Chapter 19 - Human Effects on Ecosystem
Carbon Cycle
![]()
- Green plants convert atmospheric carbon dioxide into glucose during %%photosynthesis%%. Within green plants, glucose can be converted to other organic molecules.
- These carbon compounds are transferred to consumers through the process of feeding.
- Carbon dioxide is returned to the atmosphere when %%cellular respiration%% takes place in living organisms.
- When the green plants and animals die, %%decomposers%% break their %%organic matte%%r down into carbon dioxide and other simple substances.
- %%Fossil fuels%% are formed from the fossilised remains of dead plants and animals. Carbon compounds from these dead organisms are stored as fossil fuels.
- When fossil fuels and wood are burnt, %%carbon dioxide%% is produced.
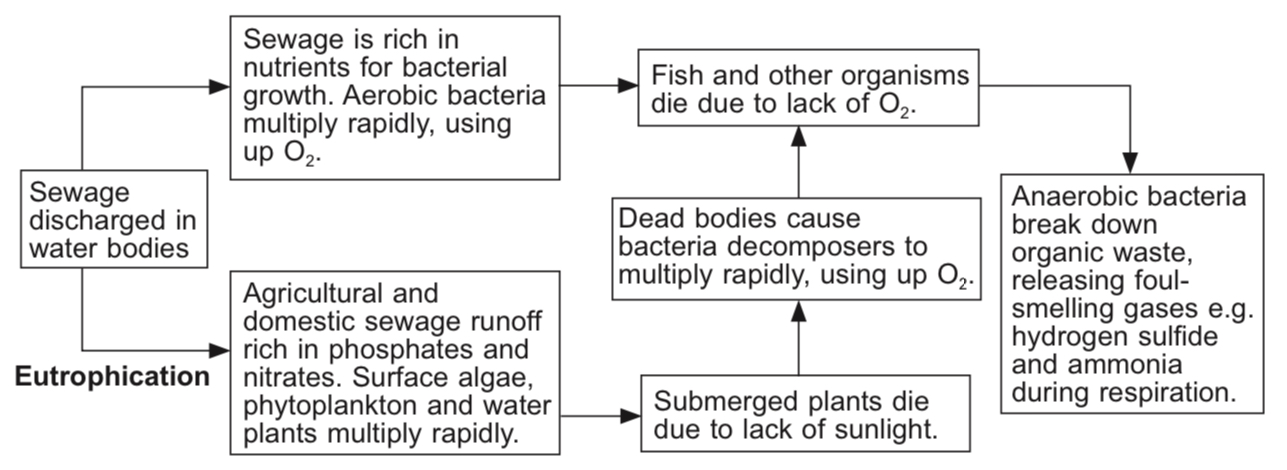
Water pollution
%%Pollution%% is the %%contamination%% of the environment causing harm and damage to the %%ecosystem%%. It is usually the result of human activities.
Water pollution occurs when pollutants are discharged directly into water without undergoing treatment. A common water pollutant is %%sewage.%%
Sewage is waste matter from industries and homes. It consists mainly of organic wastes such as detergents, oils and fats, insecticides and herbicides, and debris.
Inorganic substances from industrial waste include: leached nutrients and fertilisers (nitrates and phosphates) from farmland, ammonia, sulfur dioxide from power plants, and heavy metals.
Some of these pollutants can be directly toxic to the living organisms in the water, causing them to die. Others are %%carcinogenic%% and can harm humans who get in contact with the contaminated water.
Contaminated water usually encourages %%growth of microorganisms%% such as bacteria, parasites (certain protozoa and worms) and viruses. These could lead to diseases such as gastroenteritis, cholera, typhoid and parasitic infection.
Sewage treatment
- Environmental %%biotechnology%% is when biotechnology is used to treat polluted environments or in environment-friendly processes such as green manufacturing technologies. %%Sewage treatment%% is an example of environmental biotechnology.
- In sewage treatment plants, sewage is drained into settling tanks and sedimentation tanks to allow some of the solid waste to settle and be removed.
- The sewage then enters the %%aeration tank%%, where pure oxygen is bubbled in and bacteria added. The bacteria oxidise carbon compounds to carbon dioxide, oxidise ammonium and nitrogen compounds to nitrates and eventually nitrogen gas, and remove phosphates.
- The liquid from the aeration tank is then filtered and the solid contents are allowed to settle. Sewage water containing low levels of organic material and suspended matter remains. The sewage water is disinfected to reduce the number of microorganisms in the water before it is discharged back into the environment.
- The solid matter left behind from the sewage treatment process is known as %%sludge%%.
- Sludge undergoes a process of bacterial digestion to reduce the amount of organic matter and the number of disease-causing microorganisms present.
Conservation
- %%Conservation%% is the act of protecting species, their habitats and entire ecosystems from %%extinction%%.
- Conservation covers a wide range of activities. For example, reducing pollution and combating deforestation, preventing global warming, natural resource management and wildlife protection comes under conservation as well.
Conservation in fisheries
A %%fishery%% is an area with a particular species of fish or aquatic life that is harvested for its commercial value.
Wild fisheries are located in the oceans, lakes and rivers, where fish has to be captured or fished. They are prone to overfishing and pollution, which could lead to an imbalance in the ecosystem.
Farmed fisheries involve raising fish commercially in tanks. It helps to supply some of the demand for food fish but a great majority of food fish are still obtained from wild fisheries.
In order to develop %%sustainable%% fisheries so that fish stock is maintained for future fishing, certain measures have been taken:
(a) Many countries have set up ministries or government organisations regulating fishing. These organisations help to control the activities in fisheries by:
(i) Imposing taxes on fishing output
(ii) Vessel licensing, regulating the entry of ships into fishing grounds
(iii) Restrictions on catching techniques such as the prohibition of bottom trawling and dynamite fishing, regulation of fish traps etc.
(iv) Imposing a catch quota
(v) Limiting the period of fishing
(b) Breeding of endangered fish in captivity by private conservation organisations or zoos to be released back into the wild to replenish depleted stock.
Conservation of forests
The forests are the major source of the world’s timber. The clearing of forests for timber and land is called %%deforestation%%.
The indiscriminate logging without sufficient %%reforestation%% has led to many environmental and ecological problems such as:
(a) The ‘slash and burn’ practice used to clear forests for agriculture releases a large amount of carbon dioxide which contributes to global warming.
(b) Changes in the water cycle resulting in a drier climate. Trees contribute to humidity by transpiration and extract groundwater through their roots to be released into the atmosphere. The loss of this causes climate changes that could lead to desertification.
(c) Soil erosion as tree roots are needed to bind soil together.
(d) Loss of habitat for many organisms resulting in loss of biodiversity.
Forest conservation includes legislation protecting forests from indiscriminate logging such as:
(a) Regulating the rate of logging
(b) Selective logging where young trees are not cut down.
(c) Designating land as forest reserves
Other conservation practices include reforestation, which is the act of restocking forests which have been depleted. New seedlings are planted to replace trees that have been felled.