Lecture Exam 3
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
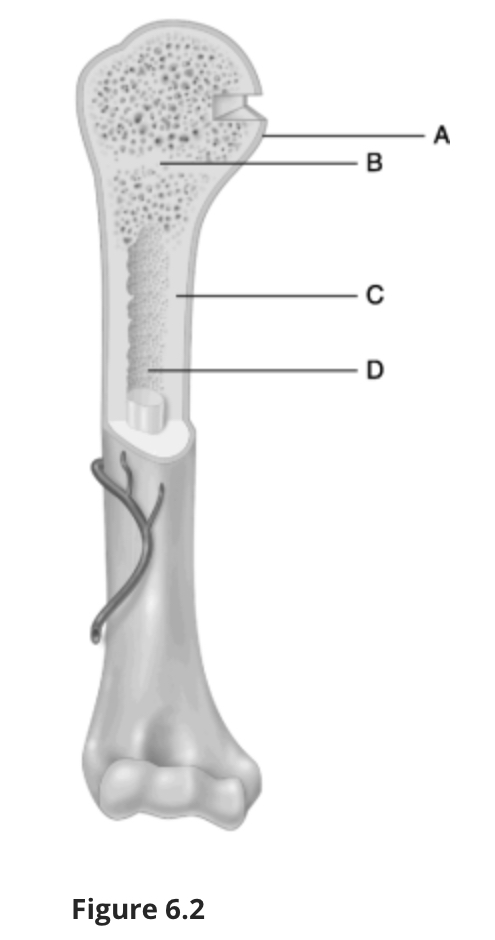
Using Figure 6.2, match the following:
Epiphysis of the bone.
A
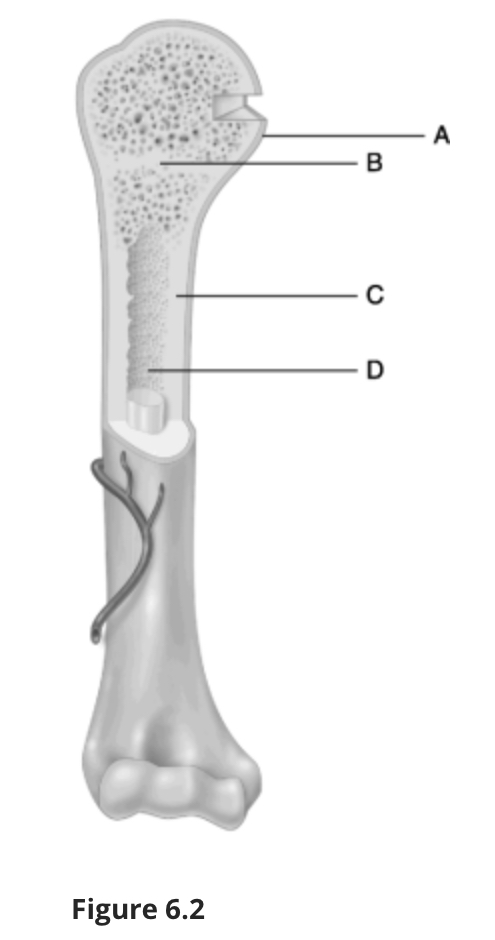
Using Figure 6.2, match the following:
Area where yellow marrow is found.
D
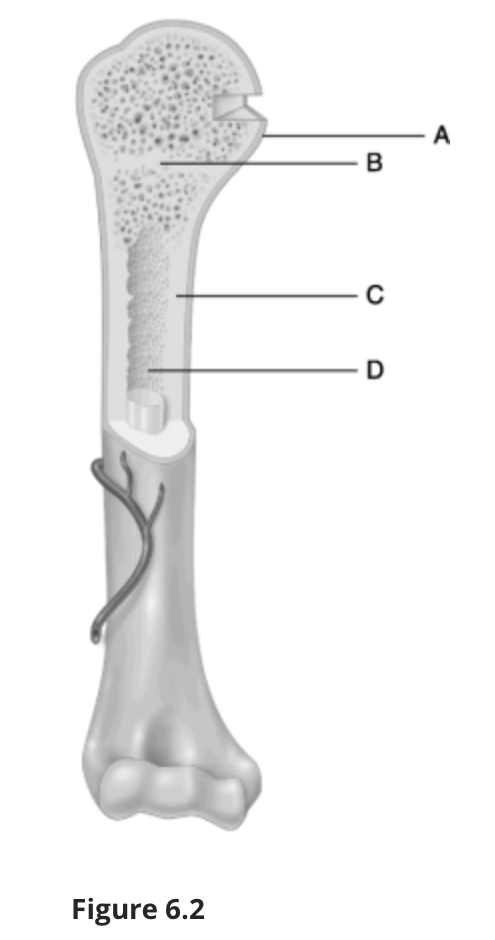
Using Figure 6.2, match the following:
Compact bone.
C
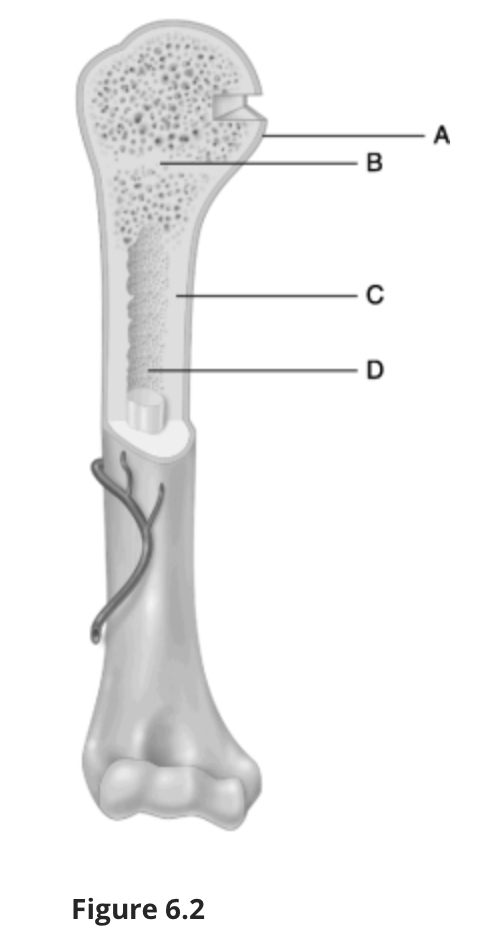
Using Figure 6.2, match the following:
Location of the epiphyseal line.
B
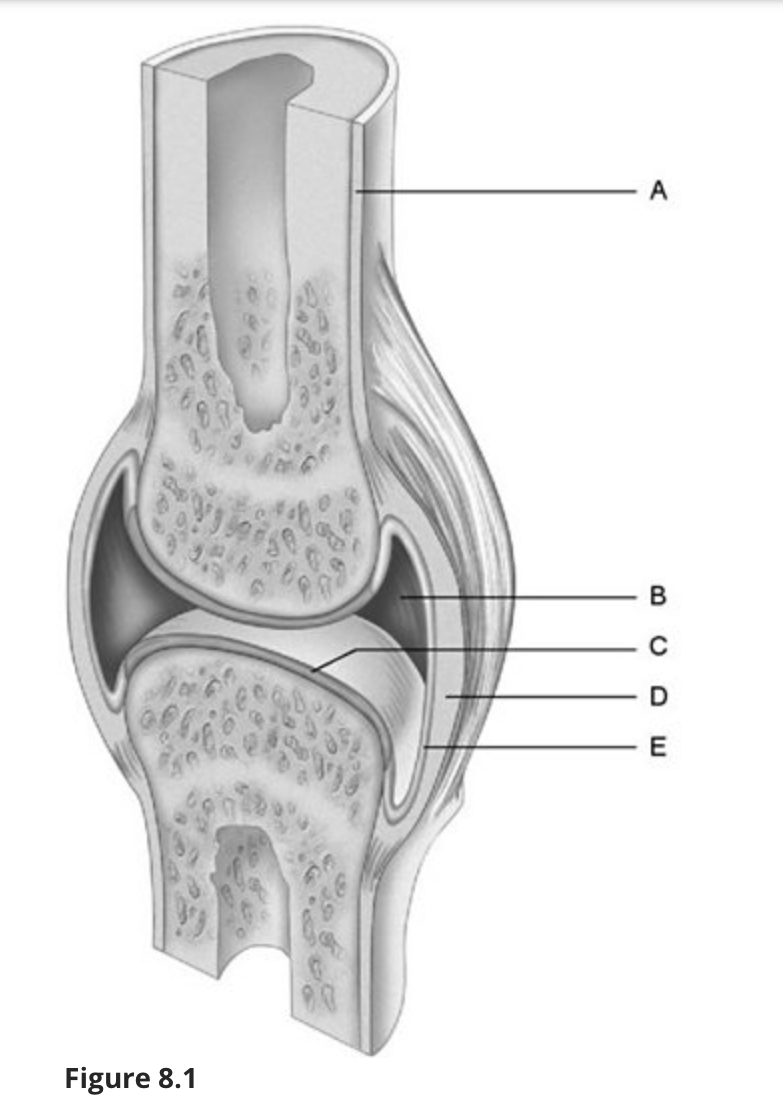
Using Figure 8.1, match the following:
Fibrous layer.
d
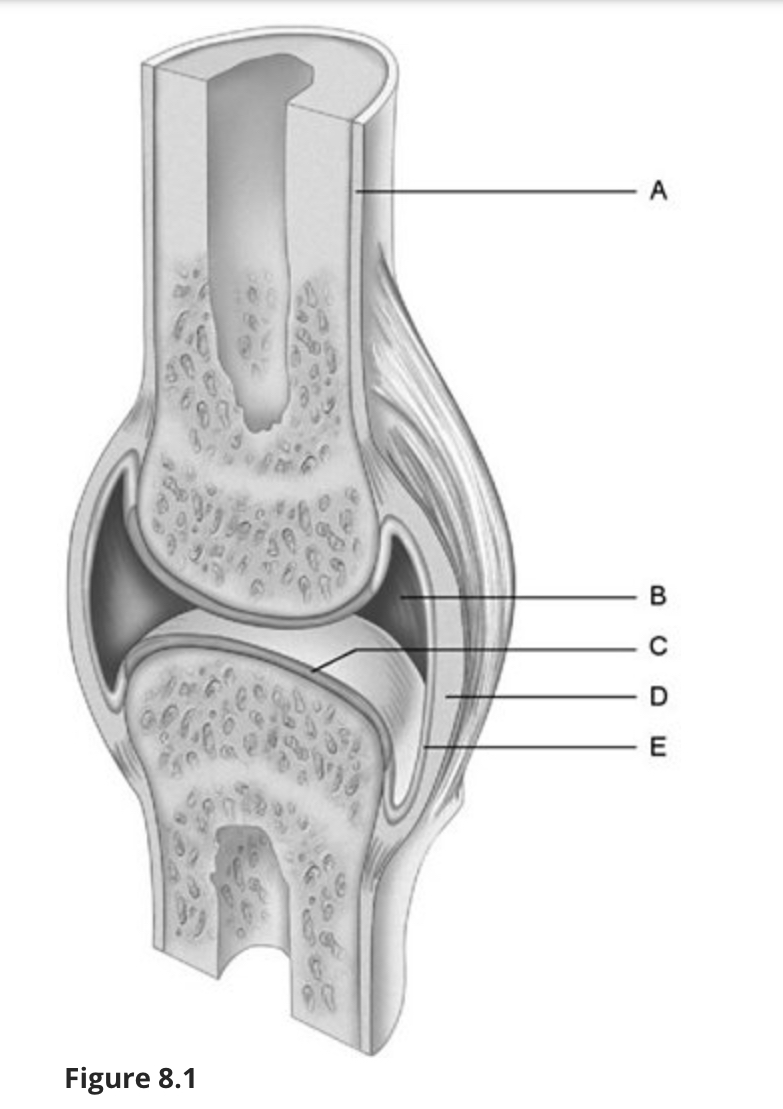
Using Figure 8.1, match the following:
Synovial membrane.
e
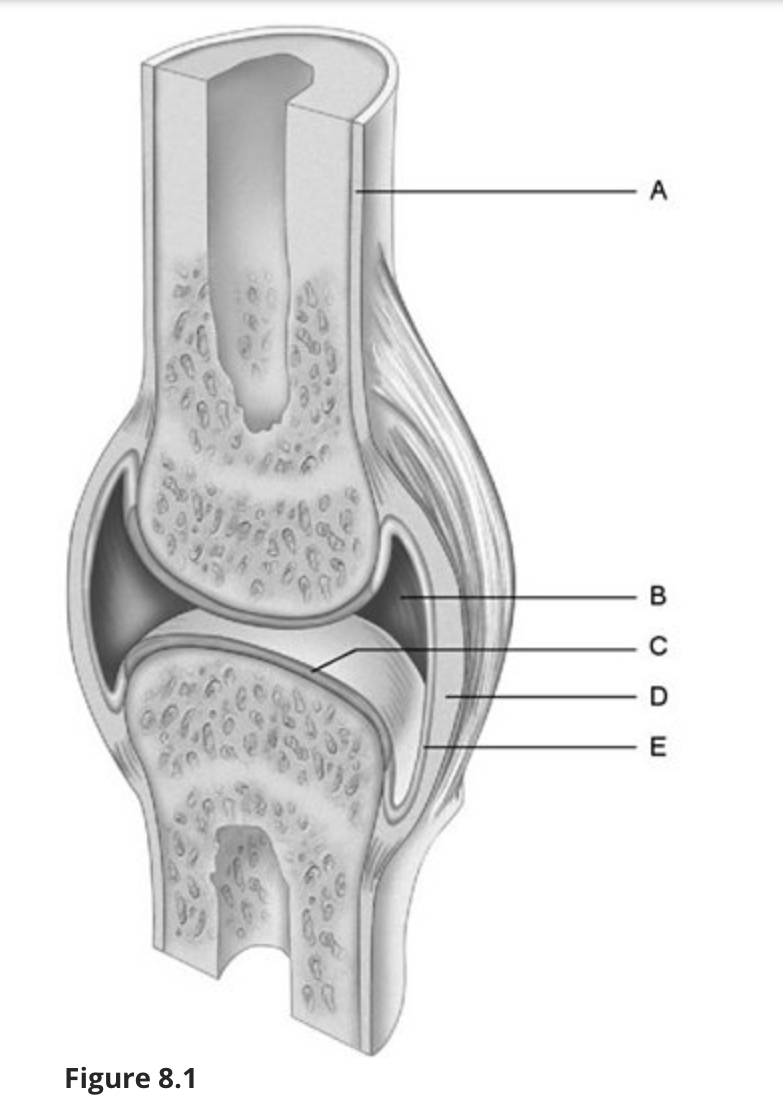
Using Figure 8.1, match the following:
Articular cartilage.
c
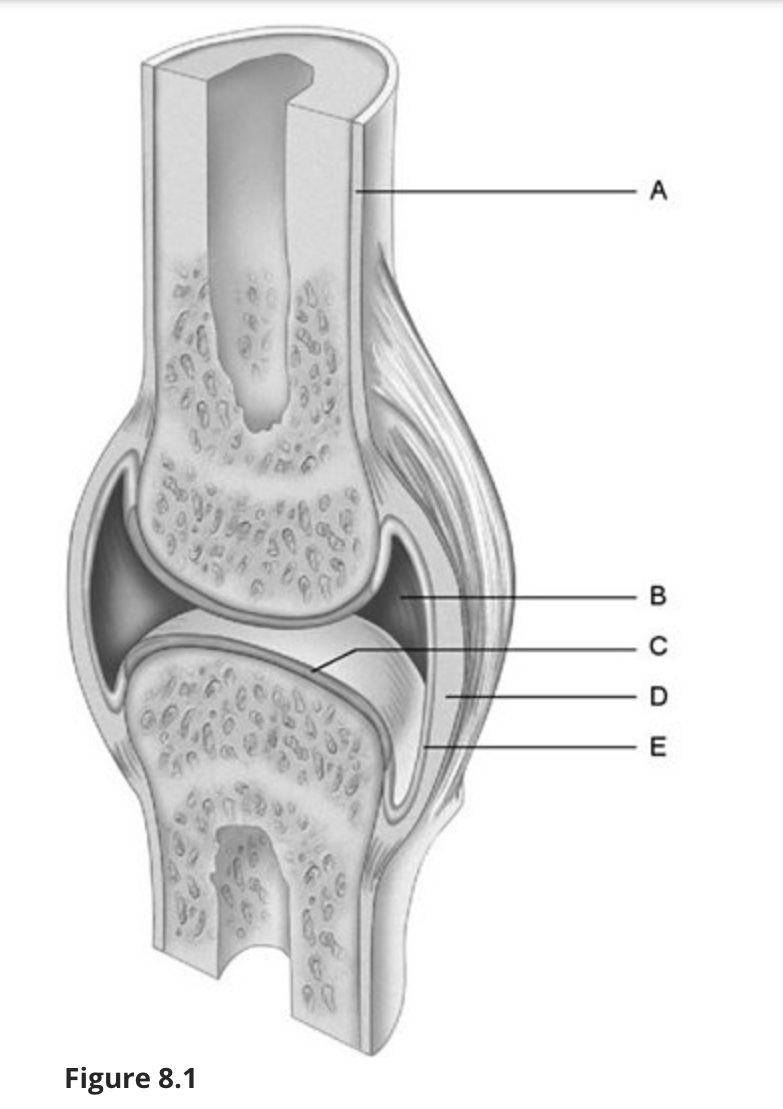
Using Figure 8.1, match the following:
Periosteum.
a
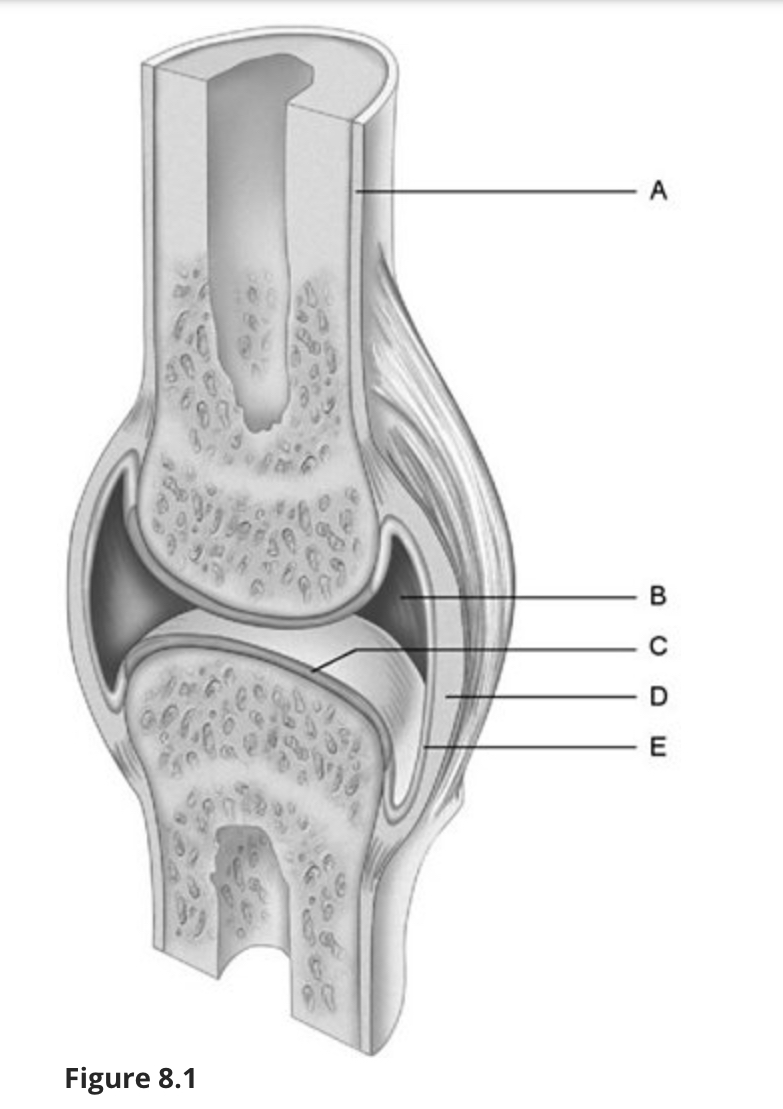
Using Figure 8.1, match the following:
Joint (articular) cavity.
b
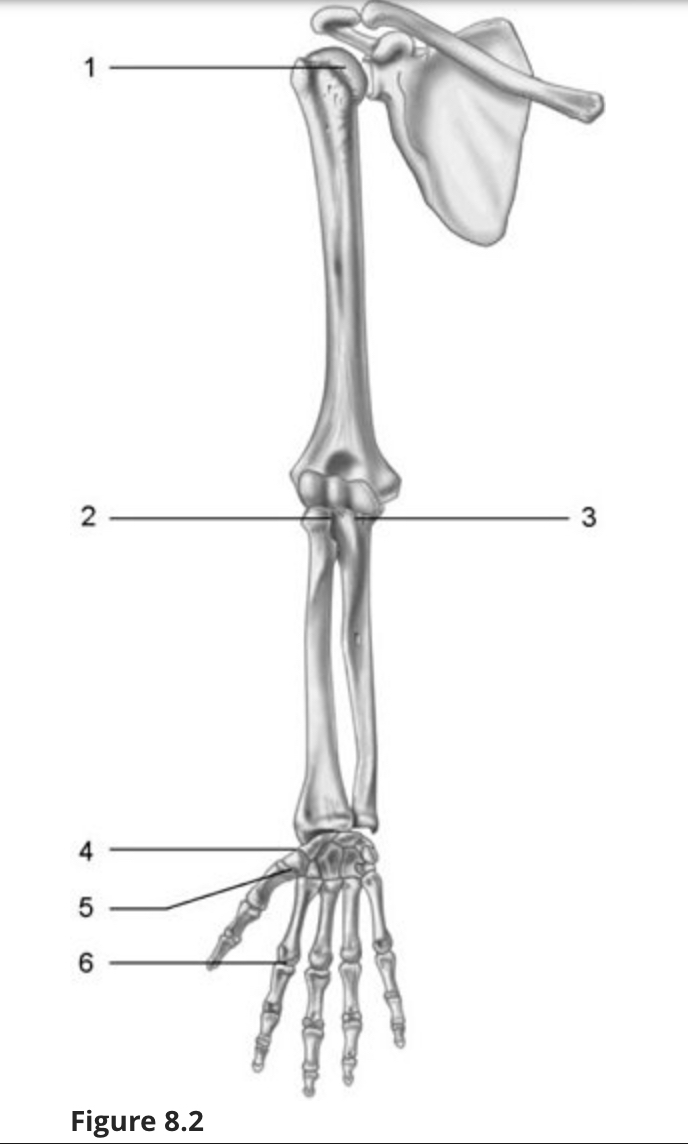
Using Figure 8.2, what type of axial movement does each joint have?
Multiaxial
Uniaxial
Uniaxial
Nonaxial
Biaxial
Biaxial
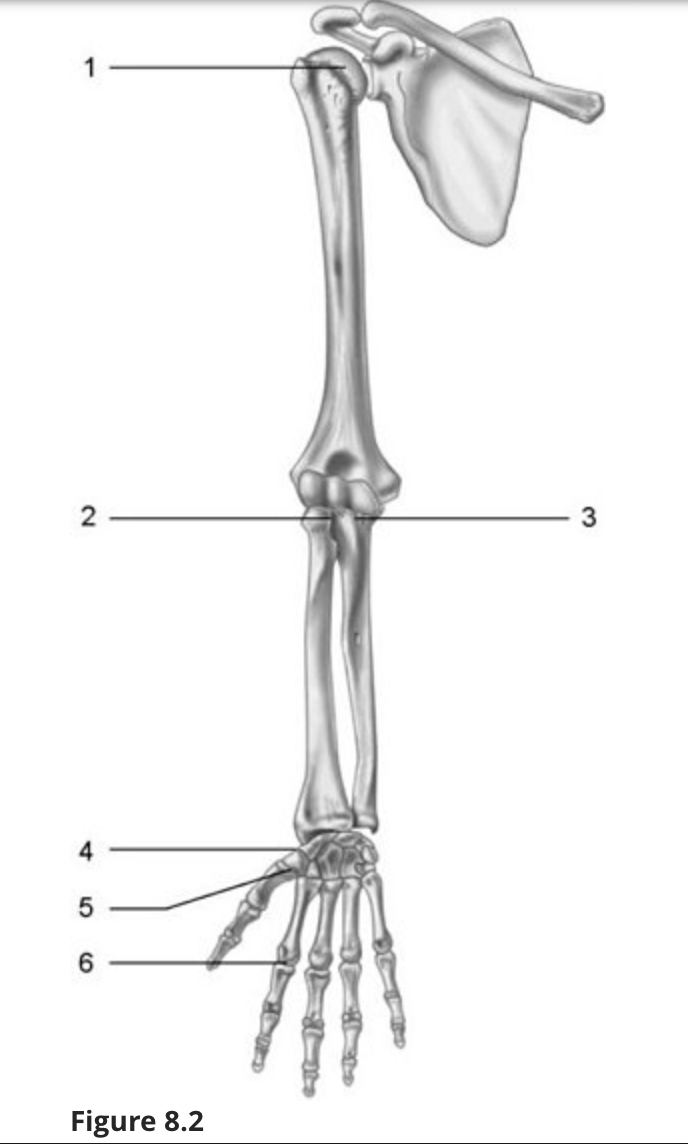
Using Figure 8.2, identify each type of synovial joint by name.
Ball and socket
Pivot
Hinge
Plane
Saddle
Condyloid
The lacunae of osseous tissue contain
bone marrow.
capillaries.
blood cells.
chondroblasts.
osteocytes.
osteocytes.
Which of the following bones is classified as "irregular" in shape?
ulna
metatarsal
patella
vertebra
frontal
vertebra
The location where two bones meet is called a joint, or an
articulation.
appendix.
adduction.
insertion.
amphiarthrosis.
articulation.
Yellow bone marrow contains a large percentage of ________.
fat
elastic tissue
Sharpey's fibers
blood-forming cells
fat
An immovable joint is a(n)
syndesmosis.
diarthrosis.
amphiarthrosis.
synarthrosis.
symphysis.
synarthrosis.
Wolff's law is concerned with ________.
vertical growth of bones being dependent on age
the function of bone being dependent on shape
the thickness and shape of a bone being dependent on stresses placed upon it
the diameter of the bone being dependent on the ratio of osteoblasts to osteoclasts
the thickness and shape of a bone being dependent on stresses placed upon it
A freely movable joint is a(n)
symphysis.
diarthrosis.
synarthrosis.
syndesmosis.
amphiarthrosis.
diarthrosis.
The structural unit of spongy is called ________.
trabeculae
osseous lamellae
osteons
lamellar bone
trabeculae
Through the action of osteoclasts,
fractured bones regenerate.
bony matrix is dissolved.
new bone is formed.
an organic framework is formed.
osteoid is calcified.
bony matrix is dissolved.
The structural units of mature compact bone are called
canaliculi.
lacunae.
osteocytes.
lamellae.
osteons.
osteons.
A slightly movable joint is a(n)
diarthrosis.
synostosis.
amphiarthrosis.
synarthrosis.
gomphosis.
amphiarthrosis.
The term diploë refers to the ________.
double-layered nature of the connective tissue covering the bone
fact that most bones are formed of two types of bone tissue
two types of marrow found within most bones
internal layer of spongy bone in flat bones
internal layer of spongy bone in flat bones
An epiphyseal line is an example of a
syndesmosis.
synostosis.
symphysis.
gomphosis.
synchondrosis.
synostosis.
A synovial joint is an example of a(n)
synarthrosis.
symphysis.
diarthrosis.
syndesmosis.
amphiarthrosis.
diarthrosis.
The carpal bones are examples of ________ bones.
flat
short
sesamoid
long
irregular
short
Lengthwise, long bone growth during infancy and youth is exclusively through ________.
interstitial growth of the epiphyseal plates
calcification of the matrix of the zone underlying articular cartilage
the secretion of bone matrix into the medullary cavity
differentiation of osteoclasts into osteocytes
interstitial growth of the epiphyseal plates
The periosteum is secured to the underlying bone by dense connective tissue called ________.
perforating (Sharpey's) fibers
a bony matrix with hyaline cartilage
Volkmann's canals
the struts of bone known as spicules
perforating (Sharpey's) fibers
Osteogenesis is the process of ________.
bone destruction to liberate calcium
making a cartilage model of the fetal bone
bone formation
making collagen fibers for calcified cartilage
bone formation
What kind of tissue is the forerunner of long bones in the embryo?
fibrocartilage
elastic connective tissue
hyaline cartilage
dense fibrous connective tissue
hyaline cartilage
A rib is an example of a ________ bone.
flat
long
sesamoid
short
sutural
flat
Bones that develop within tendons are called ________ bones.
Wormian
tendon
irregular
sutural
sesamoid
sesamoid
The canal that runs through the core of each osteon (the Haversian canal) is the site of ________.
blood vessels and nerve fibers
cartilage and interstitial lamellae
yellow marrow and spicules
adipose tissue and nerve fibers
blood vessels and nerve fibers
The cell responsible for secreting the matrix of bone is the ________.
osteoclast
osteoblast
chondrocyte
osteocyte
osteoblast
A suture is an example of a(n)
symphysis.
synarthrosis.
diarthrosis.
syndesmosis.
amphiarthrosis.
synarthrosis.
Dense connective tissue is to a suture as a periodontal ligament is to a(n)
synostosis.
synchondrosis.
amphiarthrosis.
gomphosis.
syndesmosis.
gomphosis.
Which of the following is the single most important stimulus for epiphyseal plate activity during infancy and childhood?
thyroid hormone
parathyroid hormone
calcium
growth hormone
growth hormone
Bones are covered and lined by a protective tissue called periosteum. The inner (osteogenic) layer consists primarily of ________.
marrow and osteons
osteoblasts and osteoclasts
cartilage and compact bone
chondrocytes and osteocytes
osteoblasts and osteoclasts
When the epiphyseal plate is replaced by bone,
long bones have reached their adult length.
the bone becomes more brittle.
interstitial bone growth begins.
puberty begins.
appositional bone growth begins.
long bones have reached their adult length.
The process of bones increasing in width is known as ________.
epiphyseal plate closure
concentric growth
appositional growth
closing of the epiphyseal plate
appositional growth