Circuit components AYr1
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Circuit components definitions, symbols (British) and their graphs
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
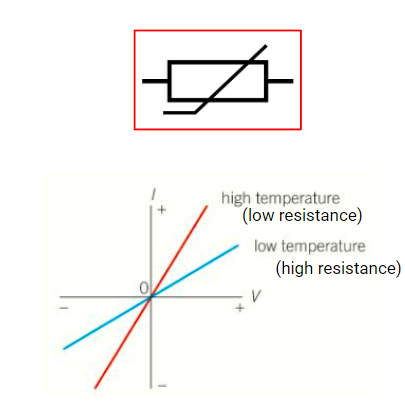
Thermistor (negative coefficient)
high temperature, low resistance
low temperature, high resistance
made from semiconducting materials
used in sensor circuits
Rheostat
c
Potensiometer
d
Sensor circuits definition
A circuit that uses a sensor (light dependent resistor/thermistor) to trigger another component in the circuit
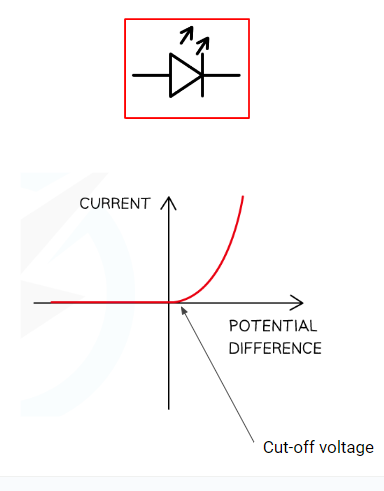
Light emitting diode
Same in all respects as a standard diode, only it emits light when a current goes through
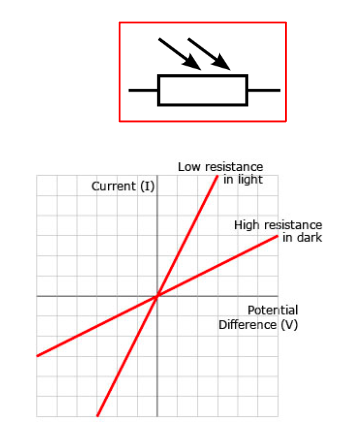
Light dependent resistor
A resistor whose resistance depends on the amount of light incident on it.
It is a negative coefficient semiconducting material - more light means it releases more delocalised electrons, decreasing its resistance.
Used in sensor circuits (e.g. triggers when the sun goes down)
Switch
breaks the circuit when open
must be closed for current to flow
Cell and battery
Provide the energy in DC circuits
Have a positive and negative terminal
Conventional flow of current from positive to negative
Have an EMF and a terminal P.D
a battery is mulitple cells linked together (in series)
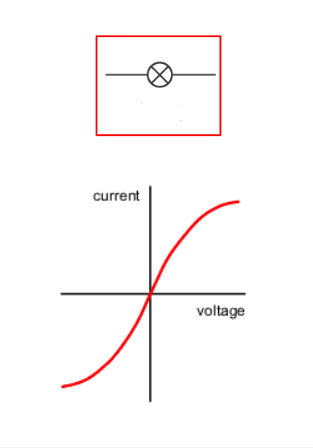
Lamps/bulbs (filament)
Convert electrical energy to Light and Heat
Resistance increases with the current and the voltage because their temperature rises
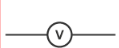
voltmeter
Measure the P.D. between its two terminals
Always connected parallel with the component whose P.D. we wish to measure
Has practically infinite resistance (current never flows through it)
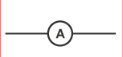
ammeter
Measures the current through a component
Always connected in series with the current we want to measure
Has practically zero resistance (does not affect the flow of current)
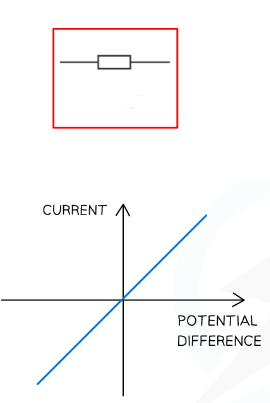
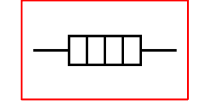
fixed resistor
Obeys Ohm’s Law
R only depends on temperature
Energy transferred to it turns to heat and dissipates to the surroundings (air, water etc)
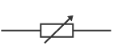
variable resistor
A resistor whose resistance we can vary at will within certain limits
Used in light dimmers and many other applications
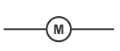
motor
A component which uses the energy transferred to it to generate motion
Motion is rotational e.g. axles, winches, washing machine drums, mixers etc
(more in YR13)
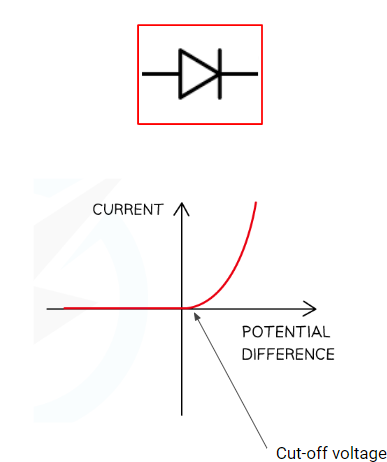
diode
Only allows current to go through in a given direction (that of the arrow)
Has a cut-off voltage - i.e. will not conduct current below a certain value even if it is in the right direction
heater
Similar to resistors, it generates heat when an electric current flows through
E.g. electric blankets, rear car window resistors etc
cut off voltage
the component will not conduct current below a certain value (even if in correct direction for a diode)
seen in diodes (not sure about other components)
equivalent resistance
total electrical resistance caused by all of the resistors in the circuit acting together against the voltage source