Bones to Know: Thoracic and Vertebral Column
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Atlas (C1)
he first cervical vertebra; supports the skull and allows you to nod “yes.”
Axis
The second cervical vertebra; has the dens, allowing the head to rotate “no.”
Cervical vertebra (7)
The seven vertebrae in the neck region that holds the head.
Thoracic vertebrae (12)
The twelve vertebrae in the upper and mid-back; each attaches to a rib.
Lumbar vertebra
The five largest vertebrae in the lower back; support most body weight.
True ribs (1–7)
The ribs that attach directly to the sternum with their own cartilage.
False ribs (8–10)
Ribs that attach to the sternum indirectly through shared cartilage.
Floating ribs (11–12
The lowest ribs that do not attach to the sternum at all.
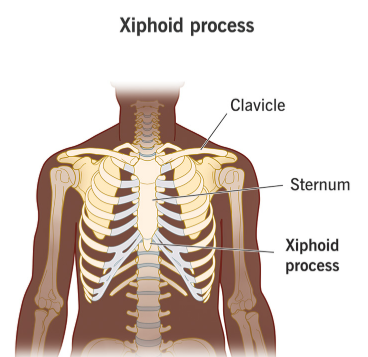
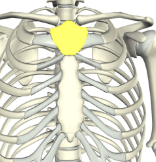
Xiphoid process
The small, lower tip of the sternum.
Spinous process
The bony projection you can feel along your back.( what they check at the doctors)
Manubrium
The upper part of the sternum that connects to the clavicles.
Transverse process
Side projections on a vertebra for muscle and rib attachment.
Vertebral foramen
The hole in the center of each vertebra for the spinal cord.
Body of vertebrae
The thick, round front portion that bears weight.
Transverse foramen
Openings in cervical vertebrae where arteries pass through.
Sacral foramen
Openings in the sacrum for nerves and blood vessels.