ENAMEL BONDING
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
what is the most mineralised substance in your body
enamel
outline what enamel is
teeth enamel is the hardest substance in your body
it covers the outer layer of each tooth and it is the most visible part of the tooth
is enamel vital or non-vital and why
enamel is non-vital
because once fully formed enamel does not contain blood vessels or nerves
remineralisation can repair damage to a certain degree but damage beyond that cannot be repaired by the body
where is enamel the thickest on a tooth
in humans, enamel varies in thickness
often it is the thickest at the cusp - up to 2.5mm
diagram of enamel on the Mohs hardness scale
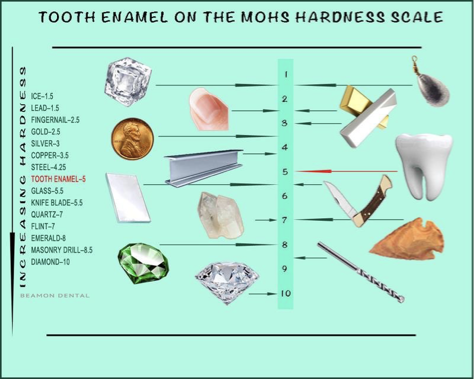
outline the composition of enamel
96% hydroxyapatite
3% water
1% organic proteins
—
hexagonal rods of mineral (5 micrometre diameter)
prismatic arrangement perpendicular to tooth surface
naturally covered in pellicle and usually plaque
why is enamel bonding done
so tooth coloured composite can be added to existing teeth and therefore:
improve the appearance of teeth
mask out discolouration
prevent further wear and tear
how much tooth preparation does enamel bonding require
no extensive tooth prep. is needed
this means the tooth stays intact underneaath
so should you need to remove the bonding materials your teeth underneath remains healthy
when did adhesive dentistry with acid etching begin
in 1955
with Buonocore
how is the enamel modified by acid-etch
surface roughness is increased
surface energy is raised
» better adhesion
how does the surface of enamel become rougher after acid-etch
acid/ base reaction prompts partial dissolution of hydroxyapatite
loss of enamel prism periphery and prism core constituents
increase of surface bonding area
how does acid-etching raise the surface energy of enamel
acid removes the pellicle which has low surface energy and exposes the underlying surface of enamel
pellicle - 28 mJ/m2
enamel - 42 mJ/m2
acid raises surface tension and therefore encourages wetting
typical surface tension of adhesive resin = 34-38 mJ/m2
what type of bonding does etching enamel allow for
micromechanical bonding
what % phosphoric acid is used to etch enamel
35%
why is the concentration of phosphoric acid used 35%
higher concentrations would not offer better results
what should be considered clinically when etching enamel to prevent problems
patient selection
enamel prophylaxis
application of etchant
outline patient selection and its importance
the bonding area of enamel must be kept free of contaminants such as saliva or water because they are highly polar and resins are non-polar
patients who will re-wet the dried surface should not be selected for the acid-etch technique » isolate with rubber dam
elderly/ frail
children
mentally ill
outline enamel prophylaxis in terms of restorative dentistry
the resin needs to bond to the enamel, not the pellicle or any plaque on the tooth surface
acid etchant will not completely remove plaque and the thick pellicle layer
so the tooth must first be cleaned with a slurry of pumice and water for 30s using a bristle brush then dried
what is the best reason for not using prophylaxis pastes to clean the enamel prior to acid etching
oil residue reduces the wettability of enamel
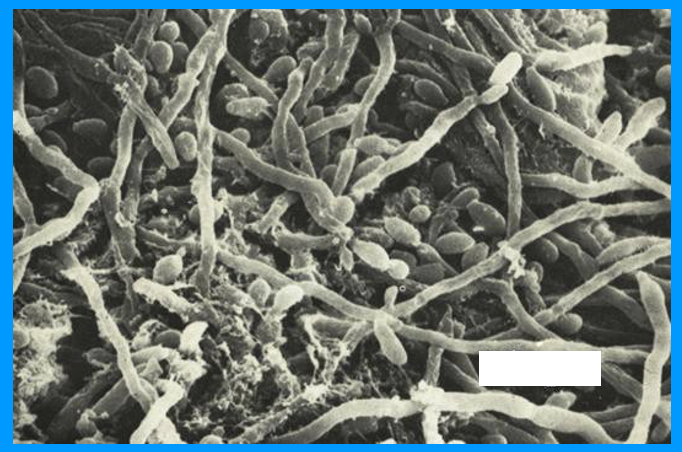
what does this image show
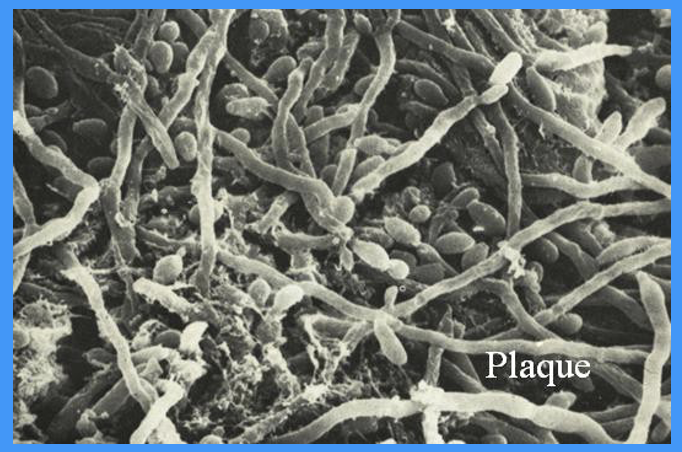
outline the application of etchant
apply the gel/ liquid by lightly dabbing the surface
do NOT rub the etchant onto the surface
rubbing breaks the tags that the resin flows into and weakens the bond
aspirate and wash the etched surface thoroughly to remove salts and excess acid
how quickly does the acquired pellicle form on a professionally cleaned tooth surface
≈ 1 minute
what is a dental material with a high contact angle
mercury