FAH101 Flashcards / Review
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
The Parthenon, Athens (447-432 BCE) - Ictinus and Callicrates
The Parthenon, Athens (447-432 BCE) - Geographical and Urban Context
The second main point is the geographical and urban context, the Parthenon was built on the Acropolis, which made the Parthenon visible from all parts of the city and beyond.
The Parthenon, Athens (447-432 BCE) - historical context and significance
The first main point about the historical context and significance of the Parthenon that Professor Kim discussed in the first lecture is the historical background behind the Parthenon, it was created during the High Classical Period and the Post-Persian War.
The Parthenon, Athens (447-432 BCE) - cultural and religious significance.
The third main point is the cultural and religious significance. The Parthenon was a Victory Monument, Treasury, the Center of Ritual and Temple to Athena Parthenos.
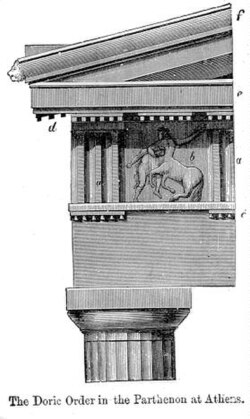
The Parthenon, Athens (447-432 BCE) - Doric Order Columns
The classical architectural order that the Parthenon columns belong to are the Doric order.
Gemma Augustea (9-12 CE) - Believed to have been made by Dioscurides or one of his disciples.
Gemma Augustea - Materials used
The first main point that Professor Kim made about the Gemma Augustea is that the Gemma Augustea is made of Sardonyx, a material which is Onyx layered with Sard. The white part of the Onyx is carved in low relief so the dark layer is revealed, and to achieve visual contrast.
Gemma Augustea - Hierarchial Message
The second main point is that the Gemma Augustea displays a hierarchical message. There are two registers which display the figures. The upper register has larger figures and a stable composition. The lower register is smaller and displays the defeated Roman soldiers and Barbarians.
Gemma Augustea, Political Statement
The third main point is that the artwork displays a political statement of undeniable power, focusing on the New Empire's structure.
The Great Mosque of Damascus (716-705 CE)
The Great Mosque of Damascus (716-705 CE) Commissioner
Al Walid comissioned the Great Mosque of Damascus. When the Church of John the Baptist in Damascus was destroyed, Al Walid also decided to keep the relics of St John the Baptist were preserved within the new Mosque.
The Great Mosque of Damascus (716-705 CE) Style
The style of the Great Mosque of Damascus is rooted in the antique and late antique, and contemporary Roman and Byzantine styles and practices.
The Great Mosque of Damascus (716-705 CE) Iconography
The iconography of the Great Mosque of Damascus is not crystal clear, but it is very unique. There is textual iconography such as the Quranic texts which are a part of the experience of the Great Mosque. These Quranic texts speak from a religious point about the end of the world and the importance of Islam.
The Great Mosque of Damascus (716-705 CE) Patronage
The Patron of the Great Mosque of Damascus and its Patrons is the caliph Al-Walid. Al-Walid wanted to build a great religious structure and something that gives him the religious credit of Islam, political credit and the political status of his Islamic caliphate.
The Great Mosque of Damascus (716-705 CE) Function
The Great Mosque of Damascus functions as a place of worship and a place where people can pray. It also functions as a symbol of the grandeur of the Umayyad Caliphate. The reception of the Great Mosque is that it's an important religious place of worship and a symbol of the Umayyad Caliphate.
The Great Mosque of Damascus (716-705 CE) Islamiate Term
The term "Islamicate" applies to the Great Mosque of Damascus because the Great Mosque is a social and cultural place which was influenced by Muslim society.
Picasso, Demoiselles d'Avignon (1907)
Picasso, Demoiselles d'Avignon (1907) Sources
Picasso's Les Demoiselles d'Avignon (1907) uses various sources, such as European art heritage, his collection of art and his own experiences as a visitor to the Paris ethnographic museums, where objects from African civilizations were displayed and the works from the museum.
Among these objects in the Paris ethnographic museums, were masks from African civilizations. The two women on the right side of the paiting seem to be wearing masks.
Picasso, Demoiselles d'Avignon (1907) Spectatorship
In Picasso's Les Demoiselles d'Avignon (1907), the figures are looking at the spectator, the painting is looking at the spectator and confronting them, which makes the spectator a part of the story.
Picasso, Demoiselles d'Avignon (1907) Space
One surprising observation about Space in Picasso's Les Demoiselles d'Avignon (1907) is that the figures are displayed from a different view, even though the figures share the same space.
Beau Dick, Killer Whale Mask , 2017
The Style in Beau Dick's Killer Whale Mask (2017)
The Style in Beau Dick's Killer Whale Mask (2017) has primary form lines, secondary form lines, which create the space for elements, it's geometric, and it uses a few primary colours.
Beau Dick's Killer Whale Mask (2017) Reception
Beau Dick's Killer Whale Mask (2017) has a positive reception, it is viewed as a connection to the Northwest Coast art style, and as a mask which is used in ritual ceremonies in the Northwest Indigenous Communities.
Beau Dick Killer Whale Mask, 2017 Iconography
In Beau Dick's Killer Whale Mask (2017), the Iconography represents the killer whale.
Killer Whale Mask (2017) Artist
The artist of the Killer Whale Mask (2017) is Beau Dick.
The purpose of Beau Dick's Killer Whale Mask (2017)
The purpose of Beau Dick's Killer Whale Mask (2017) was to display and highlight the connections between the Kwakwaka'wakw community, Northwest Coast art and the ritual ceremonies in which the masks were used.
The function of Beau Dick's Killer Whale Mask (2017)
The function of Beau Dick's Killer Whale Mask (2017) is to perform ritual functions in an art museum.
The audience of Beau Dick's Killer Whale Mask (2017)
The audience of Beau Dick's Killer Whale Mask (2017) is the Northwest Coast Indigenous communities and the Kwakwaka'wakw community. The audience can also include those who viewed the Killer Whale Mask in the Museum which it is located in.
Xi'an Terracotta Warriors (221-206 BCE)
The Terracotta Army is a collection of terracotta sculptures depicting the armies of Qin Shi Huang, the first emperor of China. It is a form of funerary art buried with the emperor in 210–209 BCE with the purpose of protecting him in his afterlife. Qin Shi Huangdi's funerary complex included sculptures of military figures, acrobats, administrators and other professions.
Style of Terracotta warriors
The style of the terracotta warriors is a realistic and individualized style. Each warrior possesses unique facial features, hairstyles, and clothing, reflecting the diversity of the Qin Dynasty's army. The figures are not merely generic representations; they are crafted with attention to detail, showcasing different postures, expressions, and even variations in armour and weaponry
Iconography of Terracotta warriors
The iconography of the Terracotta Warriors features a rich array of iconography representing the military, social hierarchy, and beliefs of ancient China during the Qin Dynasty. Each warrior, while part of a larger army, is individualized with unique facial features, hairstyles, and clothing, signifying their rank and role.
Artist of Terracotta warriors
The artist of the terracotta warriors is a large number of unknown artisans and craftsmen who were commissioned by Qin Shi Huangdi and his court to design the warriors.
The patron of the terracotta warriors
The patron of the terracotta warriors is Qin Shi Huangdi himself.
The function of the terracotta warriors
The function of the terracotta warriors is to protect the tomb where Qin Shin Huangdi, the emperor, is buried. The Terracotta Army, including the Terracotta Warriors, was created to serve as funerary art and to protect Emperor Qin Shi Huang in the afterlife.
The audience of the terracotta warriors
The audience of the terracotta warriors is tourists, history enthusiasts, and those interested in Chinese culture and archaeology. The terracotta warriors audience also expands to visitors of museums where they might be displayed.
The reception of the terracotta warriors
The reception of the terracotta warriors is positive; the terracotta warriors are seen as a funerary art piece.
Historical Significance of Terracotta Warriors
The historical significance of Qin Shi Huangdi's funeral complex is that Qin Shi Huangdi and his court saw the function of the tomb as being able to insert Qin Shi Huangdi into the political landscape and spiritual landscape. The terracotta warriors also display the military system and social beliefs of the Qin dynasty. The art-historical significance of Qin Shi Huangdi's funerary complex is that it is a display of the elaborate and intricate afterlife beliefs of the Qin Emperor, Qin Shi Huang. The tomb is distinctive because of its location, large terracotta soldiers and the unique craftsmanship of the terracotta soldiers.
The Hours of Jeanne d’Evreux by Jean Pucelle , 1324 - 1328
The Hours of Jeanne d'Evreux is an illuminated book of hours in the Gothic style. According to the usual account, it was created between 1324 and 1328 by Jean Pucelle for Jeanne d'Evreux, the third wife of Charles IV of France.
Toolkit for The Hours
The style of the book is a classic masterpiece of Gothic illumination, and the architectural surrounds to many images show typical French Gothic architecture of the period.
There are several iconographic features in the Hours of Jeanne d’Evreux that are worth mentioning. Some iconographic features are the depictions of the life of St Louis, Jesus carrying the cross and Jeanne d’Evreux in the Abbey Church of Saint-Dennis and a vision of Saint Louis. Throughout the book, there are various iconographic features of animals on the sides of the words or drawings.
The patron of the Hours book was Jeanne d’Evreux. The audience also seems to be Jeanne d’Evreux herself.
The function of the book was to serve as a book of faith and worship for Jeanne d’Evreux.
The reception of the book is that it’s a book which symbolizes the new printing technology, the French Gothic art style and the role of art in worship.
St Peters Basilica by Bernini (last person to touch the person), November 18, 1626. Toolkit
The style of St. Peter’s Basilica is Renaissance architecture. There are some Baroque elements in the Basilica.
St. Peter's Basilica has various iconography. Some iconography which the St. Peter's Basilica has is the dome, Bernini’s Baldachin and the chair of St Peter.
St. Peter’s Basilica was created by various artists. It was designed principally by Donato Bramante, Michelangelo, and Carlo Maderno, with piazza and fittings by Gian Lorenzo Bernini,
The patron of the St. Peter's Basilica is dedicated to and named after Saint Peter, one of the Twelve Apostles of Jesus and the first Bishop of Rome (Pope).
The function of St Peters basilica is a church, it is a place where people can go to pray.
The audience of the The primary audience for St. Peter's Basilica is a combination of pilgrims, tourists, and those attending liturgical functions, including Papal Masses and general audiences.
The reception of the St. Peter's Basilica is that it’s considered a masterpiece of Renaissance architecture and an important and central site for Christianity.
St Peters Basilica Main Four Points
The first piece of contextual information is that the Church was destroyed due to the various conflicts in Europe. The second piece of contextual information is that the Church's administration needed a better place to work due to the Church's ruined state. The third piece of contextual information is that Pope Julius II envisioned a grand church, which led to artists and architects being involved in the church's reconstruction. The fourth piece of contextual information is the Reformation movement, which was led by Martin Luther.
Monet, Impression, Sunrise (1872)
The painting is credited with inspiring the name of the Impressionist movement. This painting is characterized by visible brush strokes, open composition, emphasis on accurate depiction of light in its changing qualities (often accentuating the effects of the passage of time), ordinary subject matter, unusual visual angles, and inclusion of movement as a crucial element of human perception and experience.
The style of the painting is Impressionism.
The iconography of the painting is the boats on the water, with the sun in the background.
The artist of the painting is Claude Monet.
The patron of the painting is unknown.
The function of the painting is that it serves primarily to capture the sensory experience of the moment.
The primary audience for Claude Monet's "Impression, Sunrise" was initially the general public and art critics.
The initial reception of Claude Monet's Impression, Sunrise was highly controversial and critical, with many viewers and critics dismissing it as unfinished and lacking in traditional artistic skill. However, the painting also garnered praise from some contemporaries and eventually became the defining work of the Impressionist movement.
Guggenheim Museum (1959) by Frank Lloyd Wright
The style is contemporary. It was designed by Frank Lloyd Wright.
The iconography of the Guggenheim Museum includes the iconic dome,
The patron of the museum is the Solomon R. Guggenheim Foundation. The Museum is named after Solomon R. Guggenheim.
The function of Guggenheim Museum in New York City primarily functions as a museum of modern and contemporary art.
The audience of the museum is tourists and visitors of the museum.
The reception of the museum was first controversial for its design, but now it is viewed as a symbol of contemporary art design.