POCUS -Intro
1/46
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
How do strong reflections (bone) appear on US?
white dots (hyperechoic)
How do weaker reflections (solid organs) appear on US?
grey dots (hypoechoic)
How do no reflections (full bladder/blood/fluid) appear on US?
black dots (anechoic)
What is acoustic shadowing on an US characterized by?
signal void behind structures that strongly absorb or reflect US waves
What is enhancement on an US?
area of inc brightness underneath fluid dt lack of impedance when sound waves pass through fluid and inc echoes from underlying structures
What is the doppler effect?
when there is motion in the field of view → shift or difference in frequency
What is ‘BART’ for color doppler?
blue away, red towards
What transducer would be better for soft tissues and superficial structures?
Linear probes
What transducer would be better for deep structures like abdominal viscera and for obese patients?
Curvilinear and phased array probes
Which type of frequency has shorter wavelengths?
Higher frequency (more cycles/sec = better resolution, less penetration)
What probe frequency is used for soft tissues and superficial structures?
Higher frequencies: 5-10 MHz
Which type of frequency has wider wavelengths?
Lower frequency (less cycles/sec = less resolution, more penetration)
What probe frequency is used for deep structures like abdominal viscera and for obese patients?
Lower frequencies: 1-5 MHz
What frequency do Linear probes use?
Higher frequencies: 5-10 MHz
What frequency do Curvilinear and phased array probes use?
Lower frequencies: 1-5 MHz
What is the relationship between frequency and wavelength?
Inverse
Which way should the probe marker be facing?
pts’s right or the head of pt
What does the green dot on the US screen correspond to?
side of probe with the marker
What is overall gain?
effects the amplification applied uniformly to echoes from all depths; overall brightness/darkness of the image
What is high gain?
inc brightness of image
What is low gain?
dec brightness of image
What is time gain compensation (TGC)?
will change the amplification of the echoes at different depths
What does altering the depth of the field of view affect?
frame rate and line density
Why do you need transmission gel for POCUS?
Air causes the sound beam to scatter so the gel allows the sound beam to enter the body
What is long axis (longitudinal)?
probe is parallel to the structure being scanned, indicator points to the patient's head
What is short axis (transverse)?
probe is perpendicular to the structure being scanned, indicator faces the patient's right even if scanning on the left side
When scanning in transverse axis, what way does the indicator point?
towards pts right
When scanning in longitudinal axis, what way does the indicator point?
towards pts head
Which way does the beam shoot in the sagittal body cut?
Anterior to posterior
In longitudinal axis in the sagittal body plane, what is the screen showing?
Left: superior
Right: inferior
Top: anterior
Bottom: posterior
In longitudinal axis in the coronal body plane, what is the screen showing?
Left: superior
Right: inferior
Top: lateral
Bottom: medial
What type of movement is a “sweep” or a “fan”?
Transverse/short axis movements
What type of movement is a “slide” or a “rock”?
Longitudinal/long axis movements
What type of movement is a “compression” or a “rotation”?
Z axis movements
What transducer movement moves the probe cranially or caudally along the X axis?
Sweep
What transducer movement starts from a 90 angle and reduces the angle slowly from 90 to 45 cephalad along the X axis?
Fan
What transducer movement moves the probe cranially or caudally along the Y axis of the probe?
Slide
What transducer movement reduces the angle of the probe from 90 to 45 cranially along the Y axis of the probe?
Rock
What transducer movement applies steady downward force into the patient's body along the Z axis?
Compression
When would you use compression w/ US?
disperse intestinal gas or search for DVT
What transducer movement turns the probe 90 degrees clockwise along the Z axis to arrive at the longitudinal imaging plane?
Rotation
What is alignment?
sliding movement of the probe across the skin to track structures
What is rotation?
twisting movement, moving from short axis to long axis views
What is tilt?
rocking the probe to optimize the angle of reflection
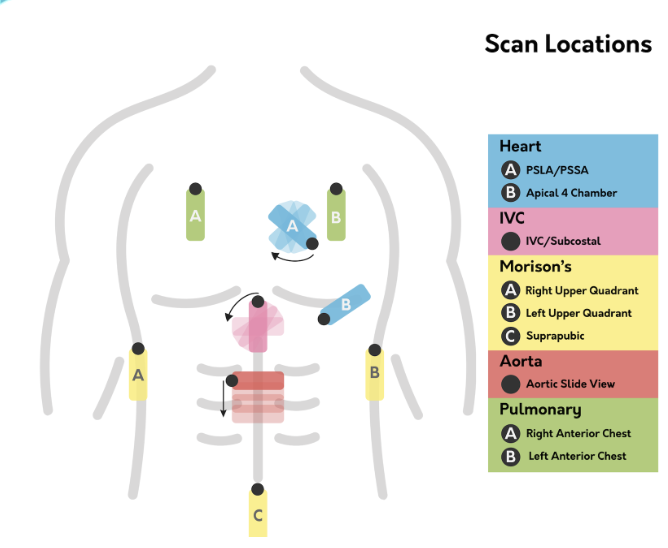
Review the probe positions
:)
What is the in-plane approach?
needle is placed in line with and parallel to the transducer → needle shaft and tip are visualized
What is the out-of-plane approach?
needle is placed perpendicular to the transducer → needle shaft and tip are visualized as a hyperechoic dot