Functional Anatomy
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
The human nervous system is divided into how many parts, and what are they?
2
Central Nervous System
Peripheral nervous system
Neurons
Nerve cell
Receive, conduct, and transmit electrochemical signals
1 neuron can receive signals from 100
Glial cells
physical and structural support for neurons
How many neurons and glial cells in humans
86 billion
100 billion
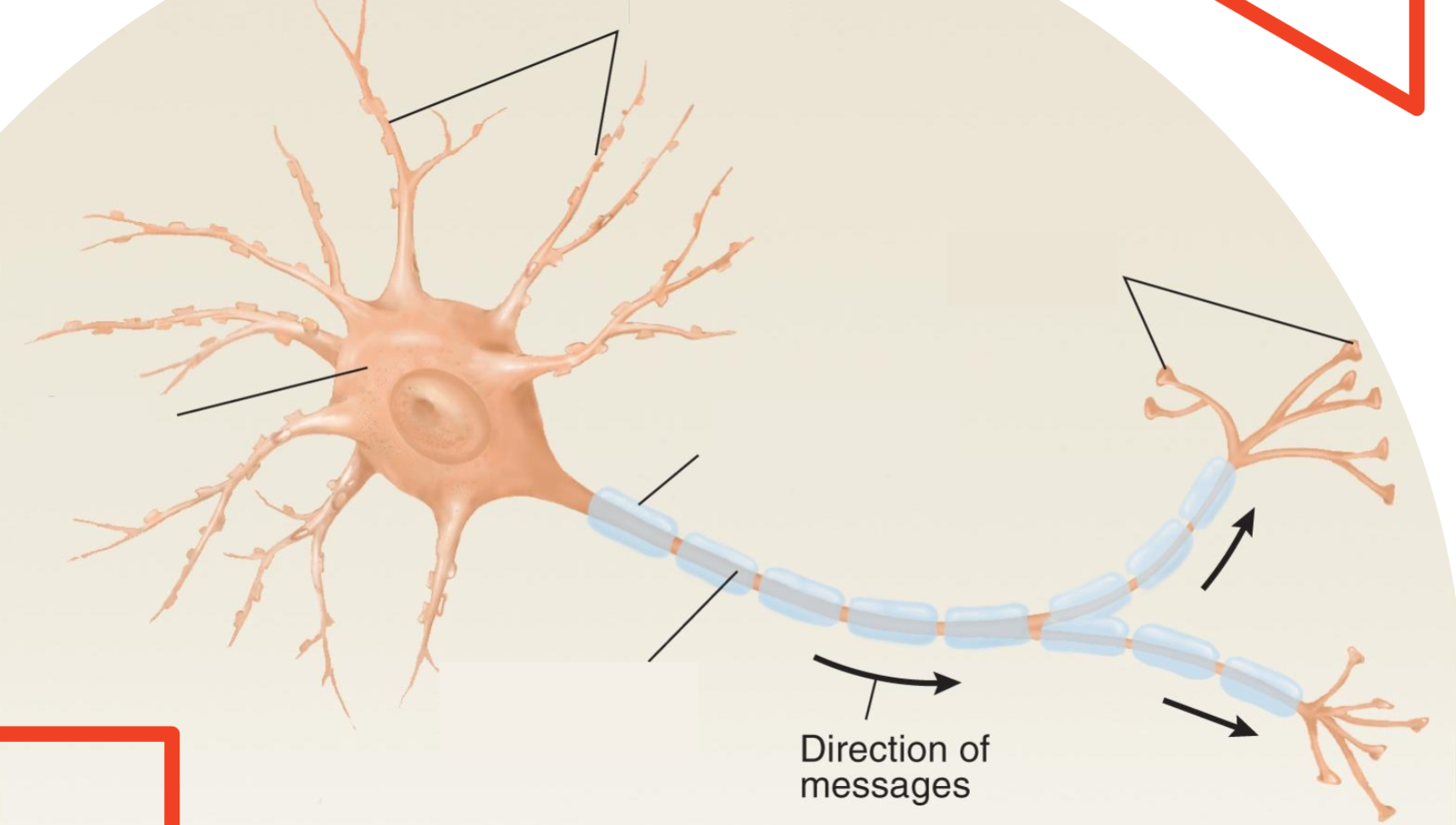
List all the parts of the neuron
Soma body, dendrites, mylin sheaths, axon, Axon terminals
Soma body
is responsible for maintaining the cell's health and function by housing the nucleus and organelles. It integrates signals received from dendrites and determines whether to send an action signal down the axon.
Dendrites
Where signal is received
myelin sheath
a protective layer that surrounds nerve fibers, allowing electrical impulses to travel quickly and efficiently between nerve cells. It also helps maintain the strength of these signals as they move along the axon, similar to insulation on electrical wires.
Axon
is responsible for transmitting electrical impulses, known as action potentials, away from the cell body to other neurons
Axon terminals:
send out signals through neurotransmitters
Parts of the Central nervous system
Brain and spinal cord
Types of neurons in the Central Nervous System
Sensory/ afferent neurons
Motor/ efferent neurons
Interneurons
Sensory/ afferent neurons
Detects changes in the internal or external environment.
Sends messages to the CNS
Motor/ efferent neurons
controls muscle contraction or gland secretion
sends messages away from the CNS
Interneuron
helps transmit signals between the sensory neuron and the motor neuron
Parts of the peripheral nervous system
everything except for the brain and spinal cord
Subsections of the peripheral nervous system
Somatic nervous system
Automatic nervous system
Somatic Nervous system
Receive sensory info from sensory organs and controls movement of muscles
controls spinal and cranial nerves
Autonomic Nervous system
Regulates the involuntary physiological processes to maintain the body’s internal balance or homeostasis.
Things regulated by ANS
Dilation of pupils
sneezing
monitoring light level in the eye, changes in blood pressure, and heart rate
sweating when exercising
movement of food through the gut,
breathing rate
Subsections of Autonomic Nervous System
Sympathetic
Parasympathetic
Sympathetic system (energy? when? where are the nerves concentrated?)
Energy expenditure
“Fight or flight”
Nerves concentrated in the small of the back and chest area of the spinal cord
Parasympathetic system (energy? when? where are the nerves concentrated?)
Energy conservation
“Rest and digest”
Nerve concentrated in cranial and lower back region of the spinal cord.
Sympathetic and parasympathetic systems
counteract eachother.
Peristalsis
movement of food through digestive system
What does Sympathetic system do?
Increase heart rate, blood pressure, blood flow to skeleltal pressure, sweating
Decreased saliva production, blood flow to digestive organs, peristalsis
Bronchodilation
Dilation of pupils
What does the parasympathetic system do?
Decreases heart rate, blood pressure, blood flow to skeletal muscle, sweating
Increases saliva production, blood flow to digestive organs, peristalsis
Bronchoconstriction
Constriction of pupils
CNS Protection
Cerebrospinal fluid
Meninges
Blood-brain barrier
Cerebrospinal fluid
circulates through the ventricles, spinal cord, and subarachnoid space
Flows through the lateral ventricles, 3rd and 4th ventricles.
What produces CSF?
Choroid plexus
Meninges. what are they
Dura: closest to the skull
Arachnoid membrane: where the CSF membrane
Pai meter: thin layer adheres to the brain
Blood Brain Barrier
Impedes passage of many toxic substances from the blood to the brain
Capillaries are tightly lined compared to the rest of the body’s capillaries
Brain blood supply
Carotid arteries - either side of the neck
Vertebral arteries - travel up through the back of the skull
Dorsal and Ventral
Dorsal refers to the back or upper side of an organism, while ventral refers to the front or lower side.
Medial and Lateral
Medial refers to a position closer to the midline of the body, while lateral describes a position further away from the midline. For example, the arms are lateral to the torso, and the nose is medial to the ears
Superior and inferior
Position closest to the head
position closest to the feet.
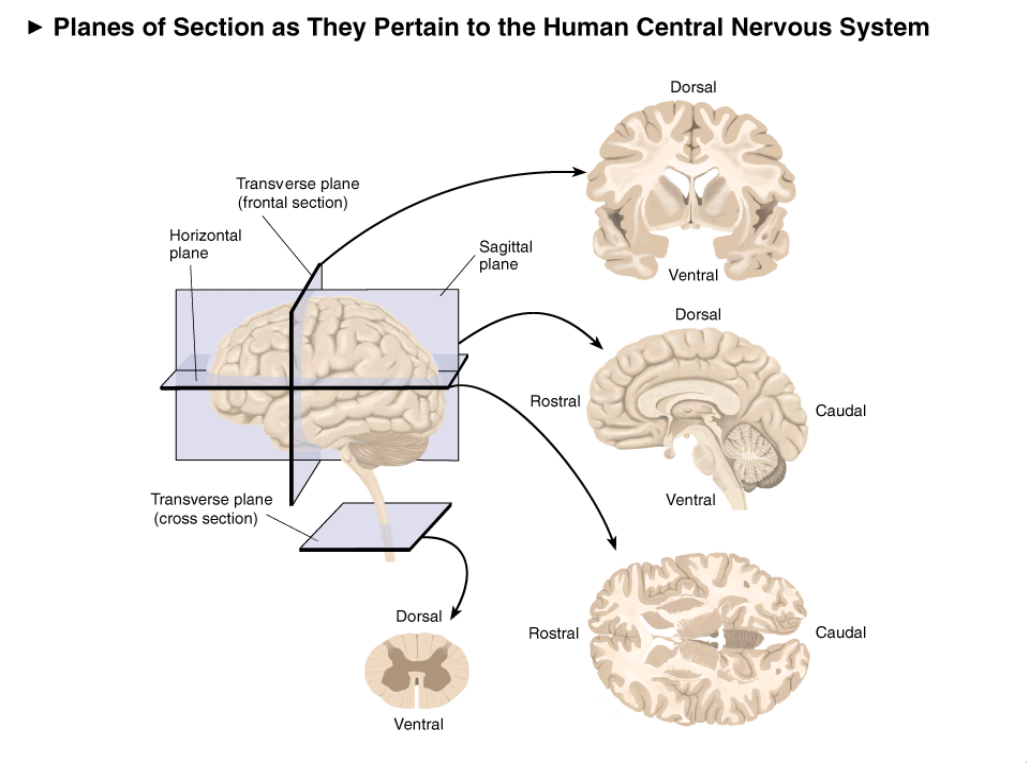
Planes of Section
Ways of cutting the brain
generates 2-dimensional representations of a 3-dimensional brain
How many planes of section and what are they? What directions do they show?
Coronial(frontal)
sagital
Horizontal (axial)
Dependent variable
dependent variable is the outcome or effect that is measured in an experiment