AP Psych - Sensation and Perception
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/74
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
1
New cards
selective attention
the capacity for reacting to selective stimuli when others are occuring simultaneously
2
New cards
inattentional blindness
* inabiity to see object/person bc of lack of attention
* ex. basketball gorilla
* ex. basketball gorilla
3
New cards
change blindness
when a change in object/enviroment goes unnoticed
4
New cards
sensation
the process by which our sensory receptiors and nervous system recieve and represent stimulus energies from our enviroment
5
New cards
perception
the process of organizing and interpreting sensory data
6
New cards
bottom-up processing
analysis that begins w/ sensory receptors and works up to the brain’s integration of sensory info
7
New cards
top-down processing
information processing guided by higher-level mental processes, constructing perceptions by drawing on our experiences and expectations
8
New cards
psychophysics
study of relationships btwn physical charactics of stimuli and our psychological experience of them
9
New cards
absolute threshold
minimum stimulation needed to detect a particular stimulus 50% of the time
10
New cards
signal detection theory
* predicts how and when we detect the presence of a faint stimulus (signal) amid background stimulation (noise)
* proved that there is no single absolute threshold and that detection varies bc of experience, expectations, motivation, and alertness
* proved that there is no single absolute threshold and that detection varies bc of experience, expectations, motivation, and alertness
11
New cards
just noticeable difference (JND)
the amount something must be changed in order for a difference to be noticeable 50% of the time.
12
New cards
difference threshold
minimum required difference between two stimuli for a person to notice change 50% of the time
13
New cards
subliminial
below one’s **absolute threshold** for conscious awareness
14
New cards
priming
the activitation of certain associations, thus influencing one’s perception, memory, or response
15
New cards
Weber’s law
the principle that, to be percieved as different, two stimuli must differ by a constant proportion/percentage (rather than a constant amount)
16
New cards
sensory adaptation
* diminished sensitivity resulting from constant stimulation
* ex. nerve cells consistantly fire when clothing is initially put on, but after constant exposure, they fire less frequently
* ex. nerve cells consistantly fire when clothing is initially put on, but after constant exposure, they fire less frequently
17
New cards
transduction
* conversion of one form of energy to another
* in sensation, the transforming of sights, sounds, smells into neural impulses
* in sensation, the transforming of sights, sounds, smells into neural impulses
18
New cards
wavelength
the distance from the peak of one wave to the peak of the next
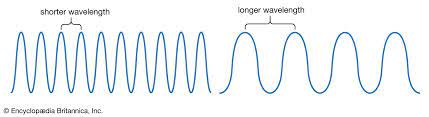
19
New cards
hue
* color (blue, green, etc.)
* determined by **wavelength**
* determined by **wavelength**
20
New cards
intensity
* amount of energy in a wave (perceived as loudness or brightness)
* determined by **amplitude**
* determined by **amplitude**
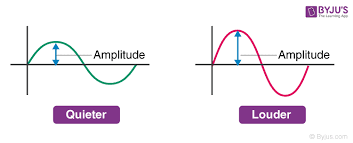
21
New cards
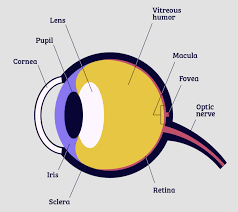
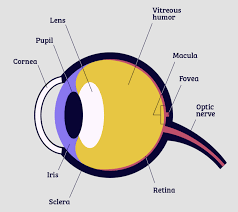
pupil
adjustable opening in center of eye through which light enters
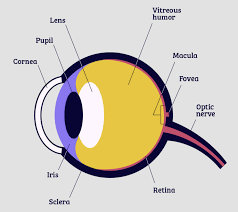
22
New cards
iris
* forms colored portion around eye
* controls size of **pupil** opening
* controls size of **pupil** opening
23
New cards
lens
* transparent structure behing **pupil**
* changes shape to help focus images on **retina**
* changes shape to help focus images on **retina**
24
New cards
retina
* inner surface of eye
* contains **rods, cones**, and neurons
* contains **rods, cones**, and neurons
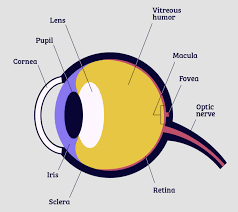
25
New cards
accommodation
the process by which the eye’s **lens** changes shape to focus objects on the **retina**
26
New cards
rods
* detect black, white, gray
* necessary for peripheral/low-light vision
* necessary for peripheral/low-light vision
27
New cards
cones
* concentrated near center of **retina**
* fine detail and color
* fine detail and color
28
New cards
optic nerve
carries neural impulses from eye to brain
29
New cards
blind spot
point at which **optic nerve** leaves eye, creating a “_____” bc no receptor cells are located there
30
New cards
fovia
* central focal point in **retina**
* where **cones** cluster
* where **cones** cluster
31
New cards
optic chiasm
place where some optic nerve fibers from one eye cross optic nerve fibers from the other eye
32
New cards
feature detectors
nerve cells that respond to specific features of a stimulus, like shape, angle, or movement
33
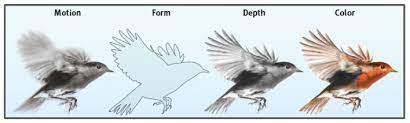
New cards
parallel processing
* processing many aspects of a problem simultaneously
* ex. vision (the brain delegates the work of processing color, form, motion, depth to different areas)
* ex. vision (the brain delegates the work of processing color, form, motion, depth to different areas)
34
New cards
Young-Helmholtz trichromatic theory
* theory that the **retina** contains three different color receptors (one most sensitive to __red__, one to __green__, one to __blue__)
* when stimulated in combination can produce perception of any color
* supported by color-deficiency
* when stimulated in combination can produce perception of any color
* supported by color-deficiency
35
New cards
opponent-process theory
* theory that opposing retinal processes __(red-green,__ __yellow-blue,__ __white-black__) enable color vision
* supported by **afterimage effect**
* supported by **afterimage effect**
36
New cards
audition
sense or act of hearing
37
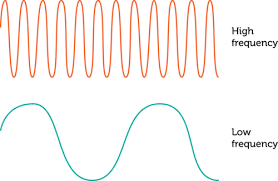
New cards
frequency
the number of **wavelengths** that pass a point in a given time
38
New cards
pitch
* a tone’s highness or lowness
* depends on **frequncy**
* depends on **frequncy**
39
New cards
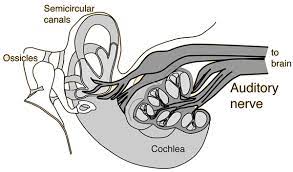
middle ear
* chamber btwn eardrum and **cochlea**
* contains **hammer, anvil,** and **stirrup**
* concentrate eardrum’s vibrations on the cochlea’s **oval window**
* contains **hammer, anvil,** and **stirrup**
* concentrate eardrum’s vibrations on the cochlea’s **oval window**
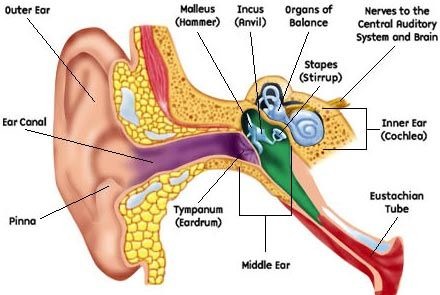
40
New cards
cochlea
* coiled tube in the **inner ear**
* converts sound waves into nerve impulses
* converts sound waves into nerve impulses
41
New cards
inner ear
contains **cochlea, semicircular canals, vestibular sac**
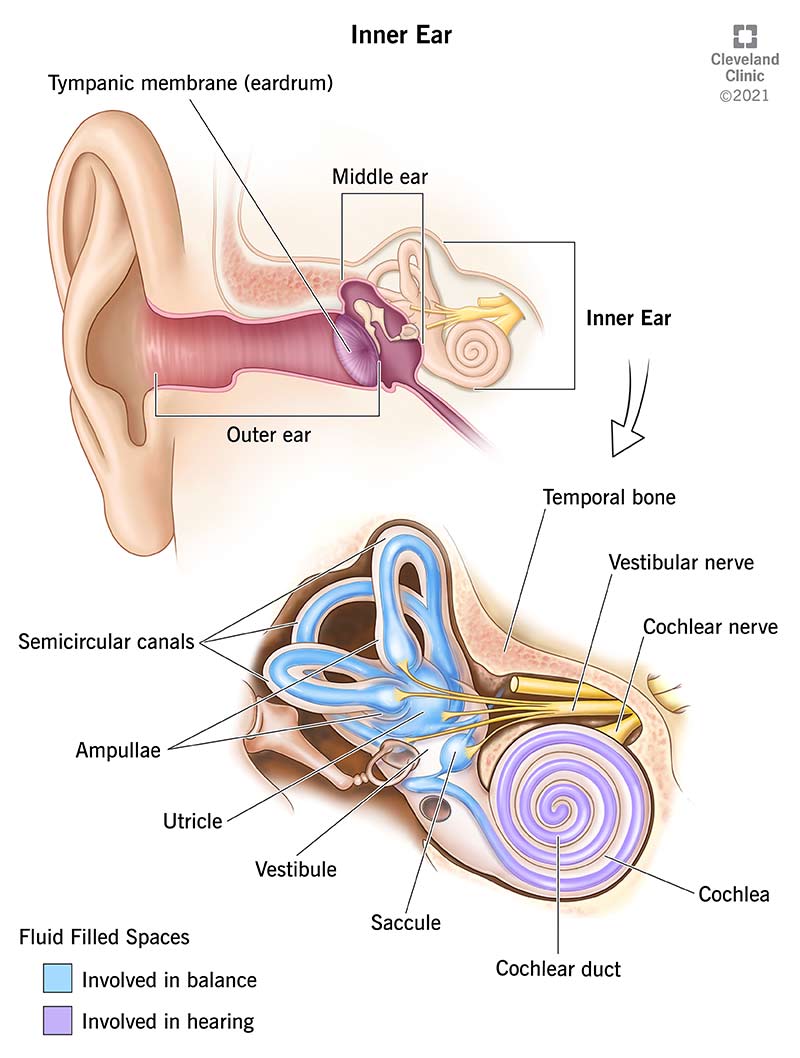
42
New cards
semicircular canals
* **inner ear**
* fluid-filled tubes that help maintain balance
* fluid-filled tubes that help maintain balance
43
New cards
vestibular sacs
* **inner ear**
* react to gravity + movement
* react to gravity + movement
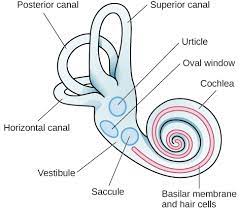
44
New cards
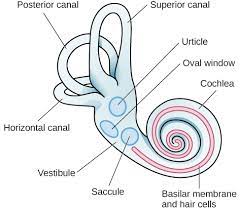
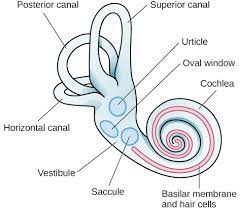
oval window
* end of **middle ear**/beginning of **inner ear**
* helps transmit vibratuons to **cochlea**
* helps transmit vibratuons to **cochlea**
45
New cards
basilar membrane
* **inner ear**
* when **oval** **window** vibrates, ripples in the ______ bend hair cells, which trigger nerve impulses
* when **oval** **window** vibrates, ripples in the ______ bend hair cells, which trigger nerve impulses
46
New cards
auditory nerve
sends neural messages to **auditory cortex**
47
New cards
place theory
in hearing, the idea that different sound waves trigger activity in different places, thus we determine pitch by recognizing the place generating the neural signal
48
New cards
frequency theory
in hearing, the idea the rate of neural impulses matches the frequncy of a tone, thus enabling us to sense its pitch
49
New cards
conduction hearing loss
hearing loss caused by damage to the system that conducts sound waves to **cochlea**
50
New cards
sensorineural hearing loss
hearing loss caused by damage to **cochlea’s** receptor cells or to the **auditory** **nerves**
51
New cards
cochlear implant
device that converts sounds into electrical signals which stimulate auditory nerve
52
New cards
kinesthesis
the system for sensing the position and motion of individual body parts
53
New cards
vestibular sense
sense of body movement and position, including balence
54
New cards
gate-control theory
theory that spinal cord cotains a neurological “gate” that regulates the passage of pain signals
55
New cards
process of smell
* scent molecules activate **olfactory receptors**
* signals travel up olfactory nerves to the **olfactory bulb,** then to brain via the olfactory tract
* signals travel up olfactory nerves to the **olfactory bulb,** then to brain via the olfactory tract
56
New cards
sensory interaction
principle that one sence may influence another
57
New cards
gestalt
* school of psychology
* “the whole is different that the sum of its parts”
* “the whole is different that the sum of its parts”
58
New cards
figure-ground
organization of visual field into objects (figure) that stand out from surroundings (ground)
59
New cards
grouping
tendency to organize stimuli into coherent groups
* proximity - group nearby figures together
* similarity - group similar figures together
* continuity - perceive smooth, continuous patterns
* closure - fill in gaps to create complete, whole object
* connectedness - elements that are thought to be connected bc of colors, lines, etc.
* proximity - group nearby figures together
* similarity - group similar figures together
* continuity - perceive smooth, continuous patterns
* closure - fill in gaps to create complete, whole object
* connectedness - elements that are thought to be connected bc of colors, lines, etc.
60
New cards
depth perception
ability to see objects in three-dimensions despite the fact the the images percieved by retina are two-dimentional
61
New cards
visual cliff
laboratory device for testing **depth perception**
62
New cards
binocular cues
depth cues that depend on use of two eyes
* **retinal disparity** - images from the eyes differ, the closer the object, the larger the disparity
* **convergence** - eyes move inward for close objects
* **retinal disparity** - images from the eyes differ, the closer the object, the larger the disparity
* **convergence** - eyes move inward for close objects
63
New cards
monocular cues
depth cues that require the use of only one eye
* **relative size** - distant image is smaller
* **interposition** - closer object blocks distant object
* **relative clarity** - hazy object is farther
* **texture** - course = close, fine = distant
* **relative hight** - higher objects seen as more distant
* **relative motion** - closer objects seem to move faster
* **linear perspective** - parallel lines converge w/ distance
* **relative brightness** - closer objects appear brighter
* **relative size** - distant image is smaller
* **interposition** - closer object blocks distant object
* **relative clarity** - hazy object is farther
* **texture** - course = close, fine = distant
* **relative hight** - higher objects seen as more distant
* **relative motion** - closer objects seem to move faster
* **linear perspective** - parallel lines converge w/ distance
* **relative brightness** - closer objects appear brighter
64
New cards
phi phenomenon
illusion of movement created when lights blink in quick sucession
65
New cards
perceptual consistancy
percieving objects as unchanging (having consistant shape, size, brightness, and color) even as retinal images change
66
New cards
perceptual adaptation
the ability to adjust to an artificially displaced or inverted visual field
67
New cards
perceptual set
a mental predisposition to percieve one thing and not the other
68
New cards
human factors psychology
a branch of psychology that examines how people and machines interact + how machines can be made safe and easy to use
69
New cards
extrasensory perception (ESP)
the claim that perception can occur without sensory input
* telepathy - sending/perceiving another’s thoughts
* clairvoyance - perceiving remote events
* precognition - perceiving future events
* telepathy - sending/perceiving another’s thoughts
* clairvoyance - perceiving remote events
* precognition - perceiving future events
70
New cards
Earst Weber
* German physician
* **Weber’s law -** to be perceived as different, two stimuli must differ by constant minimum percentage, rather than a consistant constant
* **Weber’s law -** to be perceived as different, two stimuli must differ by constant minimum percentage, rather than a consistant constant
71
New cards
Gustav Fechner
* German psysicist, philosopher, experimental psychologist
* **Weber-Fechner law**
* **Weber-Fechner law**
72
New cards
Thomas Young and Herman von Helmholtz
* proposed **trichromatic theory**
* three different color receptors (red, green, blue)
* three different color receptors (red, green, blue)
73
New cards
Ewald Hering
* German physiologist
* **opponent-process theory**
* opposing retinal processes (red-green, blue-yellow, black-white)
* **opponent-process theory**
* opposing retinal processes (red-green, blue-yellow, black-white)
74
New cards
David Hubel and Torsten Wiesal
* discovered **feature dectectors** using anethetized cat
75
New cards
Kurt Koffka, Max Wertheimer, Wolfgang Kohler
developed **Gestalt** psychology