Biol 208: Lecture 23 - Mutualism - Parasitism
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Symbiosis - define
Mutualism
Commensalism
Exploitation
Symbiosis = INTRICATE + LONG TERM living of 2 organisms
mutualism = +/+
Commensalism = +/o
Exploitation (parasitism) = +/-
Interactions can be mutualistic, commensal or parasitic depending on the context
Facultative vs. Obligate symbiosis
Facultative = occurring OPTIONALLY
Obligate = NECESSAIRY
high dependence on partner → likely to go extinct if partner goes extinct
Whale + Barnacle - What type of interaction?
Who is benefiting + who is not
is this Obligate or Facultative
MOSTLY commensal → context dependent (location of barnacles)
Barnacles on find = like brass Knuckles for fighting
Too many = creates drag + skin conditions
Barnacle (+)
benefit from substrate + dispersal provided by whale
Only found on whales = OBLIGATE (some can be facultative)
Whale (o)
No benefit or harm = FACULTATIVE relationship
Ticks + Host - What kind of Interaction
Who is benefiting + who is not
is this Obligate or Facultative
PARASITISM
Ticks (+) = OBLIGATE symbiosis
feed on host blood + receives benefit (must have blood to grow + reprod)
Host (-)
Harmed through loss of blood + disease risk
(not sure how important) Other examples of parasitic relationships
Mistletoe - Hemi parasitic plant (takes carbs from host But can also photosynthesize)
Tape worm
Tongue eating crustacean
Herbivore vs. Plant parasite
What is the difference?
Parasites = intricate + long term relationship with a host
Herbivores + Predators do not = one time interaction
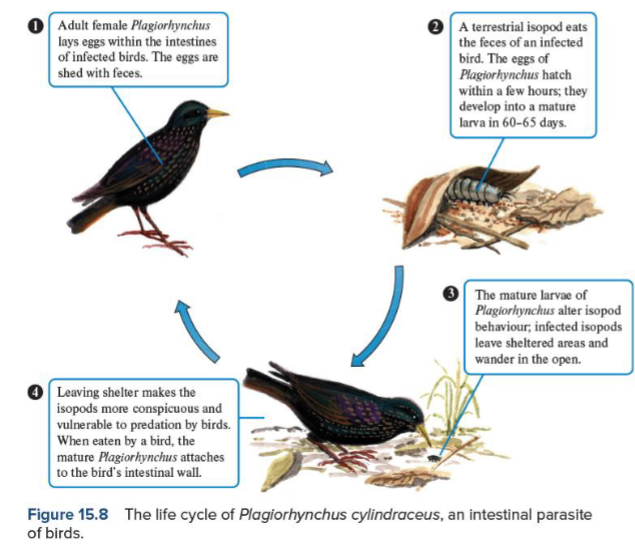
Give an example of Parasites ALTERING THE BEHAVIOUR of their hosts for their benefit
European starling, isopods + thorny head worm (parasite)
Isopod = Intermediate host (parasite grows here but does not reach maturity)
European starling = definite/ primary host (parasite reaches maturity)
What is the RED QUEEN HYPOTHESIS?
CO-EVOLUTION in host-parasite interactions = Perpetual co-evolution between the 2 is like an ARMS RACE
species must evolve to keep up with the evolutions of their parasites + vice versa
“It takes all the running you can do to keep in the same place” - Lewis Carroll, through the looking glass
Plants + Mycorrhizae - What kind of Interaction
Who is benefiting + who is not
is this Obligate or Facultative
MUTUALISM BUT mycorrhizae can also be parasitic
Plant (+)
benefit from mycorrhizae through INCREASED NUTRIENT UPTAKE in soil
Mycorrhizae (+)
Benefit from plants through consumption of their root exudates (CARBS)
What are the 2 types of Mycorrhizal Fungi (MF)?
Differentiate between the 2
Which associates with more types of species?
Arbuscular (AMF)
PENETRATE the cortical cells (store E + Nutrients) of plant roots
in 80% of plants species
Ectomycorrhizal (EMF)
Does NOT penetrate
2% of plant species (conifers, blueberries etc.)
Some plants don’t have mycorrhizae
Info dump on the experiment: Does Fertilizing soil select for less mutualistic mycorrhizal fungi?
Methods
Prediction
Results
Method:
Grew grass with AMF that either was from Unfertilized soil or Fertilized soil + one control with no AMF
Prediction:
Nutrient poor soil = more carb exudates to the roots (Optimal foraging in plants = allocate E to the most limiting factor)
Nutrient rich soil = Less carbs exudates to roots
Mycorrhiza colonizing HIGH nutrient soil will be AGRESSIVE in their carb acquisition at the express of the host b/c there is Low-release of exudates
Results:
AMF are MORE mutualistic when grown in Nutrient POOR soil (like predicted) - plant growth was not as restricted
Like predicted
Mycorrhizae: Mutualism-parasitism continuum
Experiment
Results
What does this mean?
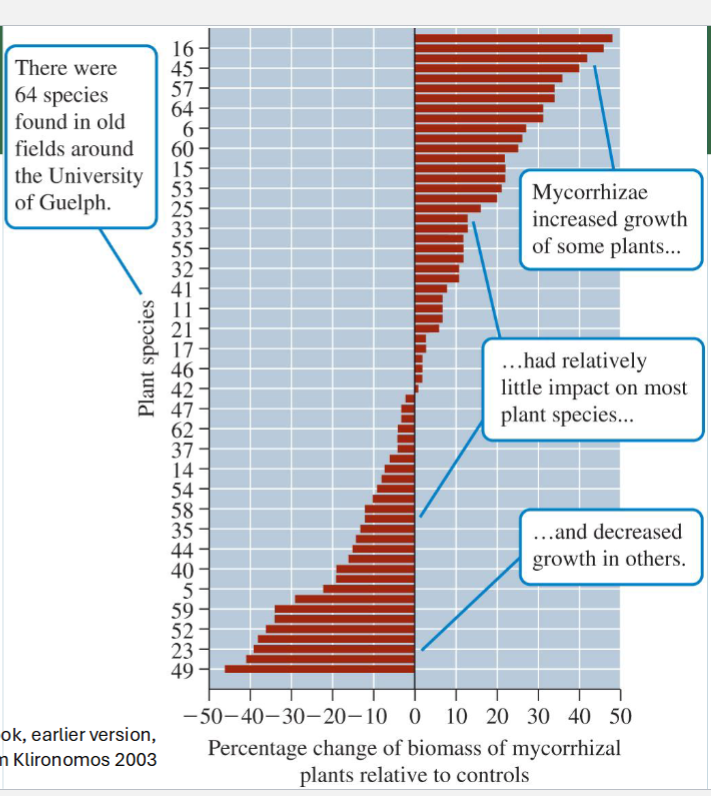
Plants were grown with and without AMF + calculated the percentage change of Biomass
Results show that Plant-AMF relationships form a CONTINUUM from mutualistic to parasitic interactions
Parasitic vs. mutualistic depends on:
Conditions of Soil
Species of plant
Other examples of Mutualistic interactions
Coral + zooxanthellae
Lichen: Fungi + algae
Legumes + Rhizobia bacteria (fix nitrogen)
Info dump on Coral Bleaching
causes
What is occuring
Causes:
temp change
Runoff + pollution
Overexposure to sunlight
Extreme low tide
Healthy coral = mutualistic interaction with zooxanthellae (FOOD SOURCE) = give coral color
STRESS = expel zooxanthellae —> bleached color
Coral dies because no mutualistic effect with zooxanthellae
Info dump on Lichen
Fungal BIOFILM creates a shelter + keeps a humid environment for algae
Algae = photosynthesize —> Nutrients for Fungus
NON-SYMBIOTIC Mutualism?
what is the difference from Mutualism (symbiotic)
Give some examples
Not all mutualistic interactions are Intricate + Long term
Symbiotic = Life LONG
NON = SHORT term + then go separate ways
Examples:
Pollination
Frugivores
Cleaning parasites off other animals
“Reciprocal Parasitism”?
Mutualism is kinda like reciprocal parasitism - beneficial actions towards the other are only because the interaction increases own fitness
Attracting pollinators
Butterflies'
Bees
Nocturnal Moths
Butterflies = attracted to BRIGHT COLOURS
Bees = red blind = attracted to YELLOW or BLUE
Nocturnal moths = attracted to HEAVY SCENTS released during night
Nectar guide (image)
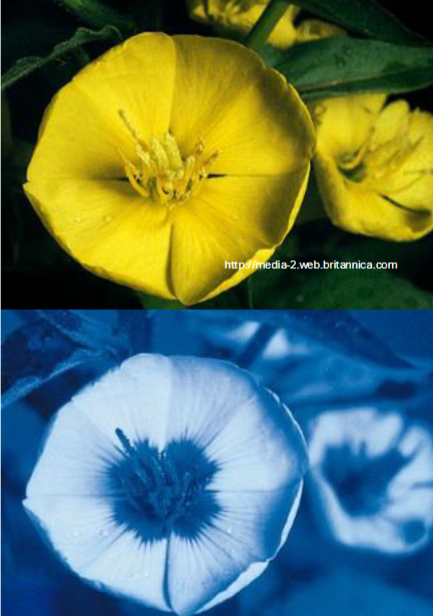

3 kinds of rewards for pollinators?
Pollen
Nectar
Prospect of mating with a female (orchid shaped like female + wasp)
Not very common in nature but this exists in this scenario b/c the interaction is not too costly for the wasp
Info dump: Bees as Commercial pollinators + Commercial pollinator Decline
amount of global food prod due to pollination
CCD
Wild pollinators why are they declining?
1/3 of global food prod
CCD = COLONY COLLAPSE DISORDER
phenomenon where worker bees would disappear or vanish from the hive despite enough food storage, leaving behind the queen, brood + a few nursing bees
Possible explanations:
Parasites, pesticides, stress (multi factoral)
Decline in wild pollinators as well
Why? - Habitat, simplifying ecosystem
eg. plant all canola, once harvested no more food for bees
Measures to counter pollinator loss
Setting up flower strips + increasing landscape heterogeneity