Humanizing the Science of Society: W.E.B DuBois's Anti-Racist Social Science
1/22
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Where does sociology stem from?
It is a social theory that emerged out of the political revolutions of the Enlightenment.
Who coined the term sociology?
Auguste Comte a notable philosopher and positivist.
What is positivism as asserted by Comte?
A system of knowledge based on the scientific method - observation, experimentation, and objective analysis
Comte saw this as the final stage of human intellection
How did Comte Classify the scientific disciplines?
He classified the scientific disciplines on the hypothesis that the sciences each developed from the simple and abstract principles to ever more complex phenomena: Mathematic(most abstract) on the bottom, and sociology (the most complex) at the top.
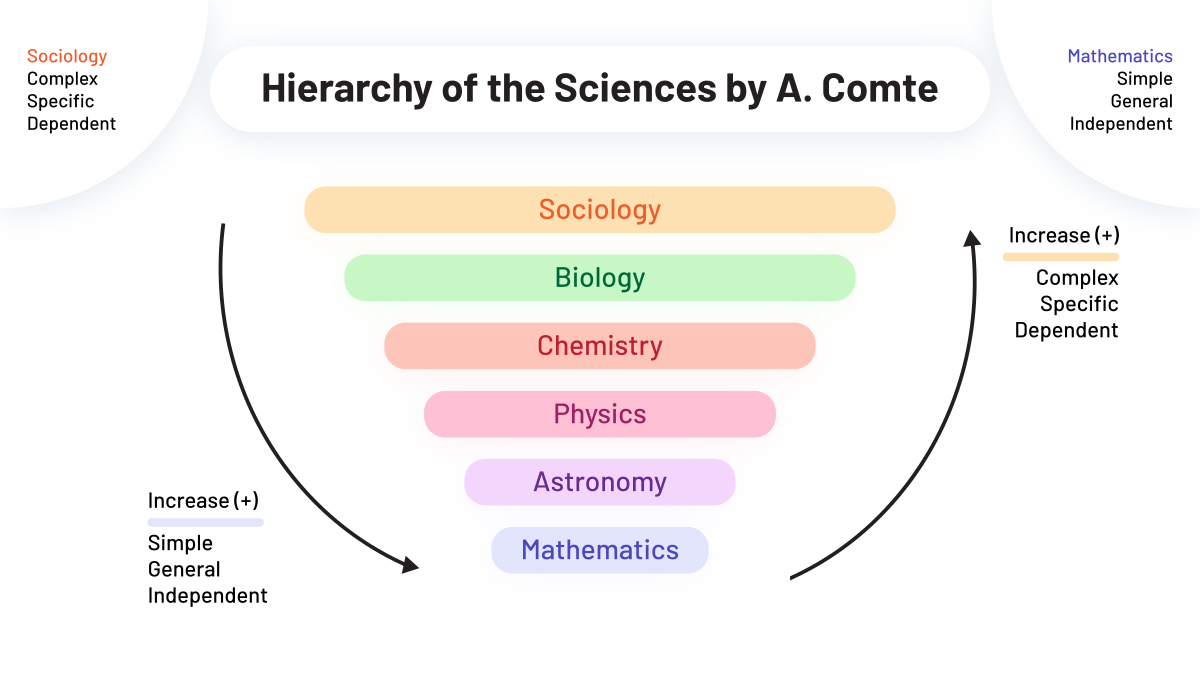
Why did Comte claim that sociology is the “queen of sciences”?
He claimed that sociology was queen because it synthesizes findings from all other scientific disciplines to generate a better understanding of social life.
What was Comte’s sacred formula for positivism?
“The only real life is the collective life of the races; individual life has no existence except as an abstraction.”
Sociology of the late 19th century was infused with what social theory?
Social Darwinism. Huge credit to Herbert Spencer who coined the term survival of the fittest.
Spencer saw the wealth gap as a natural occurrence which was the result of some sub-populations superior aptitude..
Who was William Graham Sumner(1840-1910)? And what did he believe about Social Darwinism.
First US Sociologist at Yale and popularizer of Spencer’s work on social Darwinism. Sumner believed that different racial groups and ethnic groups were different biologically in a way that could be explained by elevation.
Therefore if different races fared differently in society it was because they were evolutionarily less advanced.
Arguments from Black scholars prior to the civil war relied predominantly on what type of arguments?
These scholar relied heavily on biblical and religious arguments during the first half of the 19th century. And supported monogenesis theory.
What is the Monogenesis Theory? Polygenesis?
The mongenesis theory argues that all humans share a common ancestor where as polygenesis argues that racial/ethnic groups descended from separate acts of creation by God and/or had separate biological origins.
With Comte’s help, what replaces religion as the primary way to explanation society?
Sociology.
Who was W.E.B. Du Bois (1868-1963)?
Born Willian Edward Burghardt Du Bois in Great Barrington Massachusetts Du Bious was the sun of a domestic worker and a barber/ininerant laborer.
First Graduate of Great Barrington’s racially integrated high school.
Earned his Bachelors from Harvard 1890, MA in 1991 and His PhD 1895
Studied abroad with Gustav Schmoller from 890-1892.
Later on publishes works including “The Philadelphia Negro.”
What were DuBois’ 2 pillar approach?
Empiricism - Collect social facts and generalize from those facts
Strict Objectivity - seek truth and nothing but the truth - Insisted that personal preferences and hopes did not matter for the scientific research he was undertaking
During what years does DuBois conduct a comprehensive study of his own neighborhood in the 7th ward of Philadelphia?
1896-97
What made the 7th ward an interesting site for study?
Population - The wards was diverse and multiethnic population of which 30% were African Americans
While Philidelphia’s economy had been booming that economic success was not evenly distributed and often did not make it to the 7th ward. Why?
What were DuBois’ three methods of gathering data?
Participant observation - DuBois attended church on Sundays to understand how the church functioned as an organization
Interviews and Surveys - Door to door canvasing to collect data about family structure, wealth, and education, and literacy
Archival records and census data - Tracked the reports of freed slaves migrating to the city from the south
What does DuBois claim that the conditions of poverty in the seventh ward stem from?
Systemic denial of resources and opportunities.
Found that African Americas had more difficulty finding work and were paid less than their white counterparts for the same work
High cost of low quality housing
Did DuBois See the racial segregation as natural?
No! He did not find anything about poverty inevitable. The complex social condition that he produced was contingent on history and industrial divestments in black neighborhoods that has led to long-term racial inequality.
What is unique about the way the DuBois presents his work?
He makes color-coded and visually interesting infographics to explain his findings.
What big explosion does DuBois present at in 1900, and who helps him?
He presented “American Negro" an exhibition that sought ‘to give, in as systematic and compact a form as possible, the history and present condition of a large group of human beings’
He worked with an all-black curatorial team and collaborated with nearly two dozen institutions and universities to present 200 volumes by African American authors, 350 patents, and 500 photographs of African-American owned businesses, churches and homes.
Whose school of sociology overshadows DuBois? What did he believe?
Robert Park’s. He believed in:
Social Darwinism
Biological roots for racism
City is a self-organizing system so poverty is natural - Urban Ecology
What DuBois really revolutionary or just a product of his era?
Arguments go both ways
Kwame Anthony Appiah recognized Du Bois as a prisoner of 19th century biological theory of race - Du Bois’s use of “blood” a biological concept→ leads us “back into the now familiar move of substituting a sociohistorical conception of race for the biological one; but that is simply to busy the biological conception below the surface, not to transcend it”
Morris views Du Bois’s reference to blood as a metaphorical term of social kinship, not biology: “Nowhere in Du
Bois race analysis are biological factors elevated in causal significance over sociological ones. Appiah is right that in introducing talk of “blood” into the definition of race, Du Bois creates a tension between the biological and the sociological. Yet the tension never rises to a level where biology trumps sociological explanations of racial categories and racial outcomes”
Du Bois saw race as a contingent, historically specific social category rather than a natural object, or state
What is one way that DuBois suggests that the 7th ward can improve itself?
Among others he suggests better breeding.