C5 forming C5a (anaphylatoxin) and C5b (forms complex w/ C6-9 to become……
v
C5b-9: MAC (membrane attack complex)
Initiation steps of 3 pathways of complement
Lectin: mannose binding lectin (MBL) and ficolins recognize and bind carbs on pathogen surface
Classical: C1 complex (antibody mediated)
Alternative: C3 undergoes spontaneous hydrolysis to C3(H2O) to initiate
What is a PRR? What do they sense (broadly)?
pattern recognition receptor. Sense microbes
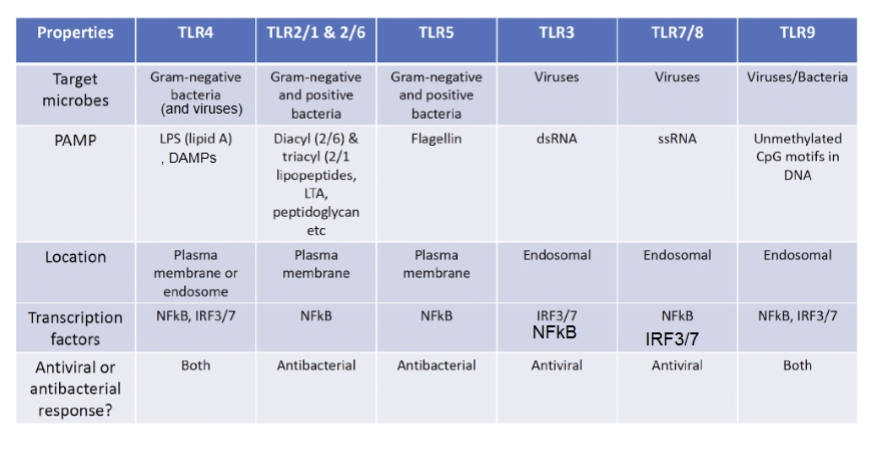
TLR4, TLR2/1+2/6, TLR5, TLR3, TLR7/8, TLR9
Target microbe, PAMP, location, transcription factors, antiviral or antibacterial response?
What does RIG-I recognize? What TFs does it activate?
triphosphate dsRNA: 5’PPP RNA, hairpin/basepaired RNA
IRF3+NFkB
What does MDA5 recognize? What TFs does it activate?
longer dsRNA
IRF3+NFkB
What does cGAS recognize? What TFs does it activate?
dsDNA (found in viruses, bacteria, protozoa)
IRF3
Describe JAK-STAT signaling
Janus kinases (JAKs) bind to cytoplasmic domain of cytokine receptor
Cytokine receptors dimerize after being bound to cytokine, activating and phosphorylating JAKs
TFs (STATs) bind to receptors and get phosphorylated by JAKs
Phosphorylated STATs translocate to nucleus to initiate gene transcriptionS
Stages of leukocyte recruitment
endothelial activation (TNF)
blood vessel dilation slows blood flow
leukocytes roll on blood vessel
chemokines chagne integran conformation to allow for tight binding
metalloproteinases chew through basement membrane
leukocytes extravasate and follow chemokine gradients
Aka rolling, tight binding, diapedesis, migration
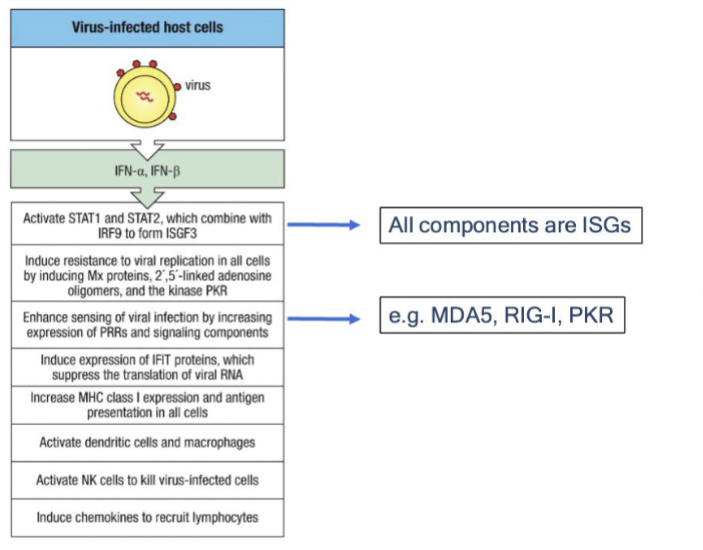
Major functions of Type 1 IFNs
viral interference, inflammation, DC/NK activation, increases antigen presentation (by increasing MHC I expression and antigen presentation of all APCs
How do NK cells kill infected/stressed/tumor cells?
Lack of MHC I (all “self” cells have MHC I)
Presence of stress ligands detected by receptors on NK cells
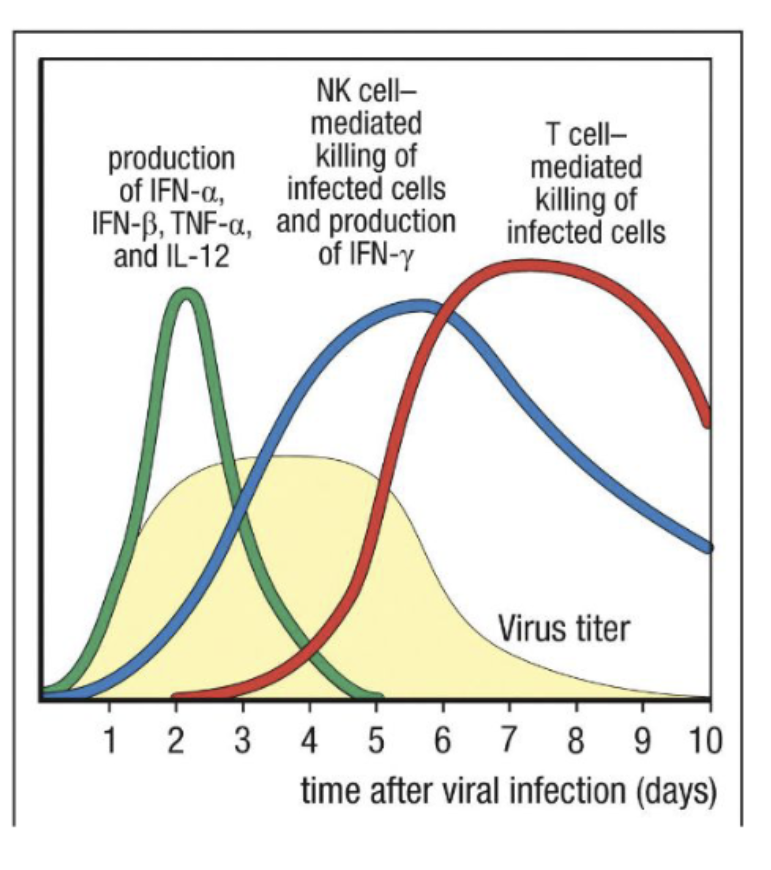
Kinetics of viral response
How does Type I IFN prime the anti tumor response?
DC recruitment and activation
NK recruitment
DC cross dressing
More MHC I presentation—> MOre CD8 T cell activation—> more killing tumor cells
Activating nucleic acid sensors RIGI and cGAS
Som examples of DAMPs? PAMPs vs DAMPs
PAMPs: molecules associated/produced by pathogens.
DAMPs: molecules produced by body’s own cells when they are stressed/damaged/dying (pyroptosis). Alert immune system to tissue damage even in absence of pathogen. Include ATP, heat shock proteins, DNA/RNA released into cytoplasm
What is pyroptosis?
inflammatory cell death (causes cells to lyse and release inflammatory molecules)
triggered by inflammasomes
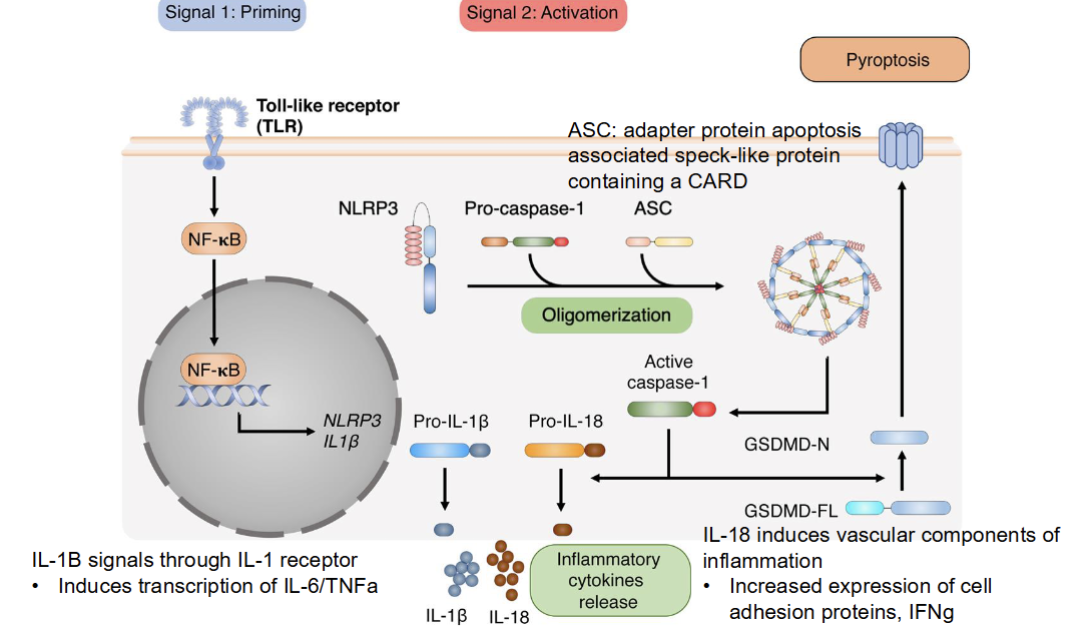
Stages of inflammasome actvation
Priming (via TLR signalling which leads to downstream NK-kB—> NLRP3 and IL1 beta)
Activation (pro cytokines cleave into active cytokines, inflammasomes assemble
Inflammasome activates caspase 1 which cleaves pro-IL1beta, pro-IL18, and gasdermin D
Pyropptosis (gasdermin D pore causes cell lysis and release of Il1beta and IL18)
What are caspases?
cysteine aspartic proteases. Execute events leading to inflammation/cell death
Know cyotkine receptor families
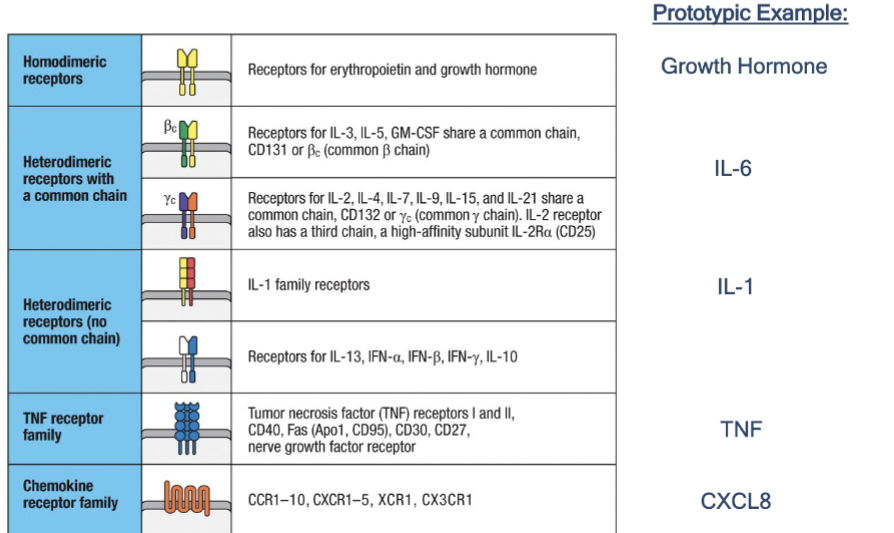
IL-1b: family, local and systemic effect (if applicable)
Family: IL-1 family; heterodimeric receptor (no common chain
Local effect: vascular endothelium, lymphocytes, increases access of effector cells
Systemic effect: fever, production of IL6
TNF alpha: family, local effect, systemic effect if applicable
Family: TNF receptor
Local effect: Activates vascular endothelium and increases vascular permeability, which leads to increased entry of IgG, complement, and cells to tissues and increase flood drainage to lymph nodes
Systemic effect: fever, mobilization of metabolites, shock
IL6: family, local effect, systemic effect if applicable
Family: hematopoietin/heterodimers (with a common chain)
Local effect: lymphocyte activation, increased antibody production
Systemic effect: fever, induces acute phae protein production
CXCL8
Family: chemokine receptor family
Local effect: chemotactic factor recruits neutrophils, basophils, T cell to infection
No systemic effect
IL-12
Family: hematopoietin family/heterodimers with a common chain
Local effect: activates NK cells, induces differentiation of CD4 to TH1 cells.
Systemic effect: NA
Describe DC transition from immature to mature
Immature: Increased phagocytic capacity (looking for foreign antigens), decreased MHC II expression
Things that trigger activation: cytokines, (GM-CSF, IFNgamma, IL4, PAMPs, DAMPs, pathogens)
Then migrates to lymph nodes upon activation. DC decreases expression of chmoekine receptors that keep it in tissue (Ex. CCR6, CXCR4) and increases expression of CCR7 (which guides DC to T cells)
Mature T cell: increased costimulatory molecules, MHC II expression, pro-inflammatory cytokines, CCR7, glycosis. Decreased phagocytic capacity
What things are upregulated/downregulated in immature DCs?
Increased phagocytic activity
Decreased MHC II presentation
What does CCR7 do for DCs?
Guides DCs to lymph nodes, allowing mature DCs to present antigens to T cells
What are MHC molecules for
MHC I is present on APCs/all cells, TCRs bind to antigen on MHC I, leading to T cell activation
What is MHC restriction
T cell’s TCR can only recognize an antigen when it’s bound to a specific MHC, determined by the T cell’s own MHC type
Difference btn MHC I and II
1: Present in all cells, presented to effector CD8 T cells
2: Presented on dendritic cellls, macrophages, B cells (professional APCs), presented to effector CD4 T cells.