Ap Biology Unit 7
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Evolution
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Evolution
The change in heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations
Adaptations
Physical or behavioral characteristics that have developed to allow an organism to better survive in its environment
Natural selection
The mechanism that drives evolution, where organisms with favorable traits are more likely to survive and reproduce
Homology
Similarity in characteristics due to shared ancestry
Homologous structures
Structures that have the same evolutionary origin but may serve different functions
Vestigial structures
Remnant structures that have lost their original function through evolution
Convergent evolution
The independent evolution of similar features in species of different lineages
Analogous
Structures that have similar functions but different evolutionary origins
Biogeography
The study of the distribution of species and ecosystems in geographic space and through geological time
Microevolution
The change in allele frequencies that occurs over time within a population
Genetic variation
The differences in DNA sequences between individuals of a species
Neutral variation
Multiple alleles present at a given genetic locus that are not distinguishable by natural selection
Population
A group of organisms of the same species living in a particular geographic area
Gene pool
The complete set of unique alleles in a species or population
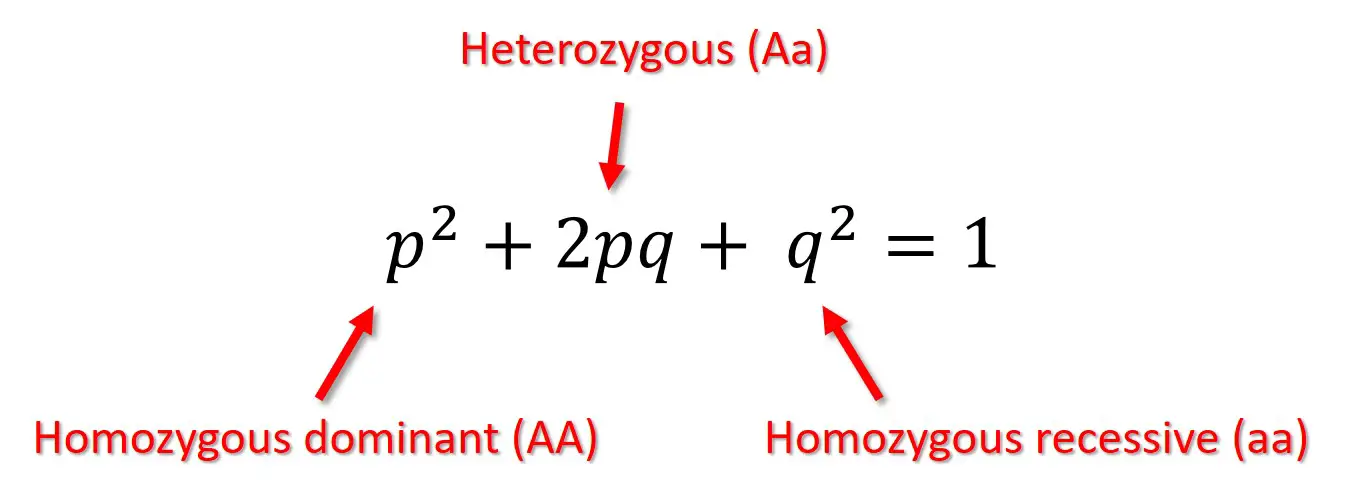
Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium
A principle stating that allele and genotype frequencies in a population will remain constant in the absence of evolutionary influences
Genetic drift
Random changes in allele frequencies within a population
Founder effect
Loss of genetic variation when a new population is established by a small number of individuals from a larger population
Bottleneck effect
Reduction in genetic diversity due to a sharp decrease in population size
Gene flow
The transfer of genetic material between populations
Adaptive evolution
The process by which organisms become better suited to their environment through natural selection
Relative fitness
The contribution of a genotype to the next generation relative to the contributions of other genotypes
Directional selection
Selection favoring extreme values of a trait
Disruptive selection
Selection favoring extreme values at both ends of a trait distribution
Stabilizing selection
Selection favoring intermediate values of a trait
Heterozygote advantage
When heterozygous individuals have a higher fitness than homozygous individuals
Sexual selection
Selection based on the ability to attract mates
Sexual dimorphism
Distinct differences in appearance between males and females of a species
Phylogeny
The evolutionary history and relationships among species or groups of species
Taxonomy
The science of naming, describing, and classifying organisms
Binomial
The two-part scientific name of a species, consisting of genus and specific epithet
Levels of Linnaean Classification
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species
Taxon
A group of organisms classified as a unit
Phylogenetic tree
A branching diagram showing evolutionary relationships among organisms
Branch points
Points on a phylogenetic tree where lineages diverge
Sister taxa
The closest relatives in a phylogenetic tree
Rooted
A phylogenetic tree with a specified common ancestor
Polytomy
A branch point on a phylogenetic tree with more than two immediate descendants
Analogy
Similarity in function but not in evolutionary origin
Shared characters
Traits shared by different species due to common ancestry
Maximum parsimony
A method for inferring phylogenies that minimizes the number of evolutionary changes
Macroevolution
Large-scale evolutionary changes, often leading to new taxonomic groups
Biological species concept
Definition of a species as a group of interbreeding populations reproductively isolated from other such groups
Reproductive isolation
Mechanisms that prevent members of different species from producing viable, fertile offspring
Prezygotic barriers
Reproductive isolating mechanisms that act before fertilization
temporal, habitat, behavioral, gametic, and mechanical
Postzygotic barriers
Reproductive isolating mechanisms that act after fertilization
hybrid inviability, hybrid sterility, and hybrid breakdown
Allopatric speciation
Speciation occurring when populations are geographically isolated
Sympatric speciation
Speciation occurring within the same geographic area