Unit 8.1 The Atmosphere
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
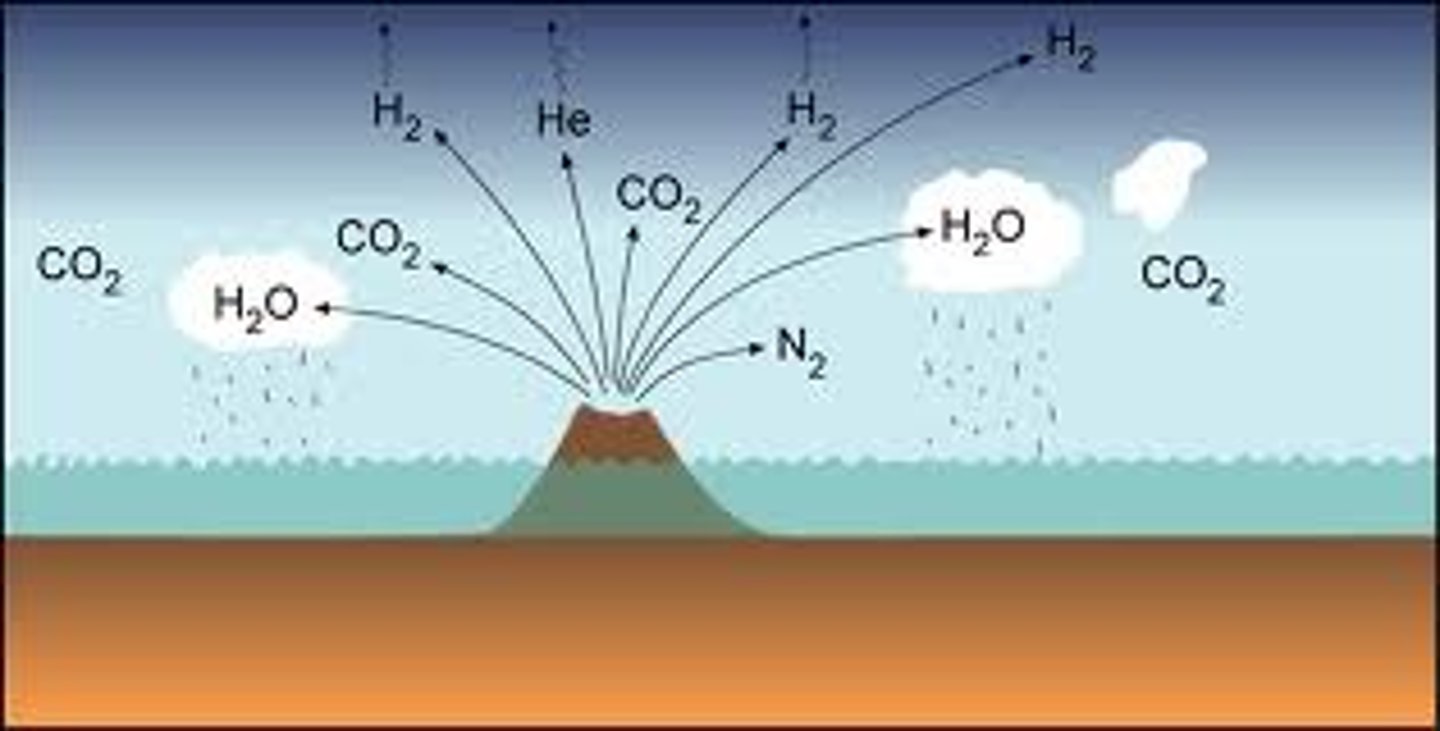
Main Gas in Earth's Early Atmosphere
Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
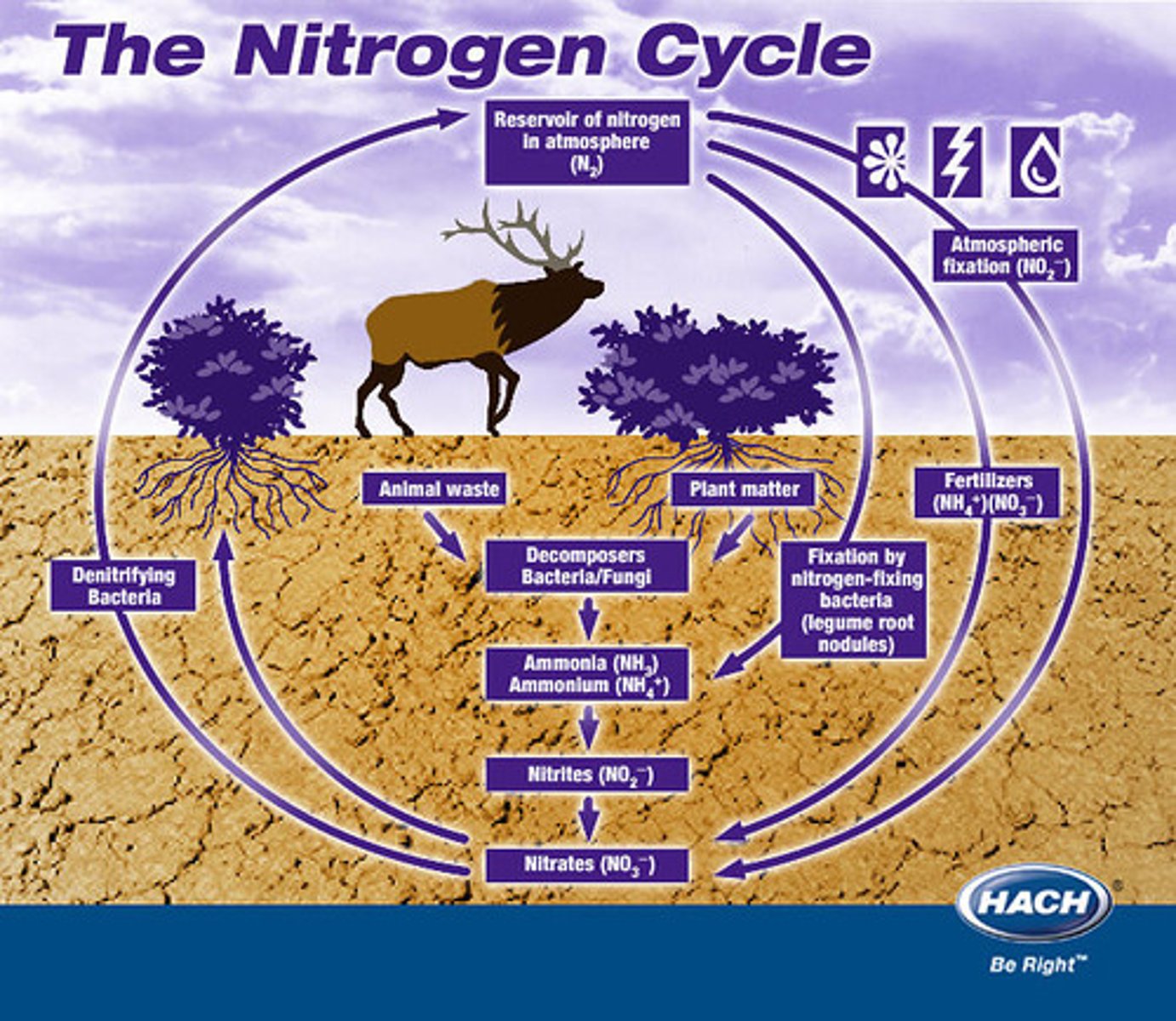
Main Gas in Earth's Current Atmosphere
Nitrogen (N2)
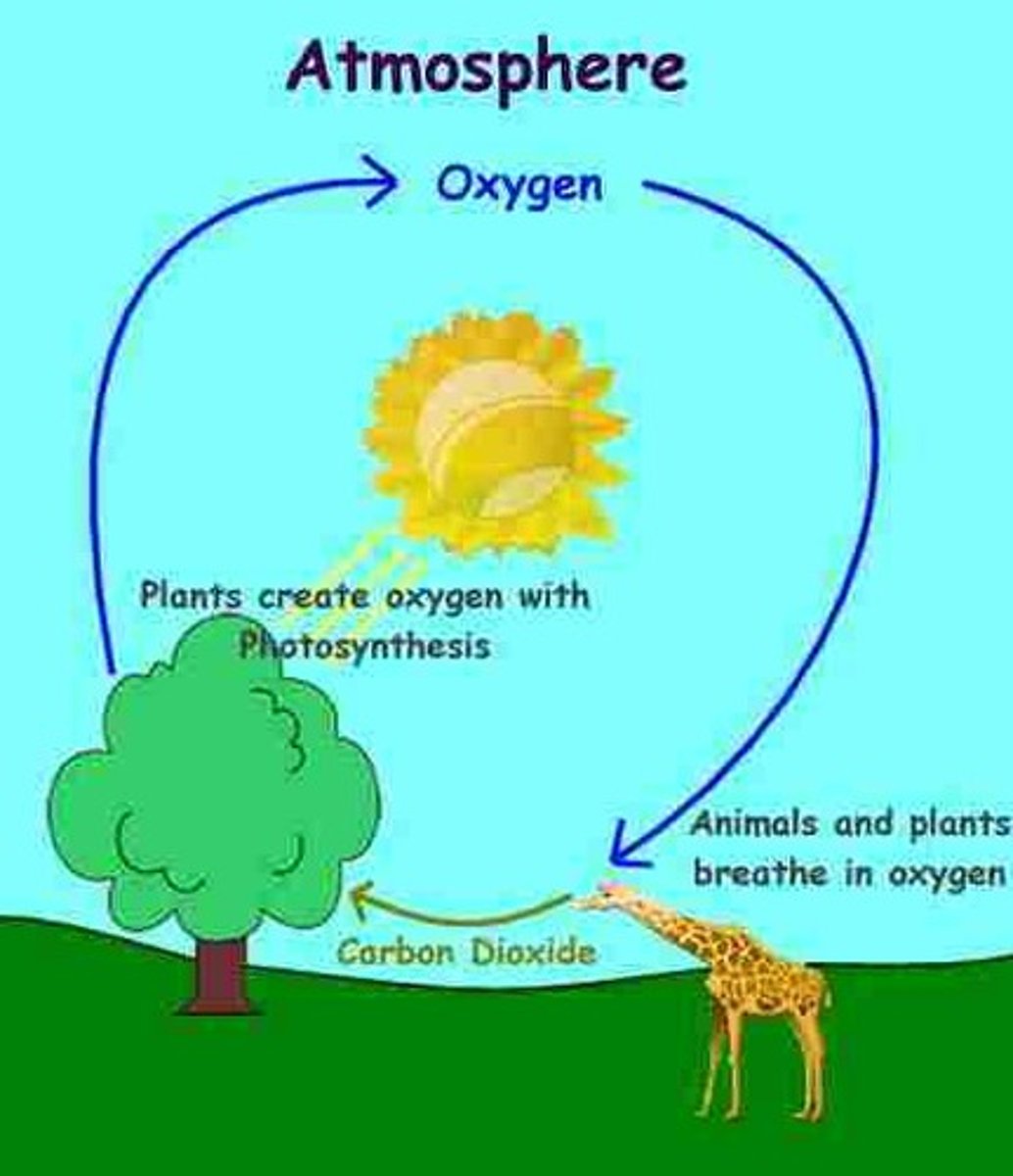
Gas that built up in the atmosphere due to photosynthesis
Oxygen (O2)
Temperature
A measure of the average energy of motion of the particles of a substance.
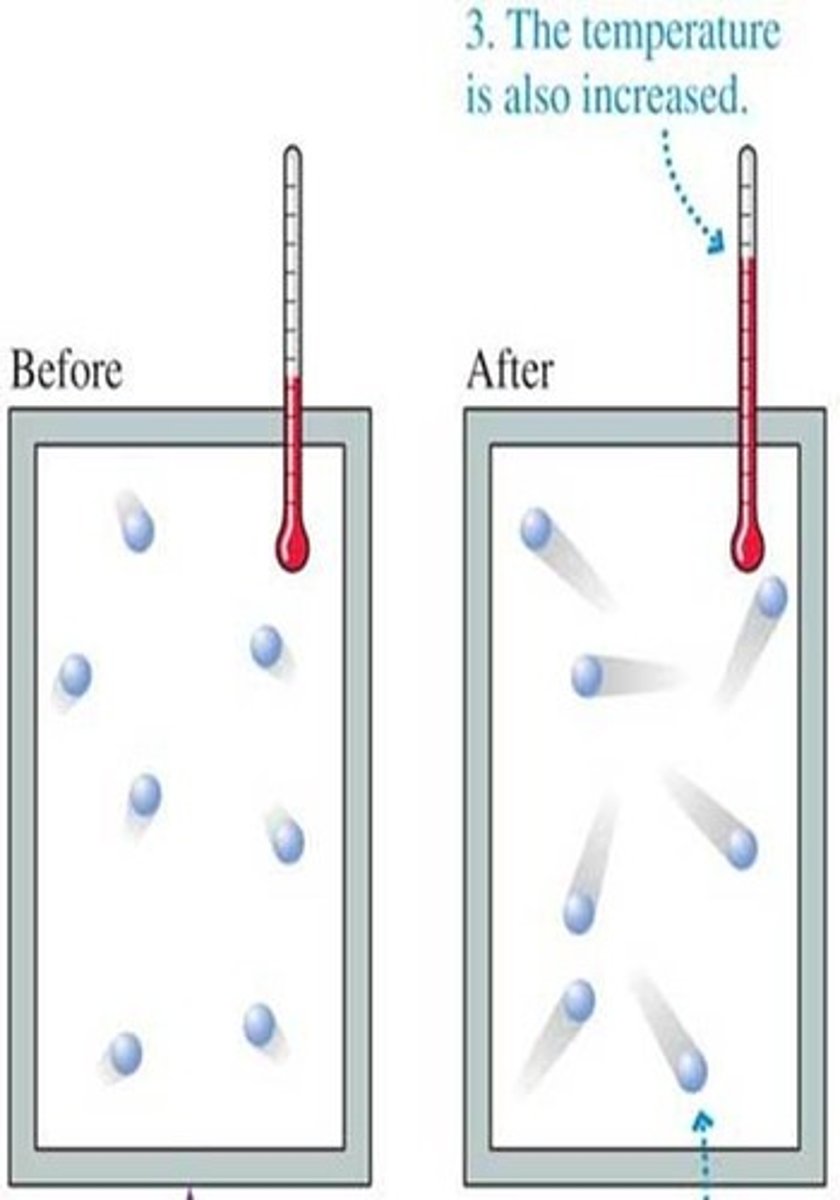
Heat
The energy transferred between objects that are at different temperatures; measured as the total amount of kinetic energy in all the particles of a substance
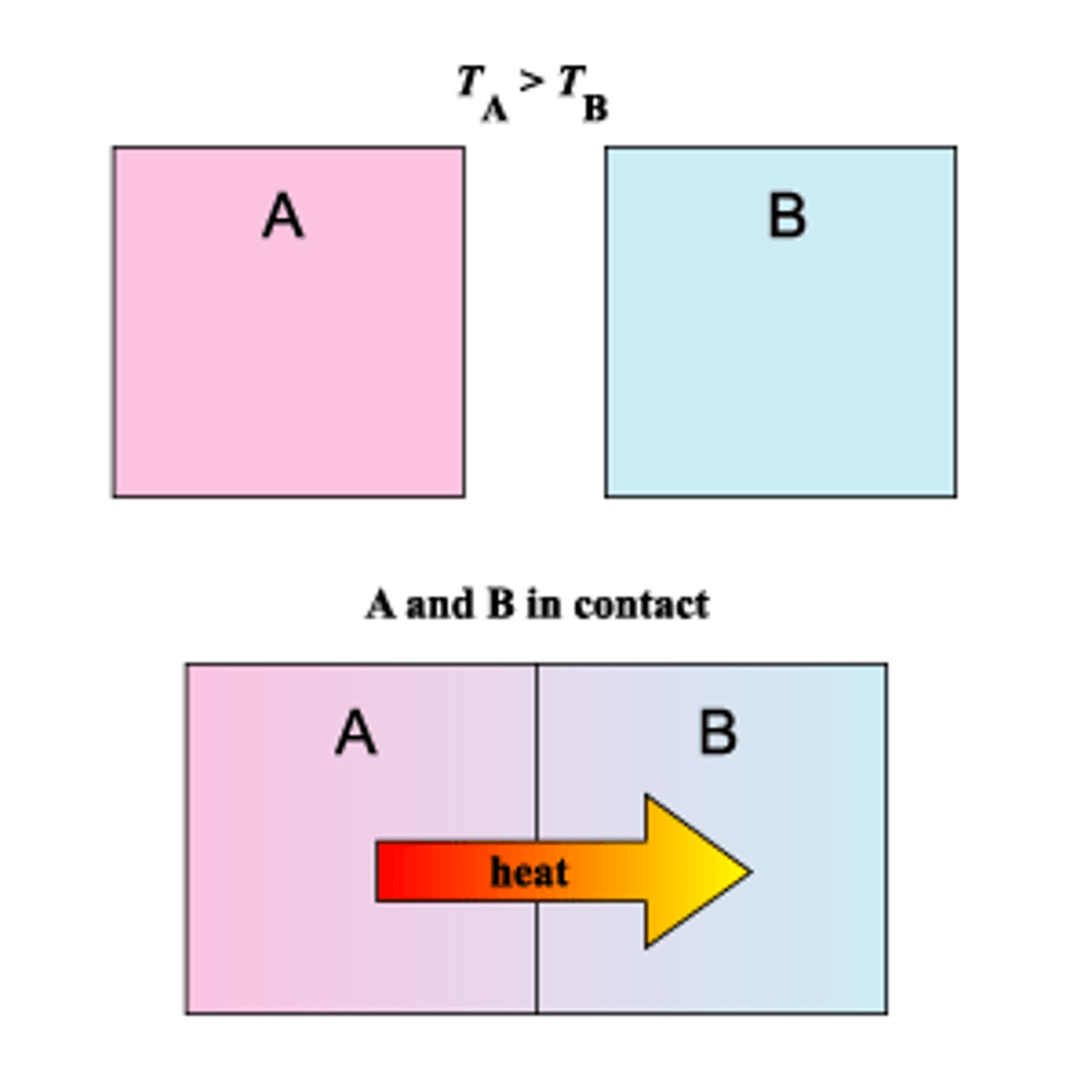
heat vs temperature
heat is about energy moving from one object to another when the temperatures of the two objects are different; temperature measures the average energy of motion of particles in one substance.
Troposphere
Lowest layer of the atmosphere, 0-10mi above Earth's surface, site of weather, organisms, contains most atmospheric water vapor; temperature decreases with increasing altitude, pressure decreases
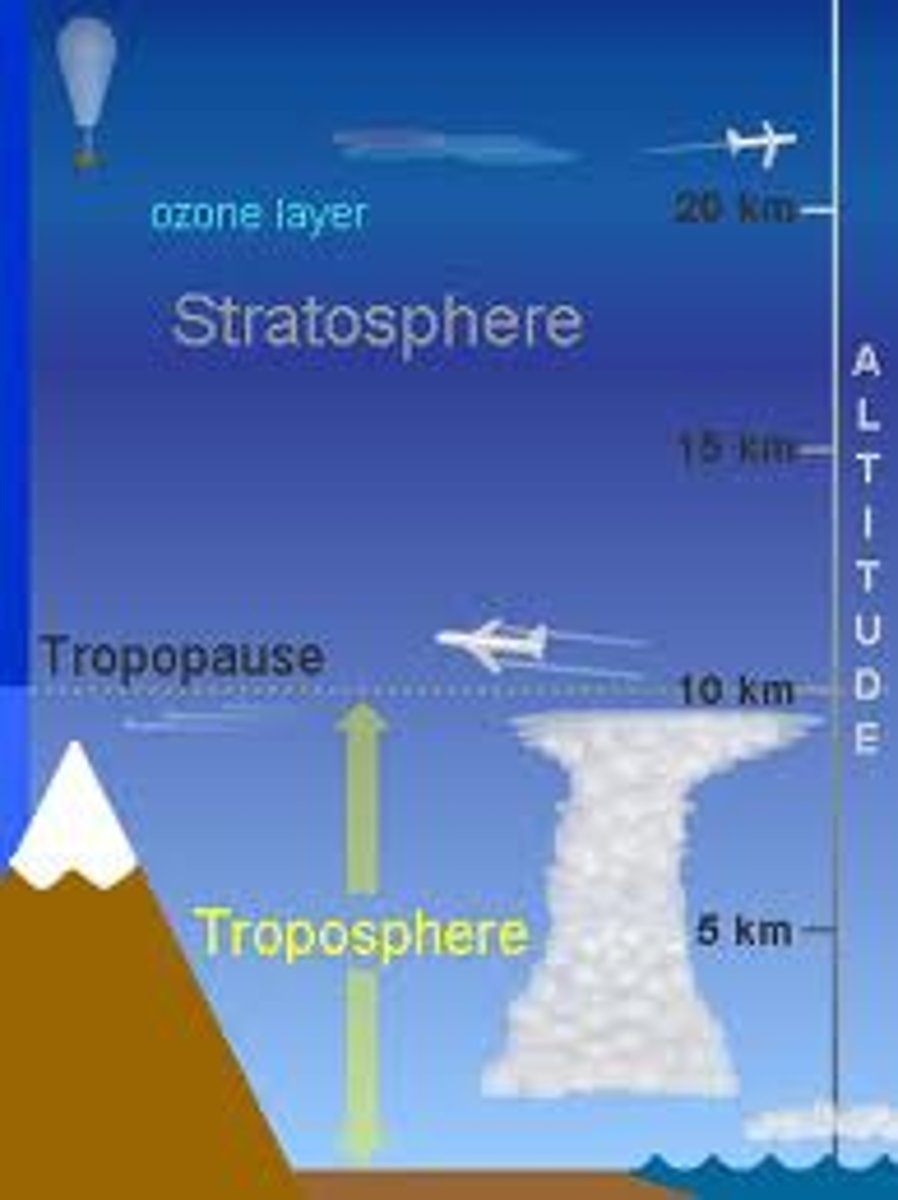
Stratosphere
2nd layer of atmosphere; extends from 10 to 30 miles up; location of ozone layer; absorbs 95% of Ultraviolet radiation; temperature increases with altitude increase.

Mesosphere
3rd layer of the atmosphere; temperature decreases with altitude; meteors burn up in this layer because of the presence of more particles than the outer layers.

Thermosphere
the region of the atmosphere above the mesosphere and below the height at which the atmosphere ceases to have the properties of a continuous medium. Temperature increases with altitude
Exosphere
The outer layer of the thermosphere, extending outward into space; the layer from which particles are lost to space

Insolation
incoming solar radiation
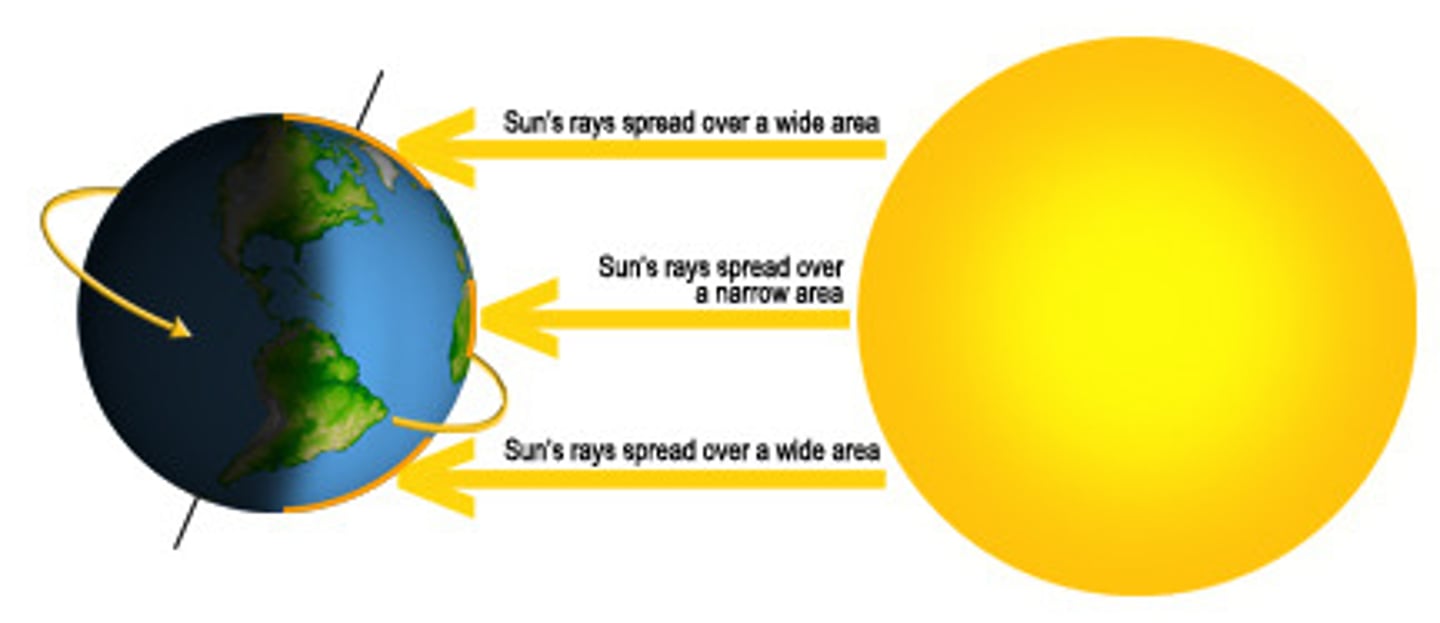
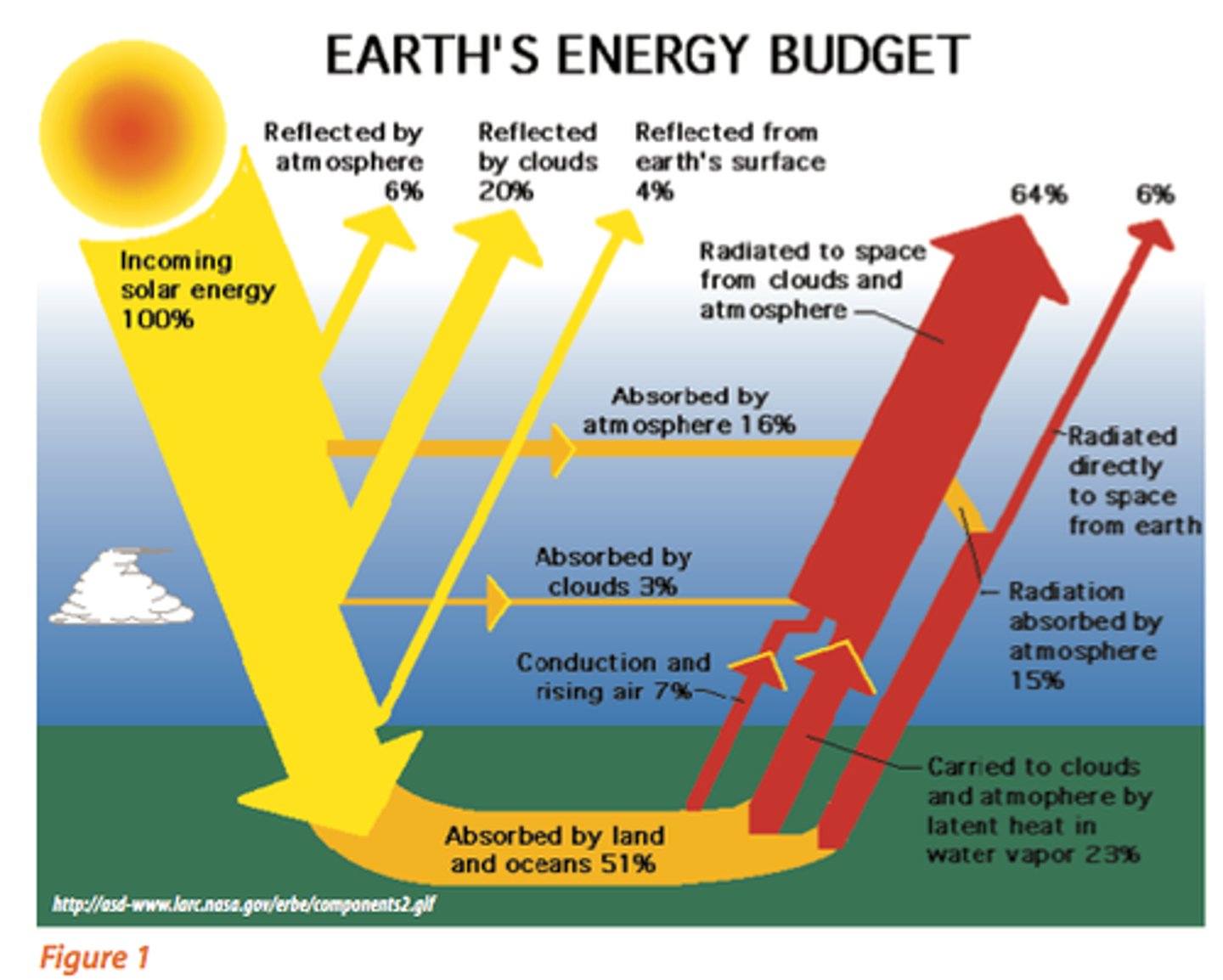
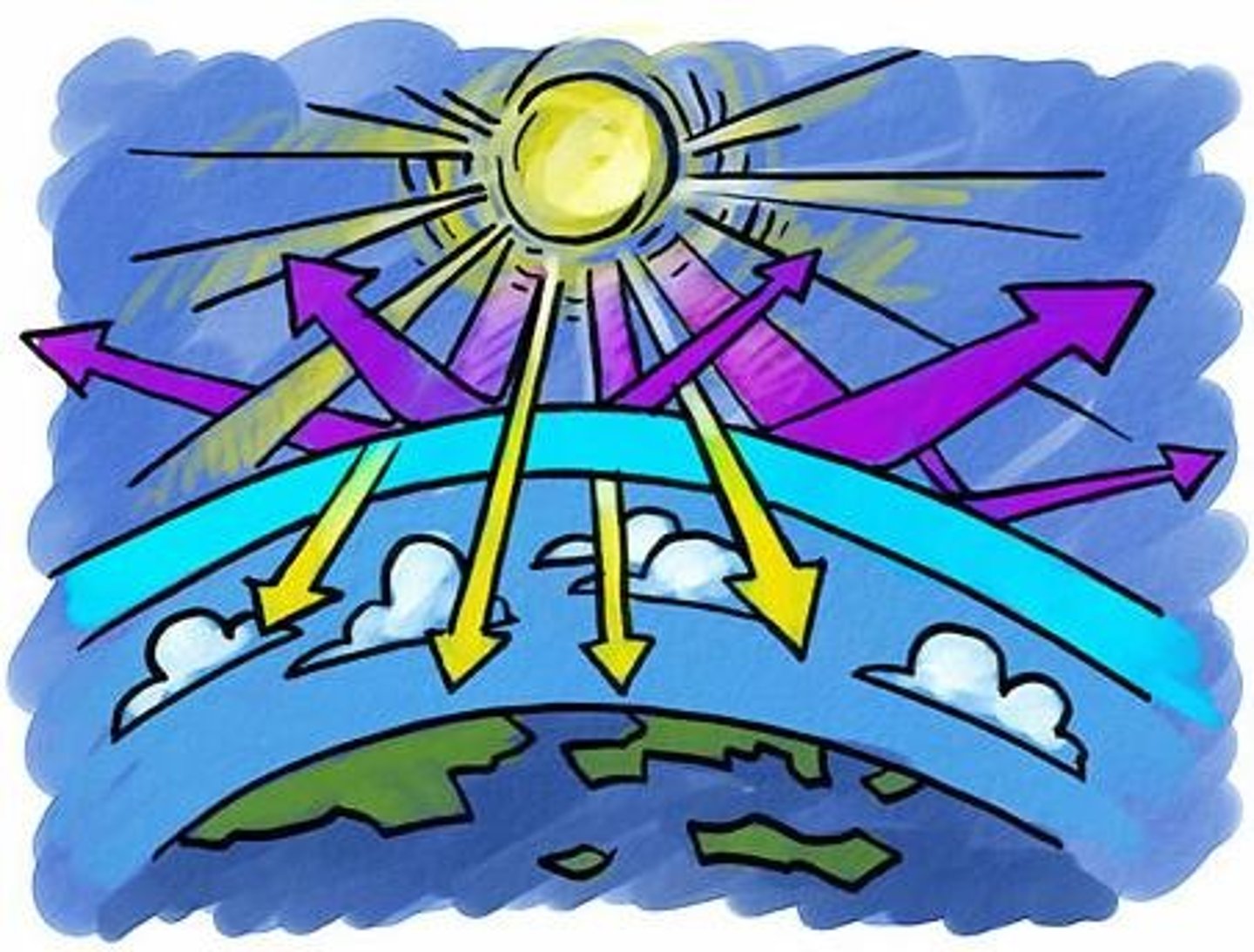
Heat budget
An expression of the total solar energy received on Earth during some period of time and the total heat lost from Earth by reflection and radiation into space through the same period.
faster
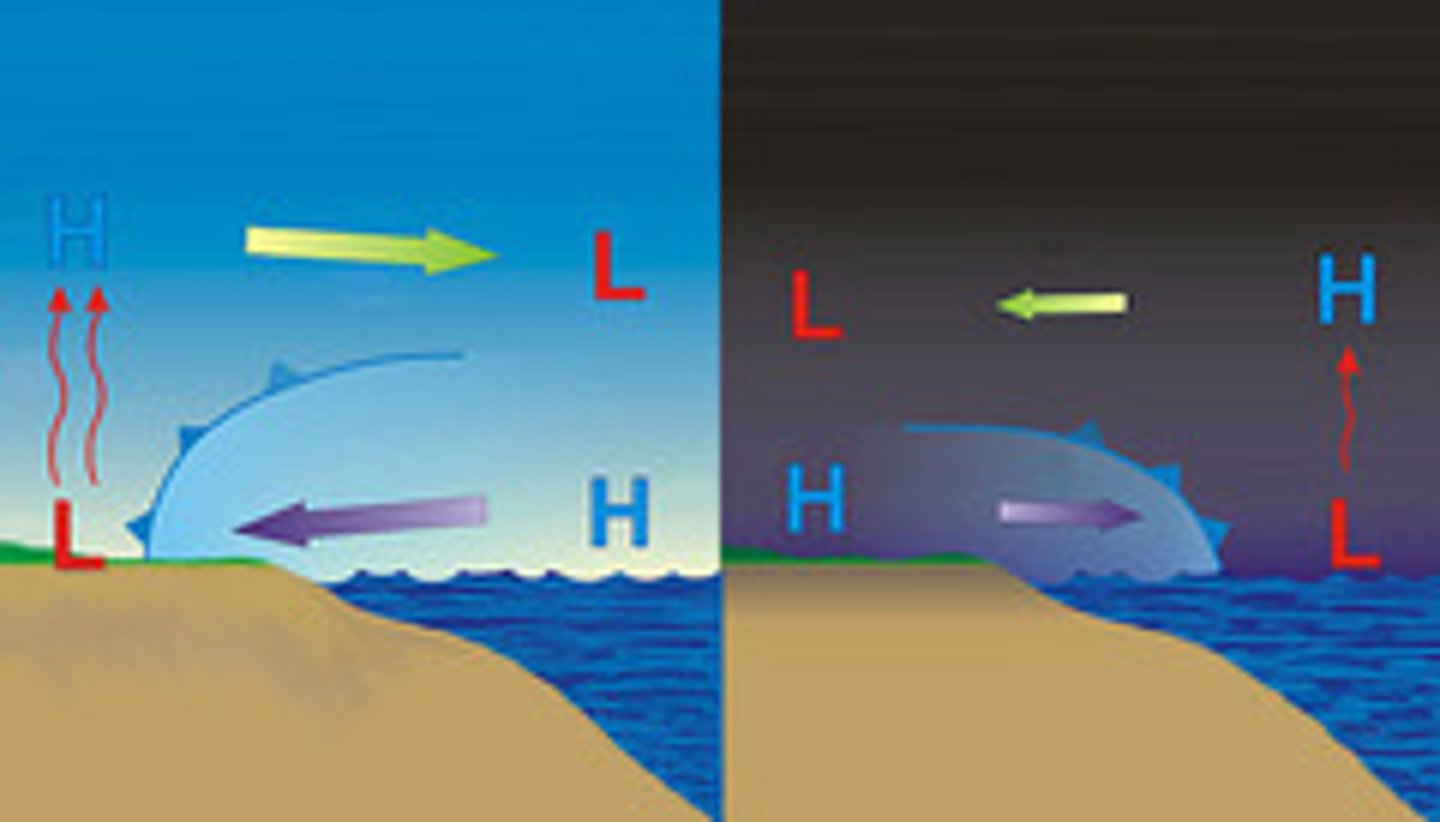
Land heats (faster, slower) than water

slower
Water cools (faster, slower) than land
smog
fog or haze combined with smoke and other atmospheric pollutants.

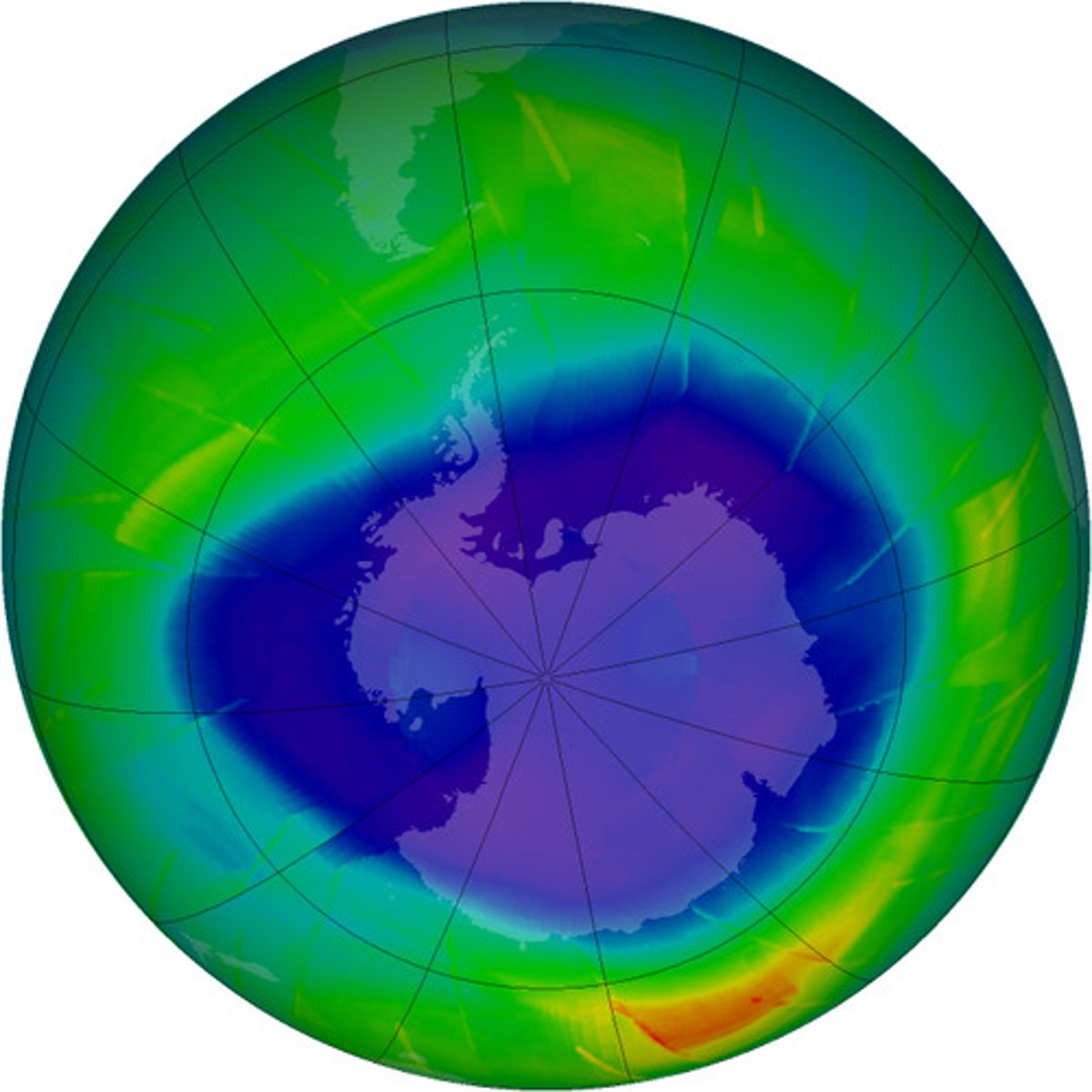
ozone layer
Protective layer in atmosphere that shields earth from UV radiation.

ozone depletion
thinning of Earth's ozone layer caused by CFC's leaking into the air and reacting chemically with the ozone, breaking the ozone molecules apart
global warming
a gradual increase in the overall temperature of the earth's atmosphere generally attributed to the greenhouse effect caused by increased levels of carbon dioxide, chlorofluorocarbons, and other pollutants.
greenhouse effect
Natural situation in which heat is retained in Earth's atmosphere by carbon dioxide, methane, water vapor, and other gases
heat budget
the annual balance of incoming and outgoing radiation to keep the Earth's temperature relatively constant
air pressure
The measure of the force with which air molecules push on a surface
