18.1 to 18.3 Organic Chemistry
Organic compounds names, structures, and types
- Organic chemistry is the chemistry of carbon compounds
- Carbon forms a vast number of compounds because it can form strong covalent bonds with itself
- This enables it to form long chains of carbon atoms, and hence an almost infinite variety of carbon compounds are known
- Carbon always forms four covalent bonds which can be single, double or triple bonds
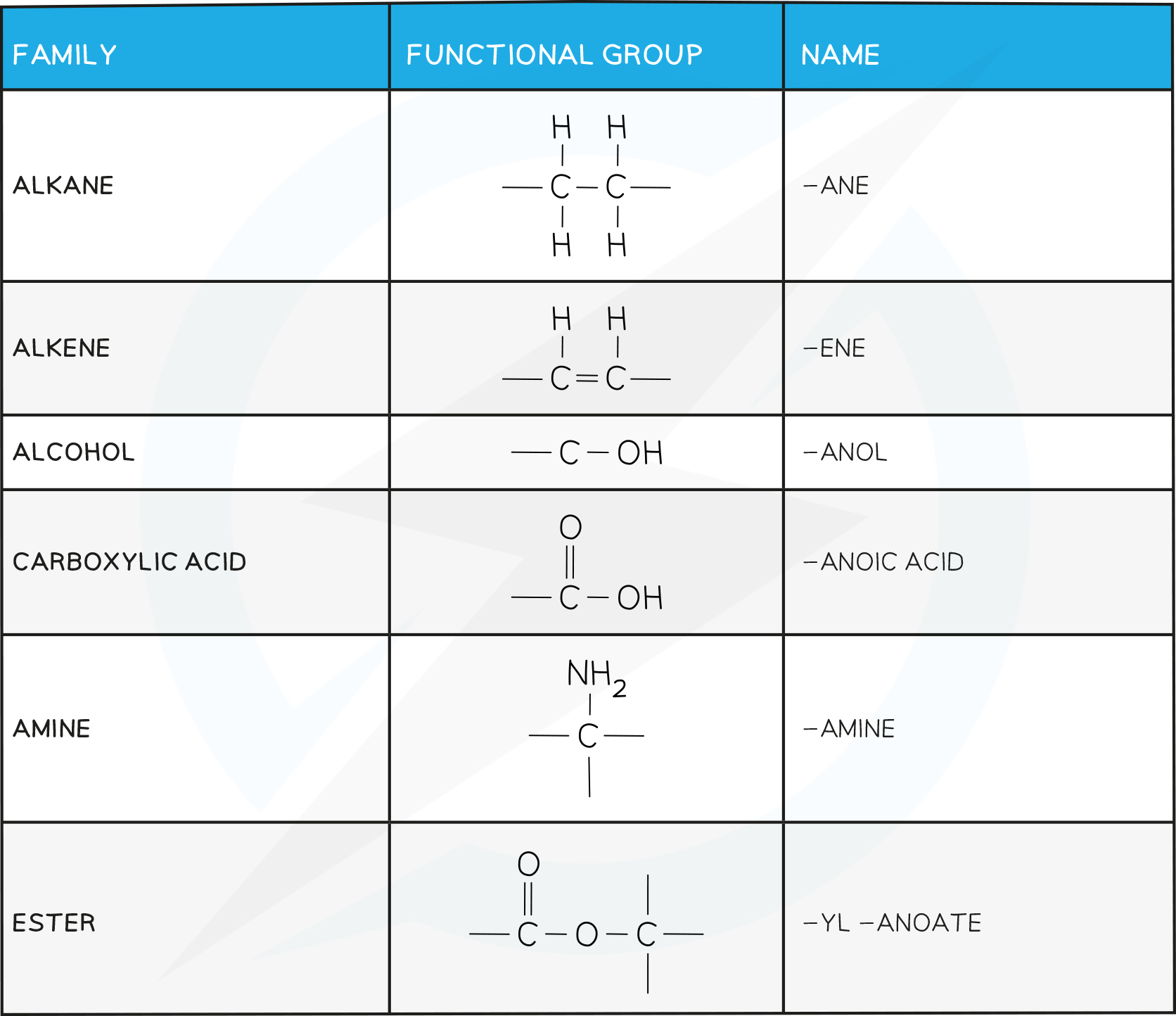
- A functional group is a specific atom or group of atoms which confer certain physical and chemical properties onto the molecule
- Organic compounds with the same functional group, but a different number of carbon atoms, are said to belong to the same homologous series
- Every time a carbon atom is added to the chain, two hydrogen atoms are also added
- Organic molecules are classified by the dominant functional group on the molecule
- Organic compounds can be represented in a number of ways
Types of formulae
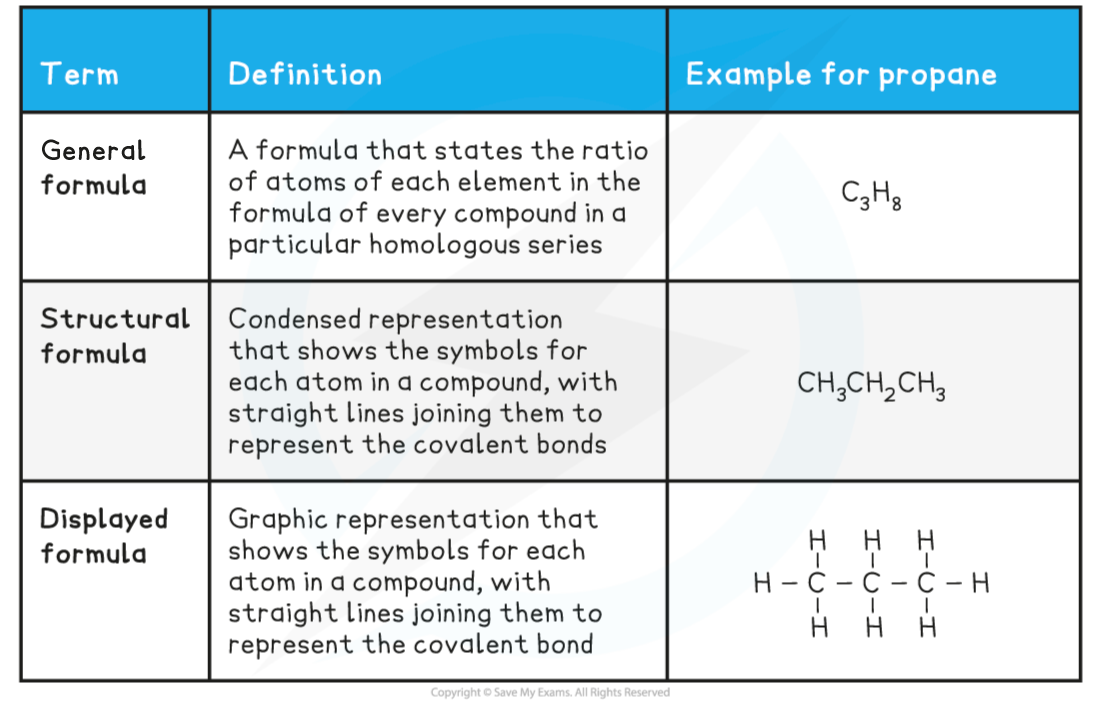
1- General Formula
- This type of formula tells you the composition of any member of a whole homologous series of organic compound
- For example, all of the alkanes have the general formula CnH2n+2
- This tells you that however many carbon atoms there are in the alkane, doubling this number and adding two will give you the number of hydrogen atoms present in the alkane
2- Displayed Formula
This shows the spatial arrangement of all the atoms and bonds in a molecule
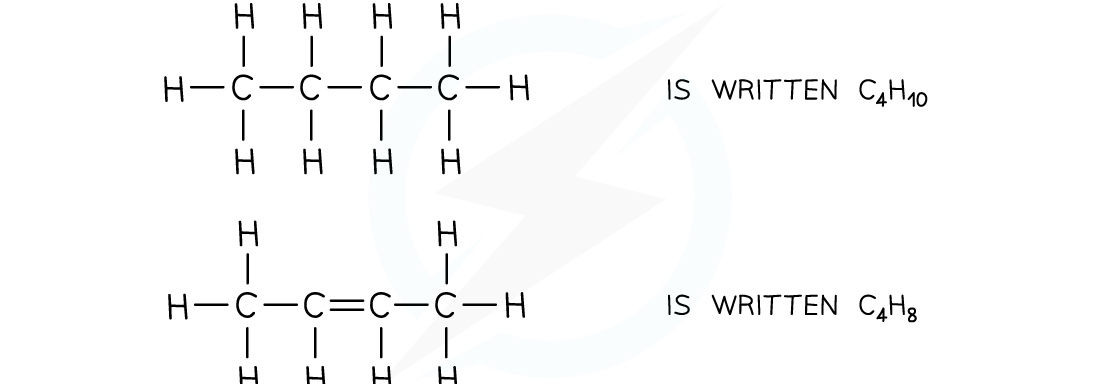
Molecular Formulae
- This shows the actual number of each atom in a molecule, one element at a time
Structural Formula
This gives enough information to make the structure clear, but most of the actual covalent bonds are omitted
Only important bonds are shown, such as double and triple bonds
- Identical groups can be bracketed together

Naming Compounds
The names of organic compounds have two parts: the prefix (or stem) and the end part (or suffix)
The prefix tells you how many carbon atoms are present in the longest continuous chain in the compound
The suffix tells you what functional group is on the compound
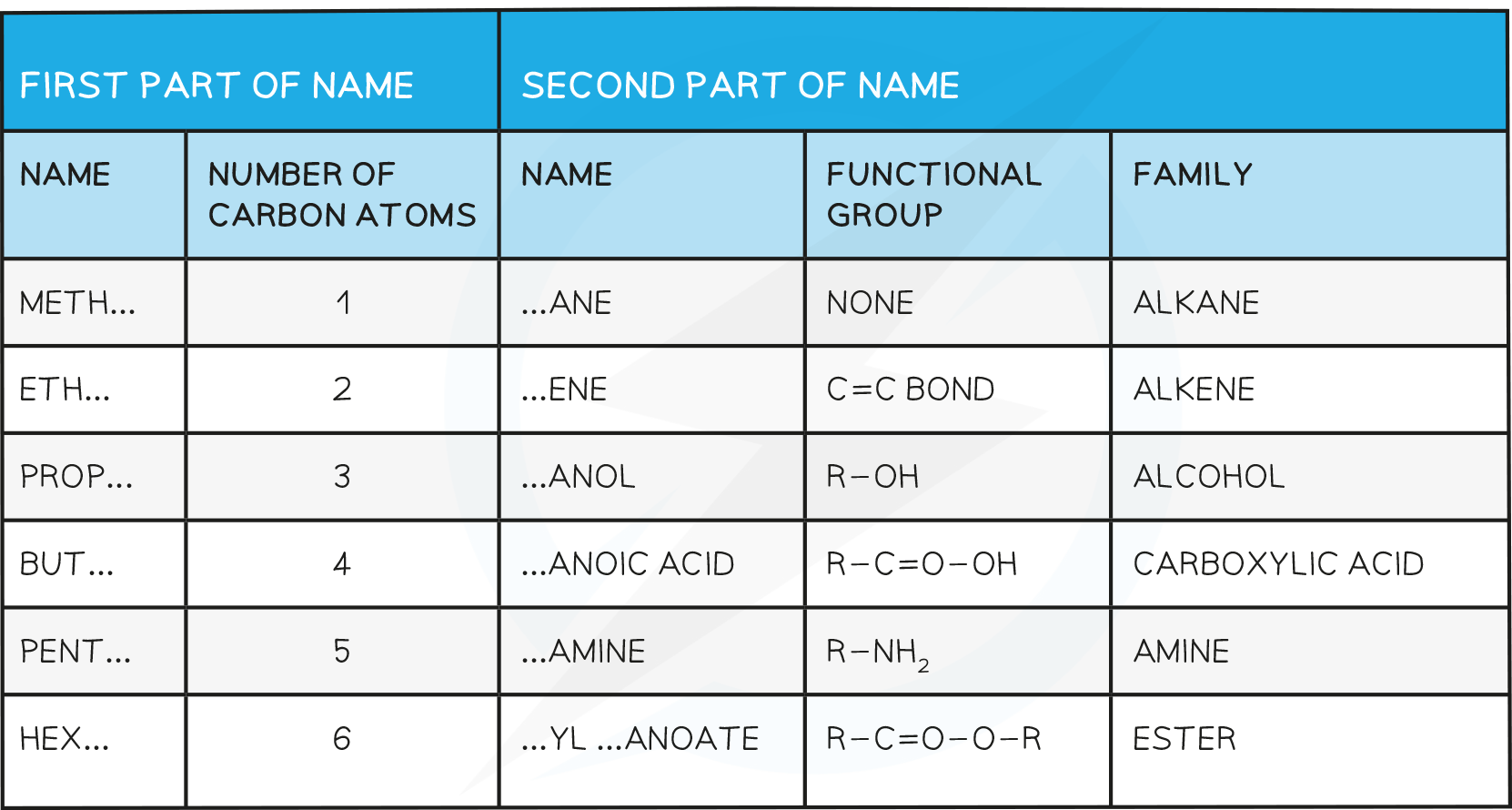
Families of Organic Compounds
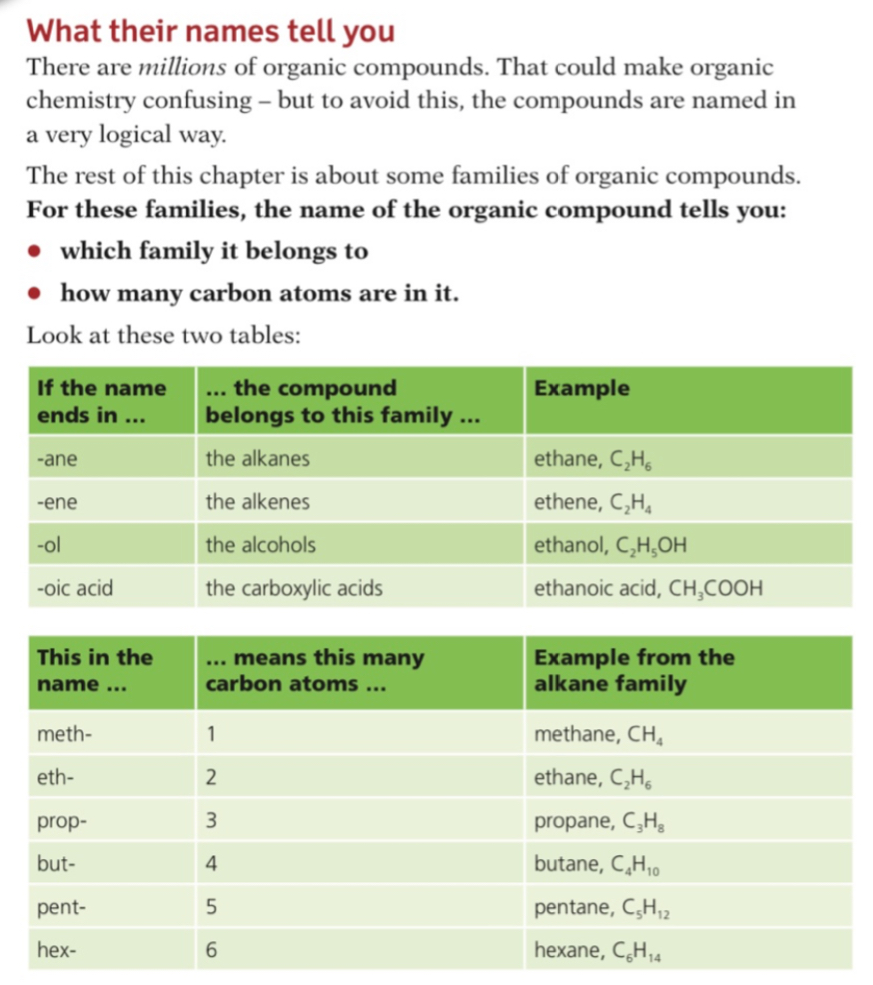
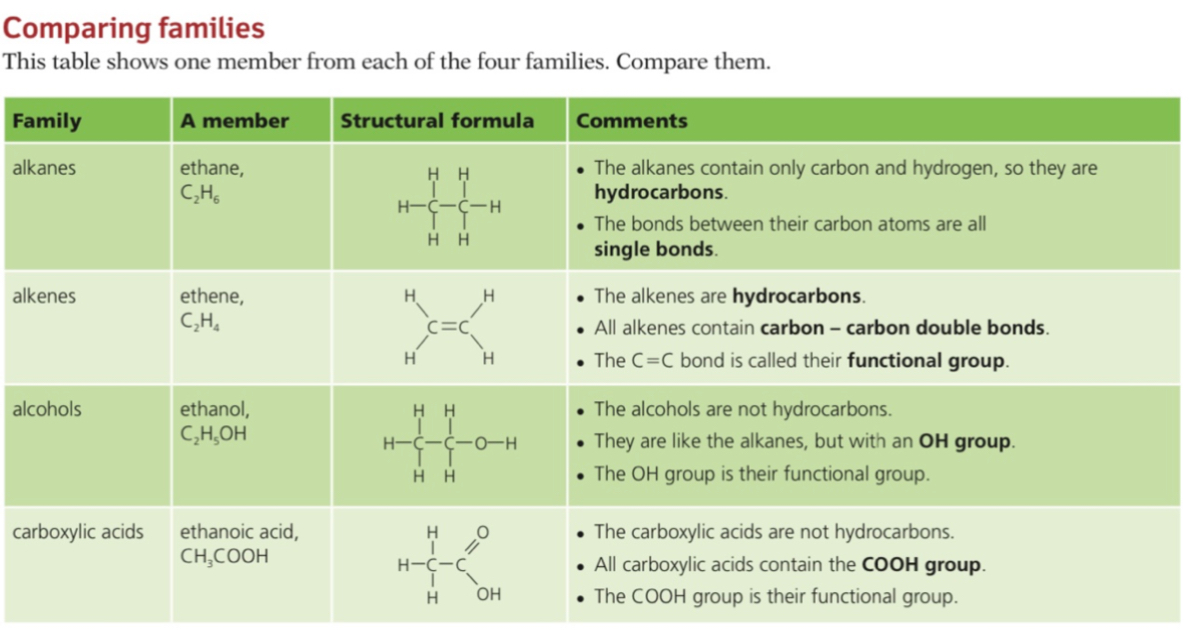
Structures
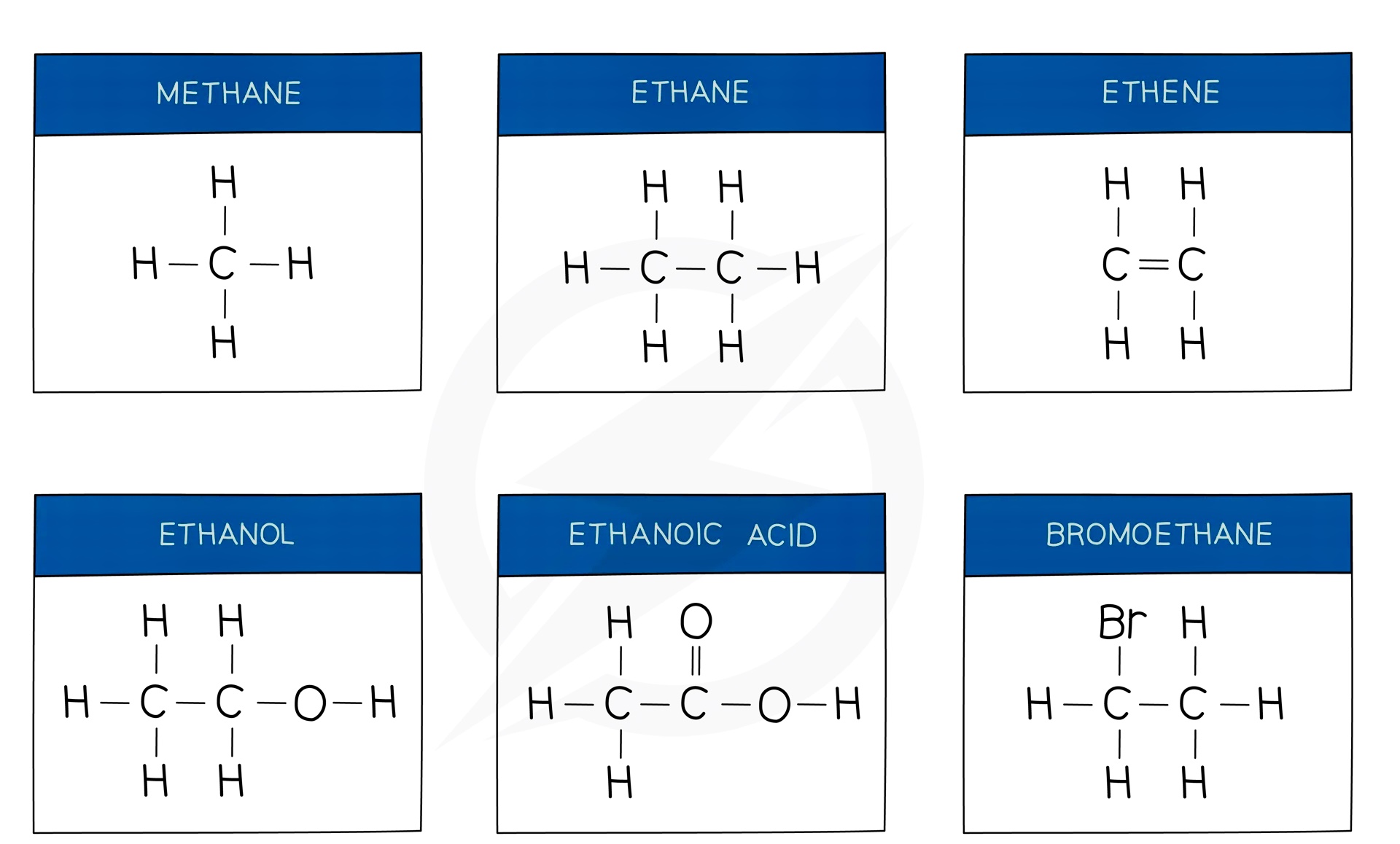
%%Structures and Formulae%%
Alkanes
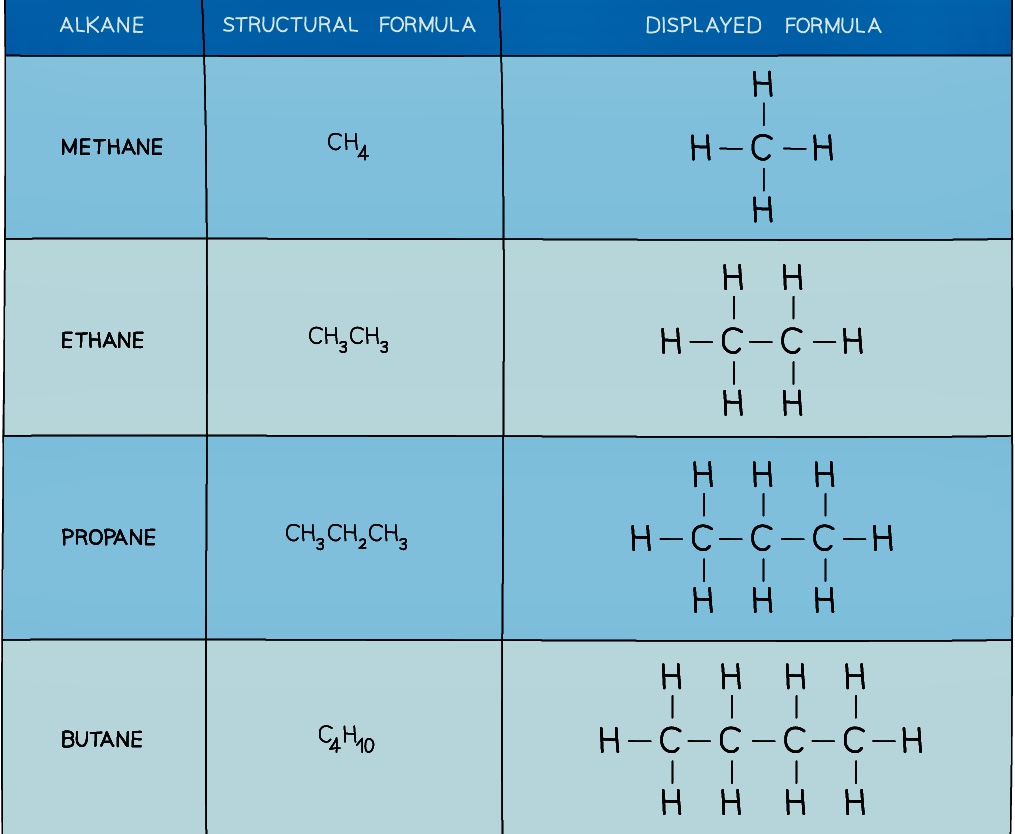
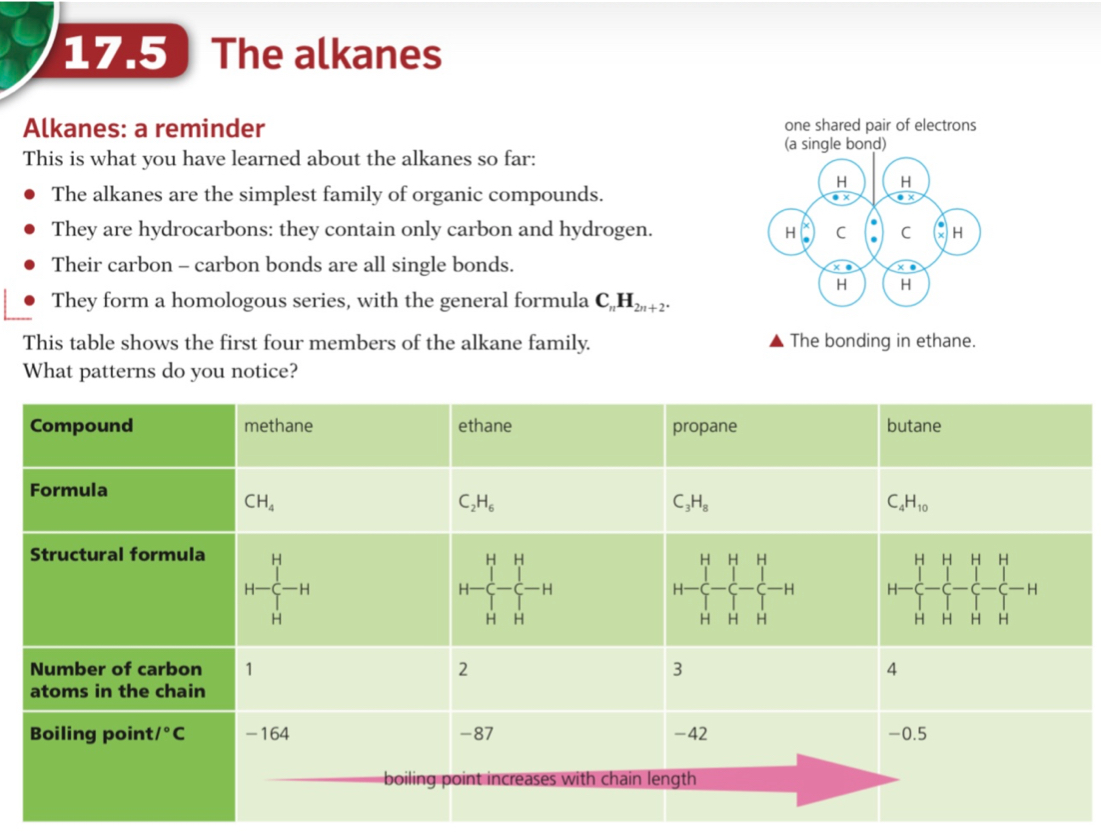
- Alkanes are a group of saturated hydrocarbons
- The term saturated means that they only have single carbon-carbon bonds, there are no double bonds
- The general formula of the alkanes is CnH2n+2
- They are colourless compounds which have a gradual change in their physical properties as the number of carbon atoms in the chain increases
- Alkanes are generally unreactive compounds but they do undergo combustion reactions, can be cracked into smaller molecules and can react with halogens in the presence of light
- Methane is an alkane and is the major component of natural gas
- Methane undergoes complete combustion forming carbon dioxide and water:
- CH4 (g) + 2O2 (g) → CO2 (g) + 2H2O (l)
Alkene
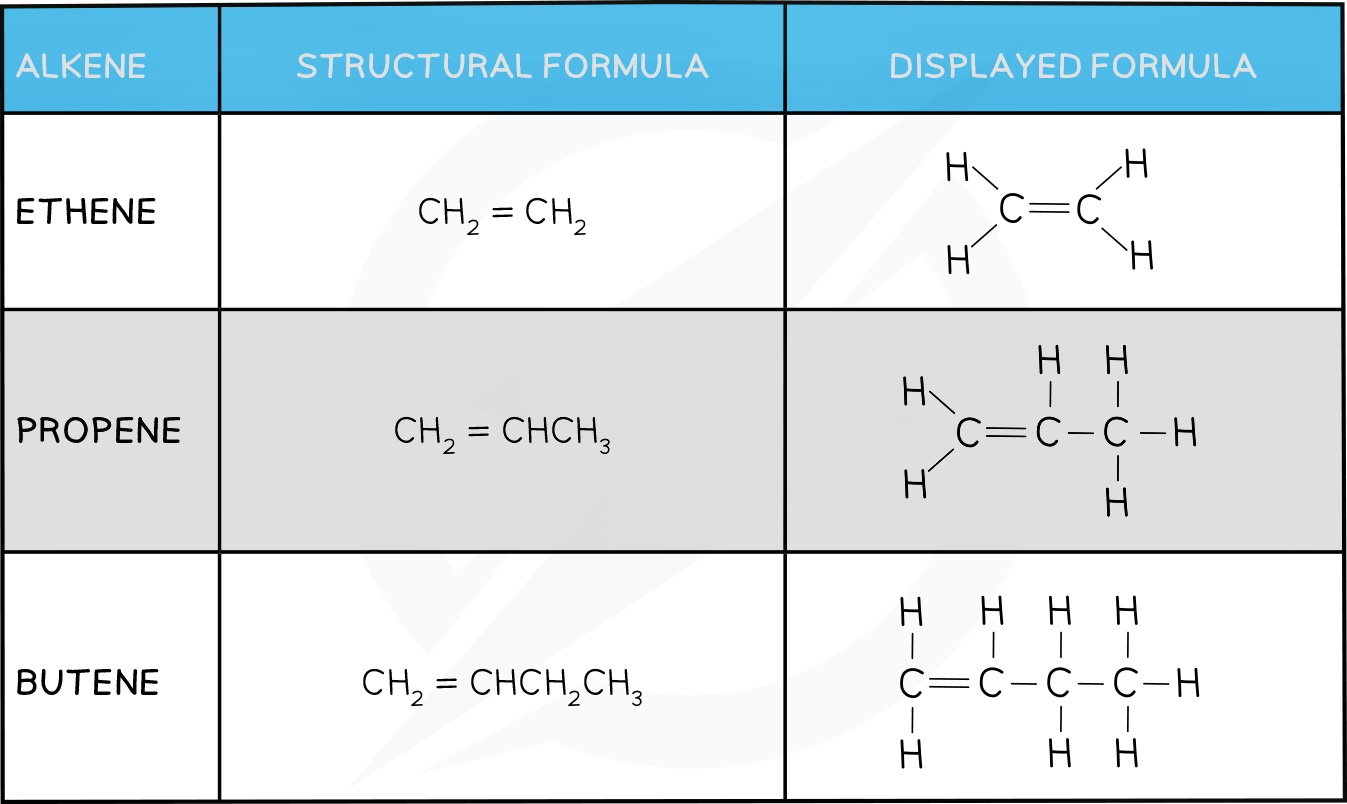
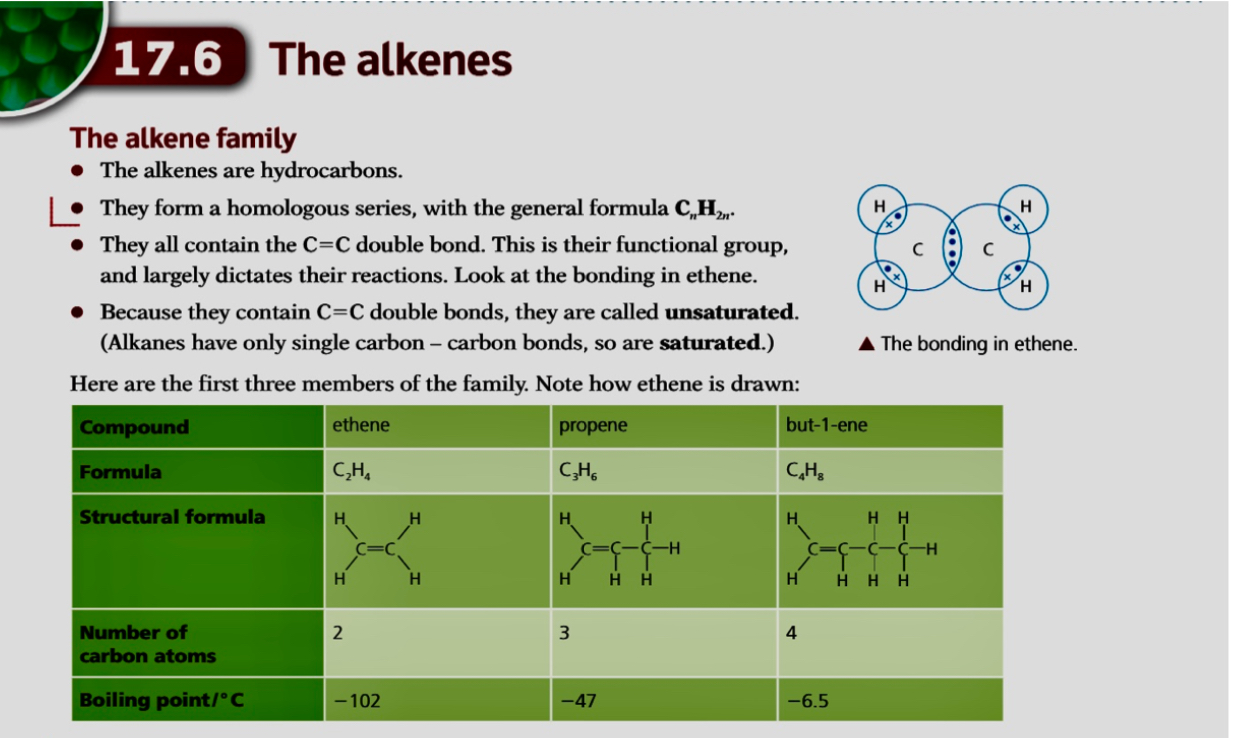
- Alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons with carbon-carbon double bonds (C=C)
- Their general formula is CnH2n
- The presence of the double bond, C=C, means they can make more bonds with other atoms by opening up the C=C bond and allowing incoming atoms to form another single bond with each carbon atom of the functional group
- Each of these carbon atoms now forms 4 single bonds instead of 1 double and 2 single bonds
This makes them much more reactive than alkanes
Manufacture of Alkenes and Hydrocarbons
- Although there is use for each fraction obtained from the fractional distillation of crude oil, the amount of longer chain hydrocarbons produced is far greater than needed
- These long chain hydrocarbon molecules are further processed to produce other products
- A process called catalytic cracking is used to convert longer-chain molecules into short-chain and more useful hydrocarbons
- Shorter chain alkanes, alkenes and hydrogen are produced from the cracking of longer chain alkanes
- Alkenes can be used to make polymers and the hydrogen used to make ammonia
- Kerosene and diesel oil are often cracked to produce petrol, other alkenes and hydrogen
- Cracking involves heating the hydrocarbon molecules to around 600 – 700°C to vaporise them
- The vapours then pass over a hot powdered catalyst of alumina or silica
- This process breaks covalent bonds in the molecules as they come into contact with the surface of the catalyst, causing thermal decomposition reactions
- The molecules are broken up in a random way which produces a mixture of smaller alkanes and alkenes
- Hydrogen and a higher proportion of alkenes are formed at higher temperatures and higher pressure
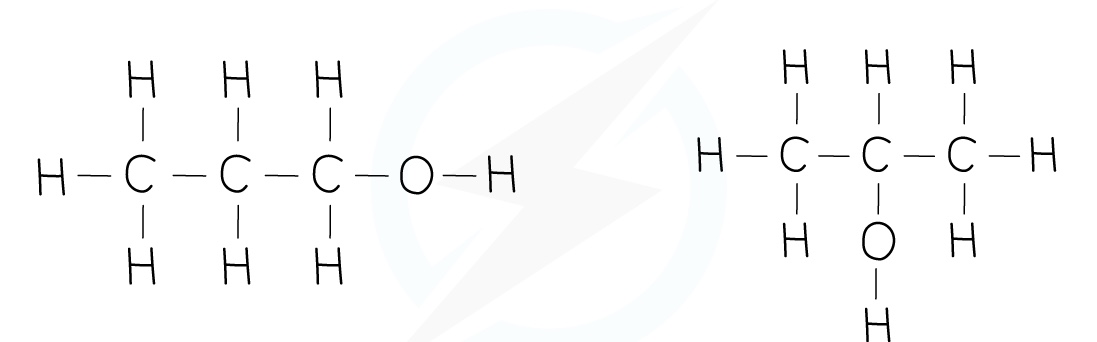
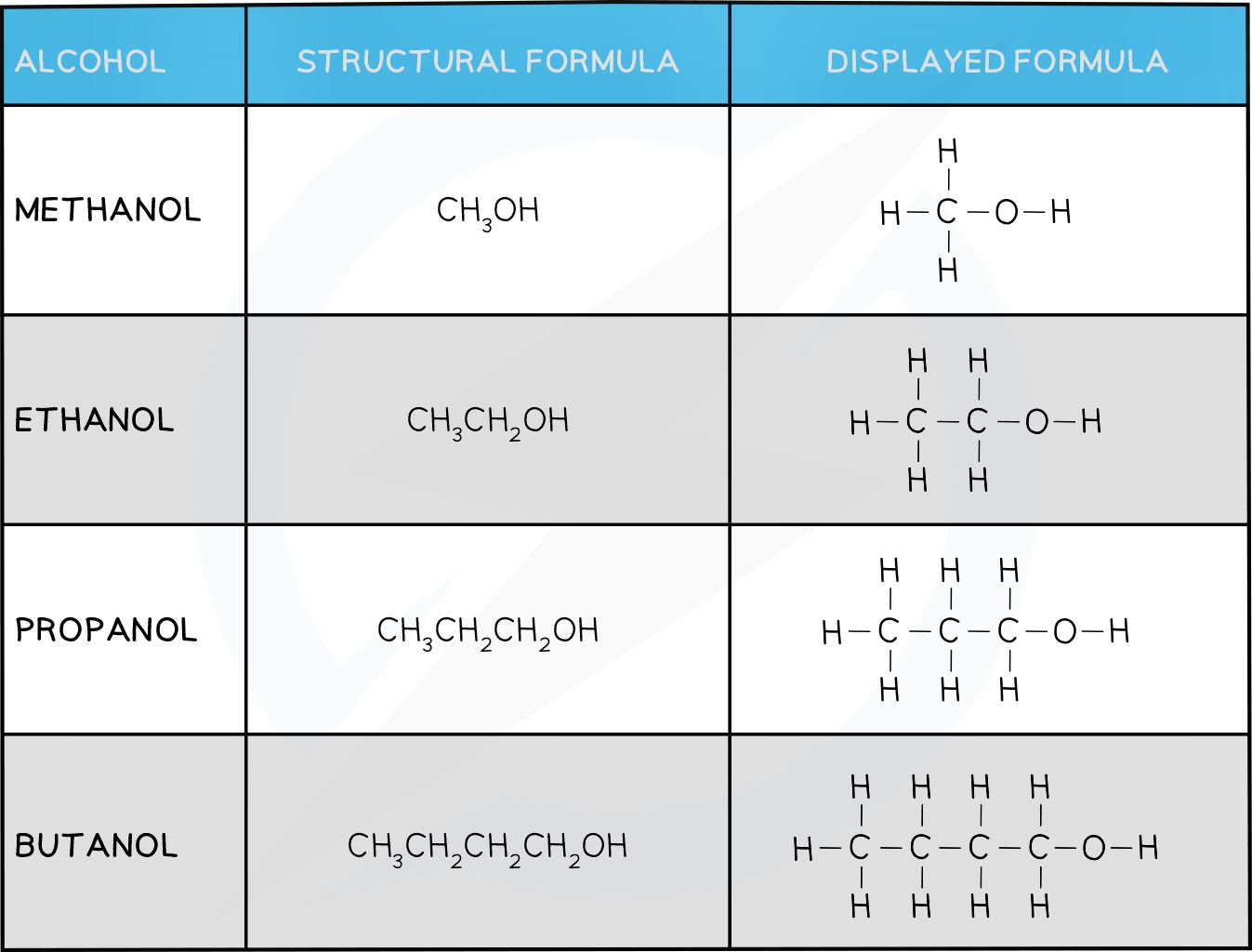
Alcohols
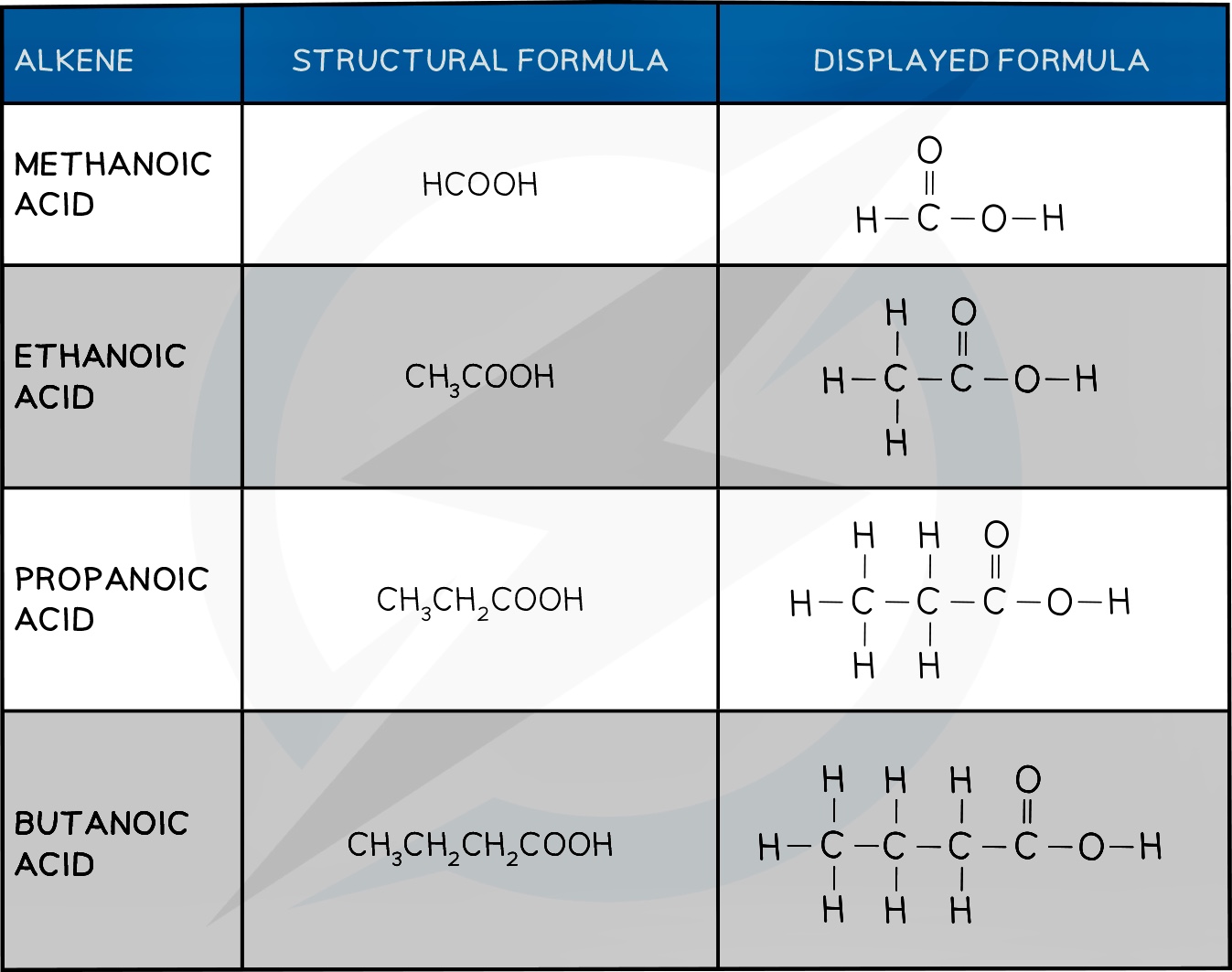
Carboxylic Acid
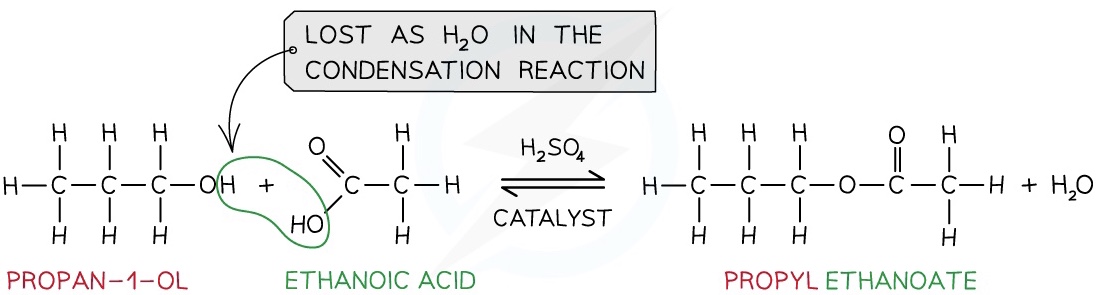
Production of Esters
Esters are compounds with an -COOR functional group and are characterised by their sweet and fruity smells
They are prepared from the condensation reaction between a carboxylic acid and alcohol with concentrated H2SO4 as catalyst
- This is also called esterification
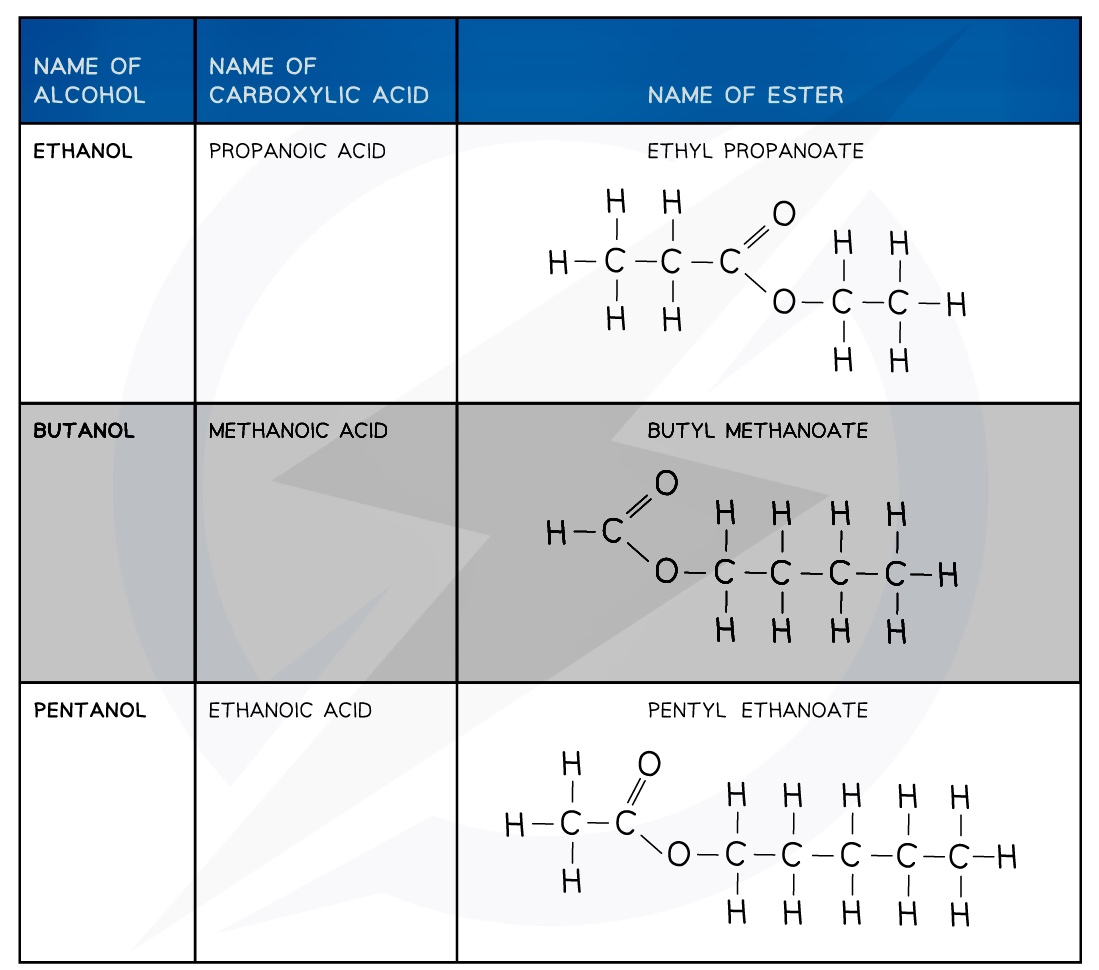
The first part of the ester’s name comes from the alcohol and the second part of the name comes from the carboxylic acid
- E.g. Propanol and ethanoic acid will give the ester propyl ethanoate
Esters
18.2 FUELS
Common Fossil Fuels
- A fuel is a substance which when burned, releases heat energy
- This heat can be transferred into electricity, which we use in our daily lives
- Most common fossil fuels include coal, natural gas and hydrocarbons such as methane and propane which are obtained from crude oil
- Hydrocarbons are made from hydrogen and carbon atoms only
- The main constituent of natural gas is methane, CH4
Petroleum
Petroleum and Fractional Distillation
Petroleum is also called crude oil and is a complex mixture of hydrocarbons which also contains natural gas
It is a thick, sticky, black liquid that is found under porous rock (under the ground and under the sea)
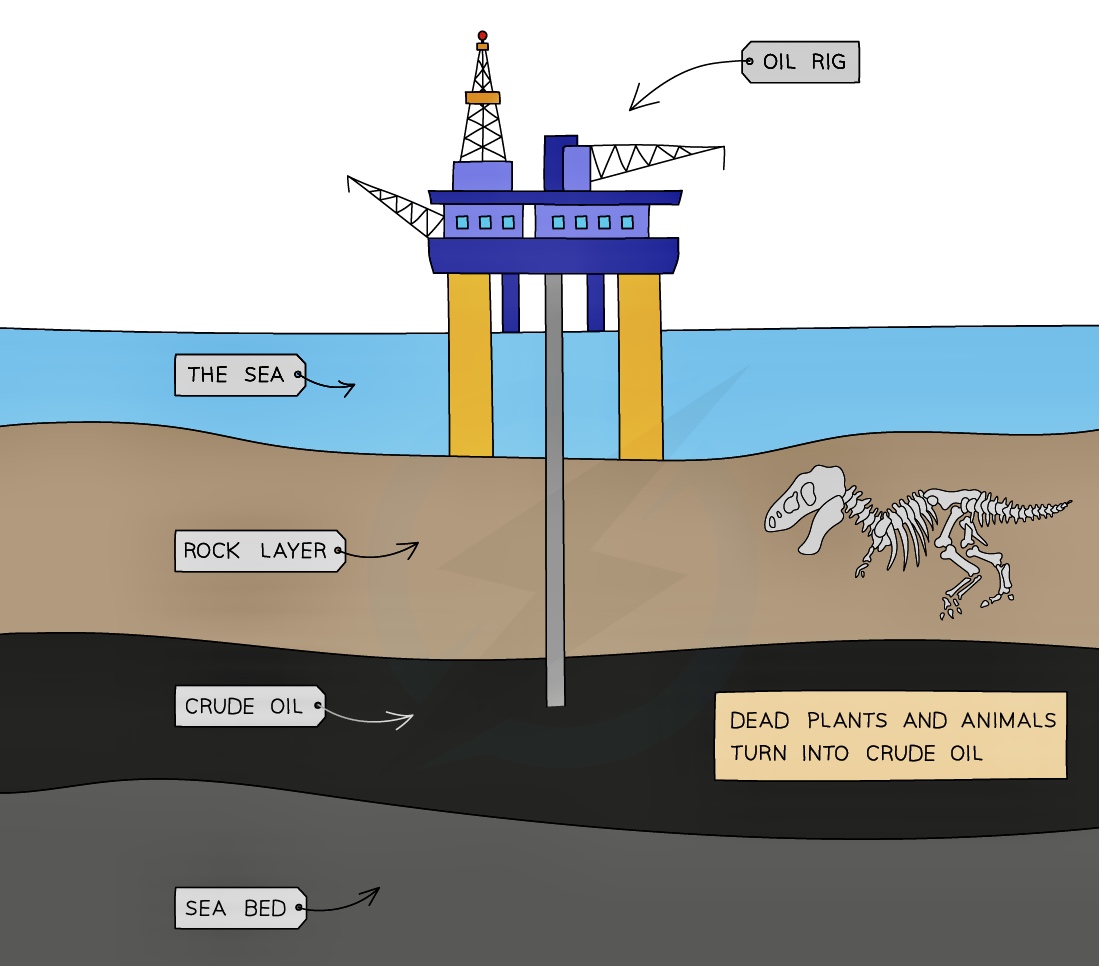
Petroleum itself as a mixture isn't very useful but each component part of the mixture, called a fraction, is useful and each fraction has different applications
The fractions in petroleum are separated from each other in a process called fractional distillation
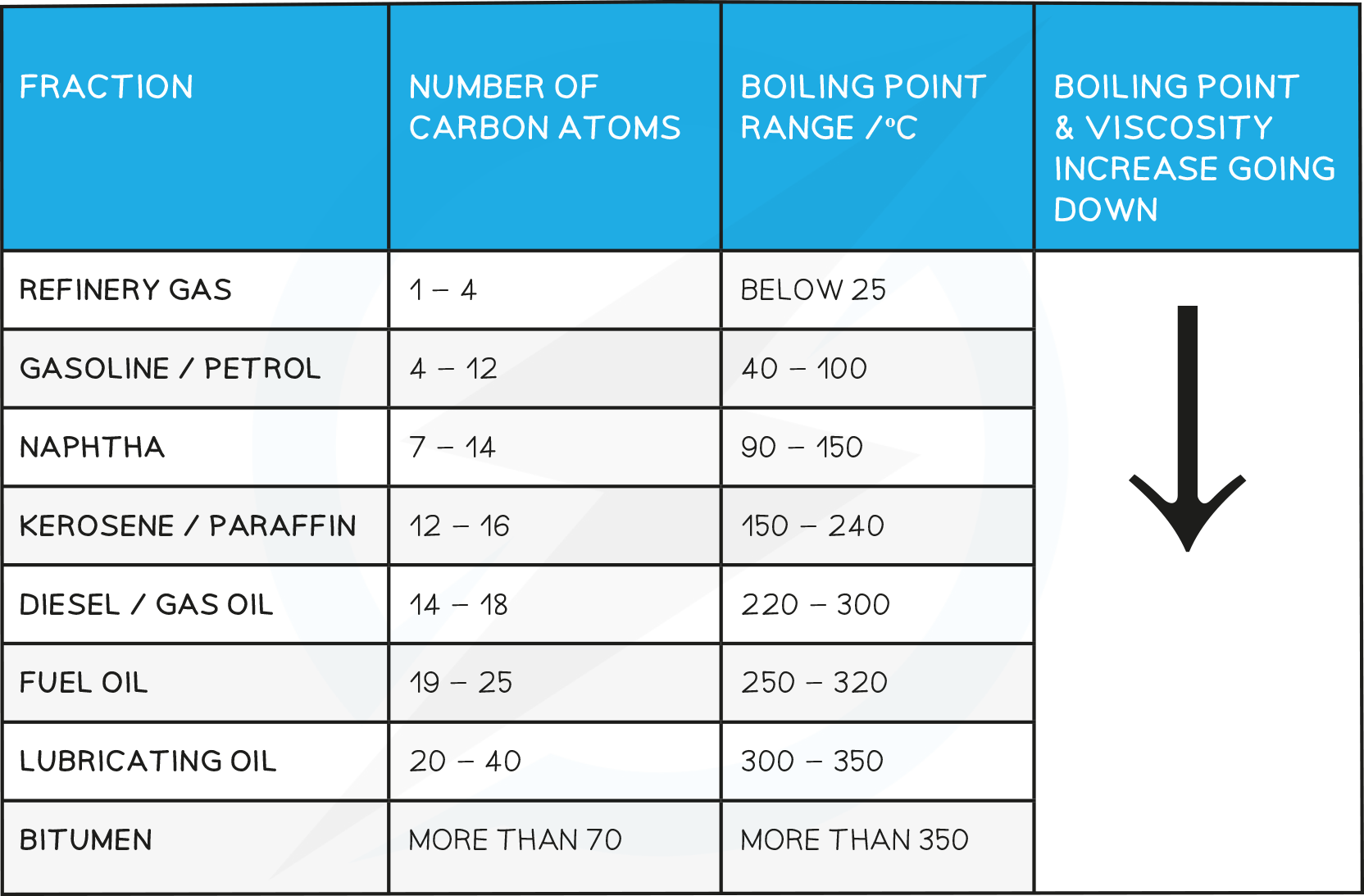
The molecules in each fraction have similar properties and boiling points, which depend on the number of carbon atoms in the chain
The boiling point and viscosity of each fraction increases as the carbon chain gets longer
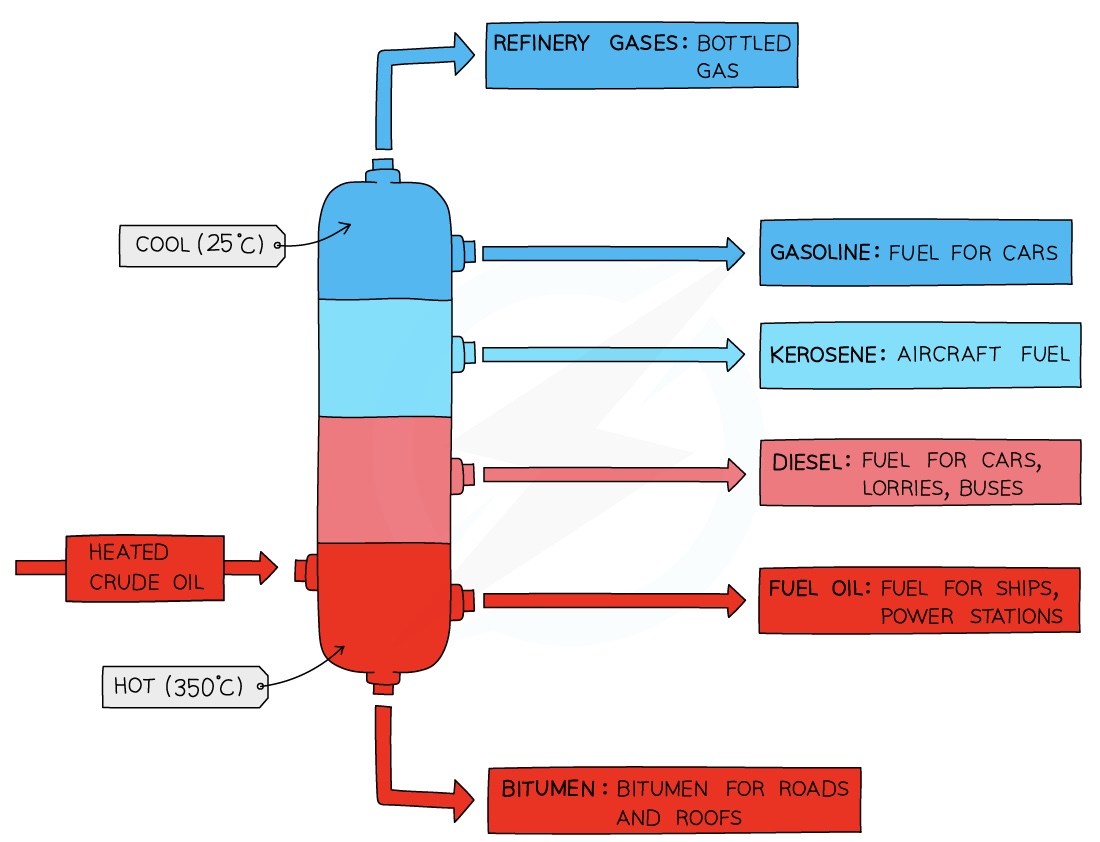
- Fractional distillation is carried out in a fractionating column
- The fractionating column is hot at the bottom and cool at the top
Crude oil enters the fractionating column and is heated so vapours rise
Vapours of hydrocarbons with very high boiling points will immediately turn into liquid and are tapped off at the bottom of the column
Vapours of hydrocarbons with low boiling points will rise up the column and condense at the top to be tapped off
The different fractions condense at different heights according to their boiling points and are tapped off as liquids.
The fractions containing smaller hydrocarbons are collected at the top of the fractionating column as gases
The fractions containing bigger hydrocarbons are collected at the lower sections of the fractionating column
Properties of Fractions
Viscosity
This refers to the ease of flow of a liquid.
High viscosity liquids are thick and flow less easily.
The number of carbon atoms increases, the attraction between the hydrocarbon molecules also increases which results in the liquid becoming more viscous with the increasing length of the hydrocarbon chain.
The liquid flows less easily with increasing molecular mass
Colour
- As carbon chain length increases the colour of the liquid gets darker as it gets thicker and more viscous
Melting point/boiling point
- As the molecules get larger, the intermolecular attraction becomes greater.
- More heat is needed to separate the molecules.
- With increasing molecular size there is an increase in boiling point
Volatility
- Volatility refers to the tendency of a substance to vaporise.
- With increasing molecular size hydrocarbon liquids become less volatile.
- This is because the attraction between the molecules increases with increasing molecular size
Uses of Fractions
- Refinery gas: heating and cooking
- Gasoline: fuel for cars (petrol)
- Naphtha: raw product for producing chemicals
- Kerosene: for making jet fuel (paraffin)
- Diesel: fuel for diesel engines (gas oil)
- Fuel oil: fuel for ships and for home heating
- Lubricating oil: for lubricants, polishes, waxes
- Bitumen: for surfacing roads
Trends in Properties
18.3 Homologous Series
This is a series or family of organic compounds that have similar features and chemical properties due to them having the same functional group
The functional group is a group of atoms which are bonded in a specific arrangement that is responsible for the characteristic reactions of each member of a homologous series
\n
Characteristics, Formula & Structural Isomerism
Characteristics of Homologous Series
- All members of a homologous series have:
- The same general formula
- Same functional group
- Similar chemical properties
- Gradation in their physical properties, such as melting and boiling point
- The difference in the molecular formula between one member and the next is CH2
General Formula
- This type of formula tells you the composition of any member of a whole homologous series of organic compound
- For example, all of the alkanes have the general formula CnH2n+2
- This tells you that however many carbon atoms there are in the alkane, doubling this number and adding two will give you the number of hydrogen atoms present in the alkanes
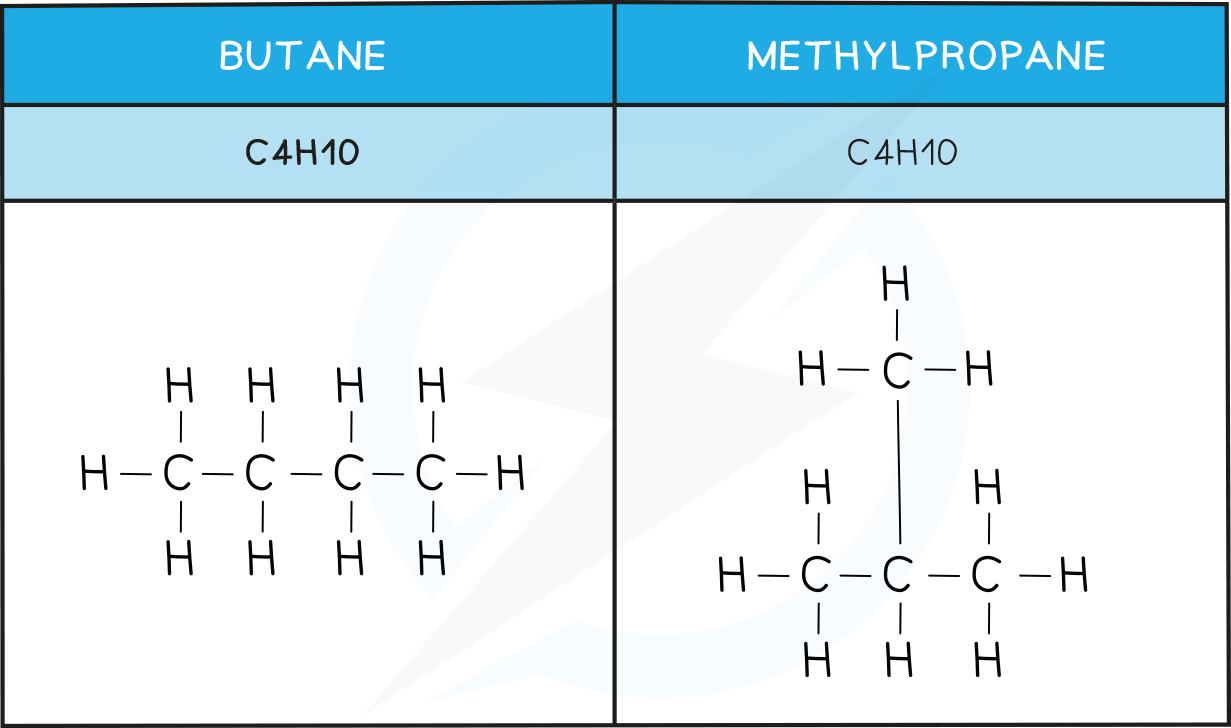
Structural isomers
Structural isomers are compounds that have the same molecular formula but different structural formulae
This is due to the different arrangement of their atoms in space
There are two types: chain and position
In chain isomerism the structure of the carbon chain differs
In position isomerism, the position of the functional group differs