Dopaminergic/Parkinson's Disease Drugs
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
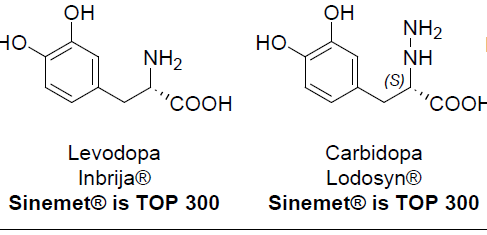
To Increase Dopamine Biosynthesis in the Brain: MOA and What is it used for/treats?
Marketed in a 10:1 ratio
Available has tablets, capsules, and enteral suspensions
Goal of the preparation is to increase the concentration of Levodopa in the brain, which can then be metabolized to dopamine
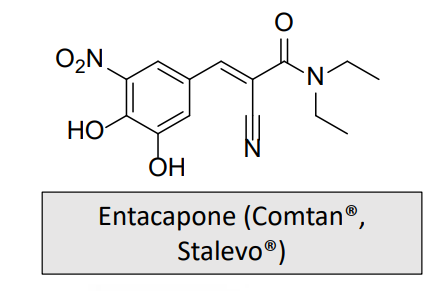
To Increase Dopamine Biosynthesis in the Brain: MOA and What is it used for/treats?
Indicated as an adjunct to levodopa and carbidopa to treat end-of-dose “wearing-off” in patients with Parkinson’s disease
It is a COMT inhibitor, which will slow the breakdown of levodopa
Plasma levels of levodopa are greater and more sustained than after administration of levodopa and an aromatic amino acid decarboxylase inhibitor alone.
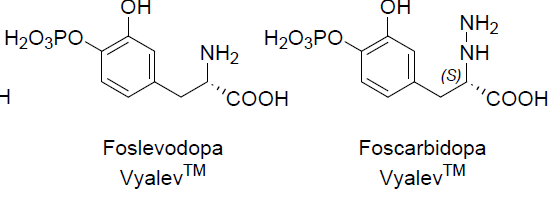
To Increase Dopamine Biosynthesis in the Brain: MOA and What is it used for/treats?
Prodrug of levodopa and carbidopa
The first and only subcutaneous 24-hour infusion of levodopa for the treatment of motor fluctuations
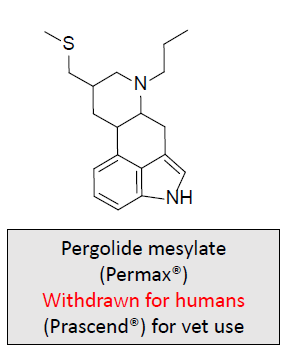
Dopaminergic Receptor Agonists-Ergot Alkaloids: MOA and What is it used for/treats?
Long-acting dopamine agonist
Indicated as adjunct therapy with levodopa/carbidopa, but found to cause cardiac valvulopathy and was withdrawn from the market
Used only for veterinary purposes; for horses that have Cushing’s syndrome caused by decreased production of dopamine
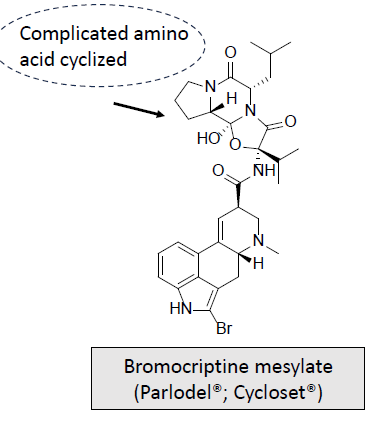
Dopaminergic Receptor Agonists-Ergot Alkaloids: MOA and What is it used for/treats?
Full D2 agonist and a partial agonist at D1
Used off-label to treat restless legs syndrome
Inhibits prolactin secretion, and can treat galactorrhea and other prolactin related disorders
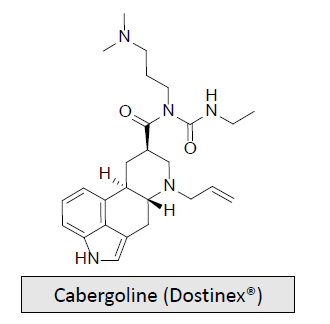
Dopaminergic Receptor Agonists-Ergot Alkaloids: MOA and What is it used for/treats?
Long-acting dopamine receptor agonist with a high affinity for D2 receptors
Primarily used to decrease elevated prolactin levels, which can cause menstrual changes and unwanted lactation in women as well as impotence in men
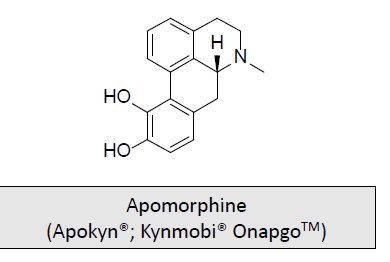
Dopamine Receptor Agonists- Morphine derivative: MOA and What is it used for/treats?
Dopamine D2 agonist indicated to treat hypomobility associated with Parkinson’s
It is synthesized from morphine (a rearrangement product of morphine in concentrated HCl) and it is an infusion device
Also has been investigated as an emetic, sedative, a treatment for alcoholism and other movement disorders
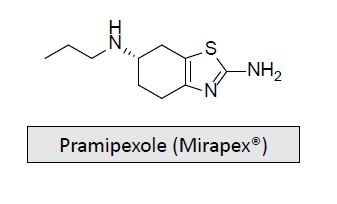
Dopaminergic Receptor Agonists: Parkinson’s Disease/Restless Legs Syndrome: MOA and What is it used for/treats?
Activates the presynaptic D2 receptor, but is more potent in activating the D3 receptor
Allows the typical dosage of levodopa to be decreased by 30%, but patients should be warned about the possibility of hallucinations
Marketed as the S-enantiomer, and it is excreted unchanged
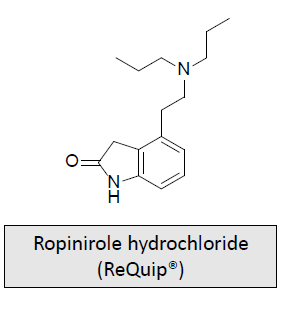
Dopaminergic Receptor Agonists: Parkinson’s Disease/Restless Legs Syndrome: MOA and What is it used for/treats?
Activates the presynaptic D2 receptor, but is more potent in activating the D3 receptor
Extensively metabolized by CYP1A2
Has possibility of several drug-drug interactions; inhibitors of CYP1A2 can significantly increase ropinirole plasma levels
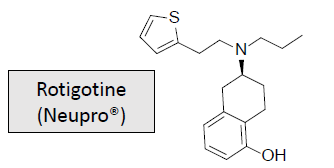
Dopaminergic Receptor Agonists: Parkinson’s Disease/Restless Legs Syndrome: MOA and What is it used for/treats?
First transdermal synthetic dopaminergic agonist
Has more affinity for the D1 receptor
Thiophene ring system aids in D2 receptor affinity and enhances the lipophilicity of the compound to allow transdermal administration
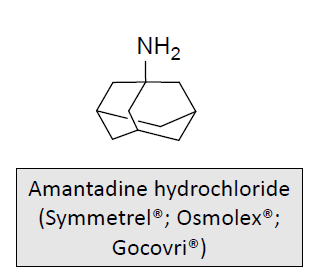
Drugs that Increase Dopamine Release: MOA and What is it used for/treats?
Initially used as an antiviral agent in the prophylaxis and treatment of influenza A
Usually combined with levodopa therapy when levodopa responses decline, also approved for dyskinesia
Appears to release dopamine, stimulate the NE response, and has NMDA receptor antagonistic effects
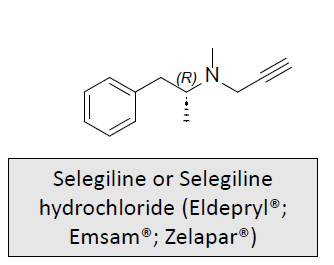
Monoamine oxidase B inhibitors: MOA and What is it used for/treats?
May slow progression of the clinical disease and delay the requirement for levodopa therapy
Inhibits the metabolism of dopamine in the CNS
Allows the dosage of levodopa to be decreased by 10-30%
Metabolized to amphetamine and methamphetamine which can cause anxiety and insomnia
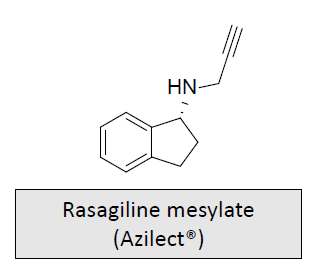
Monoamine oxidase B inhibitors: MOA and What is it used for/treats?
Used as a monotherapy in early Parkinson’s disease or as an adjunct in more advanced cases
CYP1A2 is the major enzyme involved in its metabolism to non-amphetamine derivatives
May slow the rate of neuronal deterioration in Parkinsonism
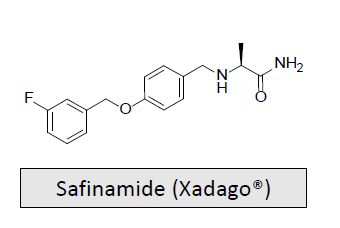
Monoamine oxidase B inhibitors: MOA and What is it used for/treats?
It combines potent, selective, and reversible inhibition of MAO-B with blockade of voltage-dependent Na+ and Ca2+ channels and inhibition of glutamate release.
Very high therapeutic index
Indicated as adjunctive treatment to levodopa/carbidopa in patients with Parkinson’s disease (PD) experiencing “off” episodes.
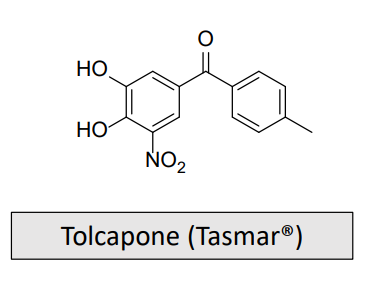
Catechol O-Methyltransferase Inhibitors-COMTi: MOA and What is it used for/treats?
Must be used with caution as it can cause serious liver disease
Adjunct with carbidopa and levodopa
Most lipophilic of COMT inhibitors
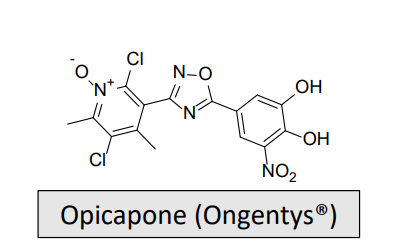
Catechol O-Methyltransferase Inhibitors-COMTi: MOA and What is it used for/treats?
Contains an oxadiazole and a pyridine
Used as adjunctive treatment to levodopa/carbidopa in patients with Parkinson’s disease (PD) experiencing “off” episodes
Offers the benefit of a duration of action exceeding 24h, allowing for once-daily administration
Demonstrates the lowest risk for cytotoxicity in comparison with other COMT inhibitors