Module 7 - Axial Movement
1/145
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
146 Terms
accessory nerve
cranial nerve XI (eleven) extending from brain stem area to the neck muscles through jugular foramen
action potential
change in voltage of a cell membrane in response to a stimulus that results in transmission of an electrical signal; unique to neurons and muscle fibers
activation gate
part of the voltage-gated Na+ channel that opens when the membrane voltage reaches threshold
axon
single process of the neuron that carries an electrical signal (action potential) away from the cell body toward a target cell
axon hillock
tapering of the neuron cell body that gives rise to the axon
axon segment
single stretch of the axon insulated by myelin and bounded by nodes of Ranvier at either end (except for the first, which is after the initial segment, and the last, which is followed by the axon terminal)
axon terminal
end of the axon, where there are usually several branches extending toward the target cell
axoplasm
cytoplasm of an axon, which is different in composition than the cytoplasm of the neuronal cell body
dendrite
one of many branchlike processes that extends from the neuron cell body and functions as a contact for incoming signals (synapses) from other neurons or sensory cells
depolarization
change in a cell membrane potential from rest toward zero
external oblique
superficial abdominal muscle with fascicles that extend inferiorly and medially flattened bony process that extends laterally from the scapular spine to form the bony tip of the shoulder
facial nerve
cranial nerve VII (seven) extending from brain stem area to the facial muscles through stylomastoid foramen
foramen ovale of the middle cranial fossa
oval-shaped opening in the floor of the middle cranial fossa
hyperpolarization
while the K+ channels are open, membrane goes slightly over the resting potential
inactivation gate
part of a voltage-gated Na+ channel that closes when the membrane potential reaches +30 mV
insertion
end of a skeletal muscle that is attached to the structure (usually a bone) that is moved when the muscle contracts
internal oblique
flat, intermediate abdominal muscle with fascicles that run perpendicular to those of the external oblique
jugular foramen
irregularly shaped opening located in the lateral floor of the posterior cranial cavity
lateral pterygoid
muscle that moves the mandible from side to side
linea alba
white, fibrous band that runs along the midline of the trunk
masseter
main muscle for chewing that elevates the mandible to close the mouth
mastication
chewing
mastoid process
large bony prominence on the inferior, lateral skull, just behind the earlobe
membrane potential
distribution of charge across the cell membrane, based on the charges of ions
nerve
cord-like bundle of axons located in the peripheral nervous system that transmits sensory input and response output to and from the central nervous system
neuron
neural tissue cell that is primarily responsible for generating and propagating electrical signals into, within, and out of the nervous system
oblique
at an angle
orbicularis oculi
circular muscle that closes the eye
orbicularis oris
circular muscle that moves the lips
rectus abdominus
long, linear muscle that extends along the middle of the trunk
refractory period
time after the initiation of an action potential when another action potential cannot be generated
repolarization
return of the membrane potential to its normally negative voltage at the end of the action potential
resting membrane potential
the difference in voltage measured across a cell membrane under steady-state conditions, typically -70 mV
phrenic nerve
nerve is connected to the spinal cord at cervical levels 3 to 5 responsible for the muscle contractions that drive ventilation
spinal cord
organ of the central nervous system found within the vertebral cavity and connected with the periphery through spinal nerves; mediates reflex behaviors
splenius capitis
neck muscle that inserts into the head region
sternocleidomastoid
major muscle that laterally flexes and rotates the head
stylomastoid foramen
opening located on inferior skull, between the styloid process and mastoid process
styloid process
downward projecting, elongated bony process located on the inferior aspect of the skull
synapse
narrow junction across which a chemical signal passes from neuron to the next, initiating a new electrical signal in the target cell
synaptic cleft
small gap between cells in a chemical synapse where neurotransmitter diffuses from the presynaptic element to the postsynaptic element
temporalis
muscle that retracts the mandible
threshold
membrane voltage at which an action potential is initiated
transversus abdominis
muscle that compresses abdominal viscera
trigeminal nerve
cranial nerve V (five) extending from brain stem area to the jaw muscles through foramen ovale
voltage-gated channel
on channel that opens because of a change in the charge distributed across the membrane where it is located
zygomaticus major
muscle that draws upper lip upwards
the muscular system
makes up half of body weight (weighs more than any other organ system)
~700
how many muscles does the skeletal system contain
skeletal, cardiac, smooth
types of muscles
axial muscles
support the axial skeleton
appendicular muscles
support, move, brace limbs
tendons
conduct the forces of contraction to perform specific tasks
parallel fascicle organization
fibers parallel to one another and along the force-generating axis (ex. biceps brachii)
belly
central body of a parallel muscle
fascicle, belly (parallel)
arrow, bracket (type of muscle)
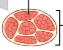
~30%
how much do parallel muscles shorten?
convergent muscles
fascicles that extend over broad area one one side and converge on common attachment site (tendon) (ex. pectoralis major)
versatility of convergent muscles
different parts can pull in different directions so does not pull as hard on attachment as parallel muscles
tendon, base (convergent)
arrow, bracket (type of muscle)
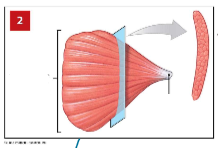
pennate muscle
at an angle from the tendon, do not move as far as parallel muscles, contain more myofibrils than parallel muscles, develop more tension than parallel muscles (ex. extensor digitorum, rectus femoris, deltoid)
unipennate muscle (ex. extensor digitorum)
1
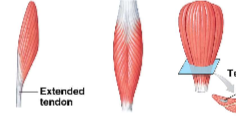
bipennate muscle (ex. rectus femoris)
2
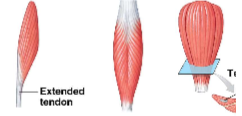
multipennate muscle (ex. deltoid muscle)
3
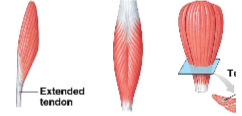
circular muscle
sphincters, fascicles in concentric circles, contraction decreases diameter of opening (ex. orbicularis oris)
origin
where the fixed end of a skeletal muscle attaches, usually proximal to insertion, mostly bones
action
specific movement produced by a skeletal muscle
agonist
the primary mover, muscle whose contraction is mostly responsible for producing a particular movement (ex. biceps brachii)
antagonist
muscle whose action opposes movement of a particular agonist (ex. triceps brachii), can have multiple per agonist
synergist
smaller muscle that helps a larger agonist work efficiently by providing additional pull or stabilization at the origin (ex. brachioradialis)
fixators
synergists that assist by preventing movement at another joint (ex. deltoid)
muscles of the head and neck
muscles of facial expression, extrinsic eye muscles, tongue, pharynx, neck
muscles of the vertebral column
muscles that stabilize, flex, extend, rotate vertebral column
oblique and rectus muscles of the trunk
broad sheets/bands forming muscular walls of thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities
muscles of the pelvic floor
span the pelvic outlet and support organs of he pelvis
orbicularis oculi
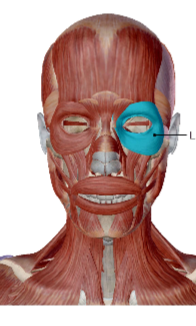
contraction closes eye
action of the orbicularis oculi
medial bones of the orbit (frontal, maxilla and lacrimal)
origin of the orbicularis oculi
circumference of the orbit
insertion of the orbicularis oculi
orbicularis oris
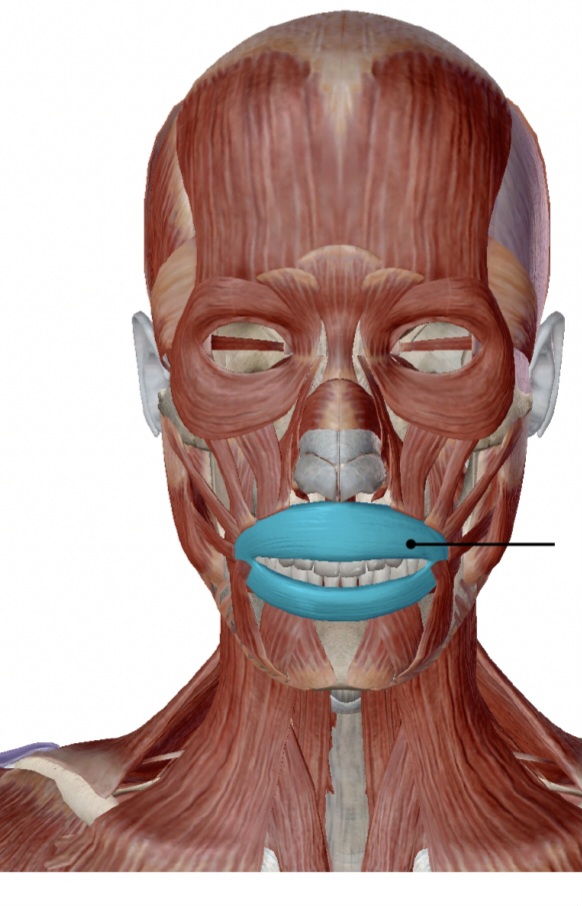
protrudes lips
action of the orbicularis oris
tissue of lips
origin of the orbicularis oris
under skin near corners of the mouth
insertion of the orbicularis oris
zygomaticus major
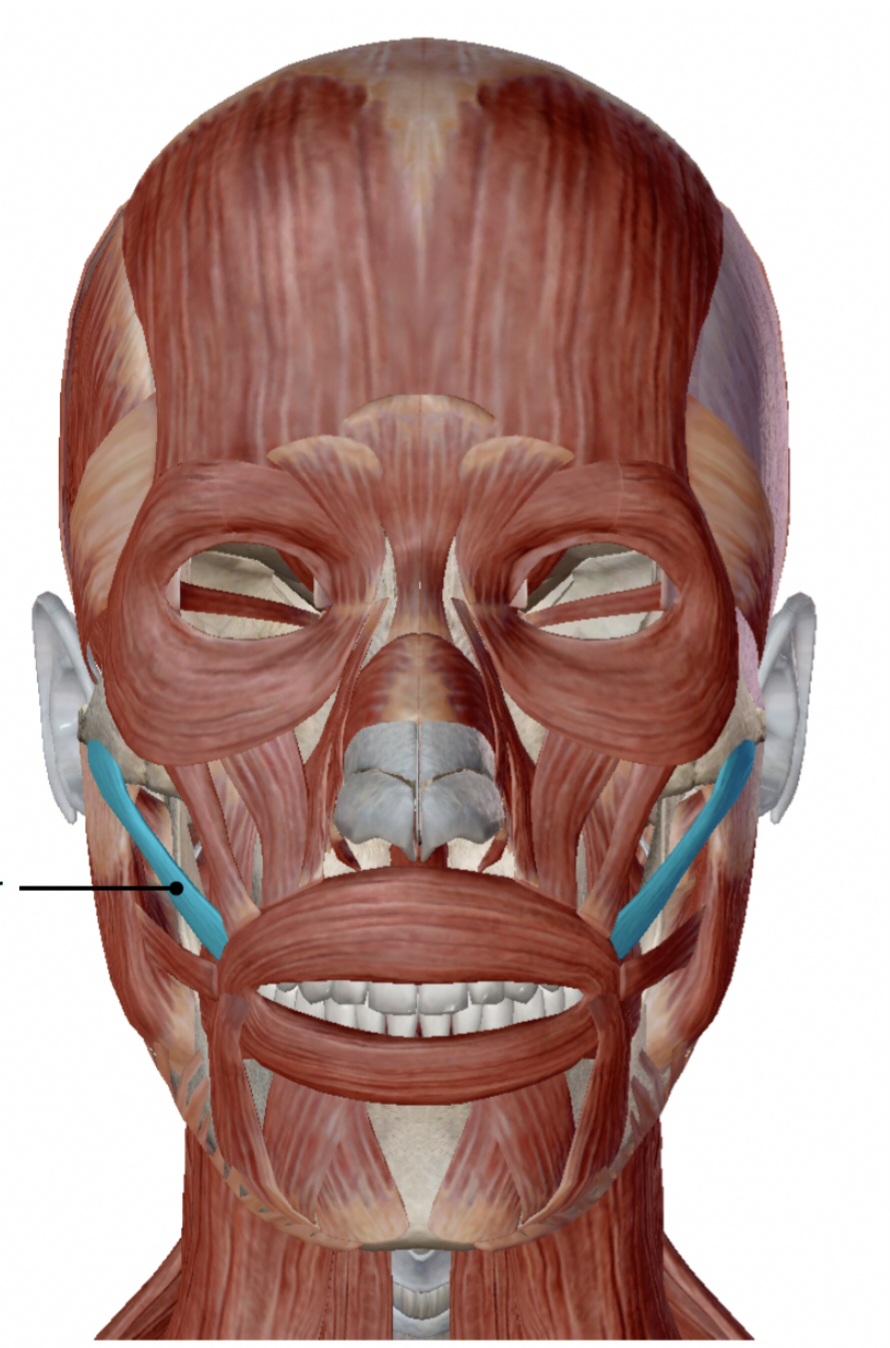
draws upper lip upward
action of the zygomaticus major
zygomatic bone
origin of the zygomaticus major
under skin near corners of the mouth
insertion of the zygomaticus major
masseter
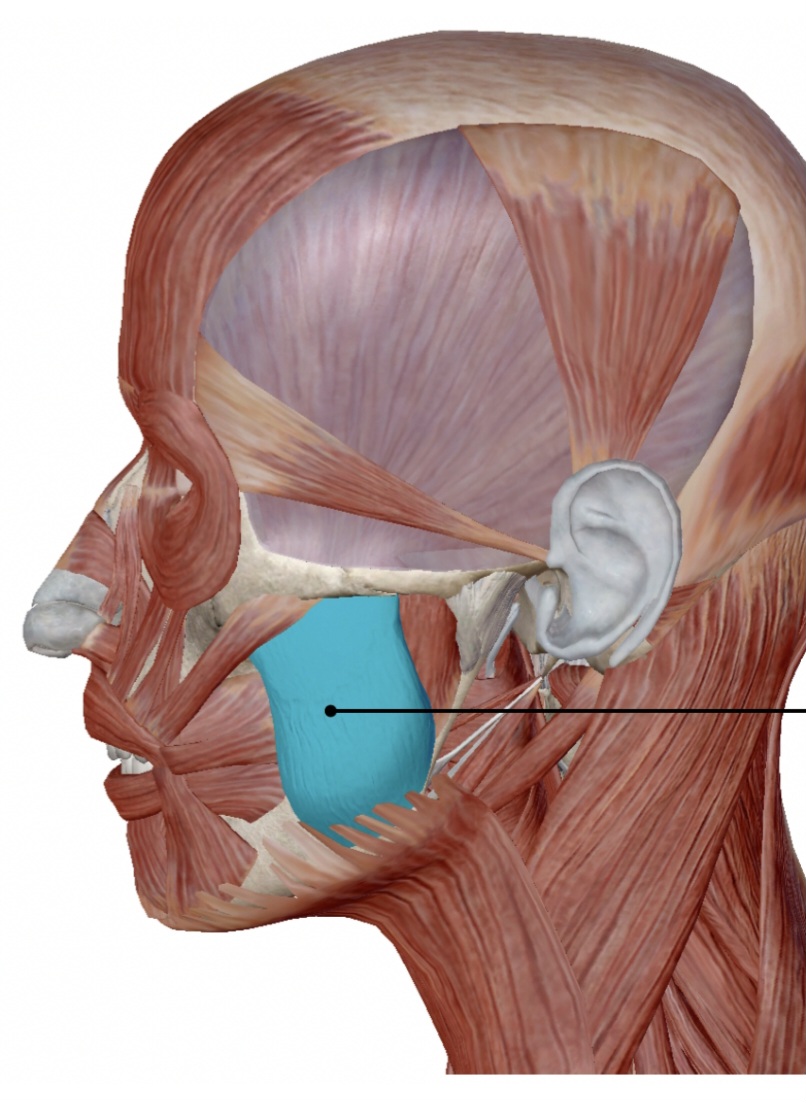
elevation and protraction of the mandible
action of the masseter
zygomatic process of maxillae, anterior zygomatic arch
origin of the masseter
mandibular ramus
insertion of the masseter
temporalis
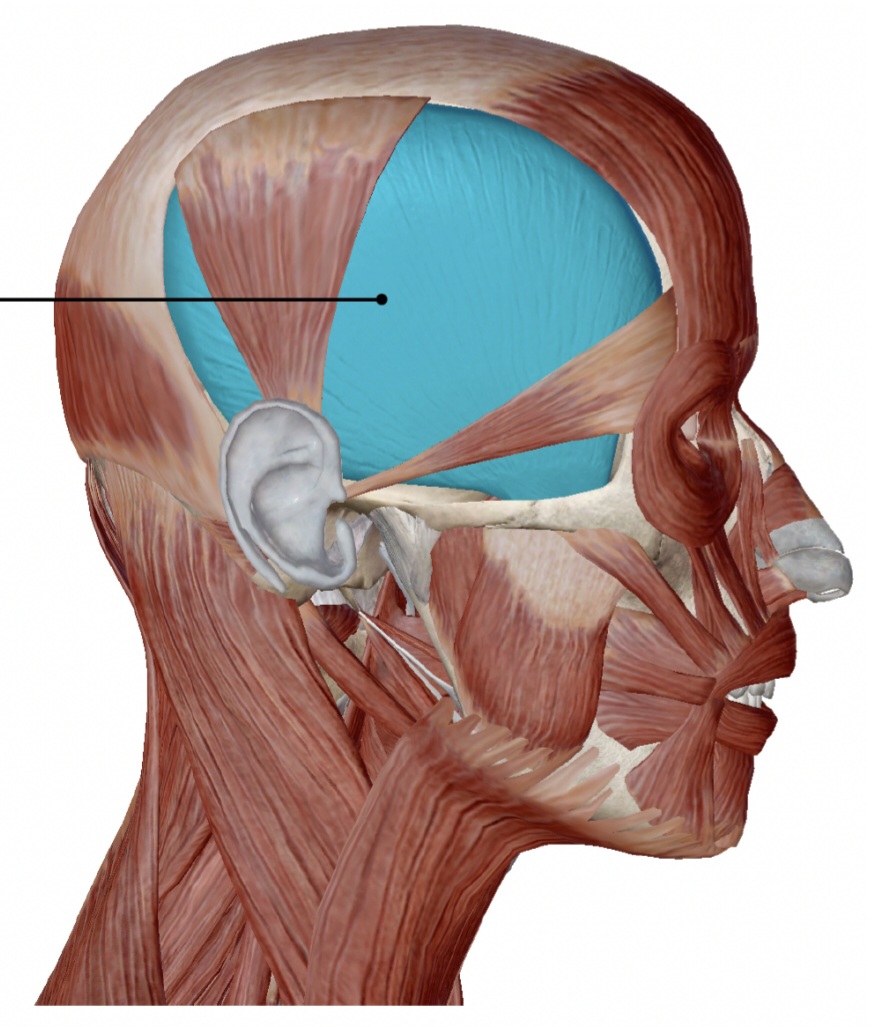
elevates mandible
action of the temporalis
temporal
origin of temporalis
mandible
insertion of the temporalis
lateral pterygoid
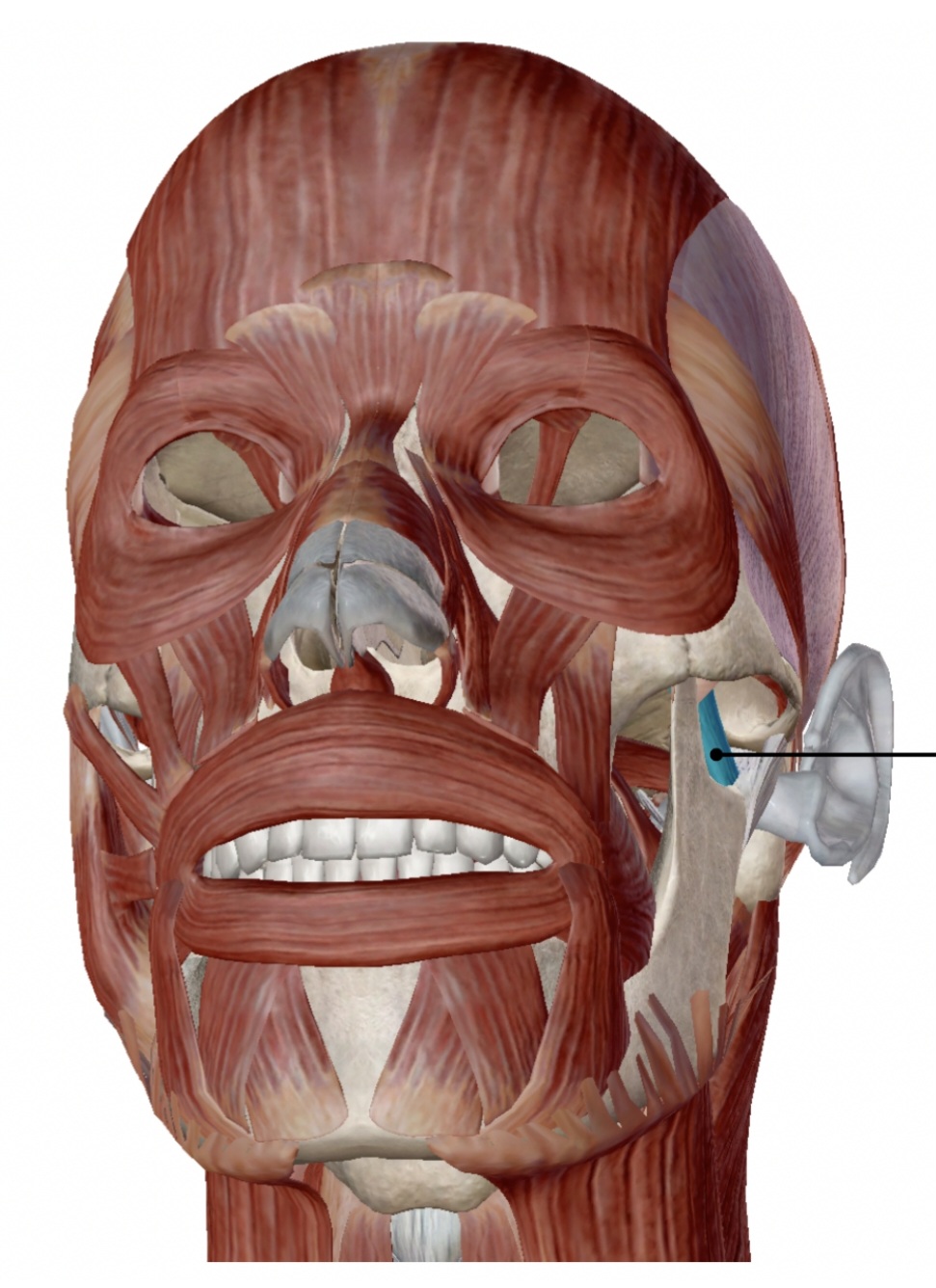
elevates mandible
action of the lateral pterygoid
pterygoid process of the sphenoid
origin of the lateral pterygoid
mandible
insertion of the lateral pterygoid
temporal branch of facial nerve
innervation of orbicularis oculi