Leukocytes
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Leukocytes
white blood cells
leukopoiesis
process of forming leukocytes.
all leukocytes originate from?
hematopoietic stem cells. Stimuli dependent in a “one way” path.
Hematopoietic stem cells
blood stem cells. immature cells found in bone marrow that can differentiate into all types of blood cells, including leukocytes.
CSF colony stimulating factors
So if its neutrophils, has to be a specific factor that’s going to stimulate neutrophil production. same thing with eosinophils and so on. in a “one way” path of development.
white blood cells form
bone marrow in most and some form in lymphoid tissues, lymphatic tissues (lymphocytes)
Are white blood cells being constantly procduced
Yes, but not released the same way as red blood cells. Only released when needed.
Granulocytes
Type of leukocyte that contatin granules in their cytoplasm. Neutrophils- neutral stain. Eosinophils- red/orange stain. Basophils- blue/purple stain.
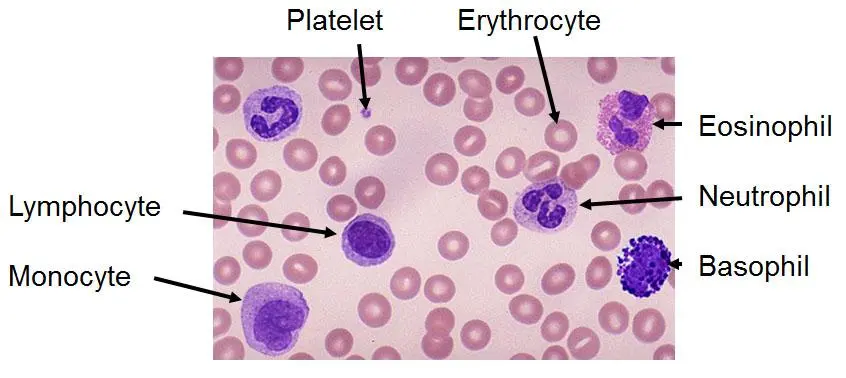
Agranulocytes
without granules. Monocytes and Lymphocytes
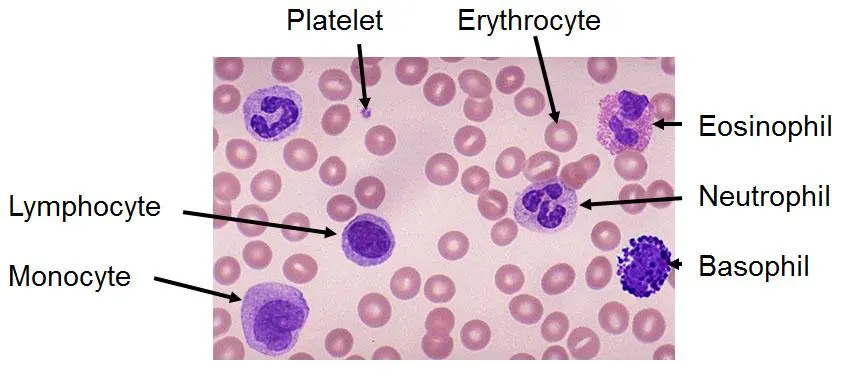
Number of WBC
way way less than RBC.
Variations in numbers of WBC
depends on species. It can vary but we have come up with normal ranges for each. like how many basophils neutrophils they need etc.
Physiology change in WBC count
may look different/ can change really fast because of stress, exercise, age, etc.
Pathology changes in WBC count
changes from infections (bacterial/viral), endocrine disorders. (cushings), immune mediated diseases (something wrong with immune system). etc.
Primary function WBC
For defense(immunity).
Phagocytes (non-specific)
Non-specific immunity. thats gonna be your granulocytes(nutraphils,basophils,eosinaphils) and Agranulal (monocytes).
Immunocytic (specific)
Lymphocytes. For specific immunity. Means creating antibodies against a specific antigen.
Immunocytic B cells
Ones that create the antibodies. or humoral immunity. In liquid (Plasma).
immunocytic T cells
cell-mediated immunity. produce cytokines(substances that draw other things in) also Natural killer cells and will kill and attack abnormal cells like tumor or virus infected.
Phagocytic process stage 1
Chemotaxis (draws things in, that attraction) because the phagocytic cells are mobile so they move it it. Really common with inflammatory responses and infection in tissues.
Potent chemotaxins
Lipopolysaccharides and substances that the immune system puts out think of abscess. all attracted to infection and inflammation puss is a bunch of white dead blood cells.
Phagocytic process stage 2
Adhere (stick to what it’s going to eat) does it because of surface receptors. Opsonization - enhances sticking together, antibody/complement more adhesive!
Phagocytic process stage 3
wbc actually engulfs whatever it’s stuck too. Endocytosis. enzymes that can get in there and kill/destroy whatever it is.
Neutrophils
Most common (dogs,cats,horses) , abundant cytoplasm, pale pink granules, dark lobulated nucleus. another name- PMN(polymorphonucluar wbc- means lobulated)
Speices variation- no neutrophils they have?
Heterophils (rabbits,avian,reptiles,amphibians)
Band neutrophils
immature , young neutrophils, look like horse shoe. (say infection so spitting out lots even immature to help fight infection.
how long does it take for neutrophils to mature
3-6 days
Neutrophils Proliferating pool (where there at) dividing
Myeloblasts(young cells) then change to promyelocytes and then myelocytes
Neutrophils Maturing pool non-dividing
Myelocytes to metamyelocytes to band cells.
Neutrophils Storage pool
already/always mature and just waiting to come out. About a five day supply of these just inside there where they are made in the bone marrow.
neutrophils wbc Inside blood vessels its called (playing)
intravascular pool. it’s a circulating pool around for about 10 hours. When taking blood sample your counting the circulating wbc. (out on field)
neutrophils another wbc inside blood vessels (on the walls)
marginating pool . In reserve. (sitting on the bench) On the vessel walls just waiting. more than circulating pool.
Diapedesis
neutrophils getting out of the blood vessels to reach tissues. then they die hopefully after destroying what they were after.
primary function of neutrophils
phagocytosis, specifically bacterial response. have bacteria infection-high neutrophil count. usually one of first responders for that inflammation cause of chemotaxis.
neutrophils limited due to differentiation
can’t divide or regenerate. the granules start to go away , membrane gets lost in phagocytosis. get small to a certain point and then they are gone.
neutrophils response
neutrophillia(likes neutrophils) means more neutrophils.
Degenerative left shift
neutrophils Band cells (young cells) and start seeing more band than mature cells. affection is really bad.
Neutropenia (neutrophils)
absence of. Not has many as there’s supposed to be. can cause leukopenia(low white cells)
neutropenia can occur cause
excessive use of them ,could be because of bad infection. Also low production like viral diseases (parvo)
Eosinophils
red/orange granules. Appearance- Canine(light,round except greyhound) Feline(darker,small rods) Equine(intense,large round) Bovine(red to pink,small round) Dark lobulated Nucleus.
Eosinophils -maturation and marrow/maturing/storage pools
same process has neutrophils. can tell the difference between the two by the granulas.
Eosinophils Intravascular pools/diapedesis
same has the neutrophils.
eosinophils functions
not fully understood what they do. They do have an anti-inflammatory response.(allergic response, mast cell degranulation, histamine inhibition, detoxification.
immunity-eosinophils
control of parasitic infection or allergic reaction. damages the parasite surface.
eosinophils- response
eosinophillia ( hypersensitivity-allergies or parasitic infection) Eosinopenia- hard to see cause theres not a lot to begin with.
Basophils
least common of the wbc. blue/purple granules. they are water soluble so may not see. nucleus lobulated.
basophil function
Initiates inflammation (due to histamine release), increases vascular permeability, and prevents coagulation by releasing heparin. May also help remove fat from blood vessels/serum.
Monocytes(agranualcytes) maturation/storage.
24-36 hours. Not stored. no storage pool. Once created and matured they are out in the circulating pool for 1-1 1/2 days.(24-36 hr)
Monocytes leaving blood vessels
Monocytes exit blood vessels via diapedesis into tissues, where they differentiate into macrophages. These macrophages are part of the Mononuclear Phagocytic System (MPS) that then leave tissue and become giant cells particularly during chronic inflammation. longest life span.
monocytes appearance
immature, largest WBC, pleomorphic nucleus(changes shape) usually no segments. abundant cytoplasm-pockets in cytoplasm , grey to blue color, big.
moncytes function
primarily phagocytosis. get ride of cellular/foreign debris. potent enzymes. non-specfic/specific immunity link. Antigen processing, numerous inflammatory mediators.
moncytes response
monocytosis (increased monocytes). generally indicative of chronic inflammation or infection.
Lymphocytes predominant
in bovine and porcine(pigs)
Lymphocytes- T cells
most common one in blood. Processed in thymus(tissue cranial to heart in young animals) then migrate into lymph nodes(most) and spleen too.
primary purpose for T-cells (lymphocytes)
activate B-cells who create the antibodies and cell-mediated immunity. also are memory cells.
Lymphocytes- B cells
Responsible for humoral immunity through antibody production against specific antigens (epitopes) for specific receptors; also form memory cells.
Lymphocytes types-natural killer cells
natural killer cell. Doesn’t require antigen but needs to come in contact with abnormal cells like tumor/ viral infected cells.
Causes of leukocytosis
bacterial infection, stress reaction(neutrophillia/eosinopenia) Malignacy(tumor) , chemical intoxication, metabolic( Uremina-urine in blood), severe hemorrhage (internal) , hemolysis (breaking done cells), tissue necrosis, granulocytic leukemia(cancer in bone marrow)
Specific changes what you see - Eosinophilia (high)
parasitism, allergies, decomposition of body protein, eosinophillic myositis eosinophillic enterities, adrenal insufficiency(addisons, not producing hormons)
Specific changes what you see - Lymphocytosis (high)
lymphatic inflammation-tonsillitis, lymphatic leukemia(associated young animals) viral infection
Specific changes what you see - Monocytosis (high)
stress, chronic inflammation, higher with bacterial or fungal disease.
Specific changes what you see - basophilia (high)
with eosinophilia- allergy or parasites. with no eosinophilia possible mast cell tumor(base cells out of tissue).