AP African American Studies: Unit 2
1/116
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
117 Terms
Ladinos
Free and enslaved Africans familiar with Iberian (Spanish & Portuguese) culture
Journeyed with Europeans in their earliest explorations of the Americas
Some of the first Africans in the US
Part of a generation known as Atlantic Creoles
Atlantic Creoles
Africans who worked as intermediares before chattel slavery
Were familiar with multiple languages, cultural norms & commercial practices
Gave them social mobility
Ladino’s Significance
Essential to European colonial claims in the Americas
Played a role in how Spain colonized “La Florida” (Florida, South Carolina, Georgia)
African Roles in 1400s & 1500s in America
Conquistadores
Enslaved Laborers
Free Skilled Workers & Artisians
Conquistadores
Helping Spain conquering indigenous land in hopes of gaining freedom
Juan Garrido
Born in Kongo & moved to Lisbon, Portugal
1st known African to arrive in North America
Explored present day Florida through a Spanish expedition in 1513
Served in Spanish military forced participating in efforts to conquer indigenous people

Estevanico (Esteban)
Enslaved African healer from Morocco
Forced to work in 1528 as an explorer and translator in Texas and in territory that became Southwesern US
Eventually killed by Indigenous groups who were resisting Spanish colonialism.

Number of enslaved Africans taken to the Americas
12.5 million
How long the Transatlantic Slave Trade lasted
~350 years (1526-1867)
Where most people came to the Americas from
Africa
More arrived from Africa than any other part of the world
Amount of slaves brought to the United States
Only 5% of all Slaves
~388,000 arrived in the US
48% of slaves brought to the US landed here
Charleston, South Carolina
Known as the center of slave trade in USA
Most dominating enslaving nation
Portugal
Most slaves taken during the Transatlantic slave trade were taken to this country
Brazil
Top 5 enslaving countries
Portugal
Great Britain
France
Spain
The Netherlands
1619 Project
A collection of essays, stories, and research first published by The New York Times in 2019
Name comes from the year 1619, when the first enslaved Africans were brought to Virginia
The Middle Passage
Brutal, forced sea voyage, enslaved Africans endured across the Atlantic to the Americas
3 parts/passages
First Passage
Africans were captured and marched to the Atlantic coast from inner states
Africans waited in dungeons that were crowded and unsanitary
Lasted several months
Second (Middle) Passage
Traveling across the Atlantic Ocean aboard Slave Ships
This was the actual Middle Passage
Signified permanent separation from communites
Horrible conditions
Physical violence, sexual abuse, disease & Malnourishment
2 million deaths (~15%)
Up to 3 months
Third Passage
Arrival at ports in Americas
They were quarantined, resold and transported to servitude
Could take as long as the First and Second parts combined
On Board slave ships
Enslaved people were stuffed into compartments
Ceilings as low as 4.5 feet
Where of the voyage was spent
Segregated by gender & age
Men were shackled in pairs
Women left unchained
Children moved freely
Conditions on board slave ships
No sanitary facilities
Relive themselves where they sat
Created hellish conditions when combined with heat + lack of ventilation
Illness was rampant
Enslaved people spent 8 hours on deck
Still segregated
Were forced to exercise
Included song and dance as entertainment
Captives deemed disobedient were tortured and beaten
Africans who profited from The Transatlantic Slave Trade
African elites/rulers, merchants and middle men profited
Most other people didn’t gain much from the trades
Destabilization of West African societies
The Transatlantic slave trade made kidnapping and violence profitable
Europeans traded guns for captives
Fueiling raids and wars between African groups
Widened the wealth gap in Africa
Coastal states grew richer from the trade, while inner states became unstable under the constant threat of capture
Created conflict between ethnic groups as leaders sold war captives to maintain dominance and gain wealth
Caused long-term instability and the loss of family lines and community leaders who would have passed on traditions and stability
What slave narratives are
Detailed accounts from formerly enslaved Africans
Poetry, novels, autobiographies, etc.
Foundational to early American writing
Historical accounts
Literary works
Political texts
Role of Slave Narratives
Designed to end slavery/slave trade
Serve as the basis for the Abolition movement
Demonstrate black humanity
Advocate for inclusion of African Americans into American society
Olaudah Equinao
Captured at 11 from West Africa
wrote the Interesting Narrative on the Life of Olaudah Equiano (1789)
Phillis Wheatley
Captured at 8 years old from Senegambia
First AA to publish a book of poetry
On Being Brought from Africa to America
Portrait by enslaved AA painter Scipio Moorhead was the first known individual portrait of an African American
Brooks Diagram
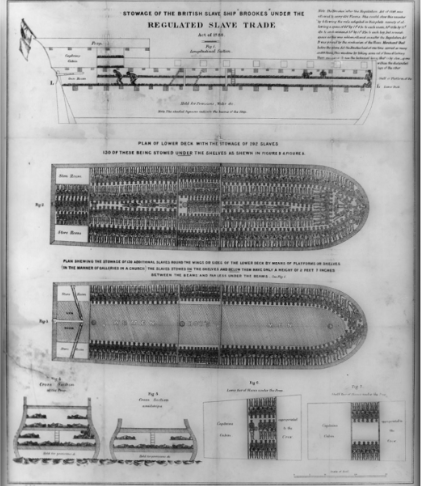
Diagram of systematic arrangement of enslaved Africans
Designed to maximize profit by transporting as many as possible
Reflects unsanitary and cramped conditions that increased disease, disability and death during a trip that could last 90 days
Information Brooks Diagram excluded
Brooks Diagram was one of the only slave documents that many normal people were familiar with; they didn’t know a lot of important details becuase the diagram didn’t include them
Brooks Diagram didn’t include:
Typically showed only half the number of enslaved people on ships
Guns
Nets (used to prevent suicide)
Iron instruments to force-feed those who resisted
Showed Africans as an anonymous, homogenous group of “goods“ for sale
African resistance on the Middle Passage
Africans resisted being displaced (deracination), being treated as a good (commodification), and enslavement. This was done through
Hunger Strikes
Attempting to jump overboard
Overcoming lingustic differences
Made slave trade more expensive and dangerous
Rebellions on Slave Ships led to
Changes in ship design
Barricades
Nets
Guns
Amistad Revolt (1839)
30 years after abolition of save trade
Sengbe Pieh (Joseph Cique)
Méndez captive from Sierra Leone
Led a group of enslaved Africans in one of the most famous slave revolts
Enslaved Africans took over the schooner La Amistad
United States v. Amistad (1839-1841)
Supreme Court granted Mende captives freedom
This garnered public sympathy for abolition
Impacts of Resistance on Abolition
Resistance fueled antislavery activism
Black & White antislavery activists used slave diagrams to raise awareness for the brutalities of the Middle Passage
Black artists reclaimed/repurposed imagery of slave ships
Process historical trauma
Honors memories of ancestors
Enslavers used white supremacy to justify
Physical, mental and spiritual assault of enslaved people
Done through slave auctions
Consequences for enslaved people who resisted sale
Severe punishment
Were whipped in front of peers
AA authors & abolition
Used many genres
Narratives, poetry, etc.
Showed the physical and emotional impacts of auctions
Sought to refute claims (from oppressors) that slavery wasn’t harmful
Solomon Northup
Free AA musician
Was captured illegally
Sold into slavery on a cotton plantation in Louisiana
Provides an eyewitness account in Twelve Years a Slave
Enslaved people could be owned by
Individuals
Institutions
Churches, factories, colleges, etc.
Variety of labor
Domestic, agricultural, and skilled labor
Urban & rural areas
Wide ranges of ages
Both men & women
Sometimes, domestic & agricultural laborers were separated
Enslaved people could be relocated depending on preferences of the enslaver
Skills brought to the Americas by Africans
Blacksmithing
Basket weaving
Cultivation of rice and indigo
Specialized skills
Painters, carpenters, tailors, musicians, healers
Enslavers exploited AAs skills
AAs used these skills to survive, create culture and community
Labor systems
Gang System
Task System
Gang system
Enslaved laborers worked in groups from sunup to sundown
Under the watch and discipline of an overseer
Grew crops like cotton, sugar, and tobacco
Created work songs with syncopated rhythms to keep with the pace of work
Task System
Worked individually until they met a daily quota
Less supervision
Allowed them to maintain linguistic practices
Gullah Creole developed in Carolinas
Cultivated rice and indigo
Gullah people
Came from many different ethnic groups in West Africa
Wolof, Mandinka, Fula, etc.
Identity is a blend of West African, European, and Indigenous cultures
Gullah Religion
Gullah people casted spells with herbs
Put newspaper in shoes
Ring shout
Religious dance
Burial customs
Drumming
Covering mirrors
Smashing dishes over burial site so no one else would pass
Leaving a portion of food for those who died
Economic effects of the slave trade
Economic interdependence between the North & the South
Northern cities benefited from the Slave economy, even if they didn’t participate
Enslaved people were integral to the American economy
African Americans were detached from the wealth they produced
Slavery caused wealth disparities along racial lines
Enslaved people had no wages to pass on & no rights to attain property
French Code Noir
Law outlining regulations for slaves in French Colonies
From the King of France
Forbid slaves from:
Carrying weapons or large sticks (save for hunting)
Slaves of different masters from meeting up at any time or anywhere
Masters who allowed slaves to evade law would be fined
Slaves were guilty even before any ruling was made on their case
Slavery in the Constitution (Article I & IV)
Refers to slavery but doesn’t use the words “slave” or “slavery”
“Slave” appeared in an early drafts but was removed
No direct mention until abolition (13th amendment)
Impact of Slave Codes
Defined chattel slavery as race-based, inherited and life-long
Restricted movement, meetings among slaves, possession of weapons, wearing fine fabrics, etc.
Restrictions can be found in Code Noir (French)/Codigo Negro (Spanish)
Harded the color line
Made opportunities for moving up in society & protections against enslavement exclusive for white people
Denied opportunities for Black Americans
“Free” States
Also denied free AAs opportunities for advancement
Some forbid the entry of free Black people into the state
Voting Restrictions
Black men couldn't testify against whites in court
Voting restrictions in Free States
Before the 15th Amendment (1870) only Wisconsin and Iowa had given Black men the right to vote
In 1860, Black men could vote in only 5 of 6 New England States
Maine, Vermont, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, New Hampsire)
Slave Codes
Created due to enslavers’ fears of slave uprisings and resistance
After resistance, AAs were met with new, stricter regulations
South Carolina Slave Code updates after Stono Rebellion
Classified all Black & Indigenous people as nonsubjects (unimportant, unworthy of discussion or attention)
Prohibited enslaved people gathering, learing to read,
Race
Not Real
Not based on biology
A lie created to justify getting rich in immoral ways
More genetic differences within racial groups than between them
Was invented to justify chattel slavery and claim their cirmes were “natural”
Notions of race developed along side slavery
Racism
Caused by slavery, not the other way around
Racist laws of slavery produced hate & ignorance , not the other way around
Racial hierarchy in Europe
During the Enlightenment Era
Philosophers believed rationality & civilization belong to whites
Thinkers belived Africans were less capable of reason
Race became the cornerstone of western thought
When Black people challenged racial hierarchy
People who benefited from the system became angry
Their status & view of the world was shaken and threatened
Responded w/ hate
Partus sequitur ventrem
17th century law
Defined a child’s legal status based on the mother’s
Allowed slavery to be hereditary
ensured a woman’s child would inherit the womans staus as property
Partus sequitur ventrem’s impact
Children inherited a status as property, witch invalidated AA’s claims to their children
Designed to prohibit the mixed-race children of Black women from inheriting free status (the custom for english common law)
Gave male slave owners the right to deny responsibility for children they fathered (usually through assault)
In order to commodify enslaved womnes reproductive rights
Hypodescent (One-drop-rule)
One’s race was determined by this
Stated that anyone with any degree of African descent as a Black person (of inferior status)
Phenotype
Ones physical characteristics
Contributed largely to the way racial identity was seen
During slavery, racial categories were defined by law, regardless of phentype
Tied rights & status to race
enslaved, free, citizen
to perpetuate slavery over generations
For AA’s who had European or Indigenous ancestry
Race classification prohibited them from embracing multiracial & multiethnic heritage
Spirituals
Blended music and faith traditions in the United States
AKA Sorrow Songs & Jubilee Songs
Enslaved people sang to articulate their hardship & hopes
Spirituals significance
Represent AA’s African heritage and American identity
Preserve rhythm and performance styles from West Africa and express American experiences
Spirituals purpose
Served social, spiritual and political purposes
Resist dehumanizing/unjust conditions of slavery
Express creativity
Communicate strategic info
Warnings, plans to run away, methods of escape
Lyrics had double meanings
Used biblical themes of redemption and deliverance to alert enslaved people of opportunities to runaway via Underground rail road
To make up for meager rations from enslavers
Enslaved people planted their own gardens
US ban of international slave trade
1808
importation of enslaved people continued illegally
percentage of African-born people in the AA population declined
American Colonization Society
Founded in 1816 by white leaders
Sought to exile growing free Black population to africa
Caused many Black people to reject the term “African” and instead emphasized their American identity.
African countries never colonized by Europeans
Ethiopia
Liberia
Ways AAs describe themselves
Since the 1800s, AAs describe themselves using a wide range of ethnonyms
Afro-American
African American
Black
Colored Conventions
Beginning in the 1830s
AAs held political meetings across the US and Canada
Emphasized shared AA heritage
Housed debates about identity and self-identification in AA communities
Promotion of the use of the term African American
Promoted by civil rights activist Reverend Jesse L. Jackson
1988
Emphasized shared cultural heritage
Emphasized community of descendants of enslaved Africans born in the US
Haitian Revolution
1781-1804
Only uprising of enslaved people that resulted in overturning a colonial slaveholding government
Transformed European Saint-Domingue into a Black republic free of slavery (Hati)
Created second Independent nation in the Americas
Saint-Domingue
Highly profitable French sugar island
Richest colony in the world
Produced more sugar than all other Caribbean islands combined
“Backside” (western side) of Spain’s Santo Domingo (Dominican Republic)
Haitian Revolutions impacts on France
France lost its most profitable colony
Caused Napoleon to sell the Louisiana Territory to the US
2x the size of the US
Made more land available for slavery
Temporary abolition of slavery throughout the French Empire (1794-1802)
Haitian Revolution brought this to the US
Influx of White Planters & enslaved Black refugees
Went to cities like Baltimore, New York, and Philadelphia
Increased anxieties about the spread of slave revolts
Maroons during the Haitian Revolution
Spread information across different groups
Organized attacks
Many freedom fighters were former soldiers
Were enslaved during civil wars in the Kingdom of the Kongo and sent to Haiti
Destruction of sugar plantation systems in Haiti
Caused the sugar market to shift to the US, Cuba, and Brazil
Haitian Revolution impacts on diaspora
For some AAs, Haiti’s independence highlighted unfulfilled promises of the American Revolution
Inspired uprisings in other African diaspora communities like:
Louisiana Slave revolt
Male Uprising of Muslim slaves (largest revolts in Brazil)
Had an impact on Black political thinking
Symbol of Black freedom and sovereignty
Haitian Constituon
Declared all citizens of Haiti to be Black
Challenges colonial ideas of blackness
Reframed Blackness as an identity that signified citizenship and belonging
Daily forms of resistance
Slowing work
Breaking tools
Stealing food
Attempts at running away
Resistance supported this larger movment
Movement towards abolition
Religion’s role in daily forms of resistance
Religious services/Churches became vital in fueling resistance to slavery
Served as multifunctional sites for community gathering, celebration, mourning, sharing information
In the North, for political organizing
Former African soldiers
Transatlantic slave trade led to a concentration of former African soldiers
Aided in enslaved communities’ ability to revolt
In some areas of the Americas
Thomas Jefferson’s letter to Rufus King
Request for British permission to transport Black rebels from the United States to Sierra Leone
Stated its a necessary security measure
Direct response to Gabriel’s Rebellion (1800)
Spanish Settlement Revolt
Earliest known slave revolts in the US
Enslaved Africans in Santo Domingo (DR) were brought to aid Spanish exploration along the South Carolina/Georgia coastline
Revolted and likely escaped into nearby Indigenous communities
Louisiana Revolt (1811)
Led by Charles Deslondes
Organized support across local plantations and maroon communities
Including self-emancipated people from Hati
Largest known slave revolt on US soil
500 enslaved people
Marched toward New orleans
Violently suppressed
Denmark Vesey
Inspired by religion
Does planning for the rebellion in an African church
Plans to revolt, but is executed before revolt can be carried out
Nat Turner
Inspired by religion
Believed he was sent a sign from god to rebel
Leads a crowd in Virginia of ~750 slaves
Kills ~60 whites (including women & children)
Creole Mutiny
Led by Madison Washington
Enslaved cook
Seized ship and sailed it to Bahamas
British owned which had abolished slavery in West Indies in 1833
Rebellion on a slave brig (ship) the Creole
Transported enslaved people from Virginia to New Orleans
Very successful
~130 AAs gained freedom in Bahamas
Great Awakenings (nice to know; not needed)
Religious revivals
Four Great awakenings
First (1730-1755)
Second (1790-1840)
Third (1855-1930)
Fourth (1960-1980; controversial)
Ideas in Why Sit Ye Here and Die by Maria W. Stewart
Demands African Americans reject passivity
Calls for immediate action to fight for social economic and educational equality
Free black populations
Late 1700s & early 1800s, free black populations grew
12% of free people were Black by 1860
More free black people in the South than in the north, but their numbers were smaller in comparison to the enslaved population
Free Black people building community
Within cities like Philly, NY, New Orleans
Mutual aid societies
Funded the growth of Black schools, businesses, and independent churches
Supported Black writers & speakers
Calling attention to Black women’s experiences (1800s)
Black women used speeches & publications to call attention to Black women’s experiences within antislavery discussions
Maria W. Stewart
1st Black woman to publish a political manifesto
1st American woman to give a public address
Advocacy in 1830s contributed to the first wave of the feminist movement
Importance of Black Women
Called attention to the intersections of race and gender discrimination
Fought for abolition and women’s rights
Paved the way for women’s suffrage movement
Highlights connection between race, gender, and class in their experiences
Women anticipated political debates that remain central to AA politics