4322 WEEK 5, LECTURE IV, Human Capital and Resource Management
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Those that deliver forms of innovation that support or grow market share are labeled
“human capital,” and those that support them are called “human resources.”
Aggregate HTC (human, technical, conceptual) Skills –
the sum of all
job assignments – are the critical factors (people, processes, place-
design-structure) for Value Chains that comprise modern
organizations.
Human Capital and Resource Management (HCRM) –
recognizing,
attracting, developing and retaining “social capital (HTCs)” of
“people” associated with the modern organization.
Social networks allow for
leveraging of individual and partial or
complete aggregates of HTCs, or social capital.
o Social networks define the field or universe for knowledge
management within any modern organization and its area of
operations.
Humans leverage Technology, not technology leveraging humans.
People build the technologies to build the products, and
administrative processes are how we support and deliver our
technological processes that comprise the Value Chain for our
product or organization. People accomplish via social networks.
Outcomes (C)
New market share
More inelastic demand and prices
Attract and retain best available stakeholders
Inputs (A)
People (culture)
Admin Processes
Tech Processes
Place (structure)
Outputs (B)
New product (business)
New production method (business)
New means for supply (business)
New market (business, corporate)
New enterprise format (corporate)
A company’s value is not derived solely from
its physical assets. Rather, it is based on
knowledge, know how, and intellectual
assets, all embedded in people.
In the knowledge economy, wealth is
increasingly created by
effective management
of knowledge workers instead of by the
control of physical and financial assets.
Intellectual capital is a measure of the value
of
a firm’s intangible assets. It is the difference
between a firm’s market value and book value.
It includes these assets:
• Reputation.
• Employee loyalty and commitment.
• Customer relationships.
• Company values.
• Brand names.
• Experience and skills of employees.
Human capital includes
the individual capabilities,
knowledge, skills, and experience of the company’s
employees and managers.
Social capital includes
the network of relationships that
individuals have throughout the organization.
Knowledge management is critical to organizational
success. Knowledge includes:
1. Explicit knowledge. Codified, documented, easily reproduced,
and widely distributed.
2. Tacit knowledge. In the minds of employees, based on their
experiences and backgrounds.
Human Capital: Three Interdependent Activities
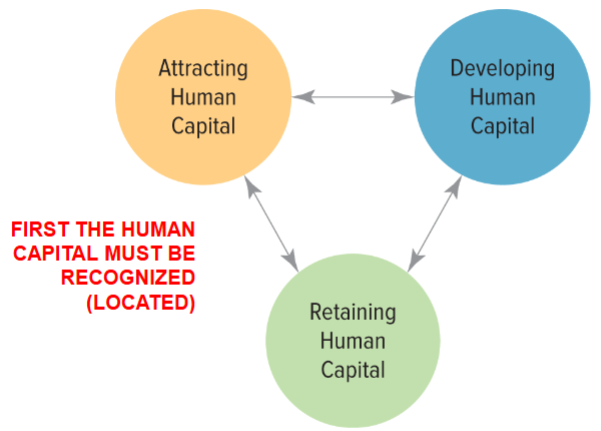
Attracting Human Capital
Hire for attitude, train for skill with an emphasis on:
1. General knowledge and experience (technical skills)
2. Inductive thinking skills (conceptual skills)
3. Social skills, values, beliefs, attitudes (human skills)
Recognize the geographical preferences of talent
Use algorithms for selection
Training and development must take place at all
levels of the organization.
1. Requires the active involvement of leaders at all
levels.
2. Includes mentoring and sponsoring lower-level
employees.
3. Emphasizes the need to monitor progress and track
development so knowledge can be shared.
Retaining Human Capital
Retention mechanisms must prevent the transfer of
valuable and sensitive information outside the
organization.
Help employees identify and associate with an
organization’s mission and values.
Provide a challenging work and a stimulating environment.
Offer financial and nonfinancial rewards and incentives.
• Money is not always the most important reason why people
take or leave jobs, but it does get the attention of most
people.
Social capital and networks:
• The friendships and working relationships
among talented individuals.
• It helps to tie knowledge workers to a given
firm.
• Interaction, sharing, and collaboration will
help develop firm specificities, with a higher
probability of retaining key knowledge
workers.
11
Social network analysis involves
the pattern of
interactions among individuals and helps to diagnose
effective and ineffective patterns.
A. Who links to whom within the network or cluster?
B. Who communicates to whom and how effective is this
communication?
Social ties can link individuals so they can
[1] convey needed resources,
[2] exchange information and support, and
[3] develop trusting relationships to improve the groups’
effectiveness.
Social Network Analysis
Two types of Relationships
Closure Relationships
Bridging Relationships
Closure Relationships
The degree to which all
members of the social
network have
relationships with other
group members.
Bridging Relationships
Relationships in a social
network that connect
otherwise disconnected
people.
Example: Social Network Analysis
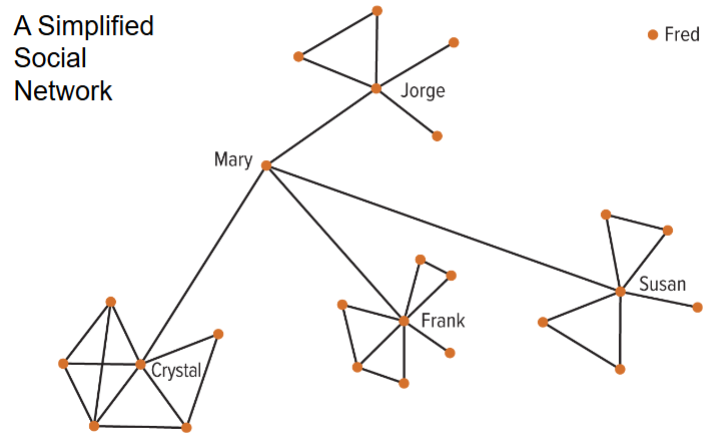
Effective social networks provide advantages for
the firm AND for an individual’s career
advancement.
Access to private information communicated in the
context of personal relationships.
Access to diverse skill sets: Trading information or skills
with people whose experiences differ from your own.
Access to power and Development of influence.
15
Social Capital: Potential Downside
1. Groupthink.
2. Dysfunctional human resource practices.
3. Expensive socialization processes
(orientation, training).
4. Distortion or selective use of information to
favor preferred courses of action.
Sharing knowledge and information throughout
the organization (formal communications).
1. Conserves resources.
2. Develops products and services.
3. Creates new opportunities.
Technology can leverage human capital and
knowledge
[1] Within the organization, [2] With
customers and [3] With suppliers.
The Value Chain.
Codifying Knowledge for Competitive Advantage
Tacit knowledge
• Embedded in personal
experience.
• Shared only with the
consent and participation
of the individual.
• Has the organization
effectively used technology
to codify knowledge for
competitive advantage?
Codifying Knowledge for Competitive Advantage
Explicit (codified)
knowledge
• Can be documented.
• Can be widely distributed.
• Can be replicated.
• Can be reused many times
at very low (marginal, per
unit) cost.
18
Intellectual property rights are more difficult to define
and protect than property rights for physical assets.
1. Intellectual property can be stolen.
2. If intellectual property rights are not reliably
protected by the state, there will be no incentive
to develop new products and services.
3. Intellectual property has significant development
costs and low marginal costs in production.
4. Effective protection is necessary before any
investor will provide financing.
Summary: Creating Value with Intellectual Assets
Human capital: Does the organization effectively attract,
develop, and retain talent?
Social capital: Does the organization exhibit professional and
personal relationships among employees?
Technology: Does the organization effectively use
technology to transfer best practices across the organization,
codify knowledge, and develop dynamic capabilities for
competitive advantage?
“Therefore, the more technological the world becomes, the more essential
will be the demand for individual freedom and the self-awareness of the
individual human being as a counterpoise to technology” (Speer, 1970).
Reflecting on Career Implications
Chapter 4 discusses the importance of intellectual assets and
students should consider the following variables or elelments
when choosing a Fortune 500 type firm for their employer. See
Human capital
• How your organization to effectively attract, develop, and retain talent.
• Diversity values of your organization.
Social capital
• Does your organization have a strong social capital?
• Are you actively building a strong social capital?
Technology
• Does your organization provide and effectively use technology?