Chemistry - 3.3.10: Aromatic Chemistry
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Arenes
Hydrocarbons based on benzene
Benzene formula (molecular and skeletal)
C6H6
How do alkyl groups affect the reactivity of (an aromatic) compound in electrophilic substitution reactions?
Alkyl groups cause a positive inductive effect
So the electrophile is attracted more
What is the effect of delocalised electrons on a molecule?
It provides some extra stability to the molecule
What is special about the structure and bonding of benzene? (2)
it is unsaturated, but doesn’t readily undergo addition reactions
All the carbon atoms were equivalent, so all the carbon-carbon bonds are the same
Describe the structure and bonding of benzene (4)
It is a planar (flat), regular hexagon of carbon atoms - each of which is bonded to a single hydrogen atom
Each carbon atom has 3 covalent bonds (one C-H, 2 C-C)
Each bond is equal and is between a single and double C-C bond
The spare electrons of each C atom
Why is the enthalpy of hydrogenation of cyclohexa-1,3-diene not double that of cyclohexane?
The double bonds are separated by a single bond, which allows for some delocalisation
Why is benzene drawn as a hexagonal ring with a circle in it?
Some of the electrons are delocalised (they’re spread over the 6 carbon atoms in the ring)
Why is benzene more stable than cyclohexa-1,3,5-triene?
Its enthalpy of hydrogenation is higher because it has a delocalised ring of electrons
How do you use thermochemical evidence to prove that benzene is more stable than cyclohexa-1,3,5-triene? (3)
Find the enthalpy of hydrogenation of cyclohexene
Multiply that by 3 to get the enthalpy of hydrogenation of cyclohexa-1,3,5-triene
This is greater than the enthalpy change for benzene
Compare benzene’s melting point and boiling point to hexane
Boiling point similar to hexane
Melting point much higher than hexane
Why does benzene have a higher melting point than hexane?
Benzene’s flat molecules pack together well in the solid state, so are harder to separate during melting
Describe the solubility of arenes
Don’t mix with water (as non-polar), but mix with other hydrocarbons and non-polar solvents
Why can arenes undergo electrophilic substitution reactions? (2)
Ring is an area of high electron density so can be attacked by electrophiles
Aromatic ring is very stable and needs energy to be put into it to break it before the system can be destroyed
Delocalisation energy
The energy needed to break the ring before the system can be destroyed
What happens when arenes undergo combustion and why?
They burn in air with flames that are noticeably smoky - They have a high C:H ratio, so there is usually unburnt carbon remaining, which produces soot
What is the most typical reaction of benzenes?
Electrophilic substitution
Why is it more likely that substitution reactions take place instead of addition reactions?
Addition reactions would need the delocalisation energy to destroy the aromatic system
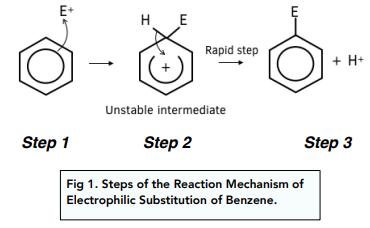
Outline the mechanism of electrophilic substitution reactions with benzene/arenes (2)
Arrow from delocalised ring of electrons to electrophile (El)
C-El bond forms, ring is broken at carbon where C-El bond formed and a + sign in the centre
C-H bond breaks, arrow from C-H to + sign
Nitration
The substitution of a NO2 group for one of the hydrogen atoms on an arene ring
How is the electrophile NO2+ generated (overall + 2 steps)?
H2SO4 + HNO3 →HSO4- + NO2+ + H2O
H2SO4 + HNO3 → H2NO3+ + HSO4-
H2NO3+ → NO2+ + H2O
What is NO+2 called?
Nitronium ion / nitryl cation
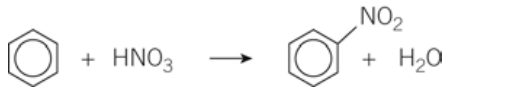
Give the overall reaction when benzene reacts with nitric acid
Benzene + HNO3 → Nitrobenzene + H2O
C6H6 + HNO3 → C6H5NO2 + H2O
What reagents are needed for the nitrification of benzene?
Concentrated nitric acid and a concentrated sulfuric acid catalyst
What are nitrated arenes used for? (2)
They are used to produce explosives e.g. TNT + to make aromatic amines, which are then used to make industrial dyes
What catalyst is used in Friedel-Crafts acylation reactions?
Aluminium chloride
What happens during a Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction between benzene and an acyl chloride? (3)
ROCl + AlCl3 → RCO+ + AlCl4-
RCO+ then used in an electrophilic substitution reaction
AlCl4- + H+ → AlCl3 + HCl
What might be substituted for a hydrogen in a Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction?
RCO, e.g. from an acyl chloride
What is the product of Friedel-Crafts acylation used for?
They’re used in the synthesis of new substituted aromatic compounds
Is benzoic acid soluble in water? Why?
No - the benzene ring is non-polar despite the COOH group’s ability to form H bonds.
Compare the structure of benzene and cyclohexa-1,3,5-triene (2)
Benzene has equal C-C bond lengths whereas cyclohexa-1,3,5-triene has bonds of different lengths
Both planar, hexagonal rings