Lecture 19: muscle fibers
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
Types of muscle fibers
1. Intrafusal: sensory receptor fibers (only a few fibers in each muscle)
2. extrafusal: force-generating fibers that make up the bulk of a muscle
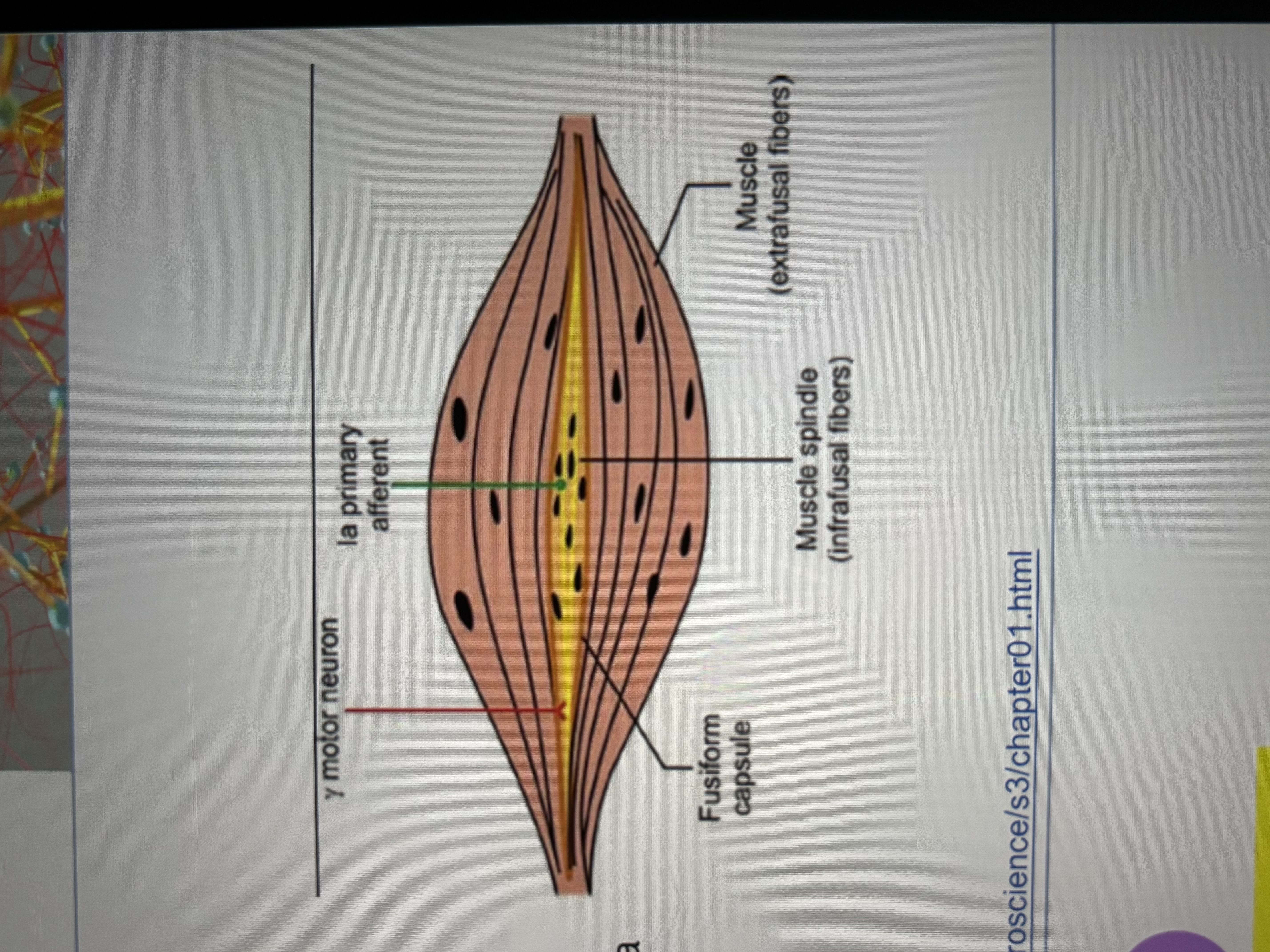
muscle spindle fibers
sensory receptor for detecting changes in muscle stretch (length and velocity)
do not contribute to force generated by the muscle
stretch along w/ the extrafusal fibers
stretch is what is registered by the receptor
also call intrafusal muscle fibers (afferent)- 1a
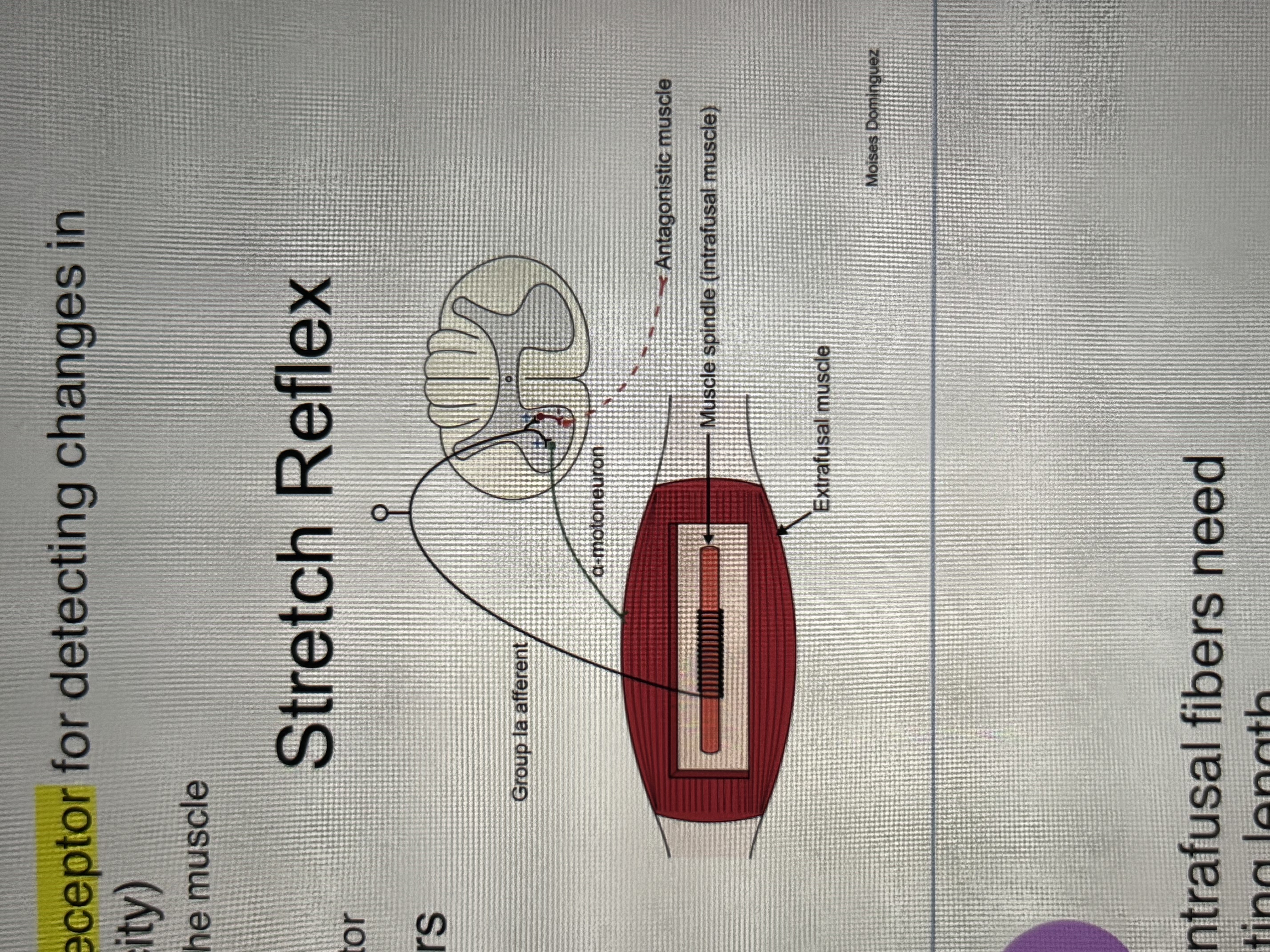
Muscle spindle fibers continued
after the muscle stretches, the intrafusal fibers need to contract to return to their resting length
intrafusal/spindle (efferent)- y gamma LMN
when contracting a muscle to generate force, extrafusal fibers are activated by a LMNS
extrafusal (efferent)- a alpha LMN
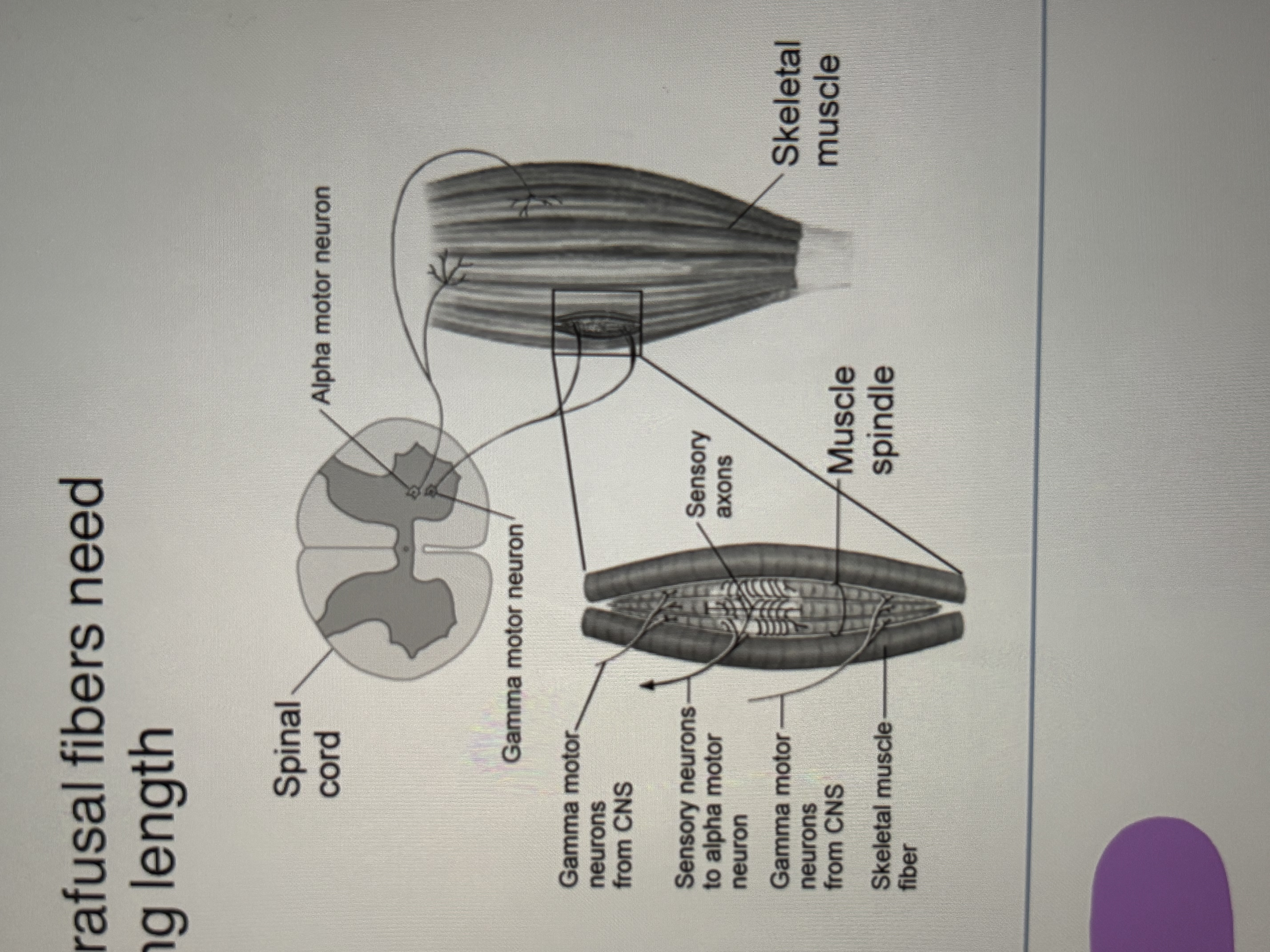
Alpha- Gamma Coactivation
when the CNS instructs a muscle to contract, it not only sends the appropriate signals to the alpha LMN to contract the extrafusal fibers, it also instructs gamma LMN to contract the intrafusal fibers appropriately
the process regulates muscle tone by ensuring the muscle is always sensitive to stretch
Low tone: always stretch out (floppy)
High tone: very tight, sensitive to stretch
Golgi Tendon Organ
sensory receptor in the tendon that detects changes in muscle force or the load applied to a muscle
GTO registers muscle contraction
Afferent- 1b
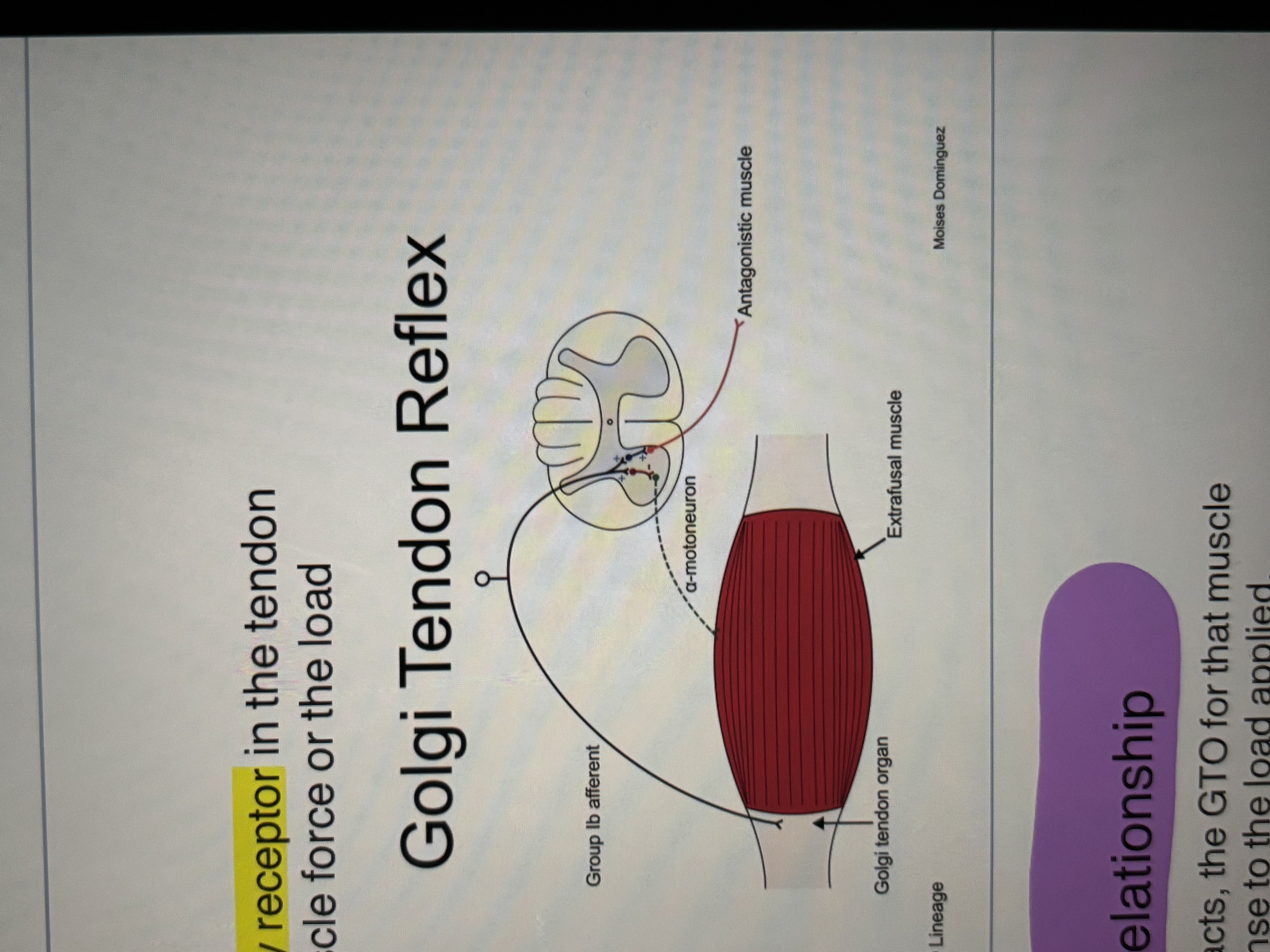
Agonist and Antagonist Relationship
when 1 muscle (agonist) contracts, the GTO for that muscle registers the contraction is response to the load applied.
at the same time, the opposing muscle (antagonist) stretches, the muscle spindles register the stretch
the two muscles maintain a balanced relationship
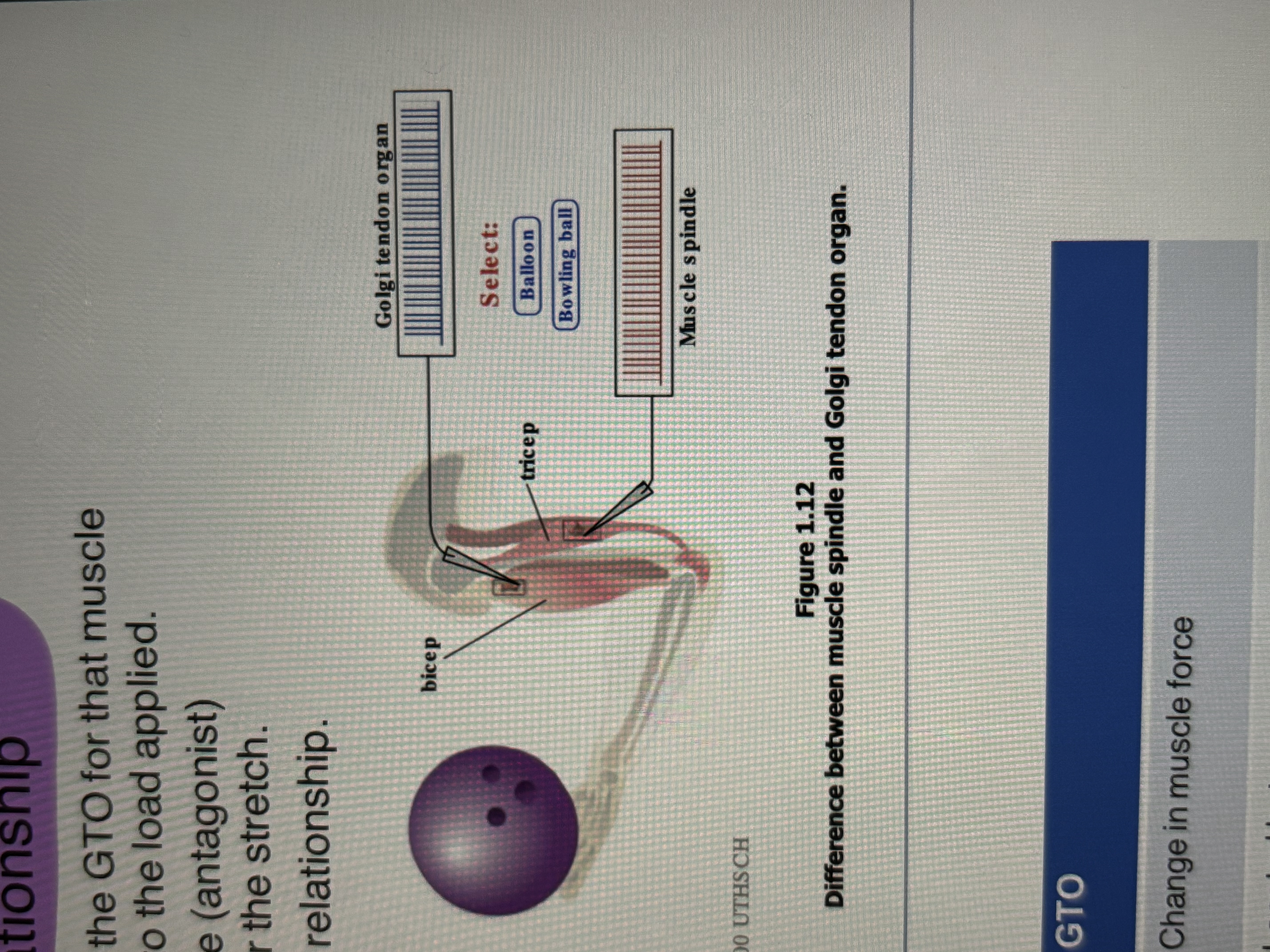
muscle spindle and GTO
chart

spinal reflexes
stretch reflex (monosynaptic)
reciprocal inhibition reflex (polysynaptic)
autogenic inhibition reflex (monosynaptic)
reciprocal excitation reflex (polysynaptic)
flexor withdrawal reflex (polysynaptic)
additional reflexes
extensor plantar response (cutaneous reflex)
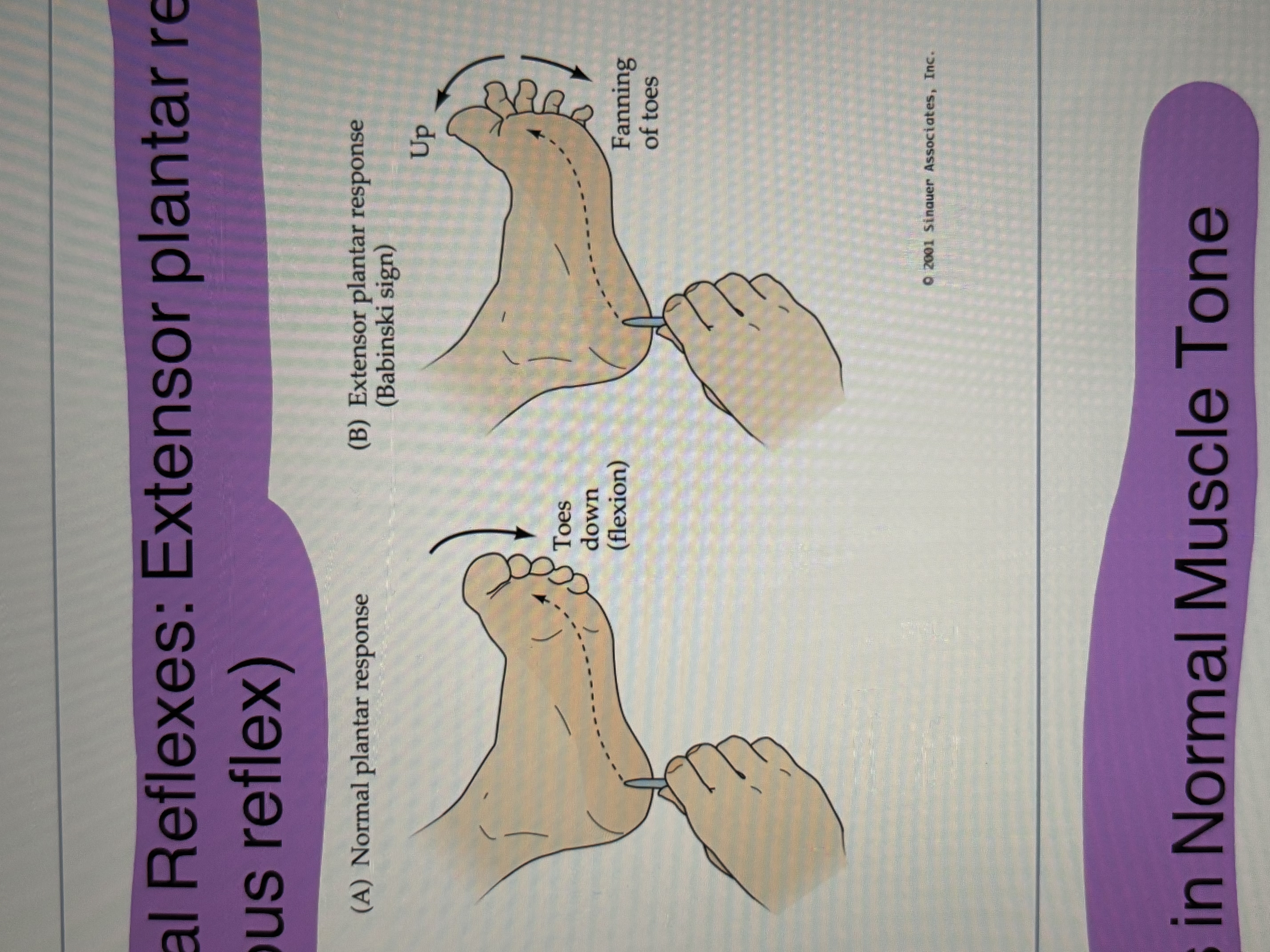
changes in normal muscle tone (muscle spindles responsible)
flaccidity- unable to do a muscle contraction
hypotonicity
normal tone
hypertonicity
spasticity, rigidity- can’t move muscles at all. too much contraction and can’t contract any further