Science 8 Study Guide
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
107 Terms
The first man-made object in space
frozen o-rings
Long-term exposure to radiation in space, little gravity causes our muscles to atrophy, lack of medical facilities and medical professionals, people living together for long periods, and it takes a lot of time
Inertia




The force exerted on an object by an object is exerted equally in the opposite direction(you push thing, thing push back)


I gave up. You got it!!!
give the Hawks' definition of energy and explain why it is better
The ability to cause change. It’s better because it doesn’t lead to a circular definition and it’s better to visualize.

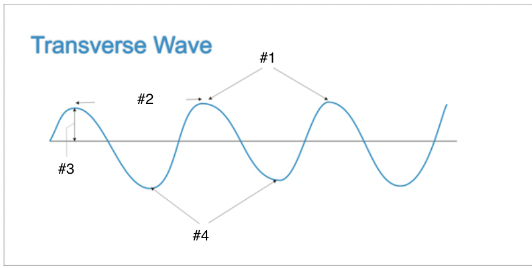
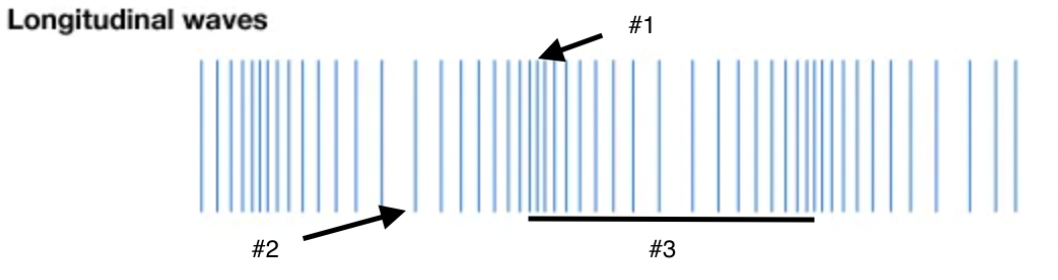
The distance from one point on a wave to the identical point on the next wave
define and recognize examples of refraction
waves bending when changing medium ex. A straw in a glass of water
define and recognize examples of diffraction
waves bending around a barrier ex. the fuzzy edges of shadows
explain the difference between constructive and destructive interference
constructive interferencemakes the wave bigger, while destructive interference makes it smaller
17. recognize visual representations of sound and describe them as loud, quiet, high pitched, low pitched, etc
Loudness and quietness relate to the height(amplitude) of the waves and pitch relates to frequency
As an object speeds up, it begins to catch up with its sound waves. This creates a higher frequency. As the object moves away from you, the waves come further apart making it sound lower-pitched
the unit of the speed of sound
As something hits the speed of sound, the sound waves it’s making line up with the sound waves previously ahead and create a sonic boom
Frequency: 20Hz-20000Hz Volume: 0dB-120dB+(threshold of pain)
Particle: Democritus and Newton
Wave: Aristotle, Faraday, Maxwell, and Thomas Young
Both: Max Planck, Albert Einstein, DeBroglie and Heisenberg
Radio, microwave, infrared, visible, ultraviolet, x-ray, and gamma ray
X-rays
the light passes through the cornea which bends the light toward the iris which determines how much light is let into the eye. The lens puts the light in the right spot, and the rods and cones determine what you see
Friction, induction, and conduction
describe how electrical impulses travel in your nerves.
Energy goes from one nerve to another through the synapse. It gets across using neurotransmitters