KK1 - gene pool and types of mutations
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Gene pool
the total aggregation of all the genes and alleles present within a particular population or species
Allele frequencies
the proportion of a particular allele appearing at a certain gene locus in a gene pool
Frequencies could be calculated by totalling the number of a particular allele by the total number of alleles present in the population
Larger and more diverse gene pool will have a larger variety of genes and alleles
Leads to a greater number of genotypes and phenotypes therefore increasing genetic diversity
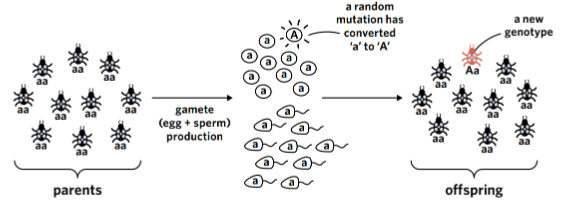
mutations
Mutations - permanent changes to the DNA sequence of an individual
Can occur either spontaneously or be induced by agents known as mutagen (e.g. UV radiation)
When mutations occur in DNA sequence of genes, they can have a significant downstream effect of the expression of the gene
Alters the folding and functionality of the resultant protein
Can be classified as advantageous, neutral or deleterious
Depending on the effect on the survivability of the individual affected
evolutionry signficance - mutations
Evolutionary significance - increases genetic diversity through mutations
Ability to create and introduce new alleles into a population
In order for mutations to be heritable, must occur in an individual's germline cells
If mutation occurs in somatic cell, then it is not heritable
POINT MUTATIONS
A change to a single nucleotide in a gene
Modifications can include substitution of a base
Broken down into silent, missense and nonsense mutations depending on their effect on the protein produced
Can also include in the addition and deflection of a single nucleotide
Triggers what is known as frameshift mutation
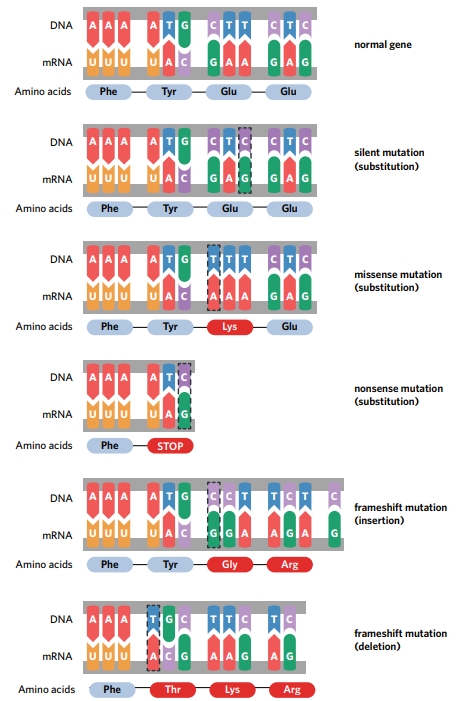
Silent mutations
Substitution mutations have no effect on the resulting amino acid sequence
Due to degenerate nature of genetic codes, multiple different codons code for the same amino acid
Despite changes to original DNA sequence, the same amino acid is incorporated into the protein
Missense mutation
Substitution mutations which code for a different amino acid, altering the primary structure of the polypeptide
Affects of the folding of polypeptide and could alter the functioning of the protein
Nonsense mutation
Substitution mutations which prematurely end the translation of a gene’s mRNA
Substitution of nucleotide can cause codon to become a stop codon
Gene will not be completely translated
Leads to a polypeptide being too short to function to intended
These mutation considered most dangerous
Frameshift mutation
Addition or deletion of one or two nucleotides, which alters the reading frame of all the following nucleotides.
Reading frame - how DNA or mRNA is divided into triplets or codons
The amino acids they code for are affected, which can cause major disruptions to the structure and function of the protein
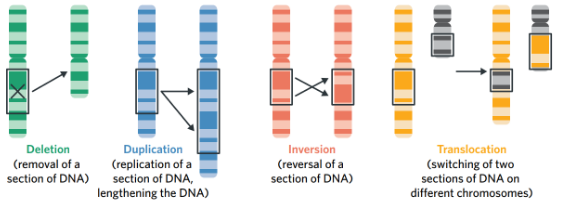
Block mutations
Involves changes to larger sections of DNA, potentially causing significant changes to DNA sequence of the organism
Involves the alteration of the structure of a chromosome by deleting, duplicating, inverting or translocating a cluster of nucleotides
May involve multiple genes
Occur during the process of meiosis
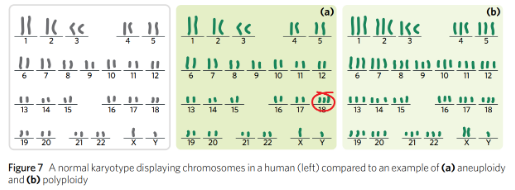
Aneuploids and polyploids
Can cause genomes to gain or lose a chromosome or in extreme cases, entire sets of chromosomes
Referred to aneuploidy and polyploid
Aneuploidy - a chromosomal abnormality in which an organism possesses an incorrect number of total chromosomes caused by the addition or loss of an individual chromosome
Polyploidy - to a chromosomal abnormality in which an organism has an incorrect number of sets of each chromosome - there is an entire set of chromosomes added or missing
Environmental selection pressures
factors within the environment that influence the survivability of a species within a given environment
predation, disease, competition, and climate change.
The process of natural selection can occur
involves the selection of the phenotype most suited to overcome the environmental selection pressure
Genetic fitness
higher genetic fitness, due to the presence of their advantageous phenotype, which arises due to the presence of certain alleles
Fitter organisms with the advantageous phenotype have a selective advantage and are more likely to survive
More likely to pass on their alleles to the next generation
increases allele frequency of the allele that codes for the advantageous phenotypes
Natural selection
Relies on the heritability of the advantageous allele and the presence of variation with the existing population
ensure that the alleles that confer an advantage are present within the environment
Variation allows for disadvantages alleles to arise
can be selected against and subsequently removed from the population
FOUR CONDITIONS OF NATURAL SELECTION
variation
individuals in a population vary generically, which leads to phenotypic differences
Selection pressure
an environmental selection pressure impacts the survivability of organisms within a population and their ability to reproduce
Selective advantages
Individuals with phenotypes that are fitter or more advantageous under the environmental selection pressure are conferred a selective advantage
allows them to survive and reproduce more successfully.
Heritability
The advantageous trait must be heritable, allowing it to be passed on from the parents to their offspring
Therefore, over time, the frequency of the advantageous allele will increase.
GENETIC DRIFT
Involves changes to a population's allele frequencies due to sudden and random occurrences
Genetic drift can occur through the bottleneck effect or the founder effect
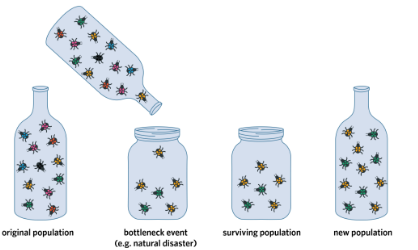
Bottleneck effect
Occurs when a large portion of a population is wiped out by a random event such as a natural disaster
Dramatically decrease the population size, impacting allele frequencies
Reduction in population size can cause individuals carrying unique alleles to be lost
New population has lower genetic diversity than the pre-disaster population
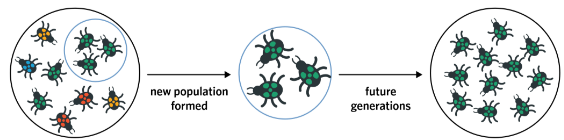
Founder effect
Occurs when a small unrepresentative sample of individuals separates from a larger population to colonise a new region and start new population
For example
Population has beetles of many different colours
If 10 beetles left their original population to form a new population, it would not mirror the initial gene pool
Would be considered an unrepresentative sample
Genetic diversity of the new population is lower than the original
If the original population were all green, the green between would not be considered an example of the founder effect as the founding colony resembles the initial gene pool
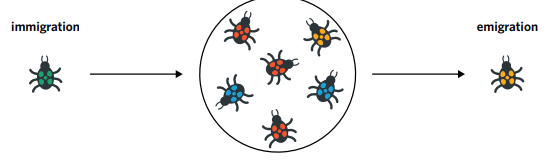
gene flow
Involves the introduction or removal of alleles between populations through migration or interbreeding
Migration occurs when populations are physically close together or due to external forces such as the clearing of geographical barrier between populations
Entering a population via migration means that their alleles are added to the gene pool of that particular population
Existing a population via emigration means that their alleles are removed from the gene pool
When individuals temporarily enter a population and interbreed with local individuals before leaving again, they contribute to the gene pool of that particular population
populations in different geographic locations can exchange alleles through either migration or interbreeding