A&P Exam 2: Chapter 4 Histology PART 1
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Epithelial Tissue
Has little extracellular matrix (consists almost entirely of cells), lines body surfaces (in and out), free border (apical surface), basement membrane attaches to underlying tissue. Avascular so gases&nutrients must diffuse across the basement membrane. Regenerates b/c skin is constanly shedding.
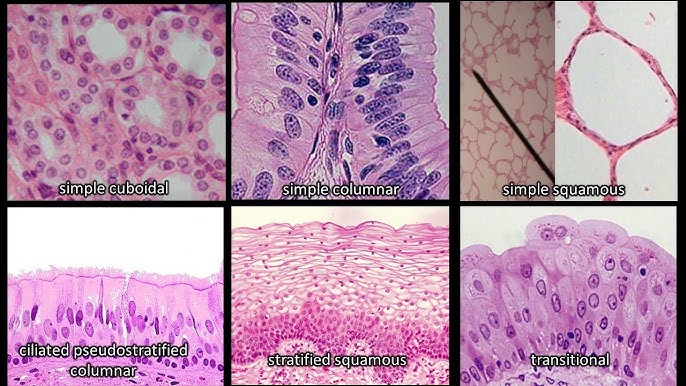
Classification of epithelial tissue
based on % of cell layers and shape
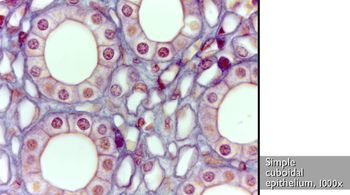
simple epithelium
monolayer. extends from basement membranw to apical (free) surface.
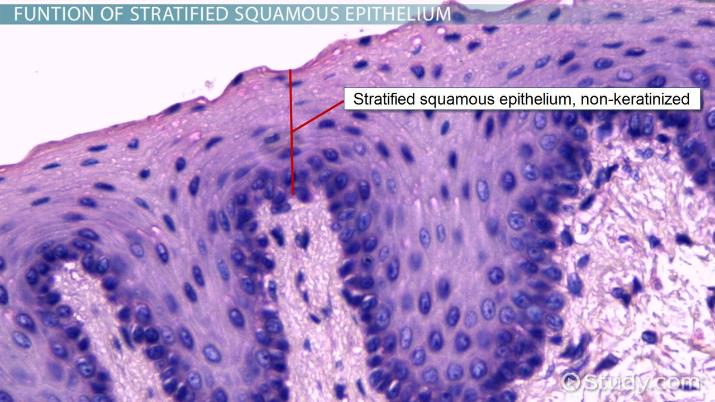
stratified epithelium
multilayer. superficial layer is used to name the tissue.
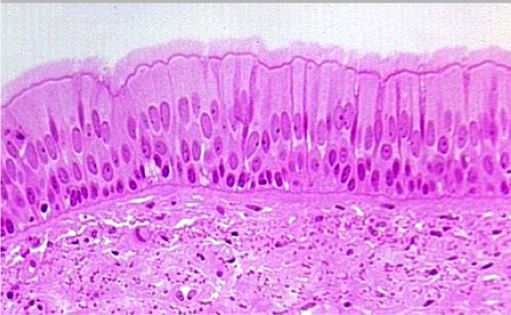
pseudostratified epithelium
false appearence of being mulilayered but it is SIMPLE. each cell is in contact with the basement membrane. ciliated. not everything reaches the apical surface.
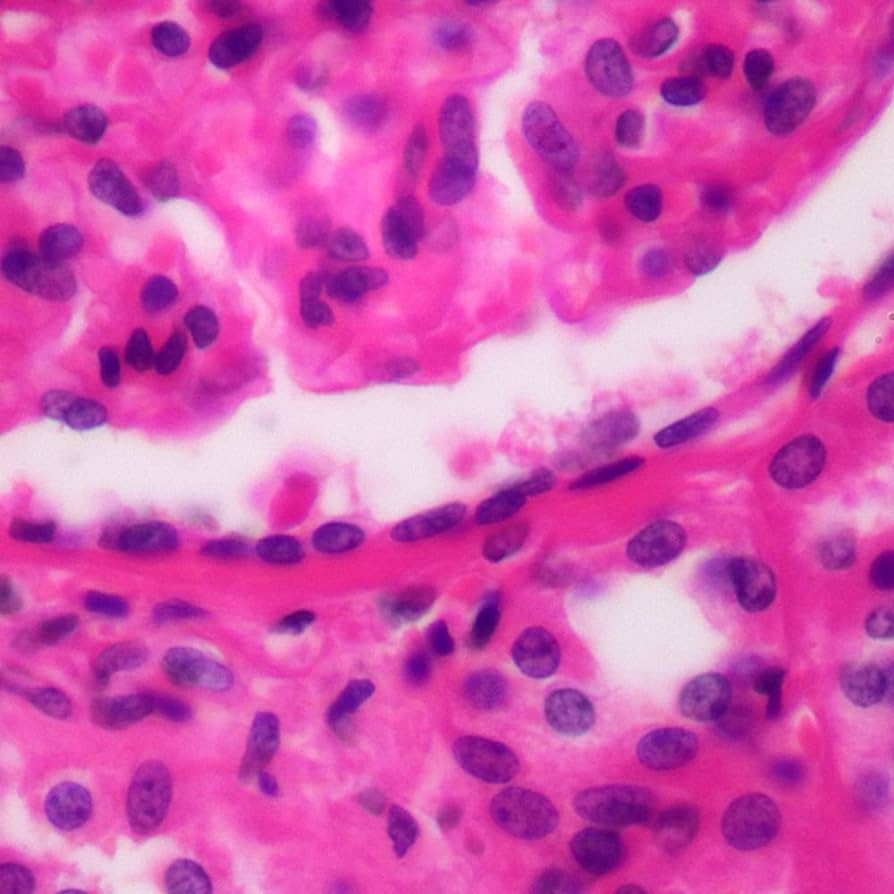
squamous epithelium
flat
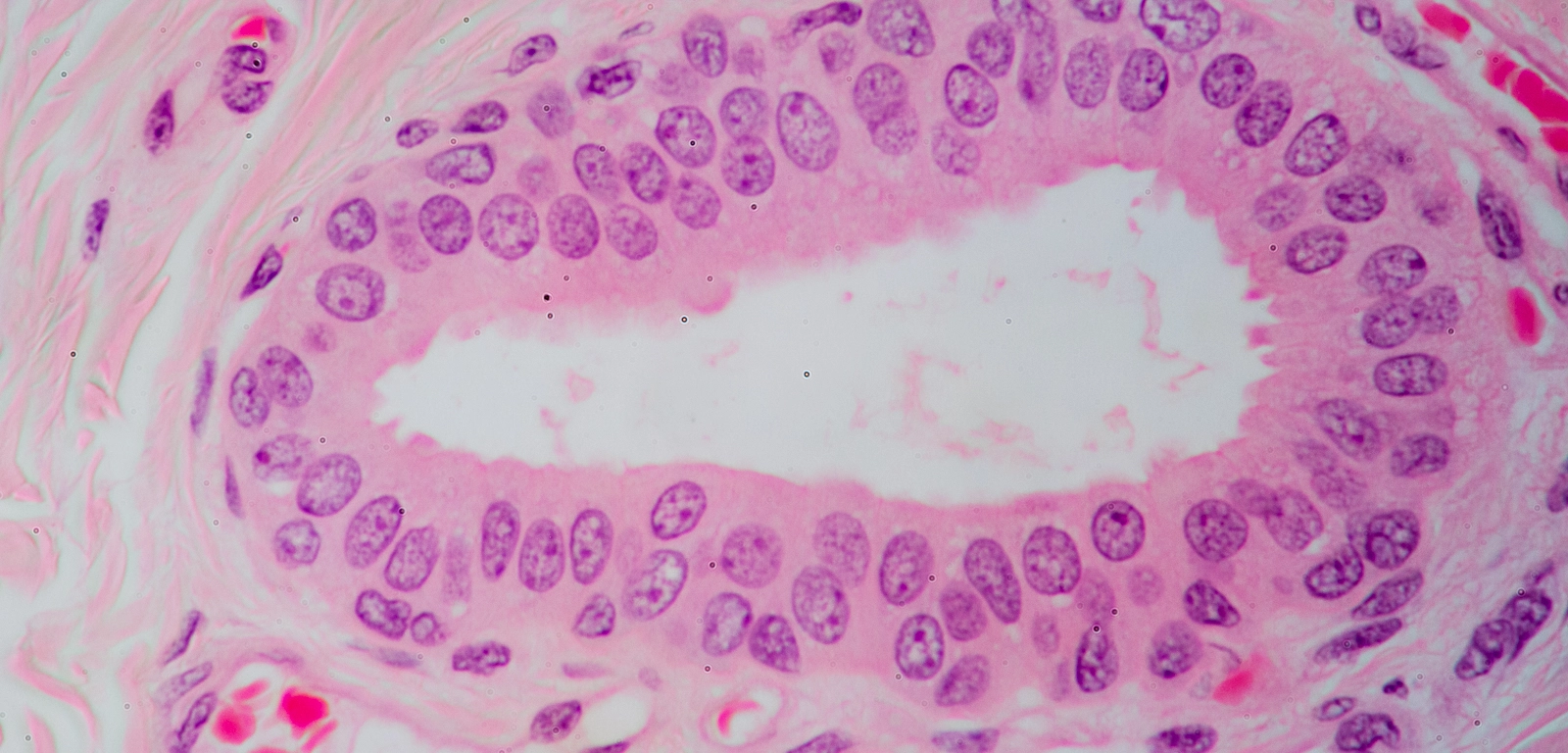
cuboidal epithelium
boxlike
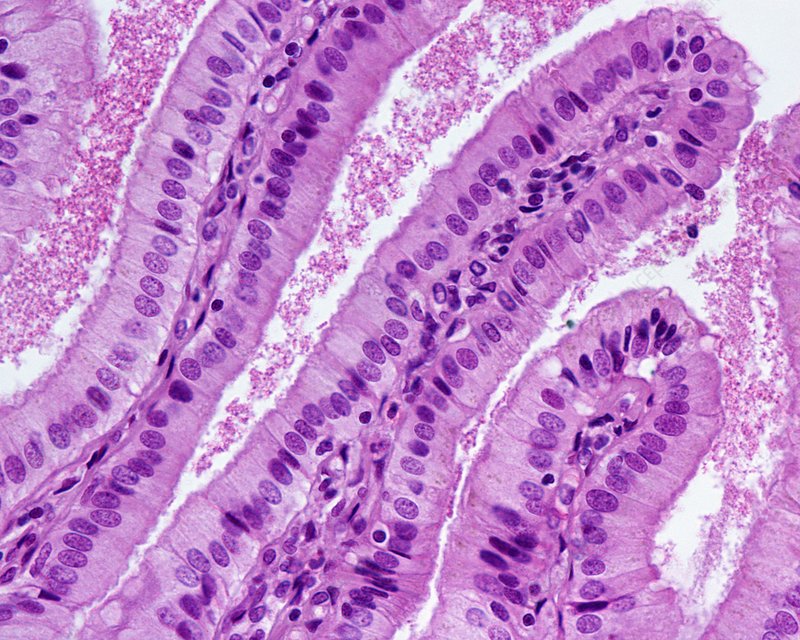
columnar epithelium
tall, narrow
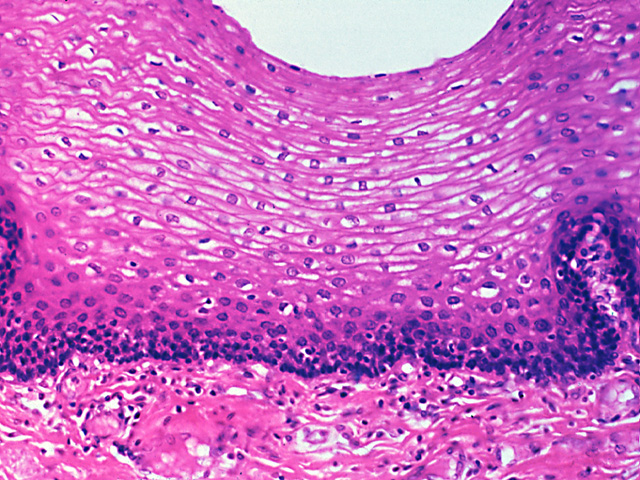
stratified squamous epithelium
may be moist (mouth, esophagus, vagina, rectum). OR keratinized
Keratinized
dead outer cells that contain the tough moisture-resistant protein known as keratin
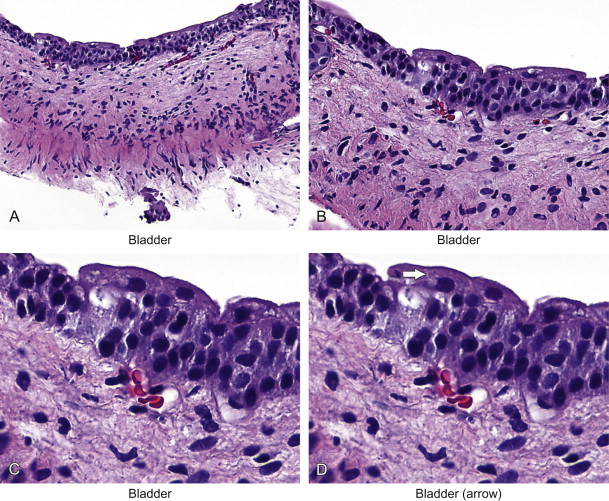
transitional epithelium
stratified. stretches without tearing. cell layers slide past one another and change shape. found in urinary bladder.
function of epithelial tissue
based on # of layers & shape of cells
function of simple epithelium
DIFFUSION (of gases in lungs), SECRETION (through glands), FILTRATION OF BLOOD (glomerulus is the kidney’s filtration system), ABSORPTION (intestines)
function of stratified epithelium
protection from abrasion & barrier function. found in areas where abrasion occurs.
function of squamous epithelium
the thinness&flatness allows for secretion, absorption & diffusion.
function of cuboidal & columnar
secretion & absorption
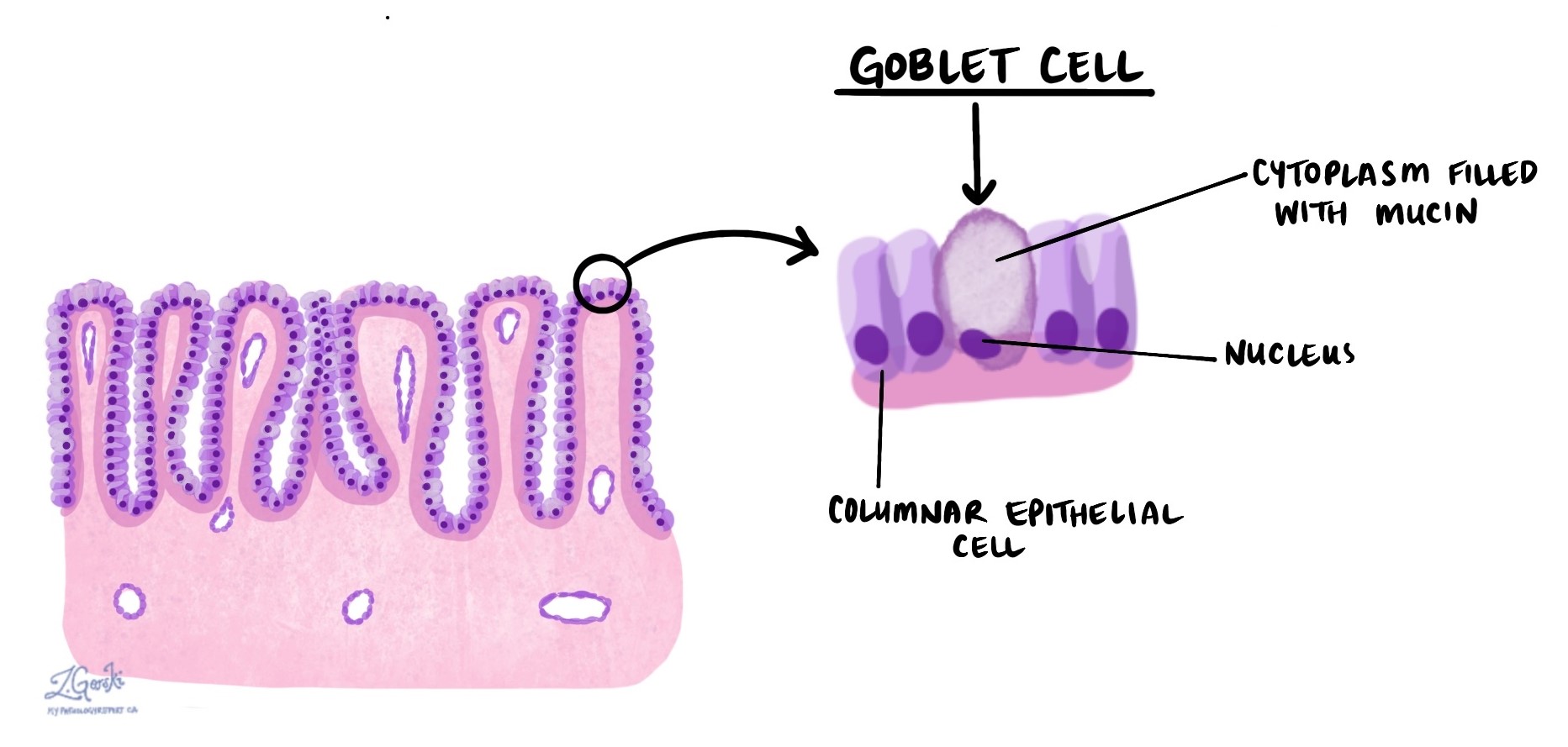
goblet cells
produce & secrete mucus. found in simple columnar epithelium (including pseudostratified) which is found in the respiratory and digestive tract. are a unicellular GLAND.
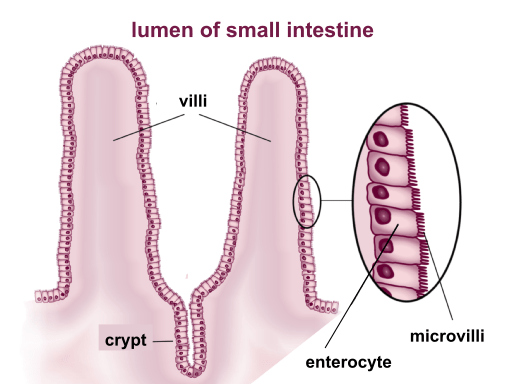
microvilli
increase surface area. don’t move/fixed. brush border of small intestine (simple columnar epithelium)
Cilia
direct movement across cell membrane. found in trachea and nasal cavity (psuedostratified columnar epithelium)
cell connections (junctions)
mechanically bind cells together, form a permeability barrier, provide mechanism for intercellular communication, epithelial cells produce glycoprotein that connects cell to each other (lateral surface) & basment membrane (basal surface).
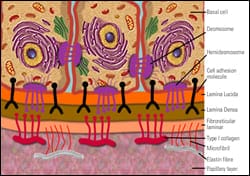
desmosomes
disk-shaped structures with sticky glycoproteins. reinforce cell-cell connections. the stickyness physically hold the cells together.
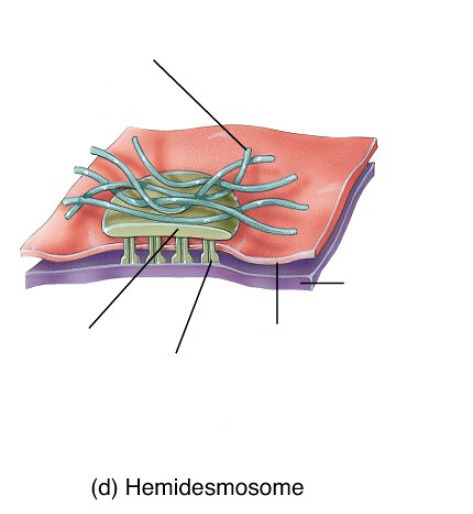
hemidesmosomes
attach epithelial cells to the basement membrane.

tight junctions
form a permeability barrier (touching). material can’t pass between cells but must pass through cells instead.

zona adherens
part of tight junction. girdle of glycoproteins that bind the cell together.

zona occludens
ring around cells. loose part.
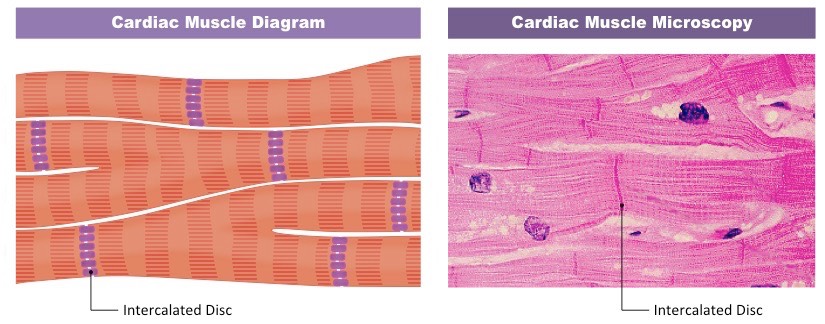
gap junctions
small protein channel that allows small polar channels to pass between cells. allow communication. found in intercalated disks of cardiac muscle.
glands
have secretory function. epithelial tissue is the main tissue that makes up a gland.
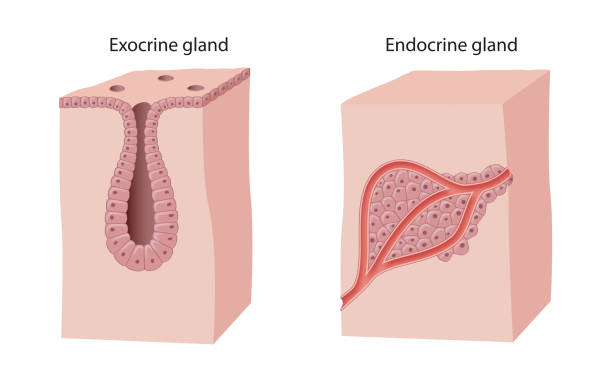
exocrine gland
has ducts. secretes sweat to surface of the body.
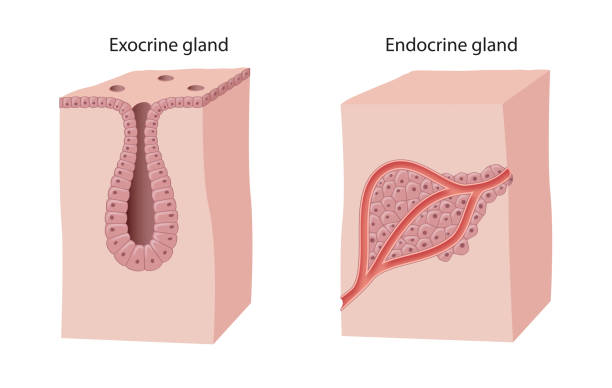
endocrine gland
ductless. produced and secretes HORMONES into the bloodstream.
multicellular gland
group of cells that function together as a gland, secreting substances through a duct onto the body surface. classified based on duct structure & secretion.
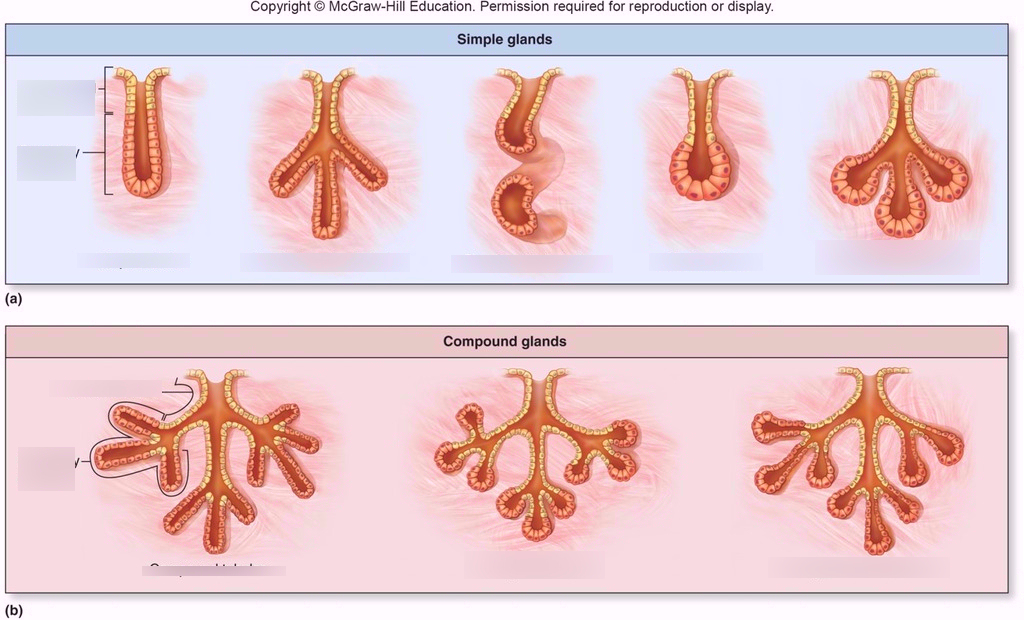
simple multicellular gland
duct with few branches
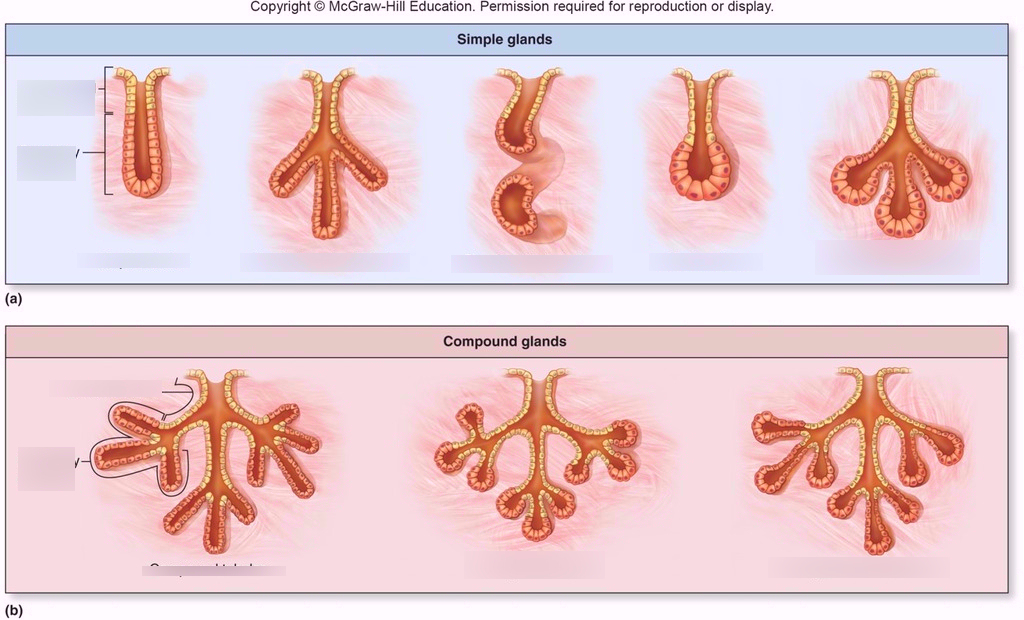
compound multicellular gland
duct with many branches
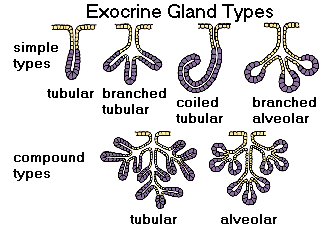
tubular multicellular gland
duct ends in striaght/coiled tubes.
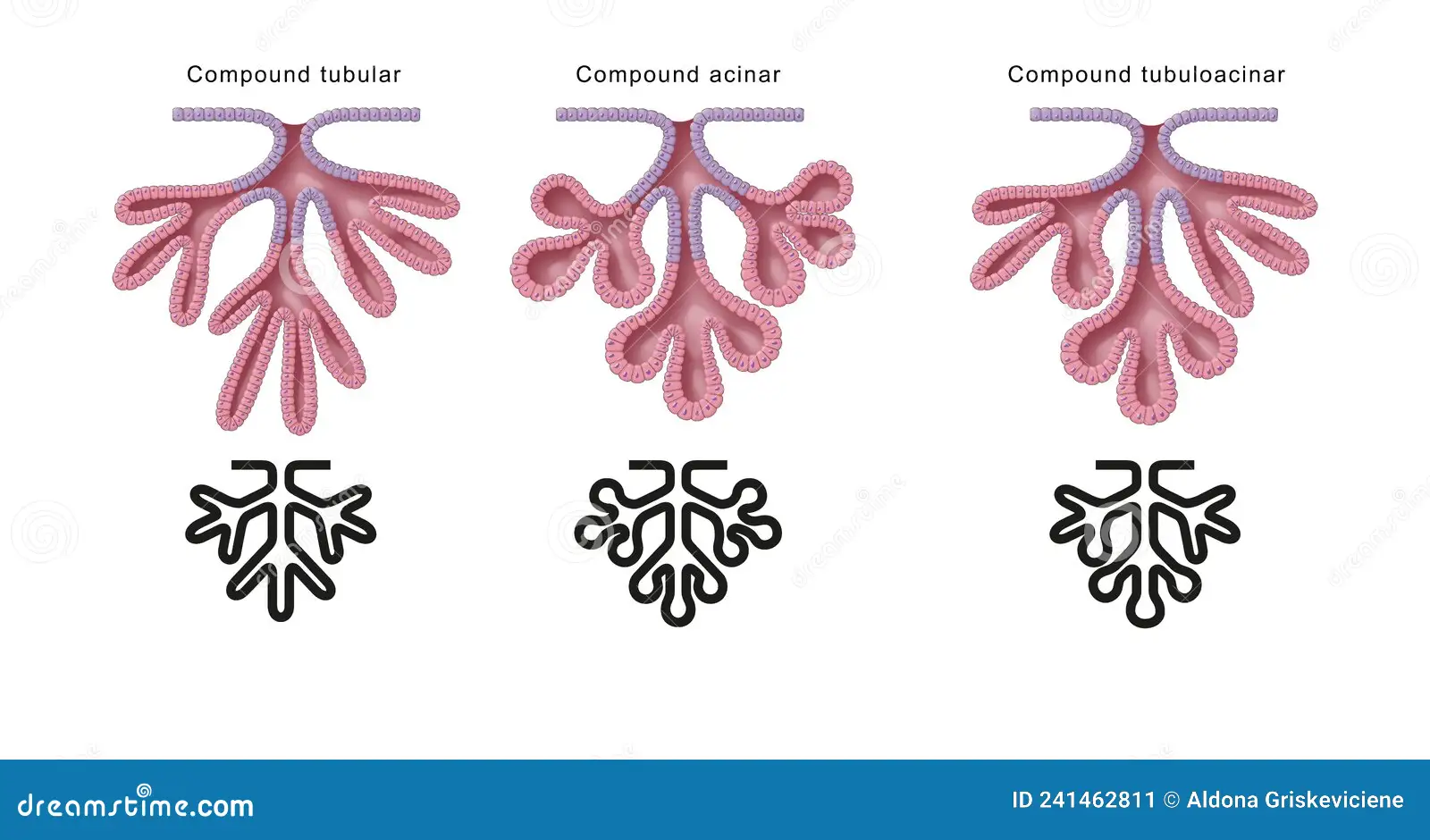
acinar multicellular gland
duct ends in cluster of small sacs
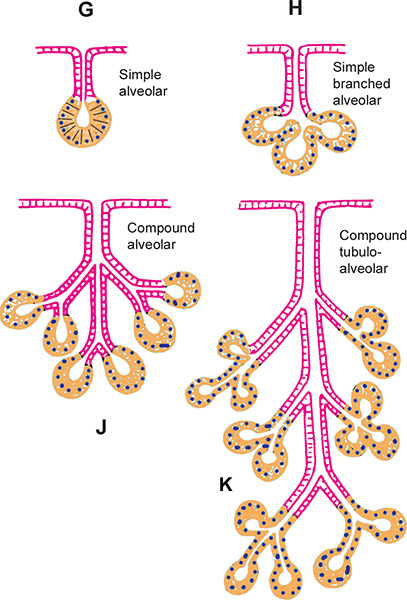
alveolar multicellular gland
duct ends in hallow sacs
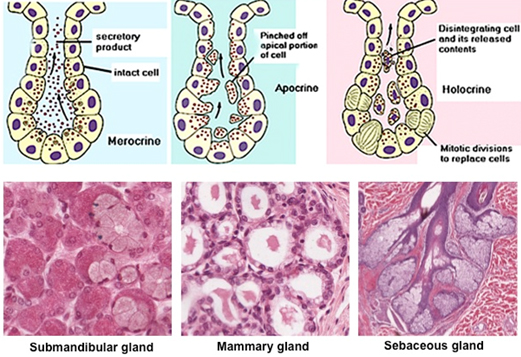
merocrine (multicellular) gland
secretion with no loss of cytoplasm. example: eccrine sweat gland
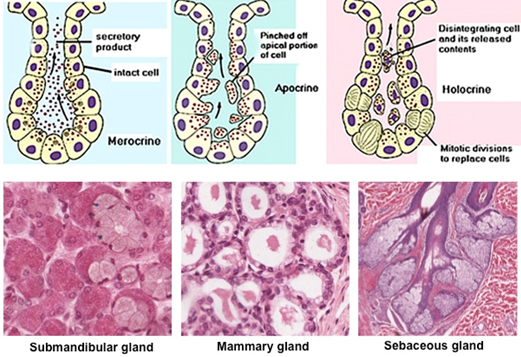
apocrine (multicellular) gland
secreition with some loss of cytoplasm. pinched off fragments. example: mammary gland.
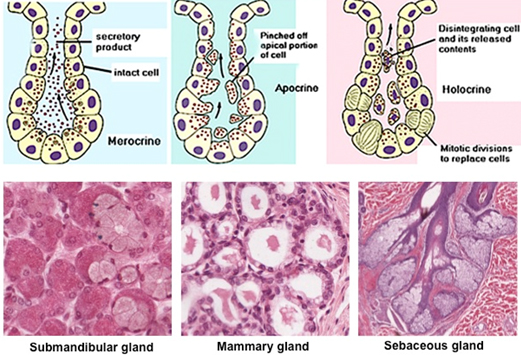
holocrine (multicellular) gland
cell becomes part of the secretion. “HOLOcrine= shedding of WHOLE cell.” mitotic divison eventually replaces cell. example: sebaceous gland.
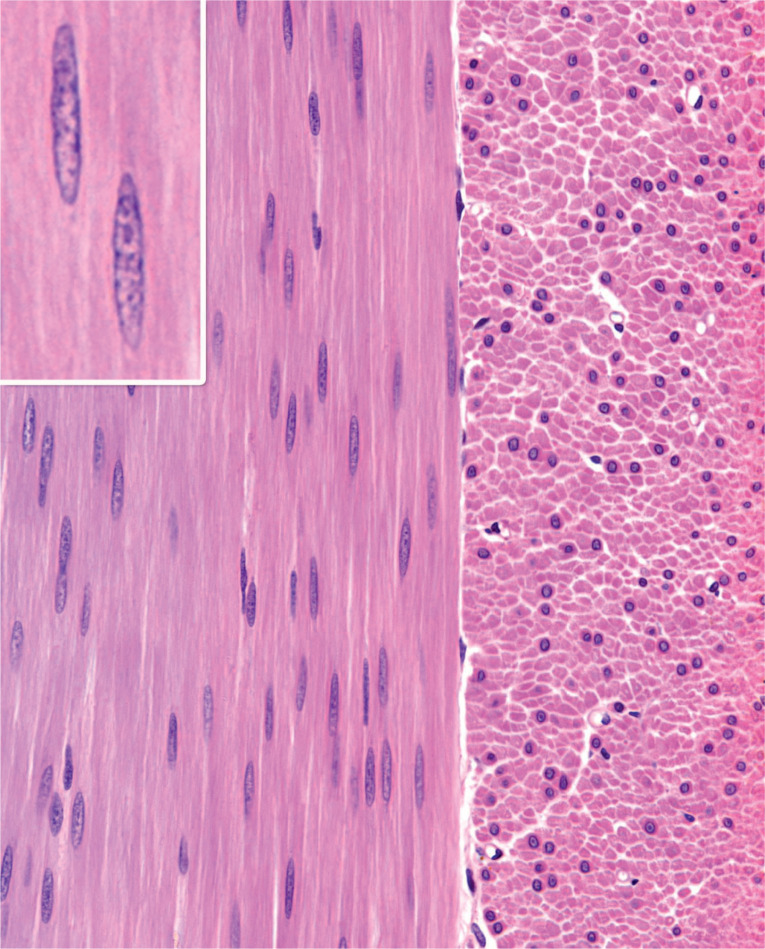
Connective tissue
most abundant tissue in the body, found in every organ. nonliving. makes up extracellular matrix.
Matrix components of CT
protein fibers, ground substance, and fluid present. well-vascularized.
blasts
cells that build/create matrix. example: osteoblasts
cytes
cells that maintain matrix. example: osteocytes
clasts
cells that breakdown/remodel the matrix. example: osteoclasts
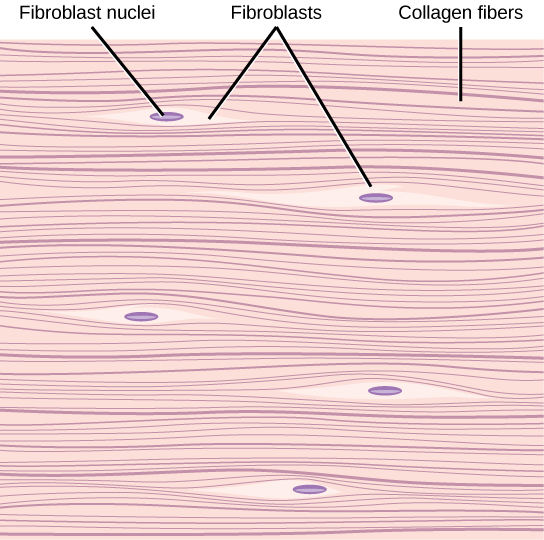
Collagen fibers
strong & flexible. doesn’t stretch. primary protein in the body.
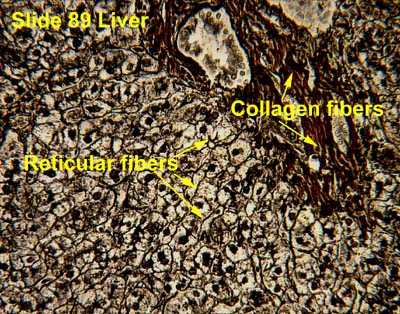
Recticular fibers
fine collagen fiber network. form a network or mesh to support organs.
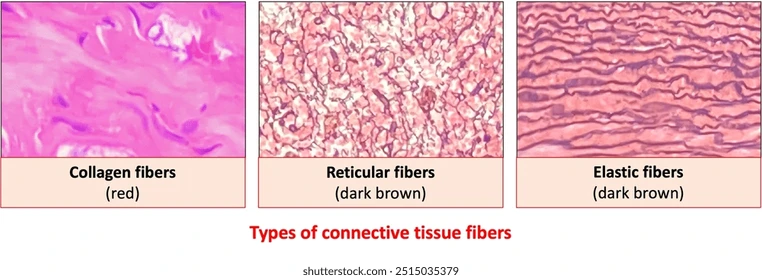
Elastin fibers
stretch & recoil but return to original shape