Geology 201 Lab Midterm
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/158
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
159 Terms
1
New cards
what are the 3 kinds of north displayed on a map?
true north, magnetic north, and grid north
2
New cards
National Topographic System (NTS)
Canada's official map index system
divides into large, numbered blocks based on lat+long
designed to locate areas, not points
divides into large, numbered blocks based on lat+long
designed to locate areas, not points
3
New cards
Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM)
designed to locate points, not areas
numeric code only, no number/letter combos
uses a decimal system rather than degrees-minutes-seconds
2cm = 1km
ex. zone 11 699 100 easting 5657 250 northing
numeric code only, no number/letter combos
uses a decimal system rather than degrees-minutes-seconds
2cm = 1km
ex. zone 11 699 100 easting 5657 250 northing
4
New cards
Latitude and Longitude
divide earth with lines
W-E = longitude
N-S = latitude
ex. 114°9'40" W 51°1'40" N
W-E = longitude
N-S = latitude
ex. 114°9'40" W 51°1'40" N
5
New cards
colour
least reliable physical property.
felsic = light
mafic = dark
felsic = light
mafic = dark
6
New cards
lustre
quality of light reflected from a mineral: metallic, vitreous, earthy
7
New cards
hardness
measure of how easily a mineral can be scratched
8
New cards
streak
refers to the colour of a powdered mineral
9
New cards
cleavage
a mineral's ability to split easily along flat points of weakness.
10
New cards
habit
the shape of an unbroken mineral crystal; shape it naturally forms
11
New cards
homogenous
made up of a single material
12
New cards
heterogenous
made up of several materials
13
New cards
biogenic
consisting of the remains of organisms or formed due to the activity of organisms
14
New cards
abiogenic
resulting from non-biological chemical reactions
15
New cards
aggregate of crystals
rock composed of many crystals
16
New cards
aggregate of grains
rock composed of fragments of: rocks, crystals, or fossils that show signs of physical reworking from current transport or erosion
17
New cards
amorphous
does not contain crystals or grains, typically glassy
18
New cards
mineral
a naturally occurring, inorganic solid that has a crystal structure and a definite chemical composition
19
New cards
fossil
any evidence of life in the rock record. includes plant and animal remains as well as traces of biological activities (footprints)
20
New cards
rock
aggregate of mineral crystals, fossils, grains, or a mass of natural glass
21
New cards
Igneous rocks form by
the crystallization of molten magma or lava (intergrown crystals)
22
New cards
intrusive igneous rock
rock that forms below Earth's surface (longer to cool, typically larger crystals)
23
New cards
extrusive igneous rock
rock that forms from the cooling and crystallization above the Earth's surface
(less time to cool, typically smaller crystals)
(less time to cool, typically smaller crystals)
24
New cards
phaneritic texture
coarse-grained, crystals are large enough to be seen by naked eye, formed by slow cooling (intrusive)
25
New cards
aphanitic texture
fine grained, crystals cannot be seen with the naked eye, formed by fast cooling (extrusive)
26
New cards
glassy/amorphous texture
A texture formed when a rock cools so fast it doesn't have time to crystallize
27
New cards
porphyritic texture
an igneous texture consisting of large crystals embedded in a matrix of much smaller crystals
28
New cards
phenocrysts
large crystals in porphyritic rocks
(igneous)
(igneous)
29
New cards
vesicular texture
describes a rock containing vesicles caused by gas being trapped during crystallization
30
New cards
mafic rocks (igneous)
dark-colored rocks that are silica poor and iron and magnesium rich. examples:
olivine, pyroxene, plagioclase, and amphibole
olivine, pyroxene, plagioclase, and amphibole
31
New cards
intermediate rocks (igneous)
examples: plagioclase, hornblende, quartz, pyroxene, biotite, k-feldspar
32
New cards
felsic rocks (igneous)
light colored rocks that are silica rich and iron and magnesium poor. examples: plagioclase, k-feldspar, quartz, amphibole, and biotite
33
New cards
sedimentary rocks form by:
sediments by compaction and cementation, evaporation of water & organic remains
34
New cards
crystalline texture (non-clastic, sedimentary)
- a term for the texture of sedimentary rocks in which the minerals form a pattern of interlocking crystals
- consist of inter-grown crystals (may resemble igneous rocks)
- consist of inter-grown crystals (may resemble igneous rocks)
35
New cards
clastic texture (sedimentary)
- a term for the texture of sedimentary rocks in which an aggregate of grains have been subsequently cemented together
36
New cards
chemical vs clastic sedimentary rocks
clastic: deposition and subsequent cementation and compaction of sediment
chemical: precipitation of minerals out of a solution (ex. limestone and rock salt)
chemical: precipitation of minerals out of a solution (ex. limestone and rock salt)
37
New cards
framework
consists of packed clasts that are partial or in full contact with one another (majority of rock)
38
New cards
matrix
consists of smaller grains that fill spaces between the larger framework grains
39
New cards
cement
bind the framework and matrix to form sedimentary rocks
40
New cards
pore space
non-solid space between grains that is filled with fluid or gas
41
New cards
conglomerate
a sedimentary rock made from small rounded stones that have been cemented together
42
New cards
breccia
coarse sedimentary rock consisting of angular fragments; or rock broken into angular fragments by faulting
43
New cards
sorting
refers to the uniformity of grain size; well sorted sediments will have grains of approximately equal size
44
New cards
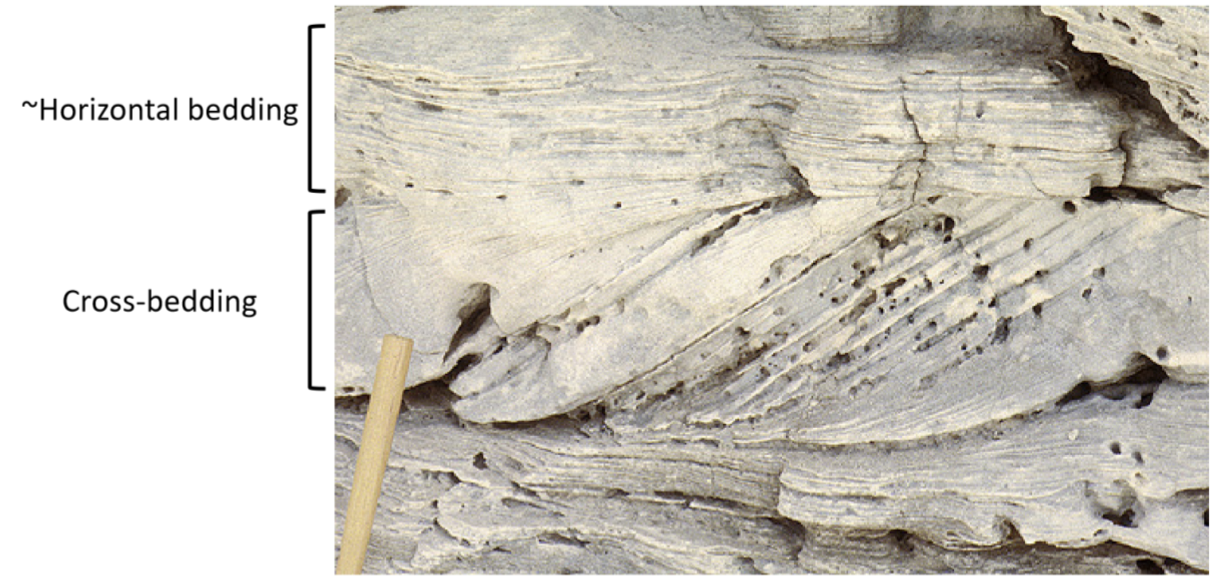

planar bedding
horizontal sedimentary beds that are roughly parallel to each other
45
New cards
ripple marks
Small waves of sediment formed by running water or blowing wind
46
New cards
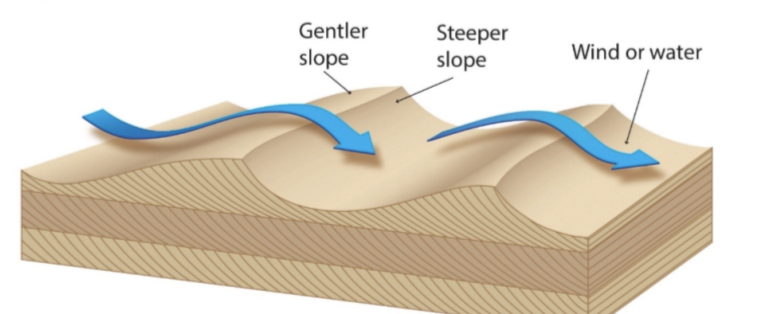
asymmetrical ripples
indicate water or wind flowing in one direction (think river)
47
New cards
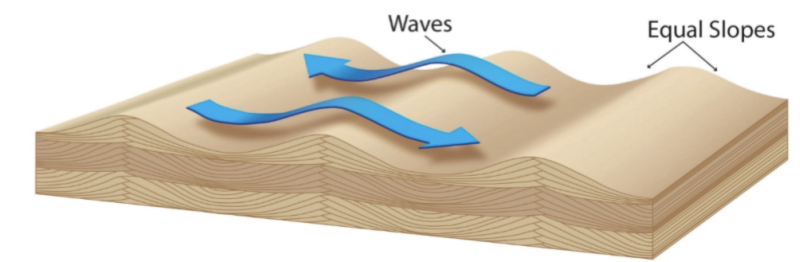
symmetrical ripples
indicate water or wind flowing in an oscillatory pattern
(think tide/waves)
(think tide/waves)
48
New cards
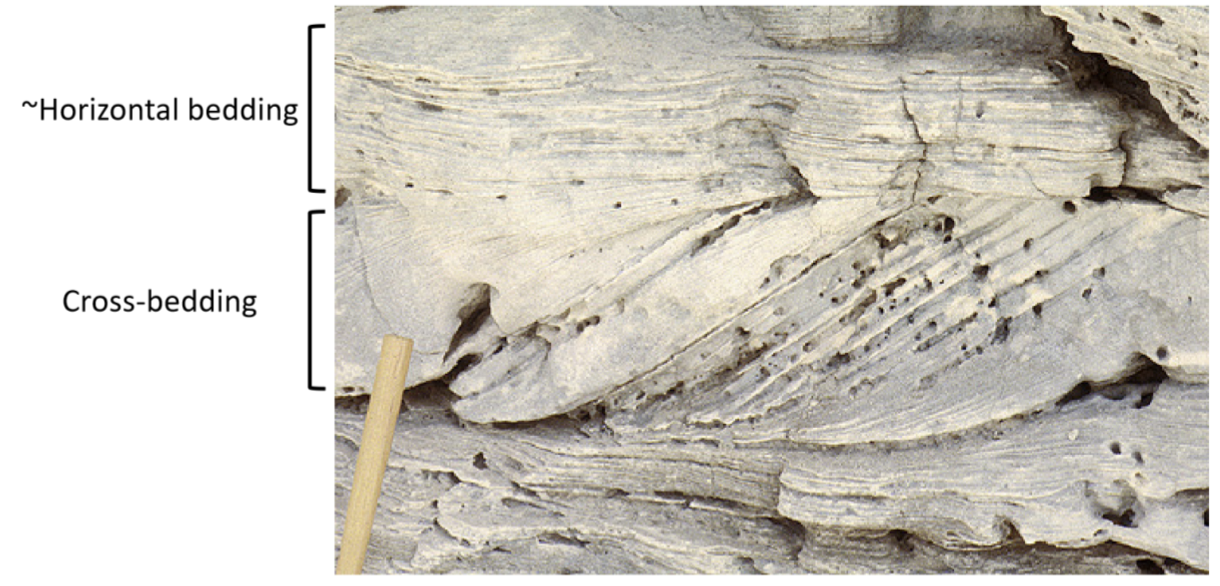

cross bedding
refers to large scale equivalent of ripple cross lamina (dip towards dominant current direction)
49
New cards
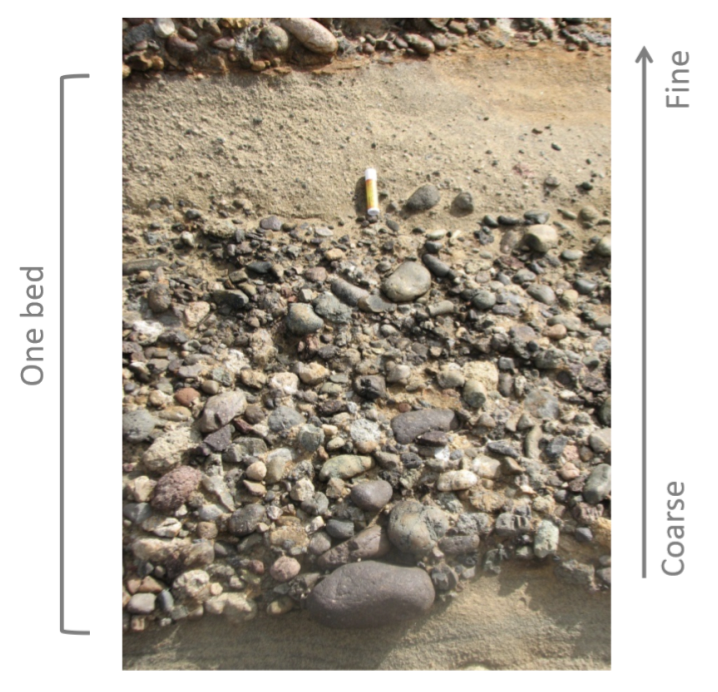
graded bedding
type of bedding in which particle sizes become progressively heavier and coarser toward the bottom layers
50
New cards
a rock is considered dolomitic when:
it reacts WEAKLY with HCl
51
New cards
Metamorphic rocks form from
igneous and sedimentary rocks that undergo a significant change in pressure or temperature. *NO MELTING OCCURS*
52
New cards
regional metamorphism
formation of metamorphic rock bodies that are hundreds of square kilometers in size
*convergent boundaries/mountain ranges
*convergent boundaries/mountain ranges
53
New cards
contact metamorphism
formation of a metamorphic rock caused by magma coming into contact with existing rock
54
New cards
foliation
an arrangement of minerals in flat or wavy parallel bands.
55
New cards
metamorphic index minerals (lowest to highest)
chlorite (green)
biotite/muscovite
garnet (red)
kyanite (blue)
biotite/muscovite
garnet (red)
kyanite (blue)
56
New cards
porphyroblast
large crystals that form in solid rock by the reorganization of atoms during metamorphism
57
New cards
protolith
the original rock from which a metamorphic rock formed
58
New cards
slate
a metamorphic rock with clean, flat breakage along closely spaced planes due to parallel arrangement of microscopic crystals of clay and mica (slaty texture). Slates are shinier than shales, generally having an egg-shell sheen
59
New cards
phyllite
a metamorphic rock with very closely spaced parallel planes and glossy appearance due to the parallel alignment of microscopic mica crystals (phyllitic texture).Phyllite is shinier than slate because the reflective mica crystals are larger, giving the rock a satin sheen
60
New cards
schist
a metamorphic rock with approximately parallel arrangement of mica crystals large enough to see with the naked eye (schistose texture). To fully name a schist, you must include one to two of its most common index minerals.
61
New cards
gneiss
a metamorphic rock with discrete layers of different mineral content giving the rock a banded appearance (gneissic texture). Typically, the dark bands are composed of hornblende and/or biotite, whereas the light bands are composed of quartz and feldspars
62
New cards
the protolith mudstone/shale can become what after metamorphosis?
slate
phyllite
schist
phyllite
schist
63
New cards
the protolith mudstone/felsic igneous rock can become what after metamorphosis?
gneiss
64
New cards
the protolith quartz sandstone can become what after metamorphosis?
quartzite
65
New cards
the protoliths limestone or dolostone (carbonate rocks) can become what after metamorphosis?
marble
66
New cards
if the protolith is a conglomerate what can this become after metamorphosis
metaconglomerate
67
New cards
if the protolith is a mafic igneous rock like basalt or gabbro what can this become after metamorphosis
amphibolite
68
New cards
3 methods of direct preservation that produce unaltered remains
unaltered, desiccation, embedding
69
New cards
unaltered preservation
hard parts remain unchanged (shells, bones, teeth)
70
New cards
desiccation
freezing or mummification under dry (desert) or acidic (bog) conditions
71
New cards
embedding
in wax and amber (desiccation also occurs in this mold)
72
New cards
5 methods of direct preservation that produce altered remains
recrystallization, replacement, permineralization, petrification, and carbonization
73
New cards
recrystallization
minerals change to a more stable form without changing chemical composition. often involves an increase in crystal size and makes shells more dull
74
New cards
replacement
minerals making up a fossil are completely replaced by a new mineral with a different composition
75
New cards
permineralization
pores, or empty body chambers are filled with a mineral
76
New cards
petrifaction
organic tissue of fossil is replaced by a new mineral. note: pores within the tissue are permineralized
77
New cards
carbonization
volatiles like water are removed (often via heat and compaction) leaving a thin, carbon film
78
New cards
what are the 2 methods of indirect preservation?
molds and casts
79
New cards
molds
impressions of remains
external: organism stamped into sediment
internal: interior of organism is filled with sediment and shell dissolves away, leaving behind an internal mold
note: mold is a negative (inverse of original shape)
external: organism stamped into sediment
internal: interior of organism is filled with sediment and shell dissolves away, leaving behind an internal mold
note: mold is a negative (inverse of original shape)
80
New cards
casts
exact replicas of remains
if an external mold is filled with sediment/minerals, a cast is created.
note: cast is a positive (same as original shape)
if an external mold is filled with sediment/minerals, a cast is created.
note: cast is a positive (same as original shape)
81
New cards
principle of original horizontality
sediments are originally deposited on horizontal or nearly-horizontal surfaces
82
New cards
principle of superposition
rocks that are highest in an undeformed sedimentary structure are the youngest and rocks that are lowest are oldest
83
New cards
principle of cross cutting relationships
the rock that cuts across a structure is younger than the structure it cuts through
84
New cards
unconsolidated sediments
recent deposits that have not yet been cemented or compacted enough to make up rocks, forming sand and gravel deposits rather than sandstone or conglomerate units
85
New cards
alluvium
unconsolidated clastic (or detrital) material deposited by a stream or other body of running water
86
New cards
bedrock
solid rock that underlies soils or other unconsolidated, superficial material
87
New cards
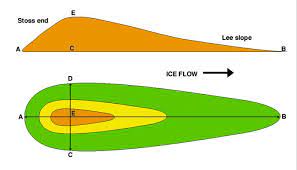
drumlin
hills of sediment (generally a quarter of a mile or more in length) that have been streamlined by glacier flow
88
New cards
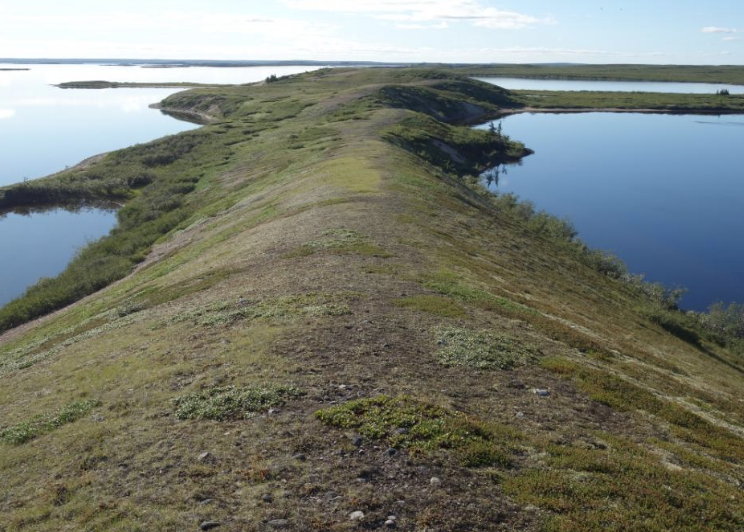

esker
ridges made of sands and gravels deposited by glacial meltwater flowing through tunnels within and underneath glaciers, or through meltwater channels on top of glaciers
89
New cards
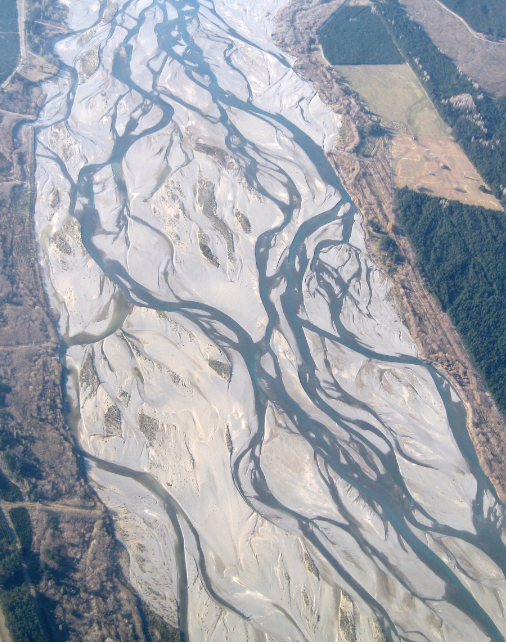

braided stream
multi-threaded channels that branch and merge to create the characteristic braided pattern
90
New cards
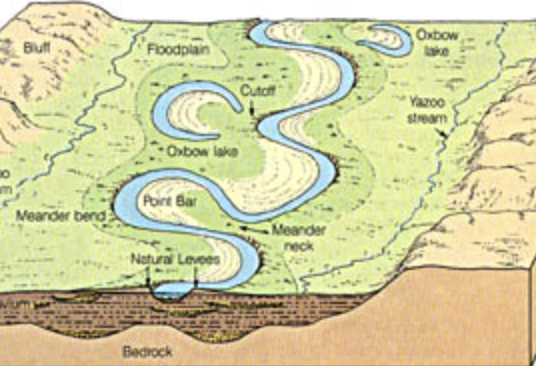
meandering stream
single-channel that winds through a valley
91
New cards

oxbow lakes
a U-shaped lake or pool that forms when a wide meander of a river is cut off, creating a free-standing body of water
92
New cards

shell with 2 valves that are not identical, but each valve is bilaterally symmetrical on itself. often ribbed valve surfaces with wing-like extensions on either side
brachiopod
93
New cards
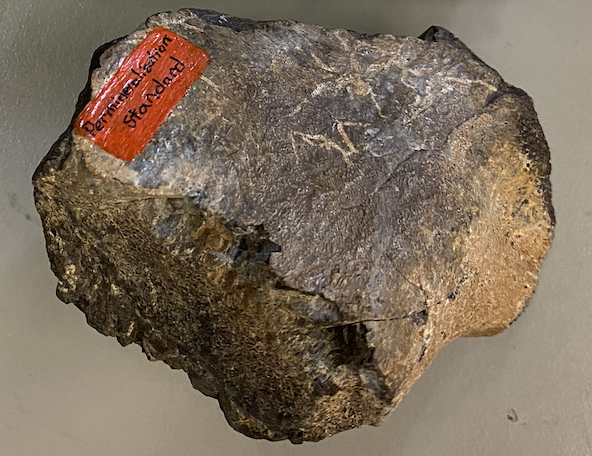

altered: permineralization
*hint this is a bone
*hint this is a bone
dinosaur bone fragment
94
New cards

internal mold
shell commonly with 2 identical valves (mirror images) joined by a hinge. has a raised protuberance called an umbo arises near the hinge
shell commonly with 2 identical valves (mirror images) joined by a hinge. has a raised protuberance called an umbo arises near the hinge
bivalve
95
New cards

external mold
segmented organism divided into 3 parts; head (cephalon), body (thorax), and tail (pygidium)
this particular fossil only shows the head of this organism
segmented organism divided into 3 parts; head (cephalon), body (thorax), and tail (pygidium)
this particular fossil only shows the head of this organism
trilobite cephalon
96
New cards

this sticky substance that hardens to a crystal-like form is capable of producing unaltered remains through embedding
amber
97
New cards

altered: recrystallization
this is an organism that was recrystallized in dolostone
this is an organism that was recrystallized in dolostone
coral in dolostone
98
New cards

unaltered remains
shell commonly with 2 identical valves (mirror images) joined by a hinge. has a raised protuberance called an umbo arises near the hinge
*hint, not a brachiopod
shell commonly with 2 identical valves (mirror images) joined by a hinge. has a raised protuberance called an umbo arises near the hinge
*hint, not a brachiopod
bivalve shell
99
New cards

altered: petrification
*hint, not an animal
*hint, not an animal
wood
100
New cards

altered: dessication
*hint, not an animal
*hint, not an animal
walnut