Exam 1 Gen Bio 1
1/121
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapter 1,2,3,4
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
122 Terms
Organization (Betty eats carrots, potatos, onions, olives on the couch on monday afternoon)
Biosphere, Ecosystem, Communities, Populations, Organism, Organs, tissues, cell, organelle,molecules, atoms
How is a cell organized?
Cell structure—→Eukarotic vs prokaryotic—→organelle
what is the cell theory?
states that all living organisms are made from cells
Information
expression and transmission of genetic information
Transcription
DNA is transcribed into RNA
Translation
RNA is translated into a protein
Transcription and translation occur?
ribosomes
gene expression
the process of converting information from gene to cellular product
Energy and matter
Transfer and transformation of energy and matter ex. consumers eat producers that energy is not lost but transferred
Interactions
Molecular level of interaction to ecosystem
Unifying themes of biology(obama is easy man in earth)
Organization , information, energy and matter, interactions, evolution
Natural selection (Darwin)
Survival of the fittest
Scientific method
-make observations and ask questions about it
-develop a testable explanation called a hypothesis
-design experiments to test the hypothesis )
(include a control . and determine dependent and independent variable)
-do experiments, and collect and analyze data
-draw conclusion
-communicate method, results, and conclusion
a scientific theory
an explanation supported by a large amount of evidence
evolution
living organisms are modified decedents of common ancestor
how does the branching tree model represent evolution?
development from prokaryotes cells or eukaryotes cells evolve into more complex organisms
matter
made up of elements
elements properties
structure of an atoms -proton, neutron, electrons
element of life
main (carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen make up 96% of living matter)
trace elements
the extra elements that is needed but make up the remaining 4%)
atomic number
number of protons
atomic mass
bottom number of the electrons
protons and neutrons
Isotopes
different number of neutrons causes it to react differently
radio activity
decay spontaneously, giving off particles and energy
electron shells
the furthers shell have the most amount of energy, electrons are found on different electron shells
when is energy absorbed (electron shells)
when it moves from first shell to second or third shell
when is energy lost (electron shells)
when it moves from high energy (third) to low energy (first)
valance shell
outermost shell (most chemical behavior)
octet rule
when atom wants to have 8 electrons to be stable
orbitals
three-dimensional space where electrons are on (2s, 2p) first shell is 2, next is 8, next is 18. (2xn²)
covalent bonds
share electrons
polar covalent bonds
one atom is more electronegative, and the atoms do not share electrons equally
Van der Waals interactions
are attractions between molecules that are close together as a result of weak bonds ex. molecules of a gecko’s toe hairs and a wall surface(electrons are unevenly distributed)
hydrogen bonds
form why a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to one electronegative atom is attracted to another electronegative atom(partial neg is attracted to partial pos) ex. velcro- with jus one its easy to break but alot together it is strong)
ionic bonds(NaCl)
transfer of an electron
molecular shape determines
how the molecules recognize and respond to one another (how it is built is directly associated to what it does)
the shape binds to
the same receptors
chemical reactions
making and breaking of chemical bonds
reactants
starting molecules of chemical reactions
products
resulting molecules of chemical reactions
nonpolar covalent bonds
atoms share the electrons equally
unequal sharing of electrons causes a
partial pos or neg charge of each atom or molecules (water form hydrogen bonds)
electronegativity of an atom(greedy)
how much an atom wants electrons for example oxygen is more electronegative and needs 2 more electrons to fill its shell. It will take or steal electrons from the hydrogen to make water (H20)
chemical equilibrium
reactions are reversible from reactants to products and products to reactants
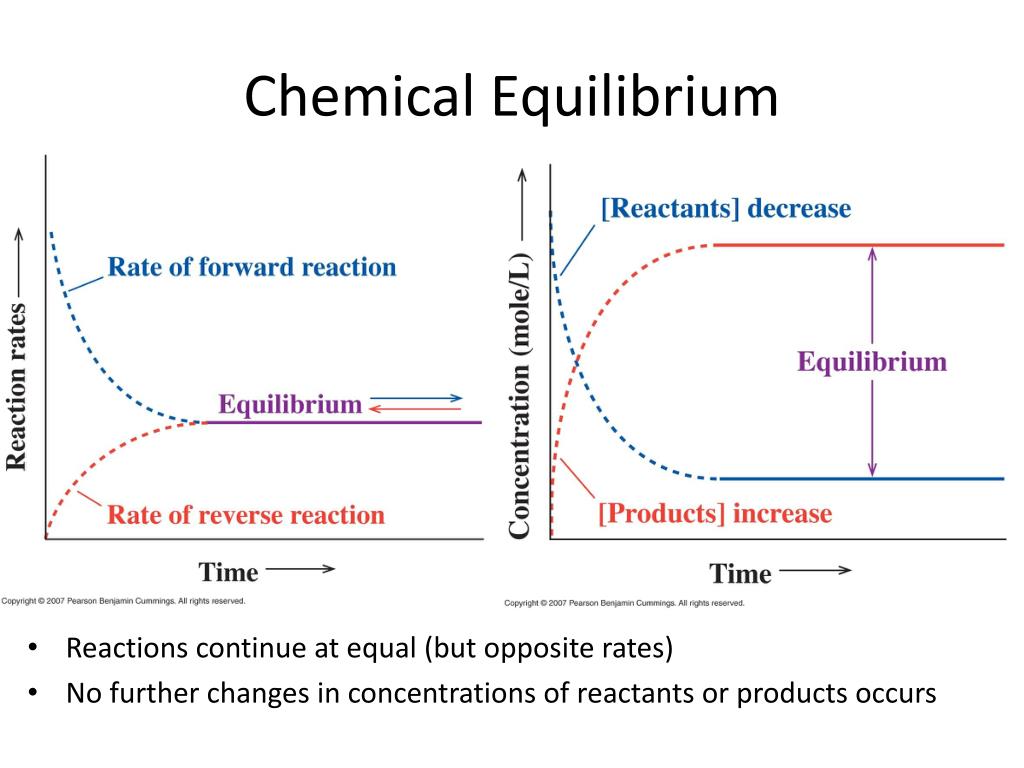
arrows 1 (chemical reactions)
can only go on way (reactant can make products but products can’t make reactant)
arrow 2
reactions can go both ways (reactant can make products and products can make reactants)
water is polar molecule
because it has a slightly positive oxygen and slightly neg. hydrogen creating hydrogen bonds
4 emergent properties of water
-cohesion
-high specific heat
-density of water
-water as a solvent
cohesion
surface tension allows for a spider to walk on water —→ molecule to stick to itself(ex. change color of flower because it uses cohesion(stick other water molecules) up the roots against gravity
high specific heat
The amount of heat absorbed to change temperature(ex. alcohol swab dry faster than water swab on arm)(water resists changing its temperature because of its high specific heat)
adhesion
stick to other substances ex. water and plant cell walls (water sticks to the walls to go up the roots )
water absorb ____from warmer air (daytime)
heat
releases ___heat to cooler air (night time)
stored
kinetic energy
energy of motion
thermal energy
kinetic energy associated with random motion of atoms or molecules(volume)
temperature
the average kinetic energy of the molecules in a body of matter
heat
thermal energy is transfer from one body of matter to another
large body of water can ___and ____a huge amount of heat from the sun in daytime and during summer then during the winter (night) the gradually ___water can warm the air. (why its hot near coastal areas)
absorb, store, and cooling
evaporative cooling
liquid to gas(sweating -getting rid of the hot molecules(highest energy) to leave the slow moving molecules that feels cooler )
heat of vaporization
the amount of heat required to change a substance from liquid to a gas at a constant temperature
evaporative cooling
as a liquid evaporates, its remaining surface cools
evaporative cooling of water helps
stabilize temperatures in organisms and bodies of water
elephants can’t sweat but…
spray cool water onto themselves instead. the water molecules with greatest kinetic energy leave as gas, making the remaining liquid water cooler
density of water (why does it float?)
because of hydrogen bonds!! water is less dense as a solid than as a liquid (the hydrogen bonds keep the molecules far enough apart to make ice 10% less dense than liquid water)
water as a solvent
aqueous solution
solution
liquid that is a completely homogeneous mixture of substances
solvent
does the dissolving
solute
gets dissolved
hydrophobic
does not like water
hydrophilic
loves water
water is ____ solvent due to its polarity
versatile(even large polar molecules such as proteins can be dissolved in water if they have ionic and polar regions)
when an ionic compound is dissolved in water, each ion is surrounded by a sphere of water molecules called a
hydration shell
Molarity (M)
the number of moles of solute per liter of solution
1 mole
6.02×10²3 molecules
why is liquid important for life
allow for swimming and staying hydrated.
reactant (why important for life)
many plants use photosynthesis to make food
density (why important for life)
ice float on water and help build a habit for polar bears, fish, and that environment to thrive
solvent (why important for life)
keeps ion in our body to stay in aqueous solution
cohesion and surface tension (why important for life)
bring water up to roots for plants, and surface tension allow for bugs to walk on water
high specific heat capacity (why important for life)
moderate the temperature so it doesn’t get too hot or cold for organisms living near water
heat vaporization (why important for life)
sweating (when bonds break it allow an organism to cool down)
acids
have more hydrogen ions(H^+)(less than pH7)
bases
have more hydroxide ions(OH^-)(more than pH7)
how to calculate pH?formulas
pH+pOH=14——>pH=14-pOH
neutral based concentration
pH7
what are buffers
substances that minimize changes in concentrations of H+and OH- so basically bring it back to an ideal concentration
organic chemistry
study of compounds that have carbon in the middle
radiometric dating (come back to look in chapter 3)
use isotopes
carbon bonds with which 3
hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen
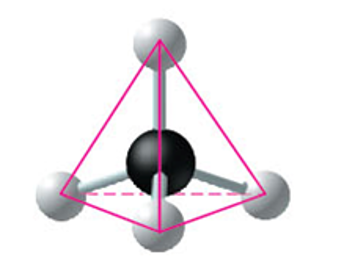
properties of carbon
can make 4 bonds and 4 valence e- and this allow for carbon to make a tetrahedral shape
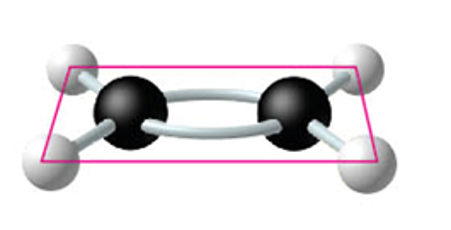
two carbon atoms are joined by
double bonds
electron configuration
how e- are arranged around the nucleus (because of carbon’s electron configuration it can bond to many different elements)
each point of hexagon is a carbon, and carbon is usually a hydrogen with it
can be linked into chains
Stanley Miller experiment
put a mixture of methane, ammonia, hydrogen, and water in a closed system. They found out that amino acids and organic molecule that were essential for life could be self-produced therefore recreating early atmosphere on earth. it was heated and electric current was placed through to mimic the lighting strikes
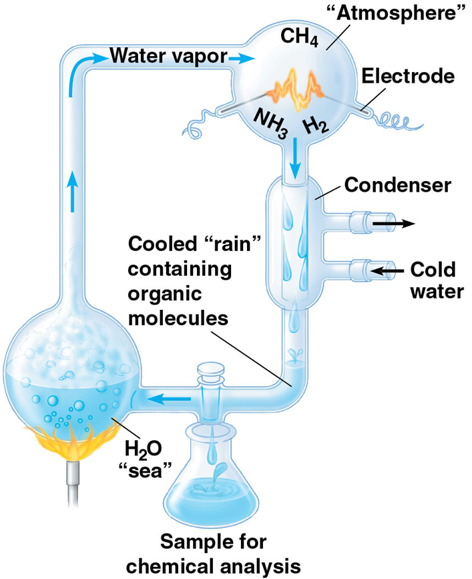
carbon chains form the _____ of most organic molecules
skeletons
what is important about a valence of 4 for carbon
making 3D shape and be able make single, double, or triple bonds. It can also bond to itself
hydrocarbons
organic molecules consisting of only carbon and hydrogen
many organic molecules such as fats have _____ components
hydrocarbons
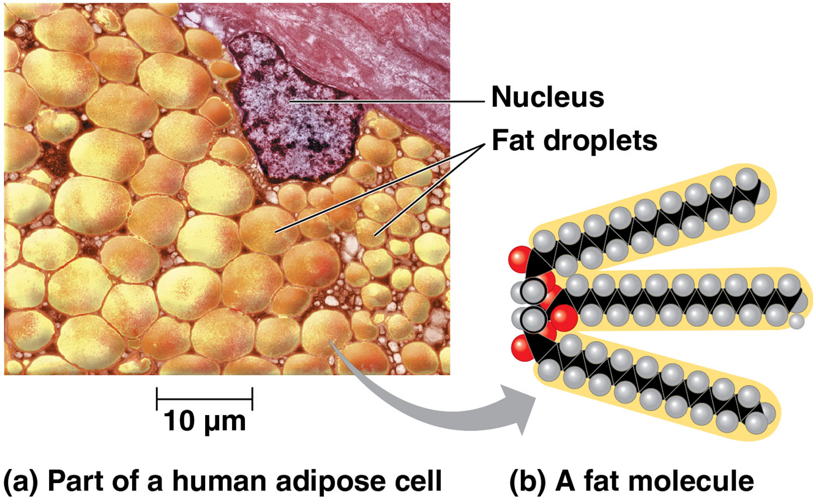
hydrocarbons can undergo reactions that _____ a large amount of energy
release
isomers
compounds with the same molecular formula but different structure and properties (basically build different)