chemistry unit 5 test
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
why do atoms bond?
atoms bond to become more stable, by filling their outer electron shell. Either through sharing electrons (covalent) or by transferring electrons (ionic).
goal is to lower enegery and to be more stable
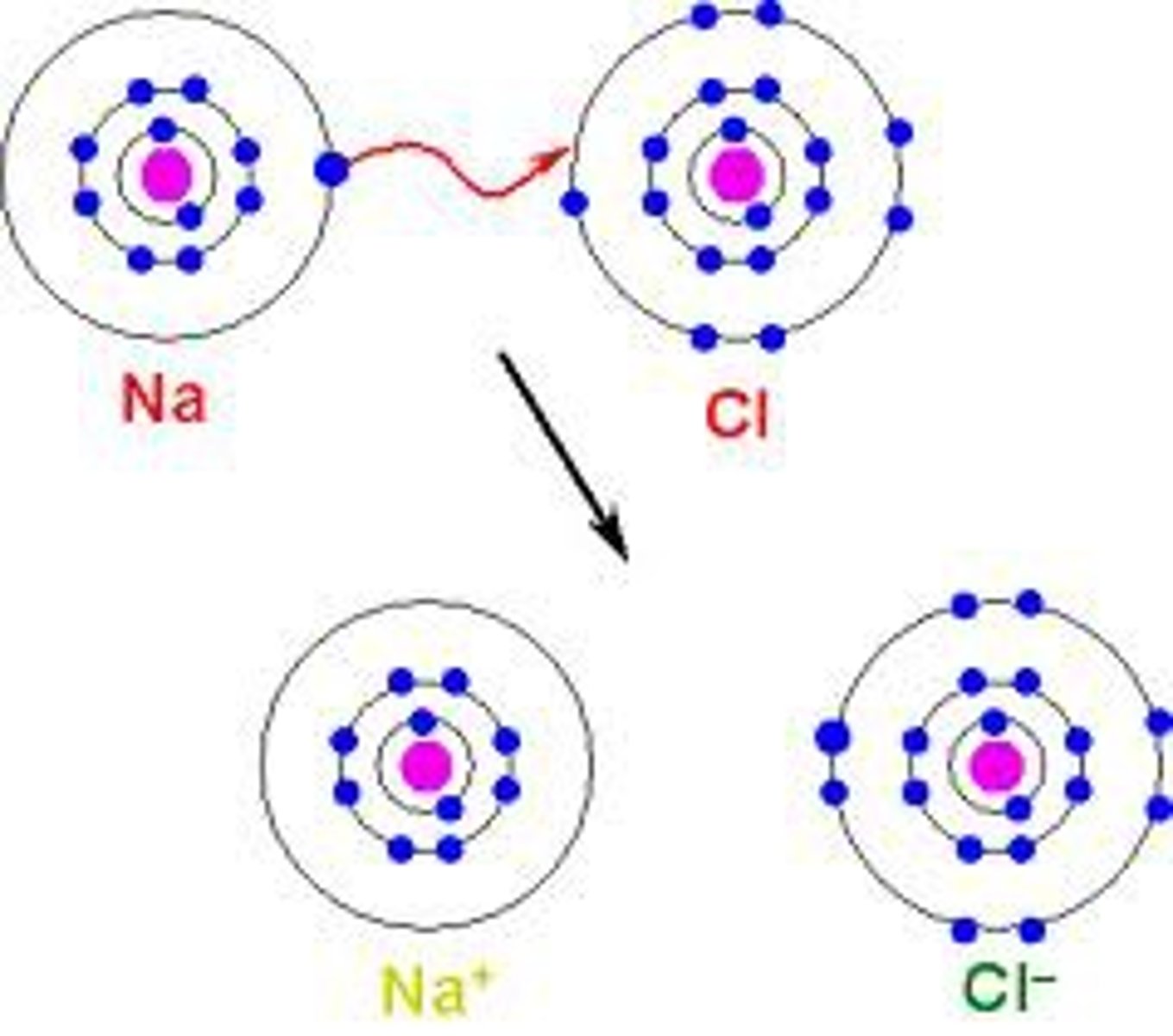
ionic bond
- metal + nonmetal
- transfer of electrons
- creates oppositly charged ions that attract each other
- one atoms looses electrons (metal) and becomes a cation and another (nonmetal) gains those electrons and becomes an anionnon
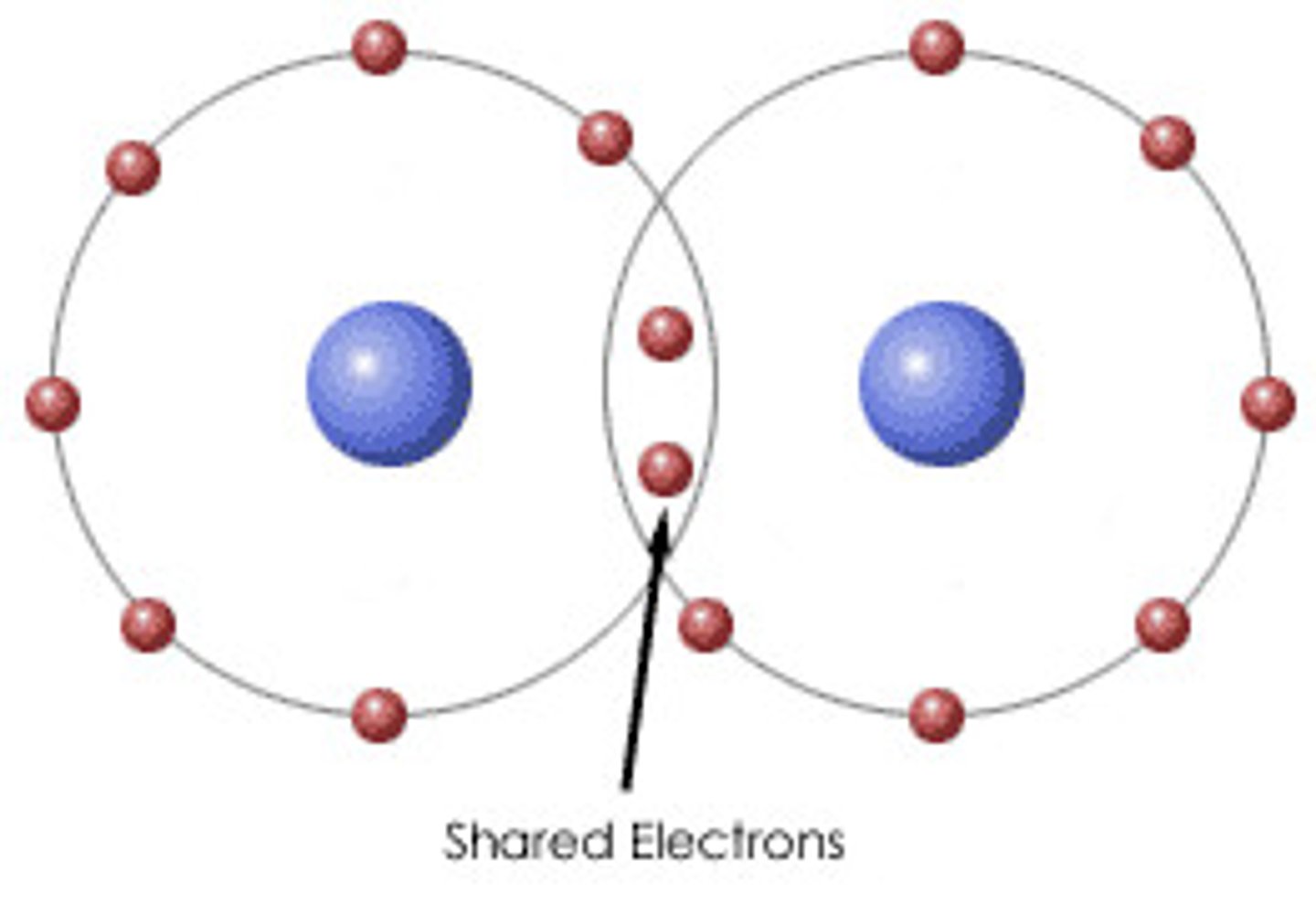
covalent bond
- nonmetal + nonmetal
- metalloid + nonmetal
- share electrons to fill outer shell
- the more electrons are share, the stronger the bond is
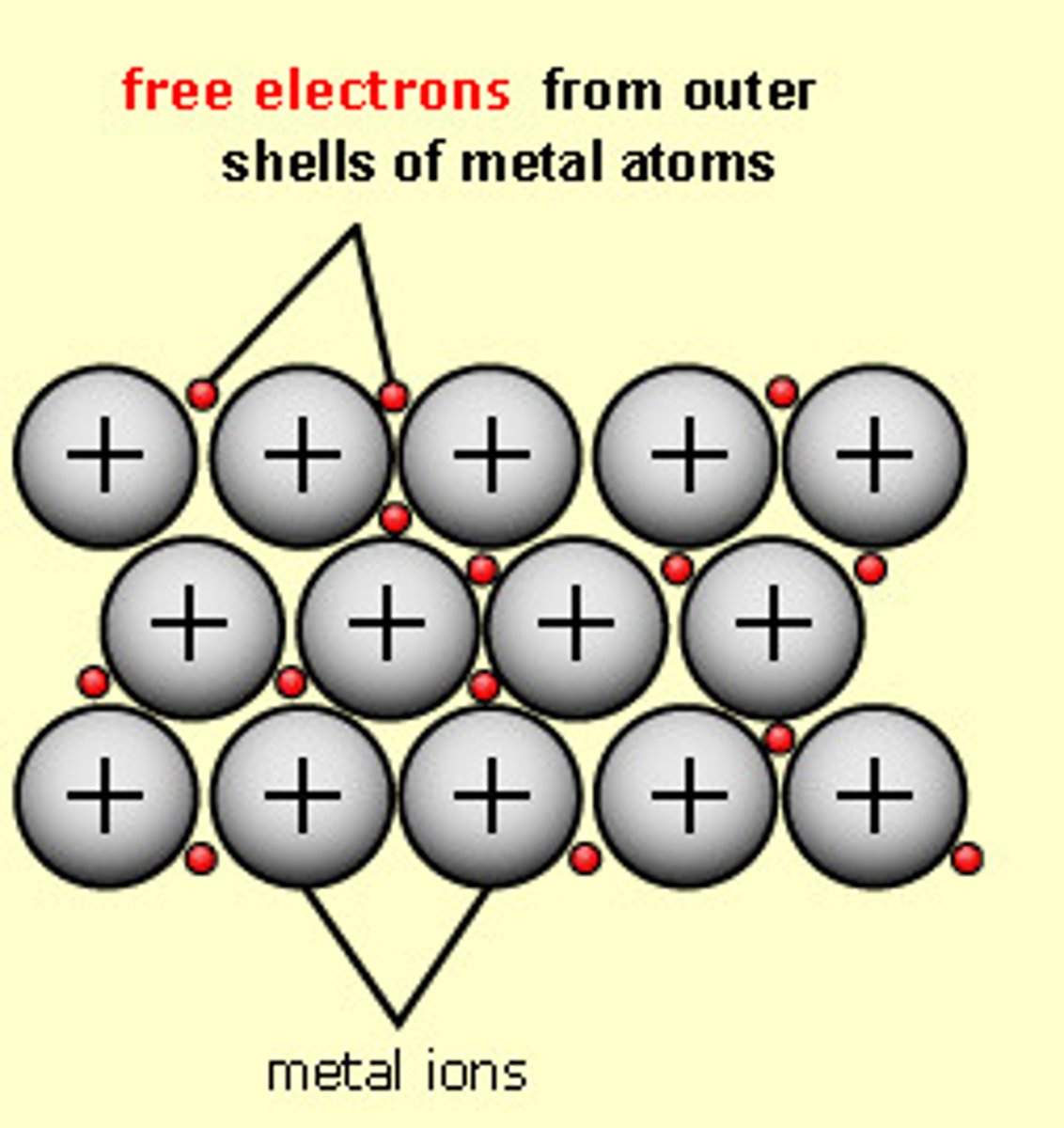
metallic bond
- metal + metal
- electrons flow freely
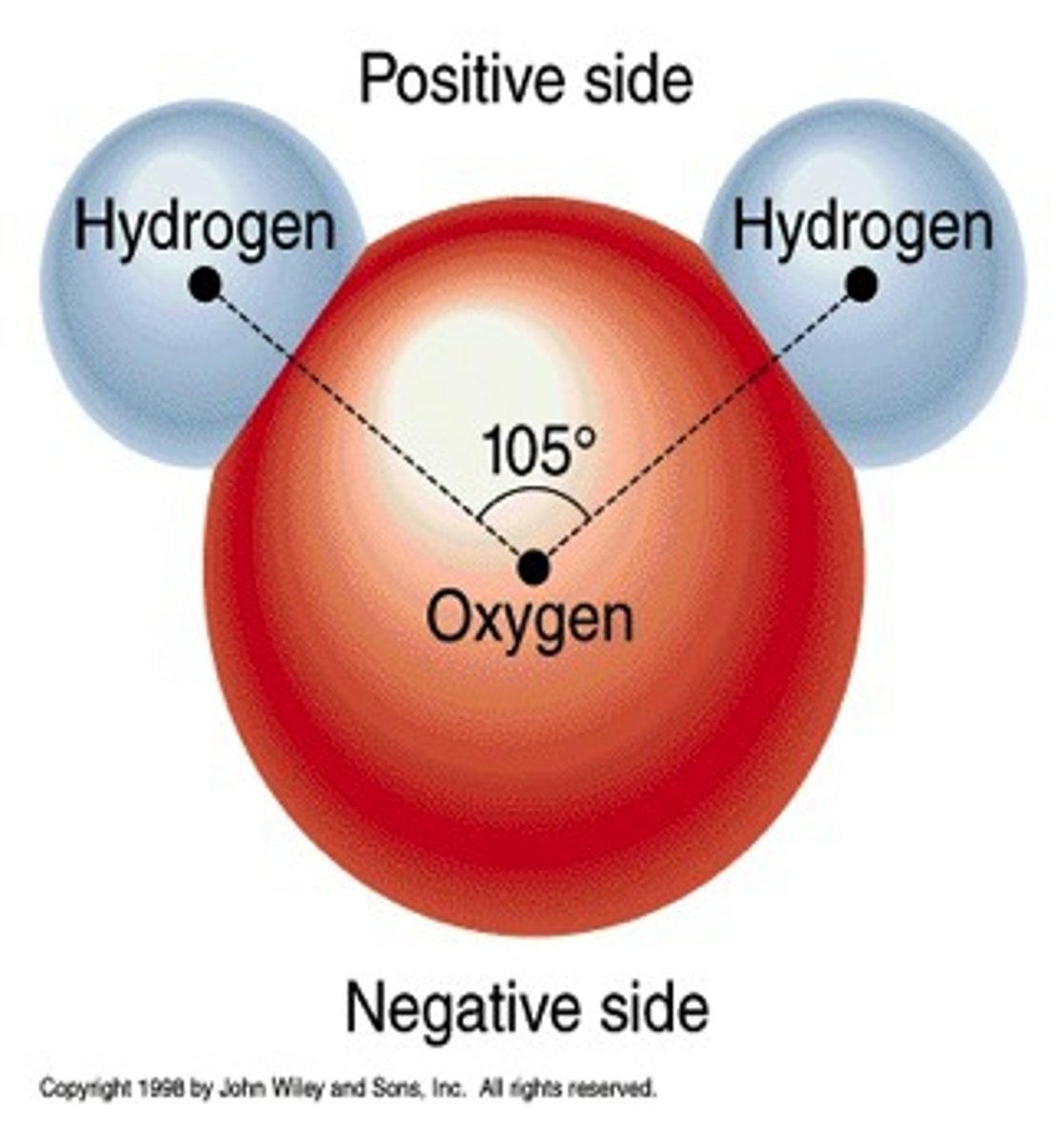
polar covalent bond
- electrons are shared unequally
- this is because one atom has a stronger electronegativity
- atom with higher electronegativity pulls
nonpolar covalent bond
- electrons are shared equally since they have similar electronegativity
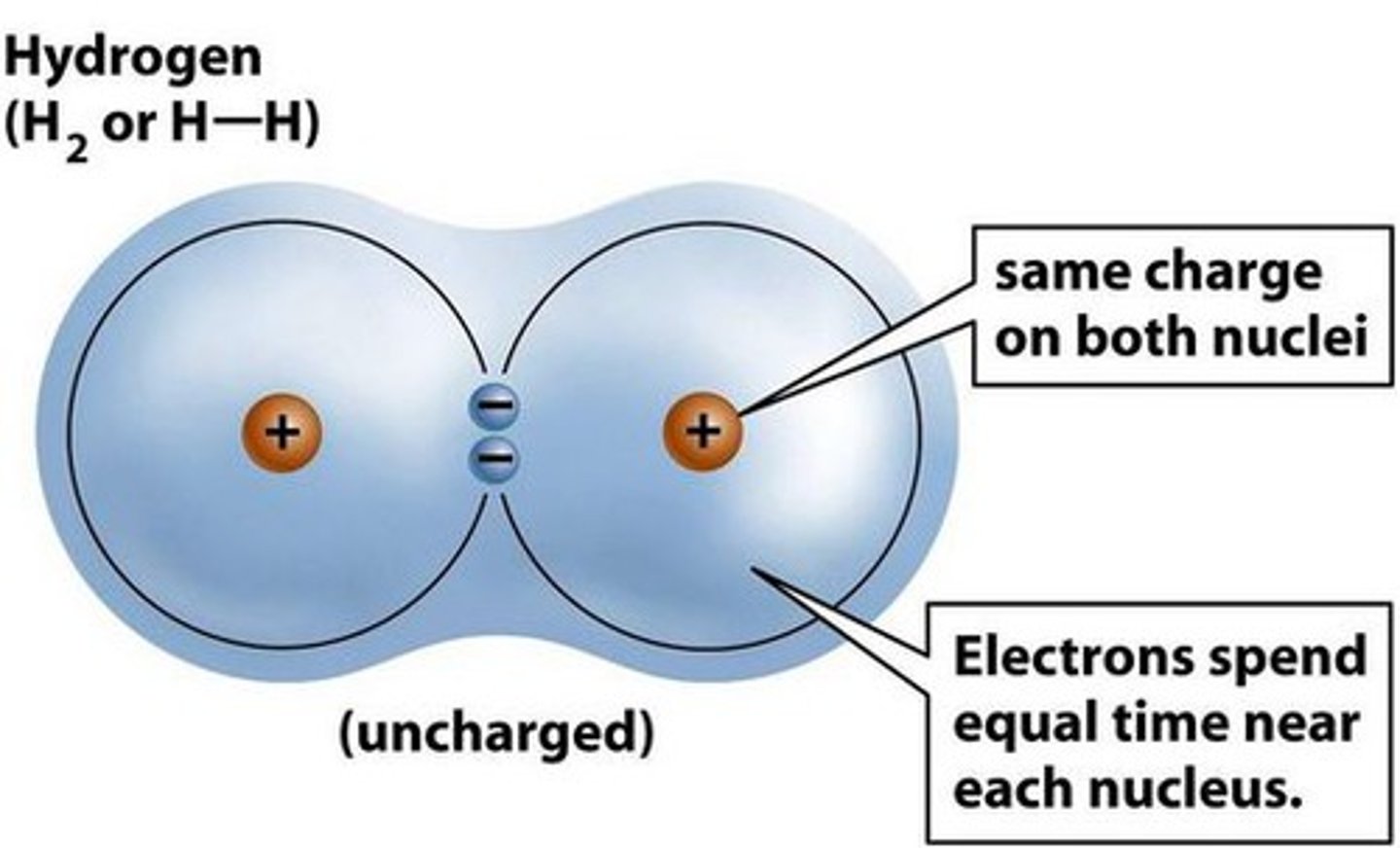
electronegativity
the ability of an atom to attract electrons in a bond
how to find electronegativity
- find electronegativity on periodic table (bottom number on the right)
- subtract to find the difference between the 2 atoms
- observe data and look at periodic table bottom left corner
Why would atoms need to form double or triple bonds rather than just single bonds ?
if a single bond is not enough to satisfy their need for a full outer electron shell
when electrons are transferred in an ionic bond, what is formed?
IONS
- cations and anions
cation
- positively charged
- formed when electrons are lost
- typically formed by metals
anion
- negatively charged
- formed when electrons are gained
- typically formed by nonmetals
molecule
a compound held together by a covalent bond
(H2O, CO2)
ionic compound
a compound that is held together by an ionic bond
(NaCl)
1
mono
2
di
3
tri
4
tetra
5
penta
6
hexa
7
hepta
8
octa
9
nona
10
deca
rules of covalent bonding naming
- "ide" is the ending of the second element in the compound
- if the prefix ends in (a) or (o), and the name of the element starts with a vowel, then the (a) or (o) is dropped
- the prefix mono is not used on the first element if there is only one atom of it
Do we need prefixes for naming ionic compounds?
no
polyatomic ion
ion that has more than one atom
- the two atoms are covalently bonded
(nitrate, sulfate...)
empirical formula
gives a simplified ratio of elements in a compound, not the exact number of atoms
molecular formula
exact number of atoms of each element in a compound
single bond
- shares 2 electrons (1 pair)
- formed by sharing one pair of electrons between 2 atoms
- weak bond strenght
- longest bond strenght
double bond
- shares 4 electrons (2 pairs)
- formed by sharing two pairs of electrons between 2 atoms
- stronger bond strenght than single bond, yet weaker than triple bond
- longer bond lenght (not the longest)
triple bond
- shares 6 electrons (3 pairs)
- formed by sharing 3 pairs of electrons between 2 atoms
- strongest bond strenght
- shortest bond lenght