Blood Vessels
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
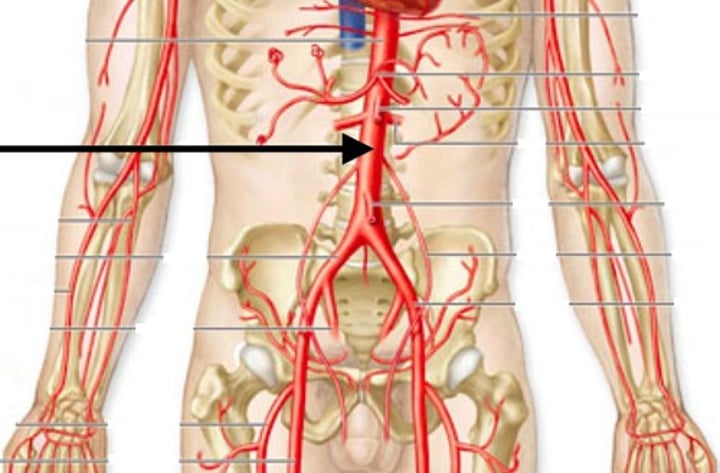
Aorta
Largest arterial trunk that carries blood throughout the whole body
Aorta
Ascending Aorta
Branches off the left ventricle; carries oxygen rich blood to parts of the body above the heart
Ascending Aorta
Descending Aorta
deep to the inferior vena cava; the largest artery of the body; carries blood away from the heart down the midline of the body
Descending Aorta
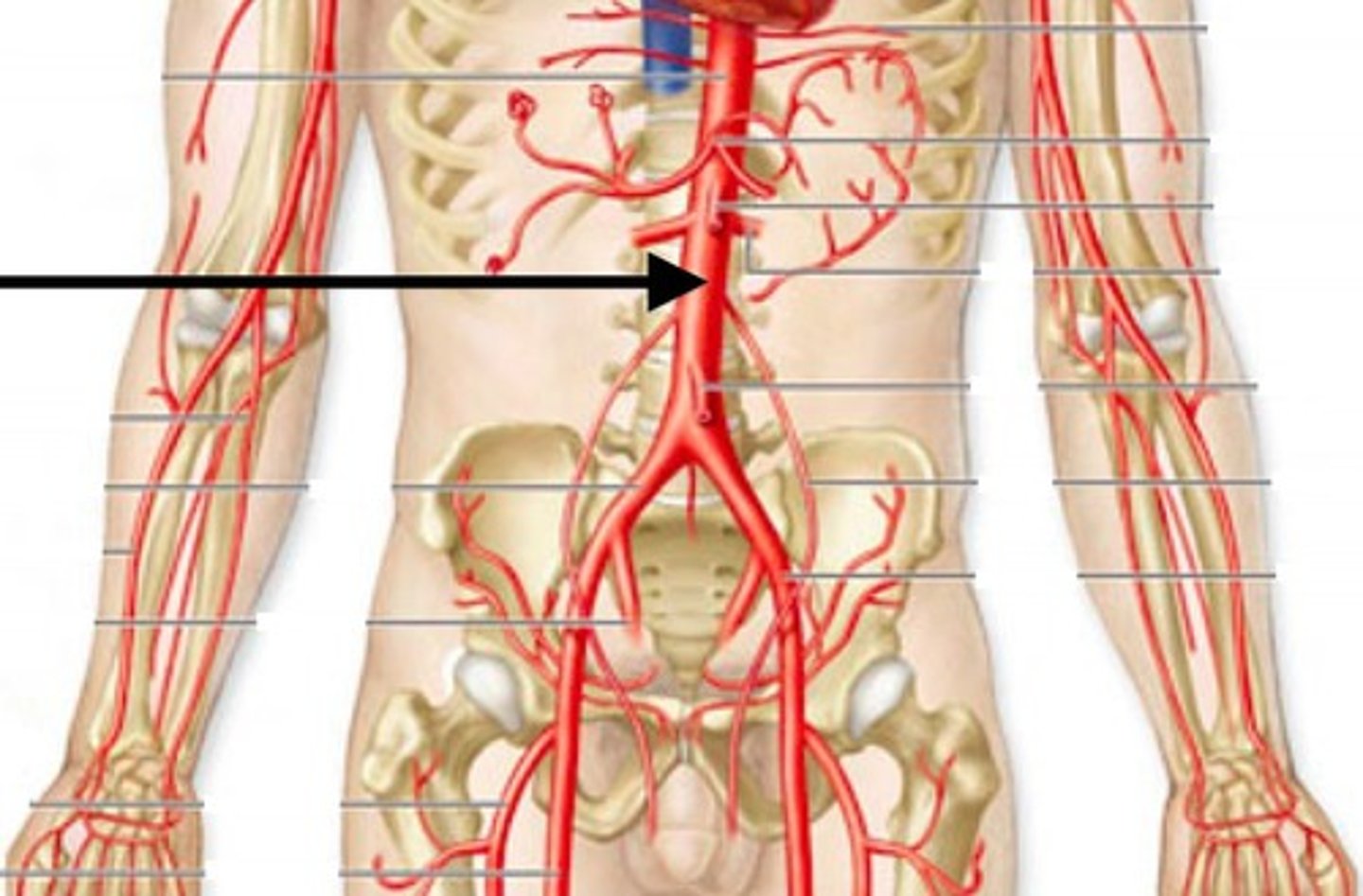
Thoracic Aorta
part of the aorta the descends from the aortic arch through the thorax to the diaphragm
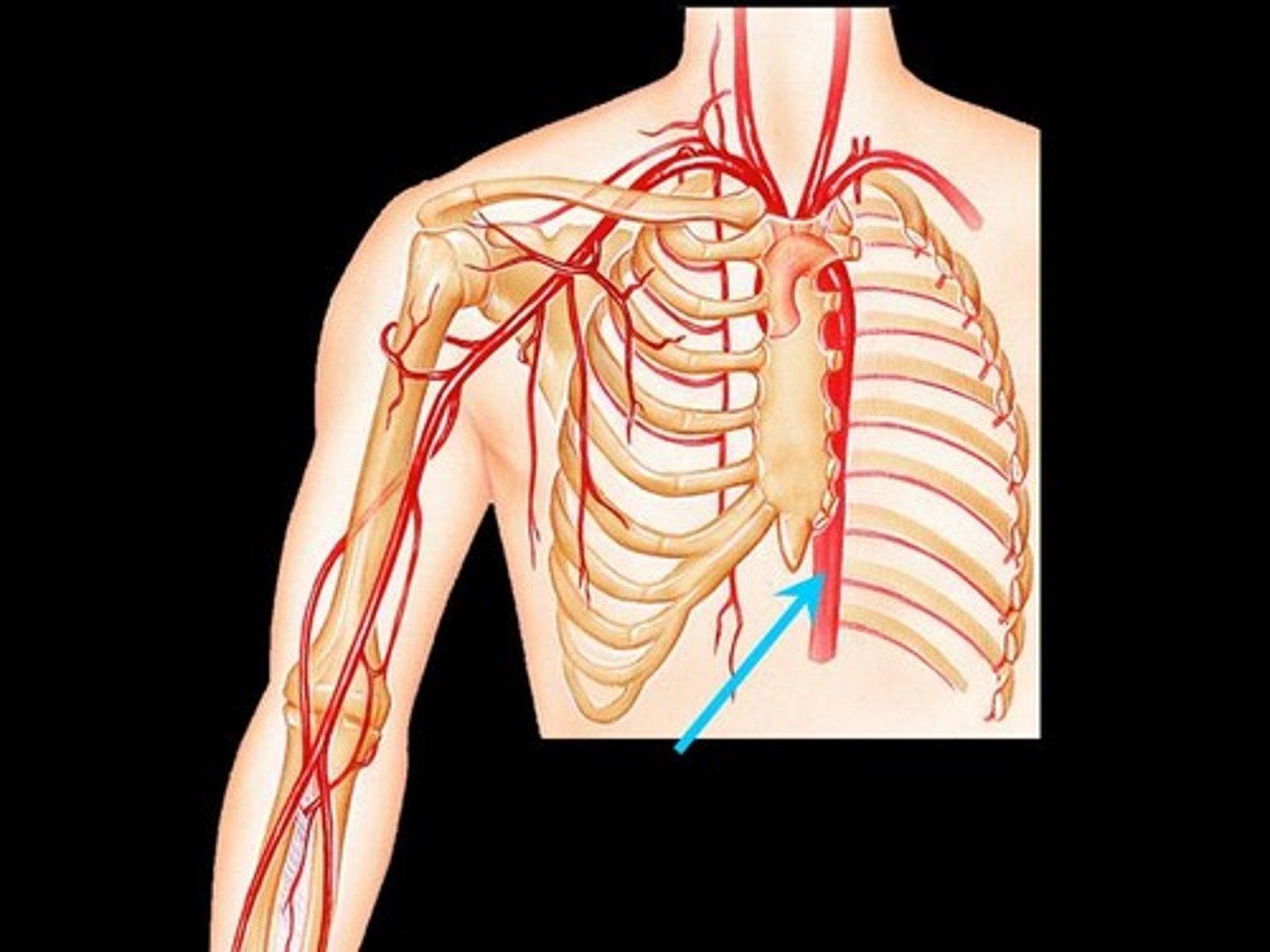
Abdominal Aorta
lower descending aorta, takes blood to lower trunk and legs
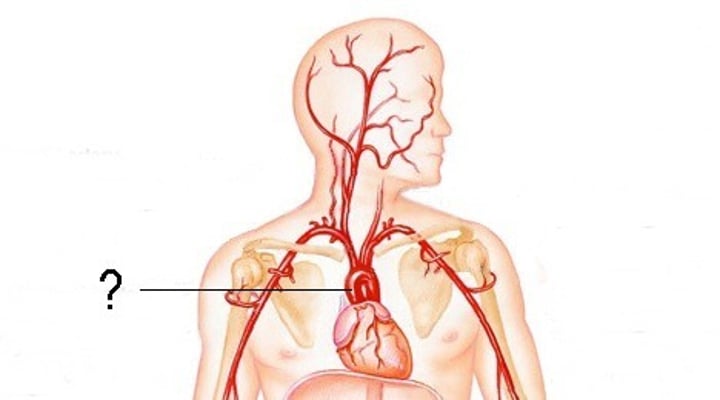
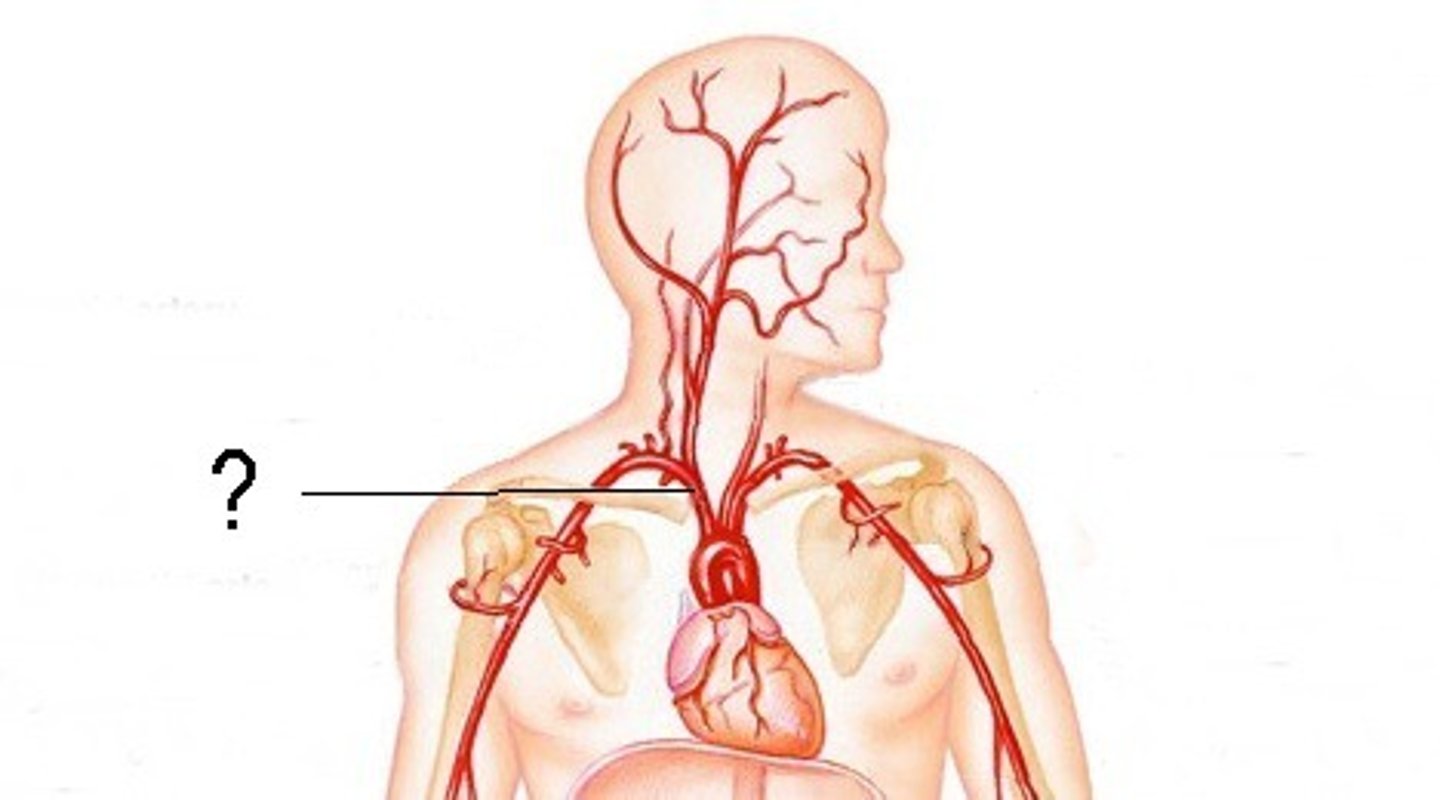
Brachiocephalic Trunk
The first large artery arising from the aortic arch. It carries oxygenated blood to the neck, head, and right forelimb.
Brachiocephalic Trunk
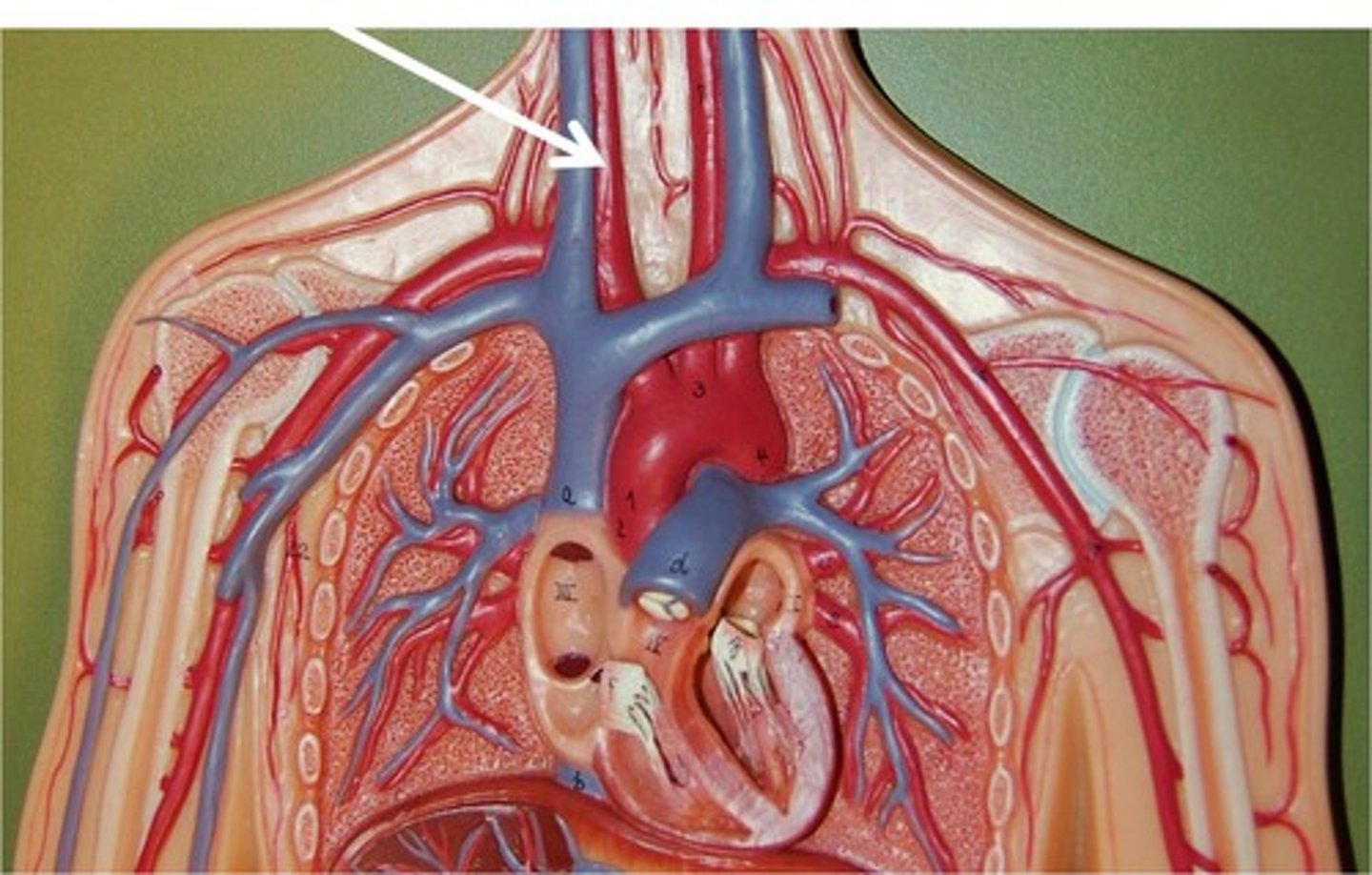
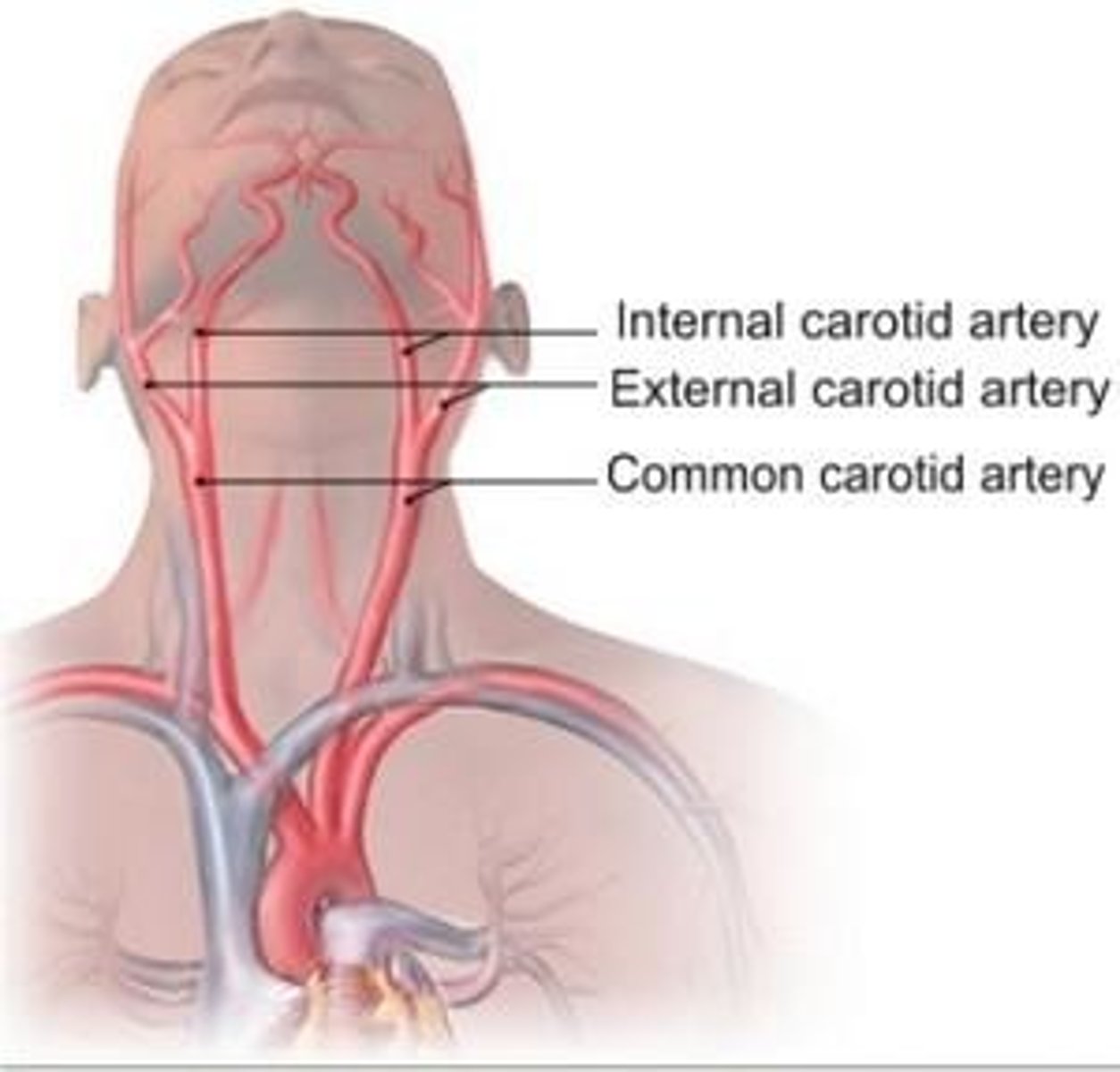
Common Carotid Arteries
Main arteries that supply blood to the head, face, and neck.
Internal Carotid Arteries
These arteries are the lateral branches of common carotid arteries. They carry blood to the brain.
Internal Carotid Arteries
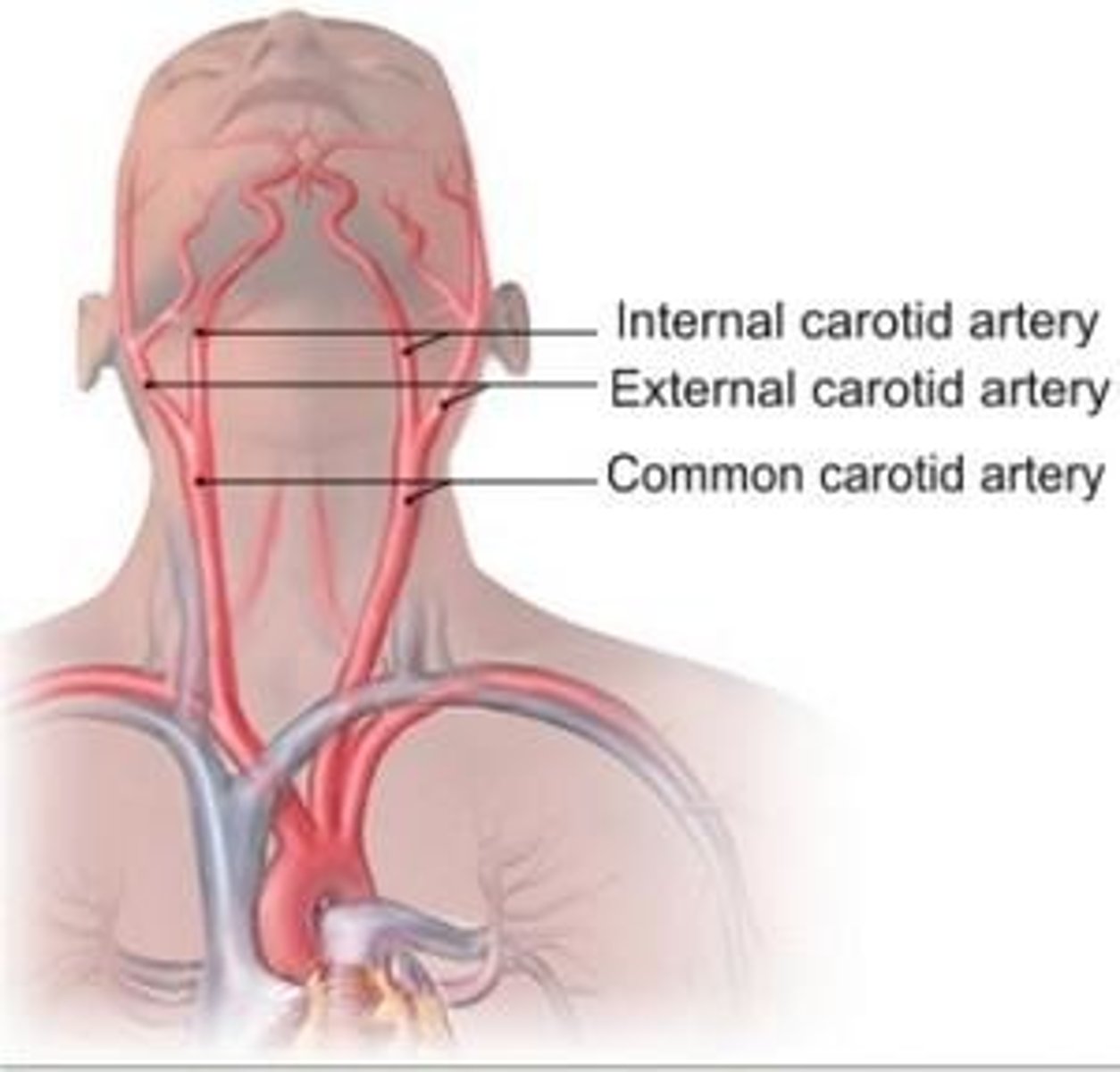
External Carotid Arteries
supply blood to the face, scalp, and neck
Ophthalmic Arteries
supply the eyes, orbits, forehead, and nose with oxygenated blood
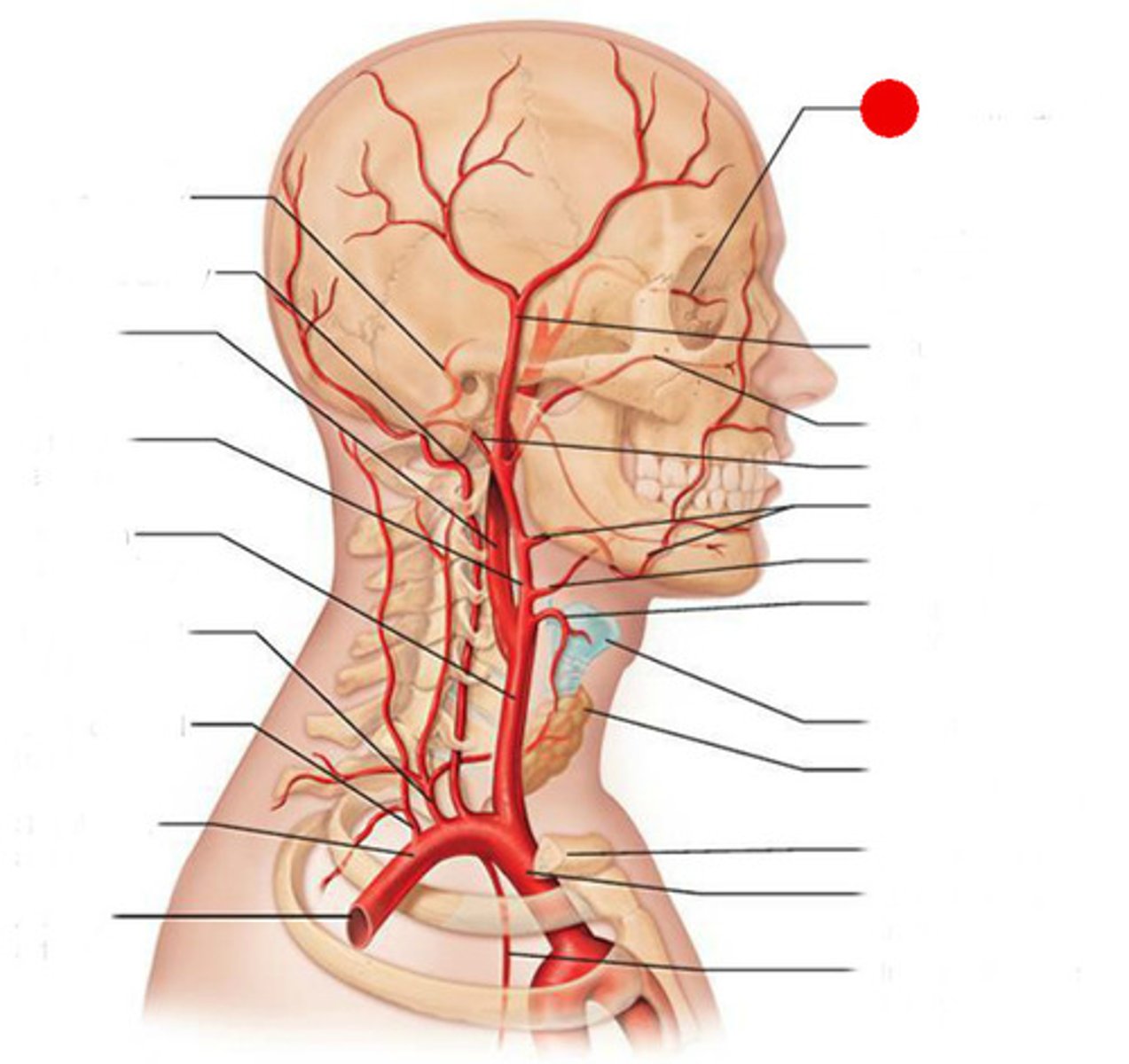
Superficial Temporal Arteries
Supplies the superficial temporal scalp.
Maxillary Arteries
provide blood to the muscles of mastication, teeth, palate, and nasal cavity
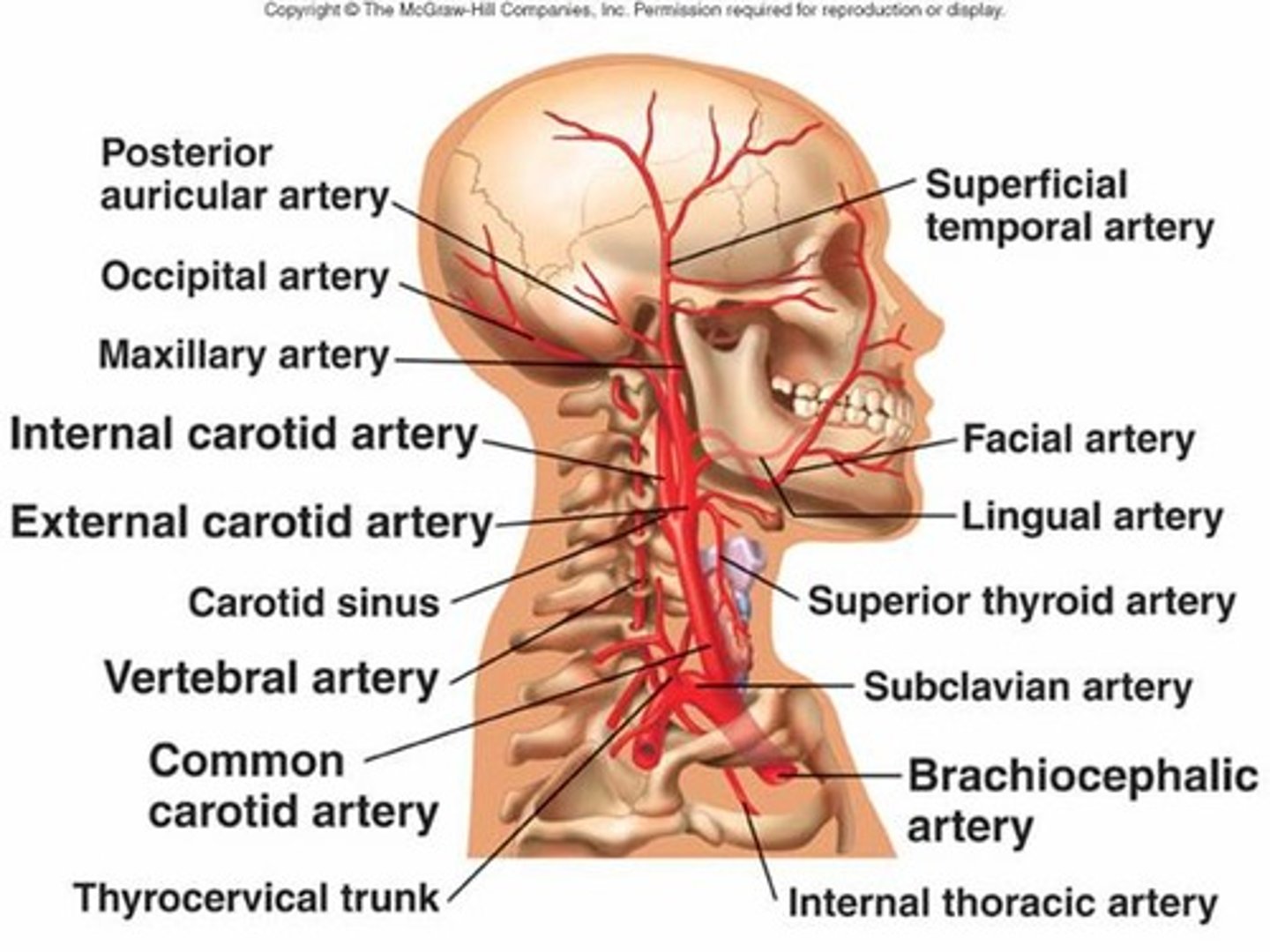
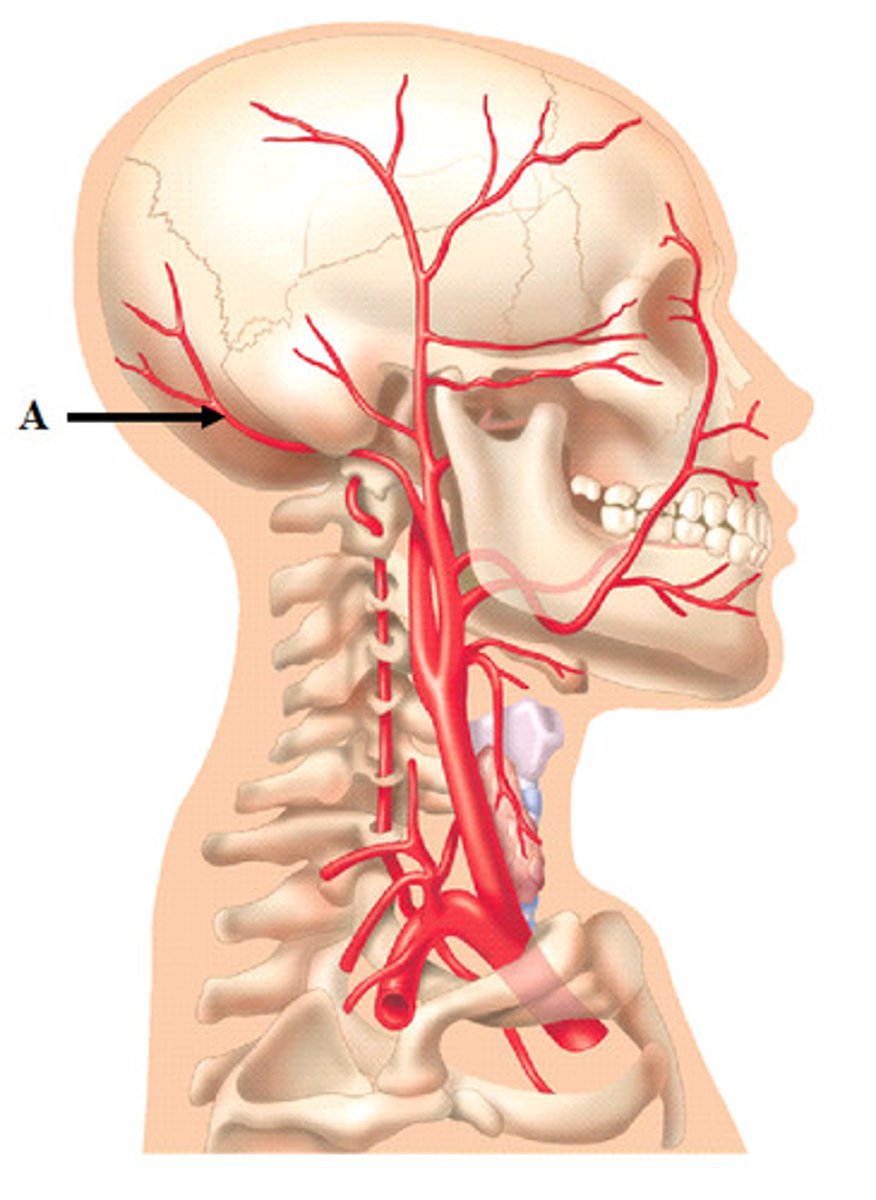
Occipital Arteries
Facial Arteries
branch from the external carotid to supply the face
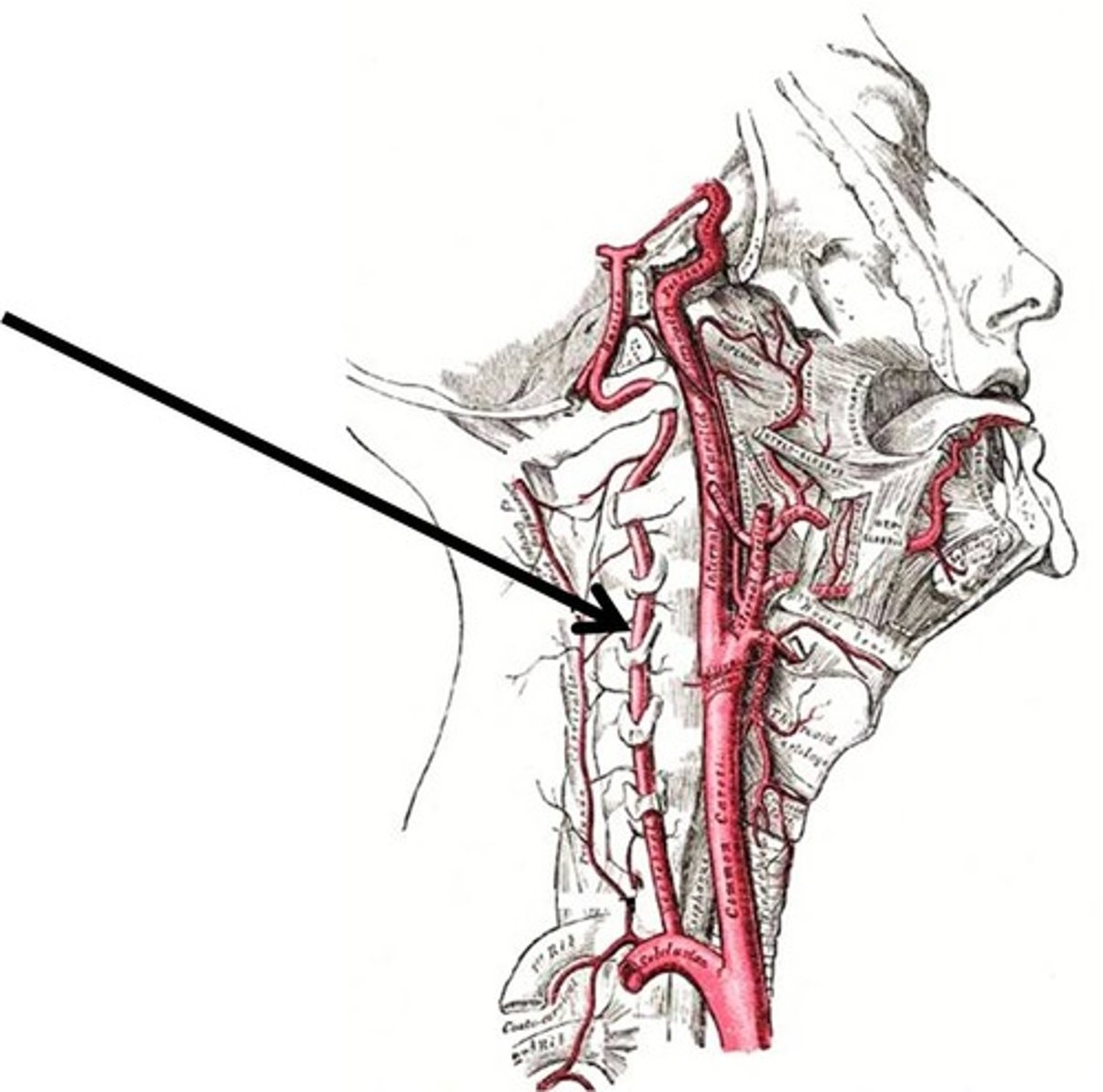
Vertebral Artery
Supplies blood to the spinal column and brain.
Subclavian Arteries
carry oxygenated blood from the aorta to the arms
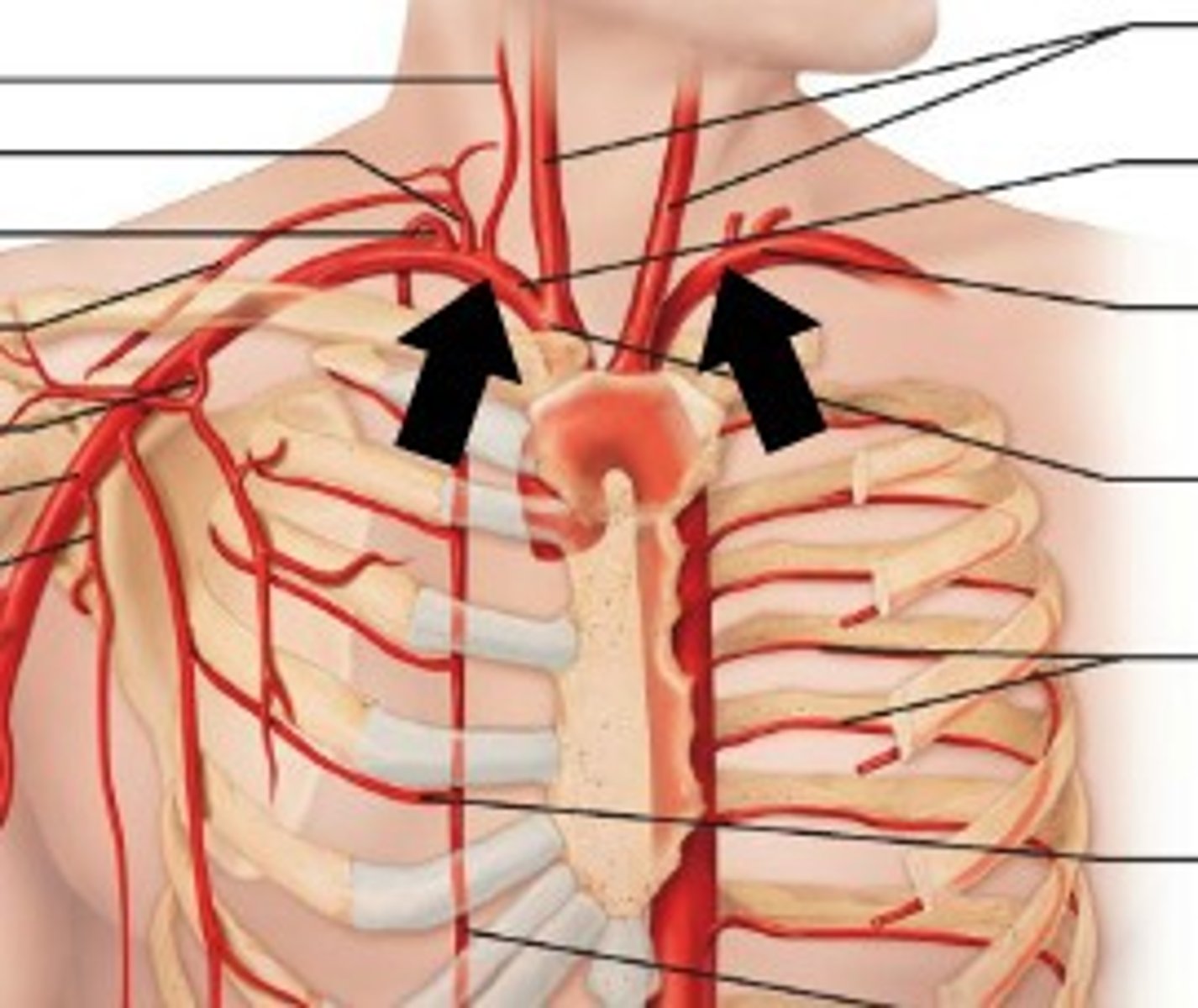
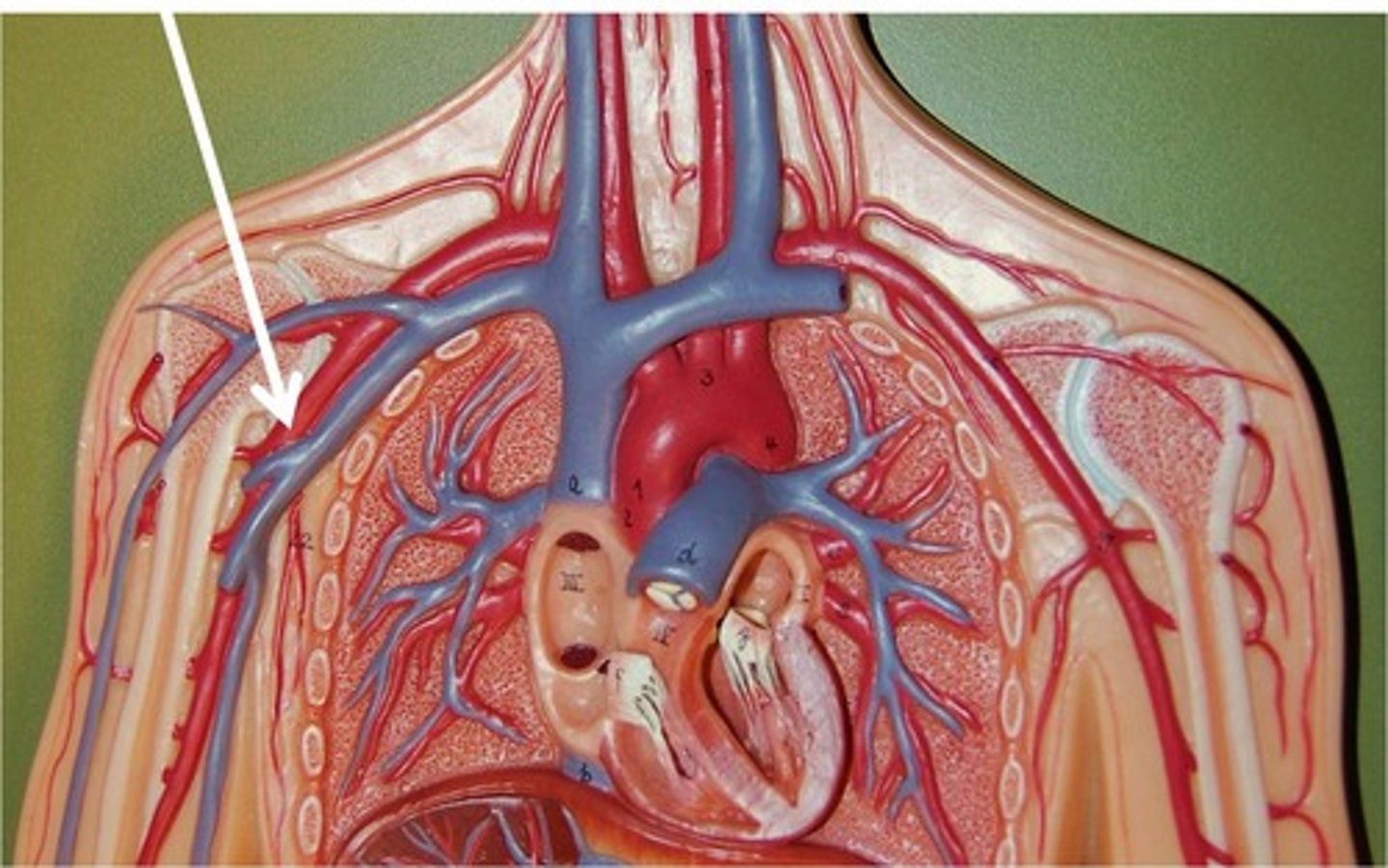
Axillary Arteries
Continuation of subclavian arteries. Carry blood to armpit, shoulder, and forelimb.
Brachial Arteries
continuations of the axillary arteries along each humerus. They bifurcate into smaller arteries in the hands. Common site for measuring blood pressure.
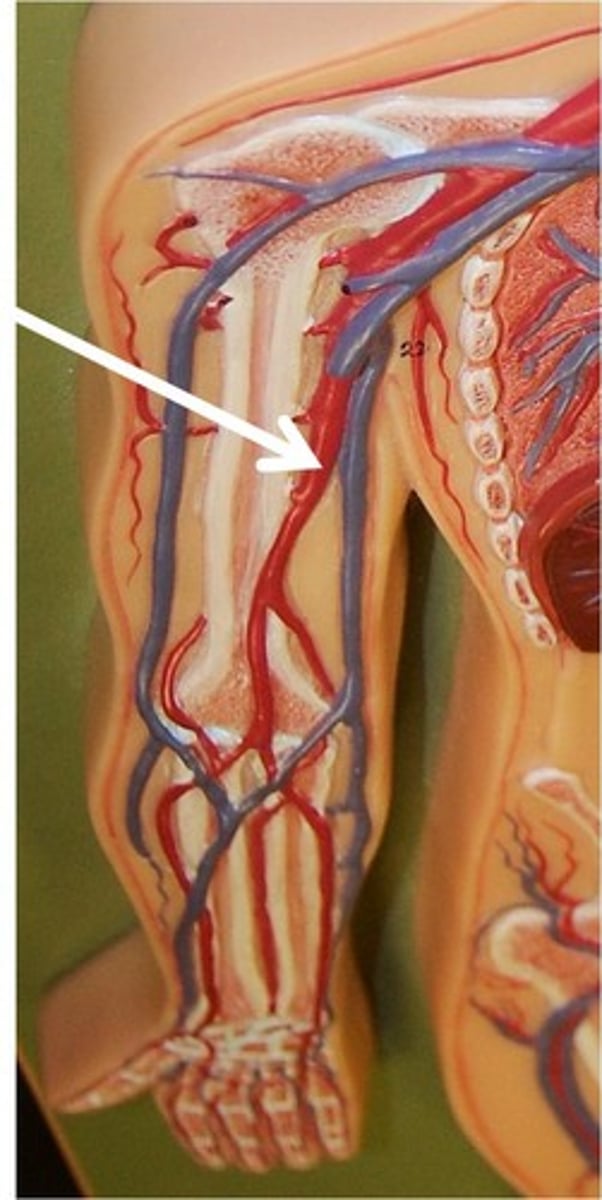
Radial Arteries
major artery of the arm distal to the elbow joint
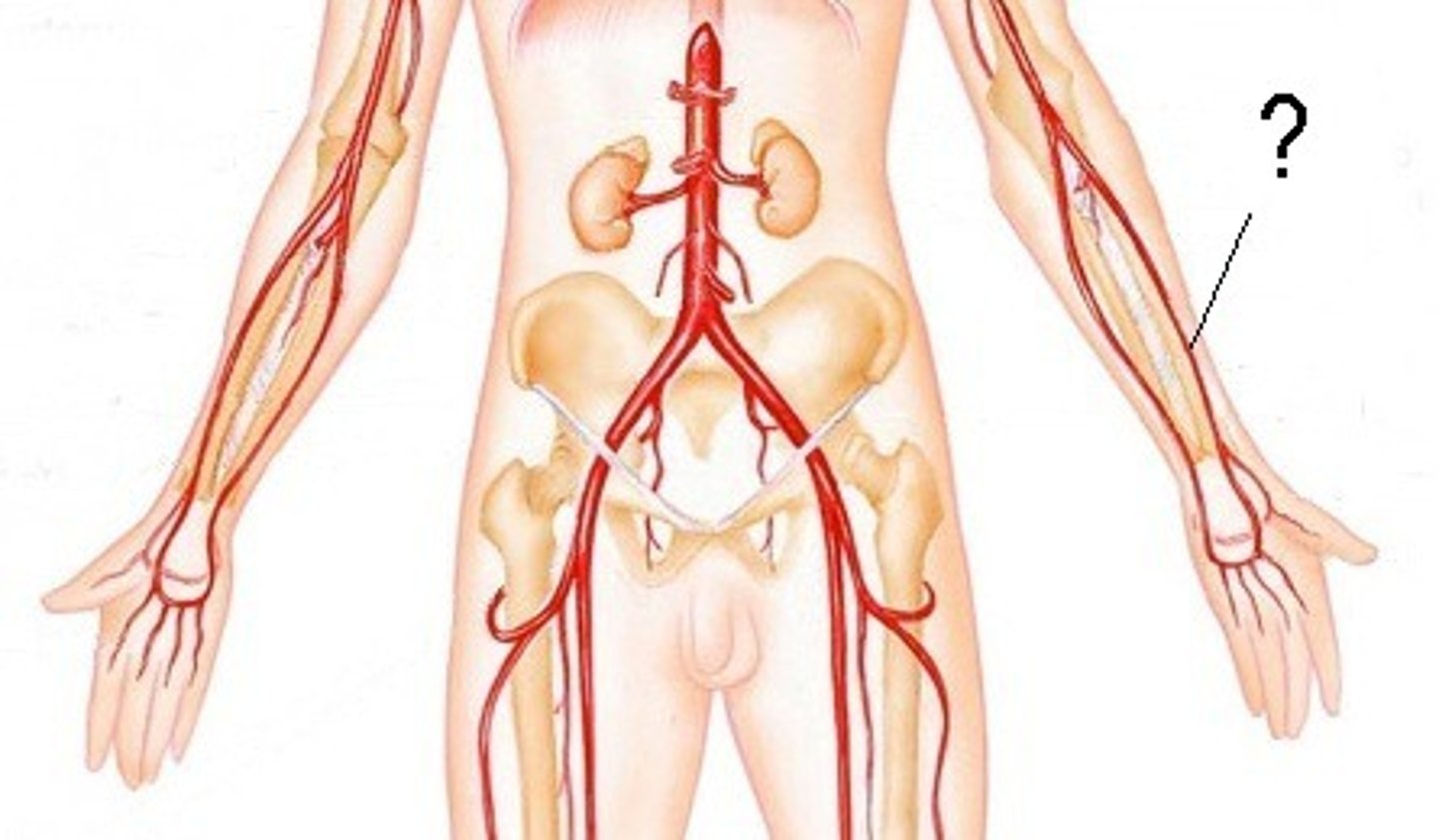
Ulnar Arteries
terminal branch of brachial artery that runs along medial surface of forearm into the wrist and hand
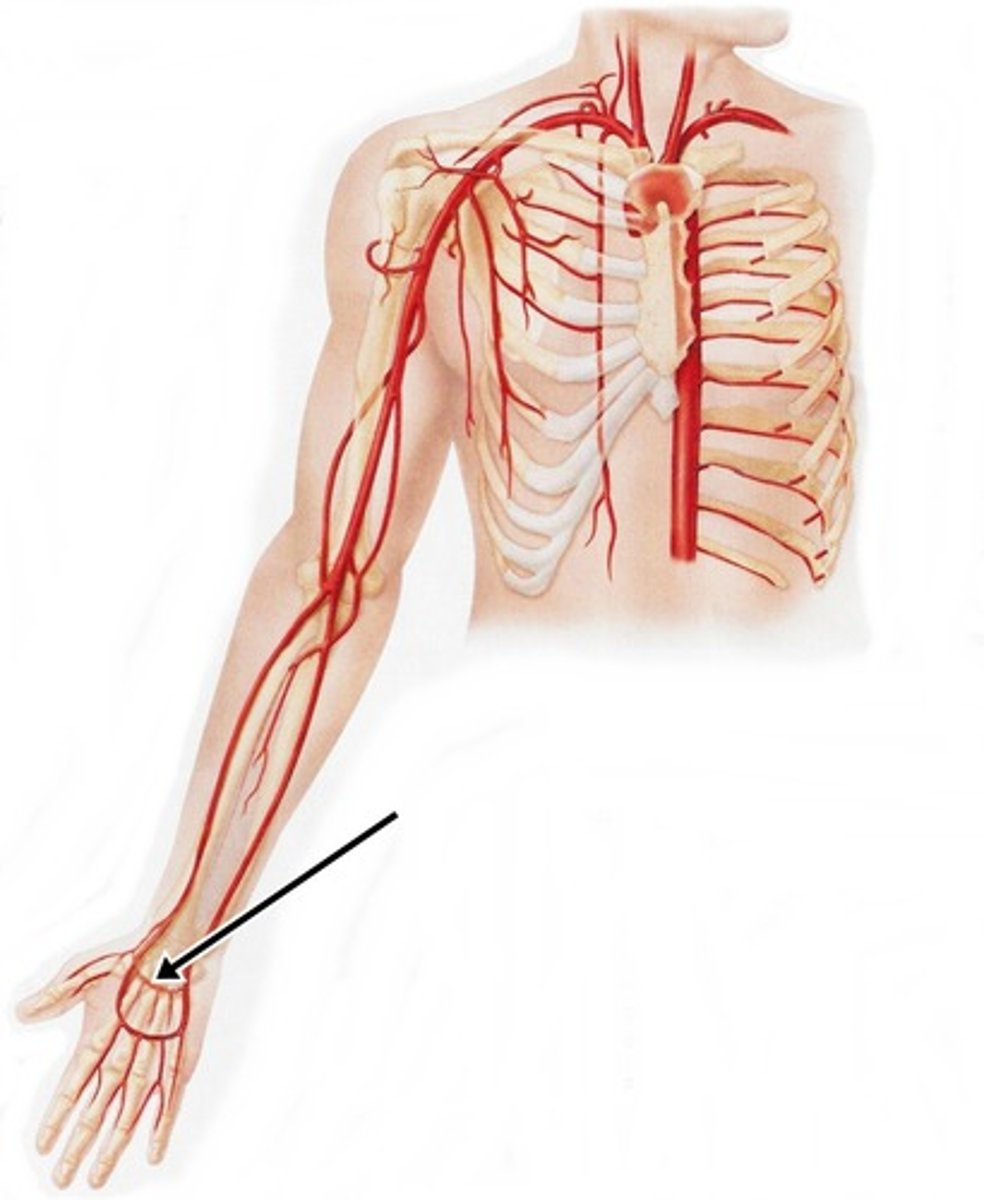
Deep Palmar Arch
An artery that is considered to be the continuation
of the radial artery is the
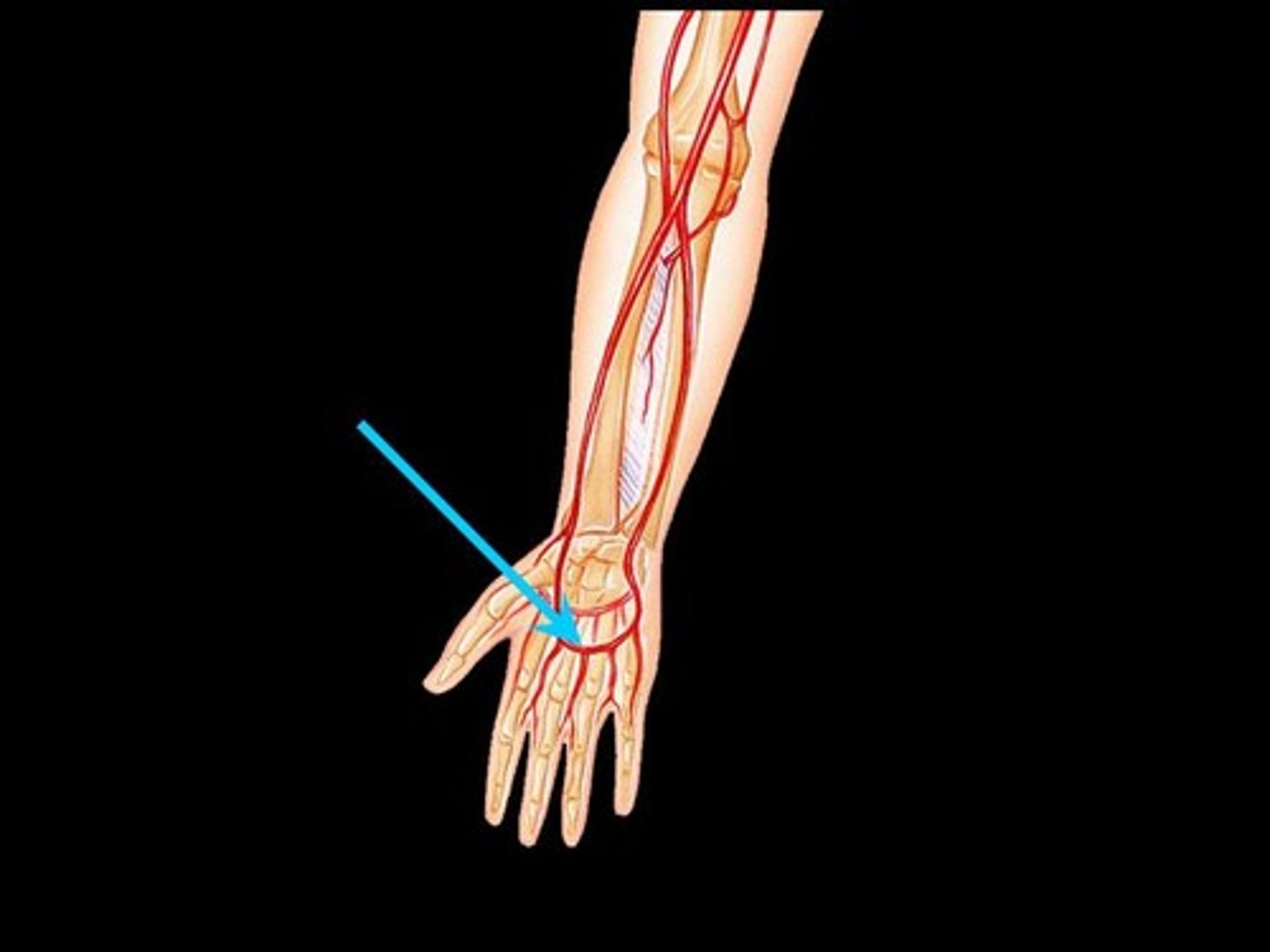
Superficial Palmar Arch
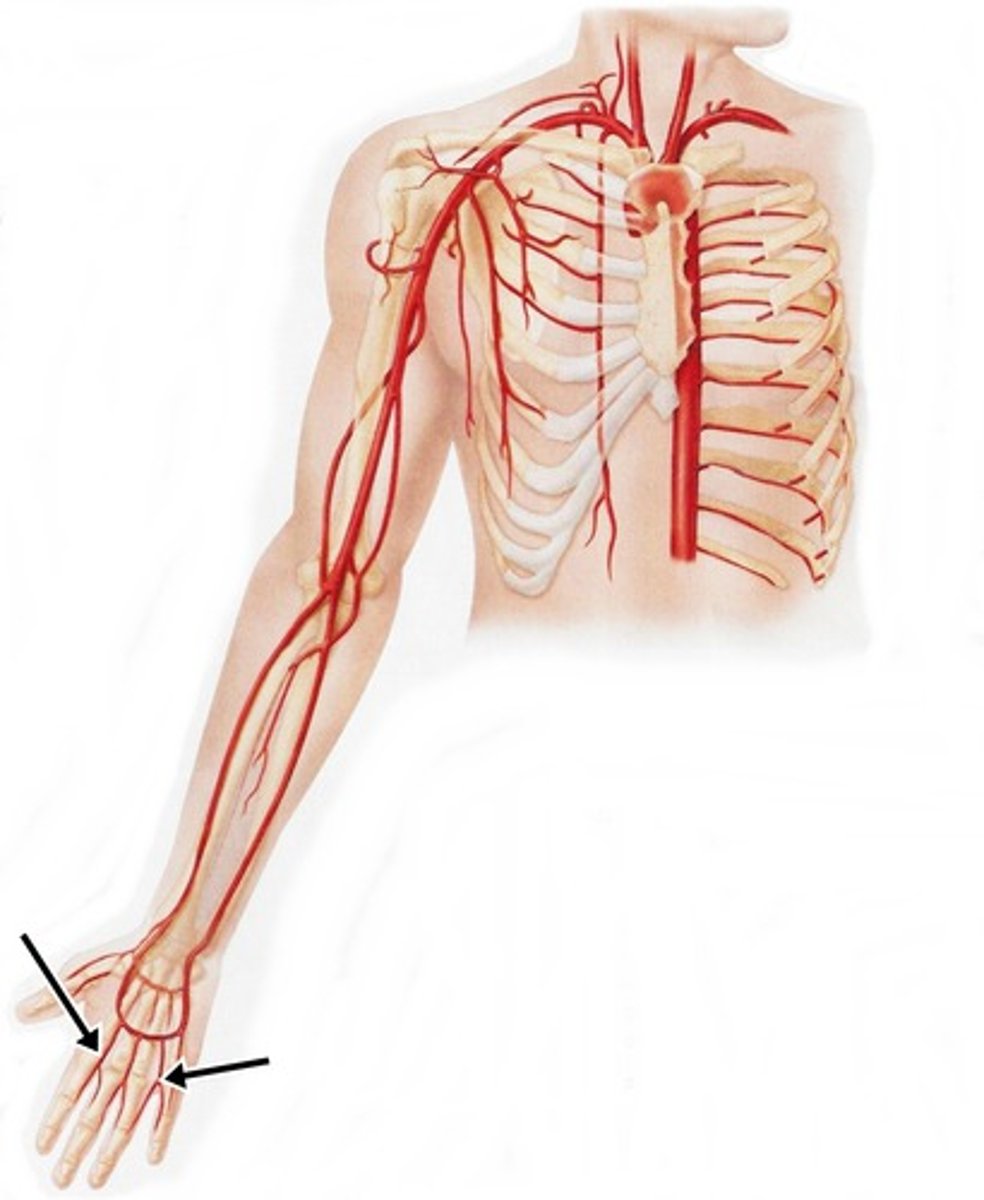
Digital Arteries
emerge from the arches to supply the fingers
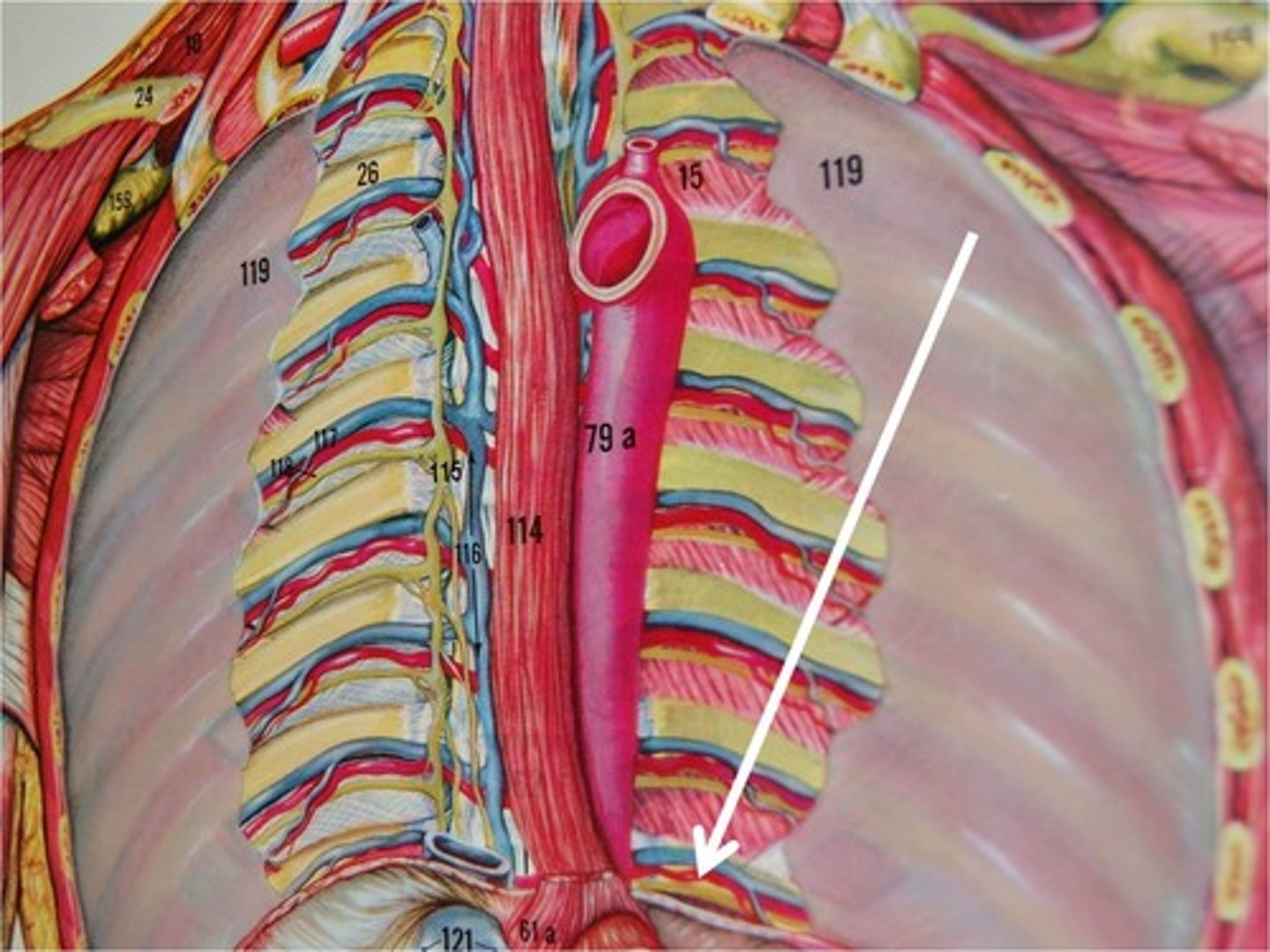
Superior Phrenic Artery
branch of the thoracic aorta; supplies blood to the superior surface of the diaphragm
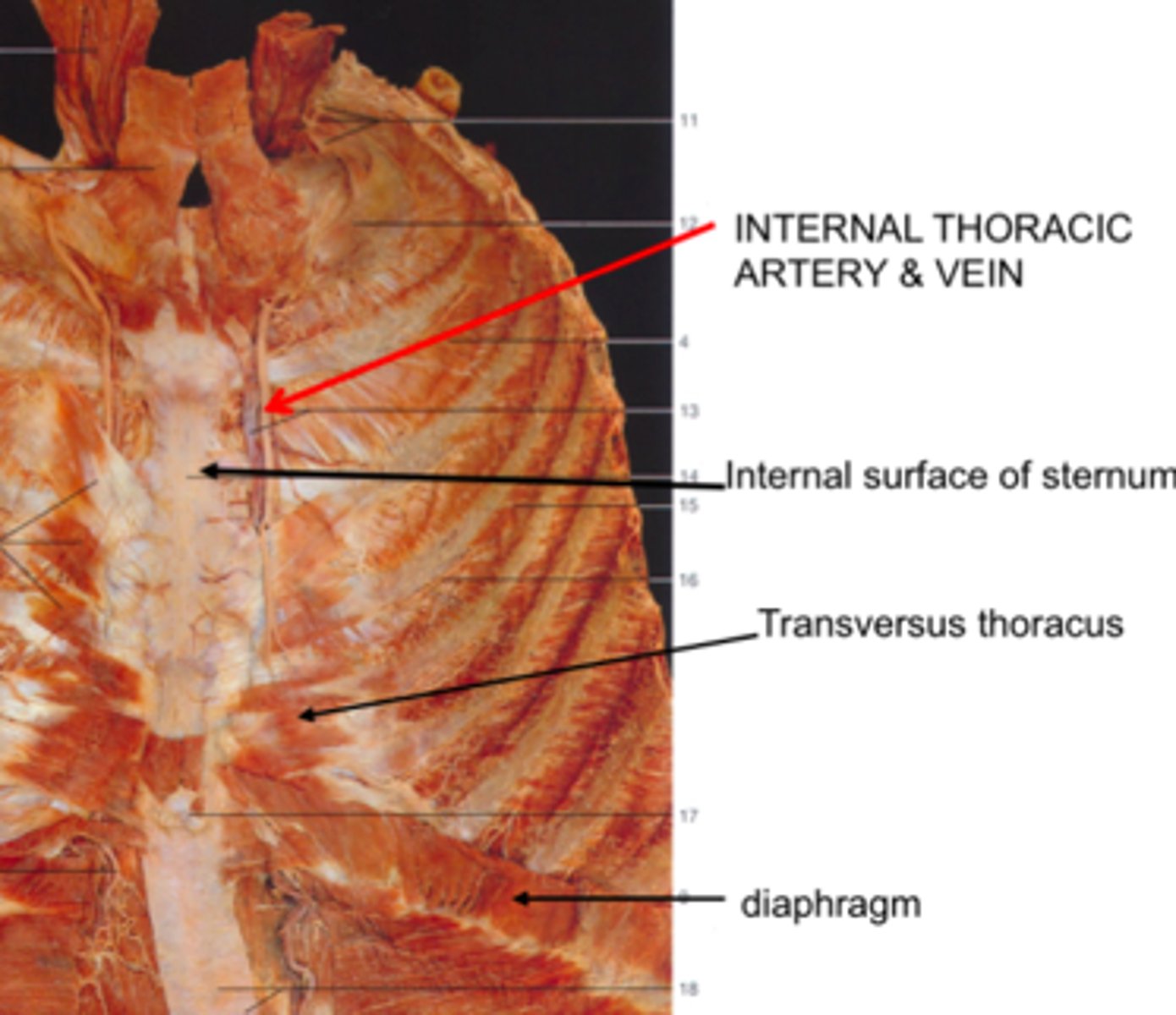
Internal Thoracic Arteries
Branch from subclavian arteries and supply mammary glands and intercostal muscles
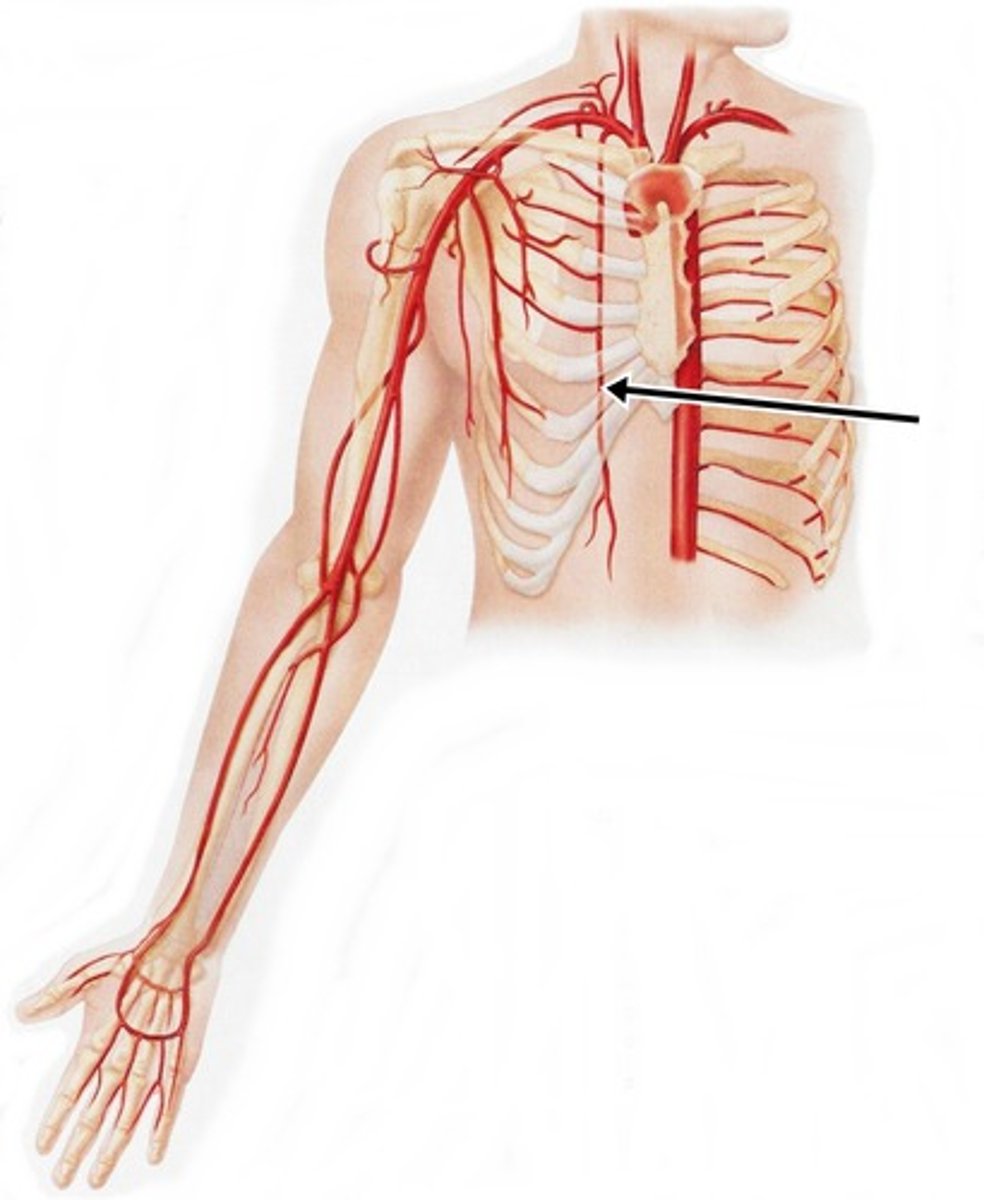
Lateral Thoracic Arteries
originates in the axilliary artery
-supplies the pectoralis major, serratus anterior muscle, and sends branches across the axilla
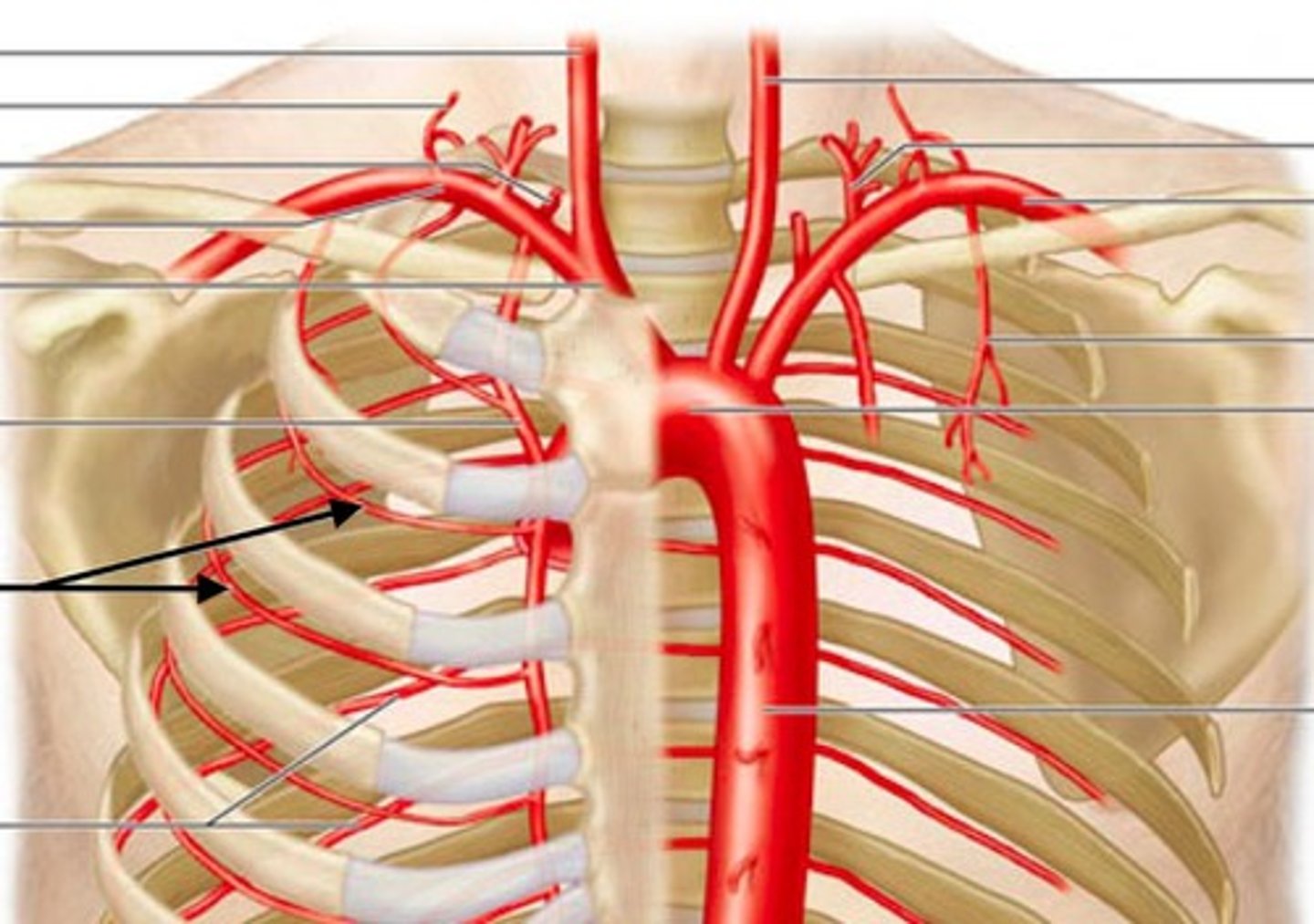
Anterior Intercostal Arteries
serves mammary glands, most of thorax wall
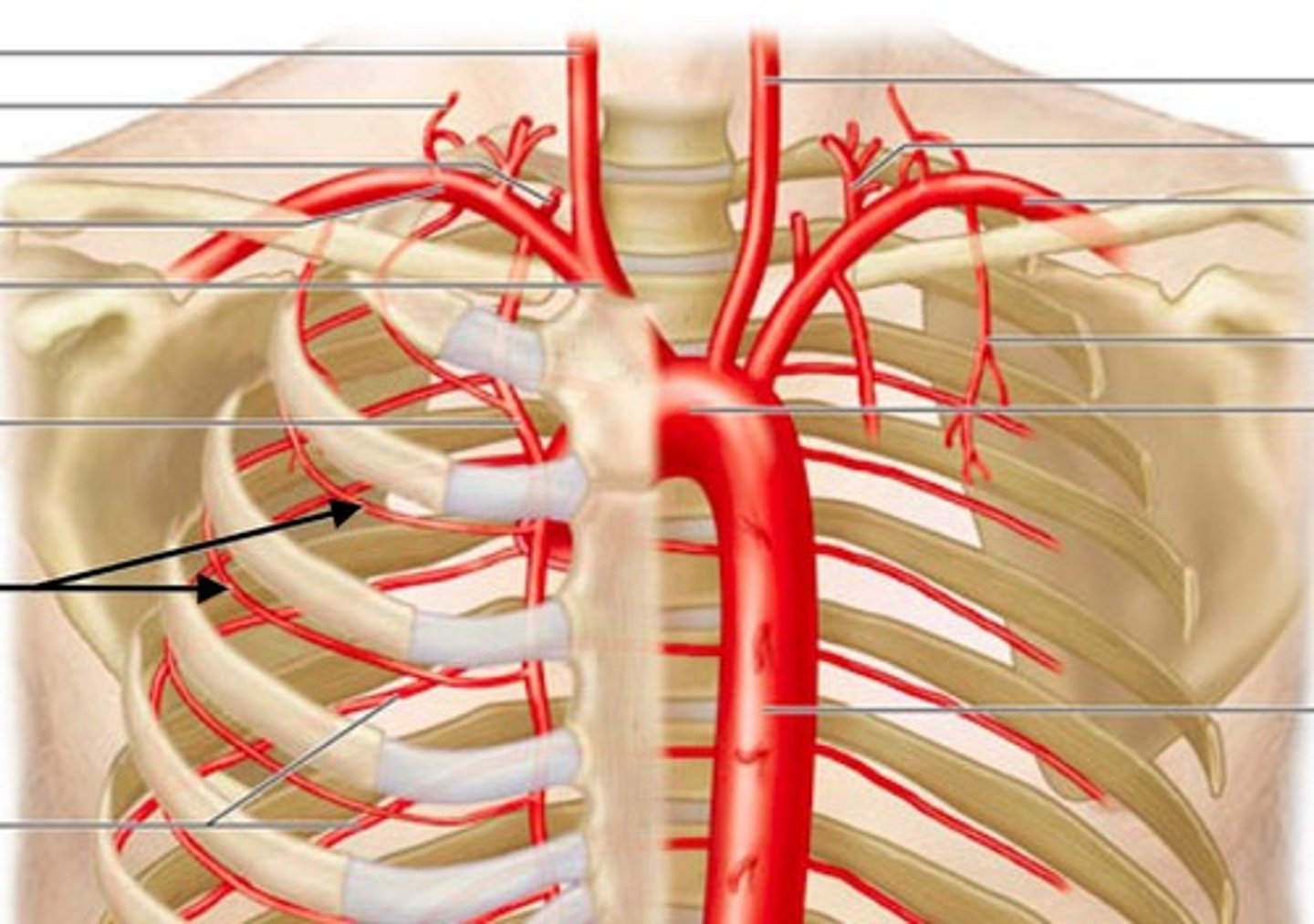
Posterior Intercostal Arteries
supply the vertebrae, spinal cord, intercostal muscles, and deep muscles of the back
Inferior Phrenic Artery
branch of the abdominal aorta; supplies blood to the inferior surface of the diaphragm
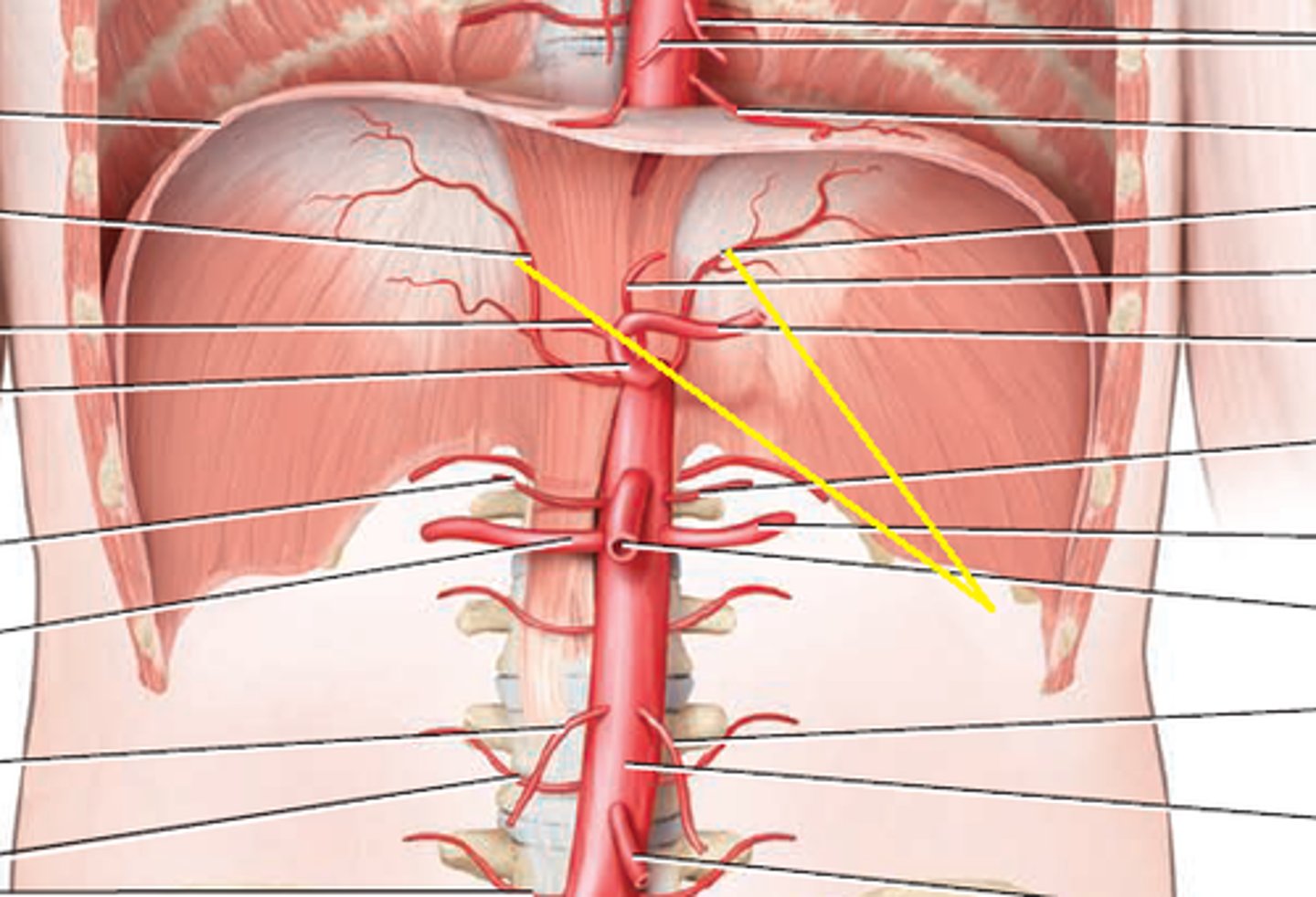
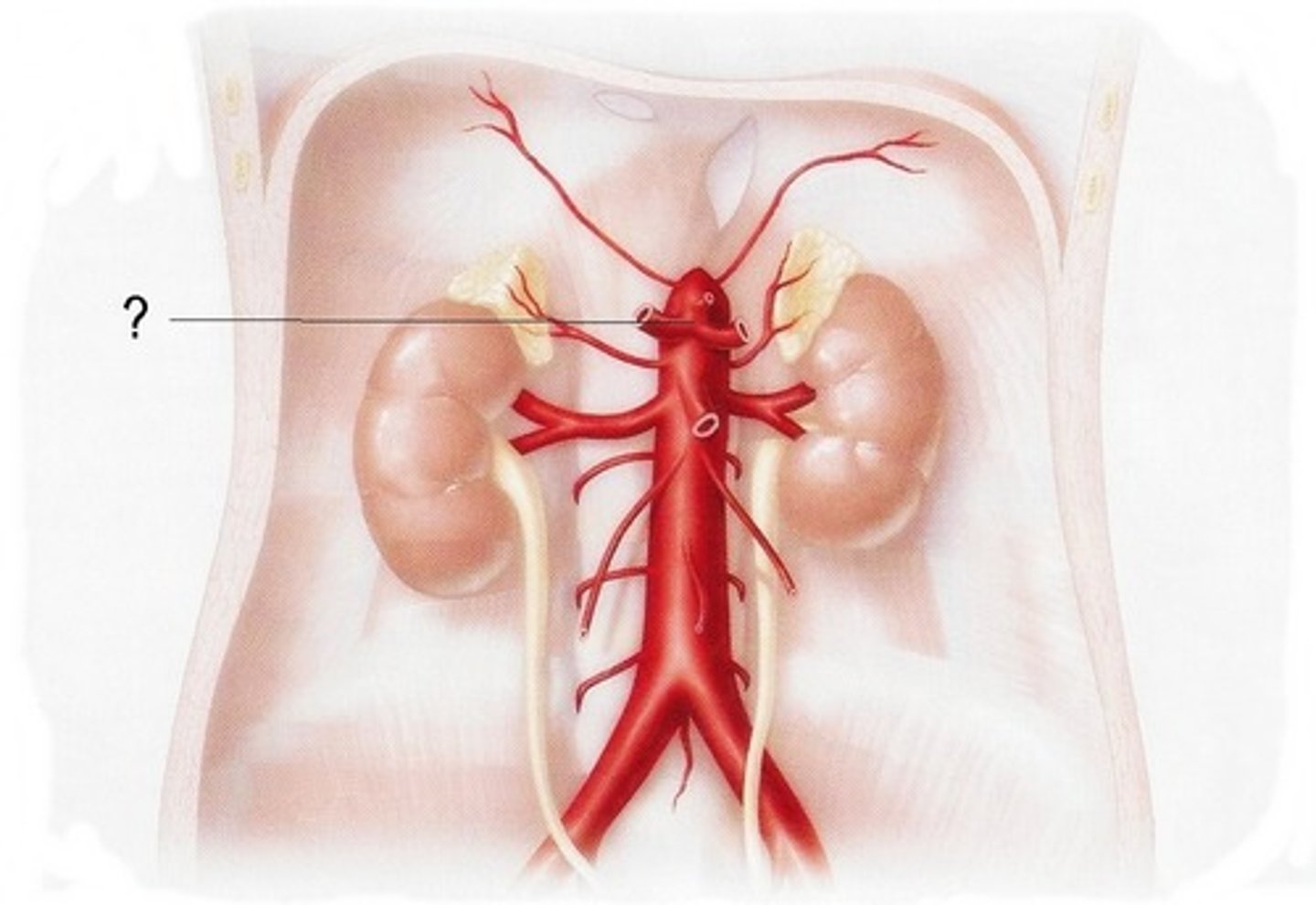
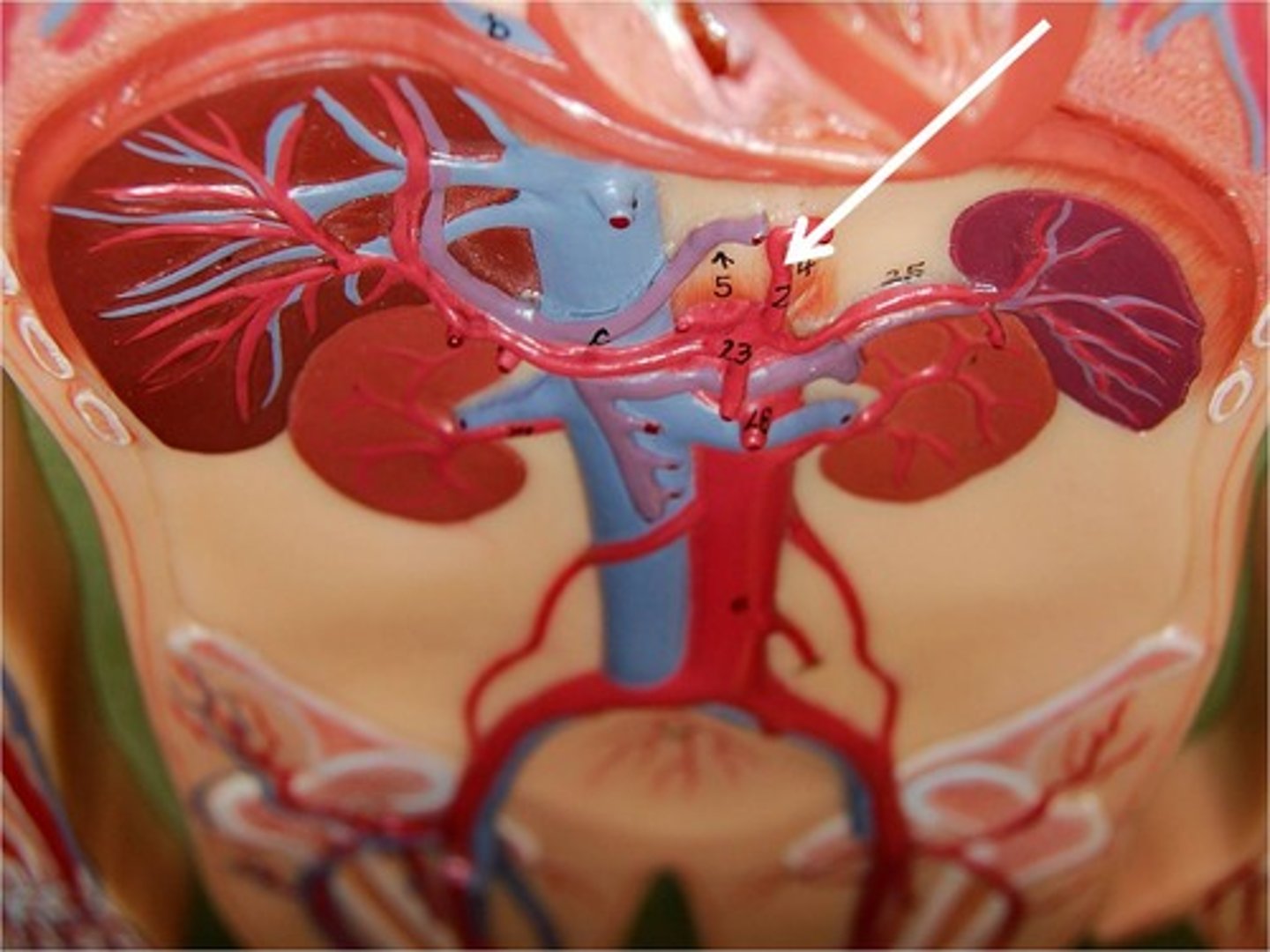
Celiac Trunk
Large unpaired branch of the abdominal aorta that supplies the liver, stomach, and spleen.
Gastric Arteries
carry oxygen rich blood from the celiac and hepatic arteries to the stomach
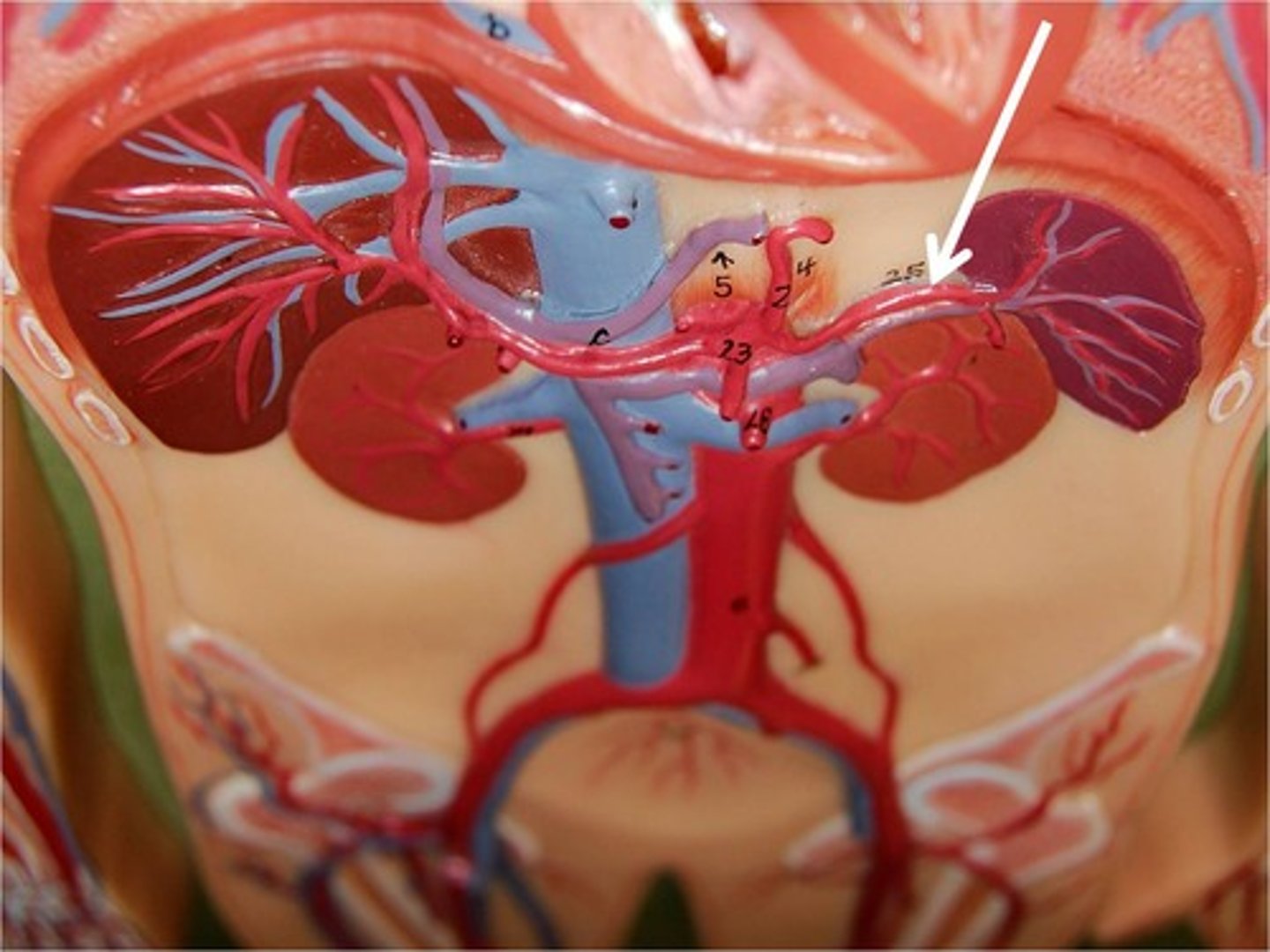
Splenic Artery
supplies the spleen with oxygenated blood
Common Hepatic Artery
arises from the celiac trunk to supply the liver with oxygenated blood
Gastroduodenal Artery
branch of the common hepatic artery that supplies the stomach and duodenum
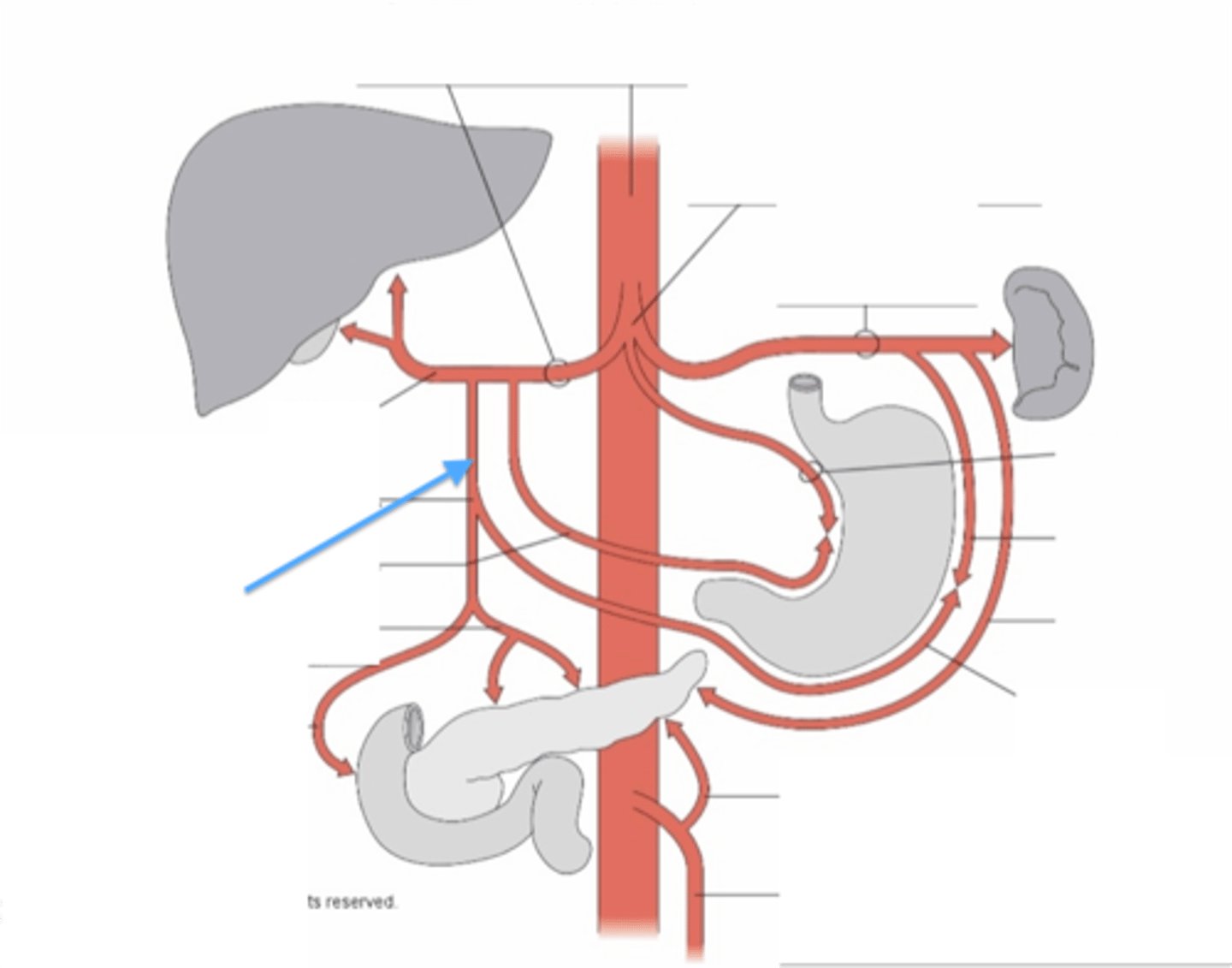
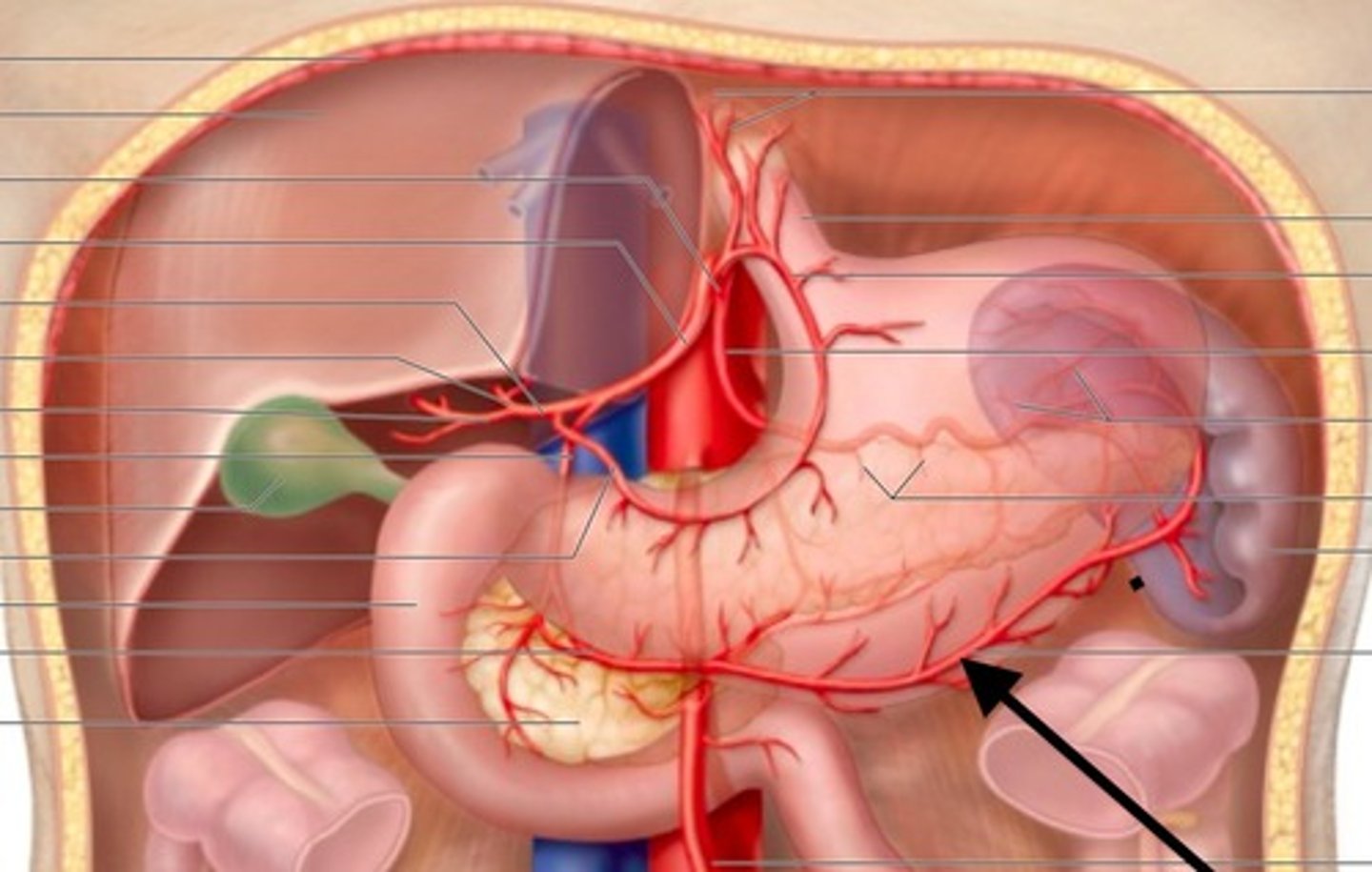
Gastroepiploic Artery
supplies the greater curvature of the stomach
Middle Suprarenal Arteries
serves adrenal glands on kidneys
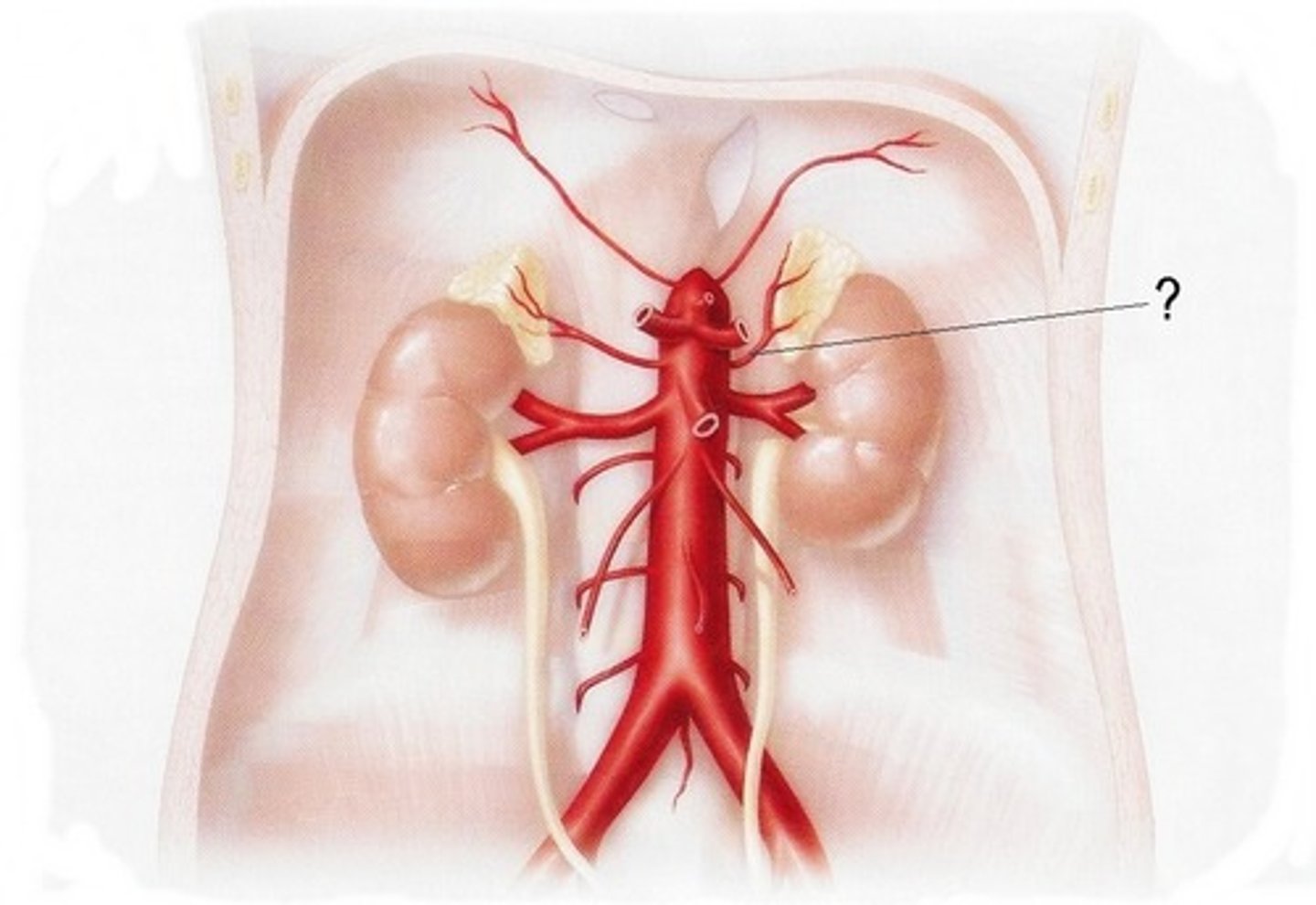
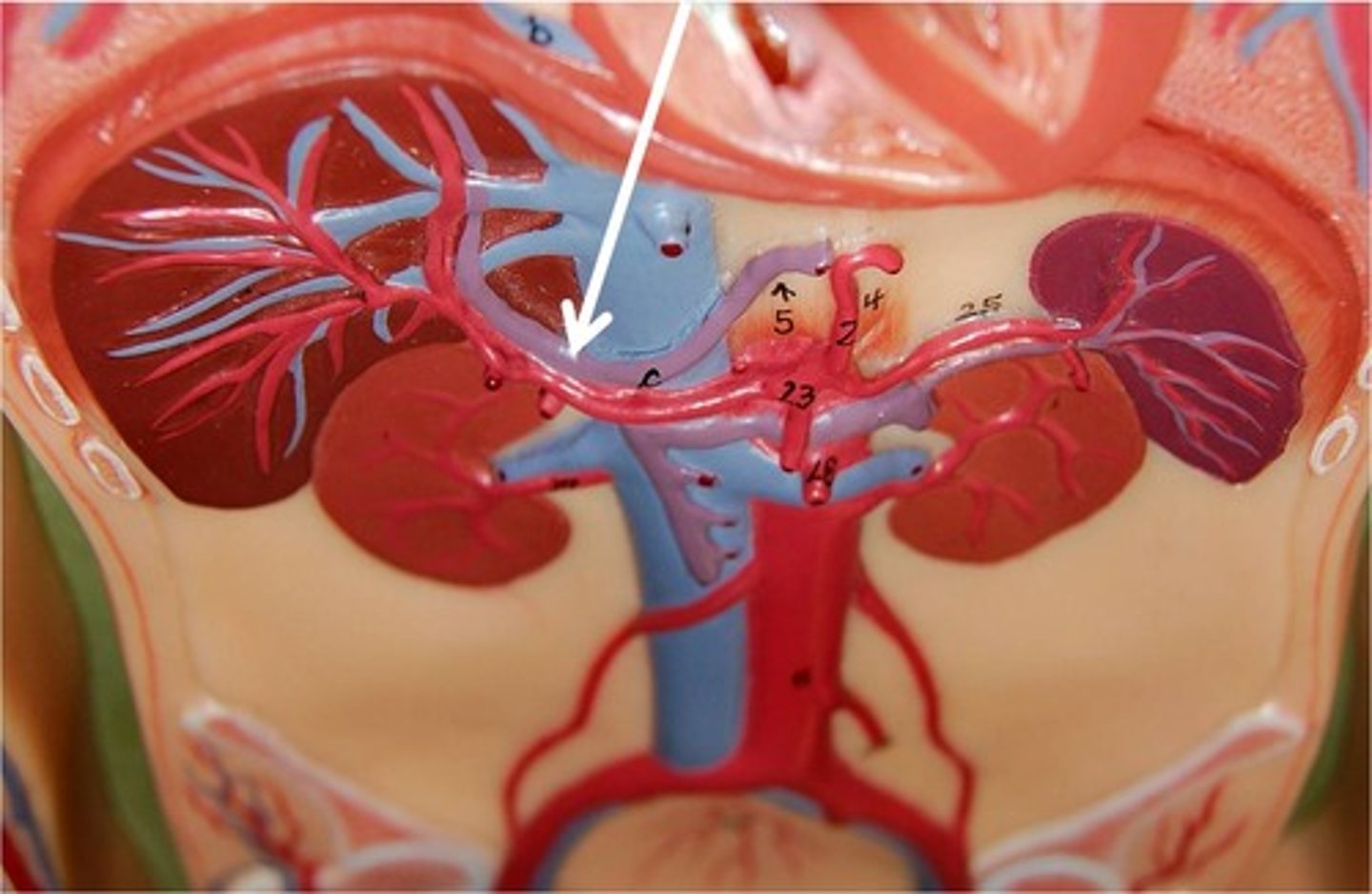
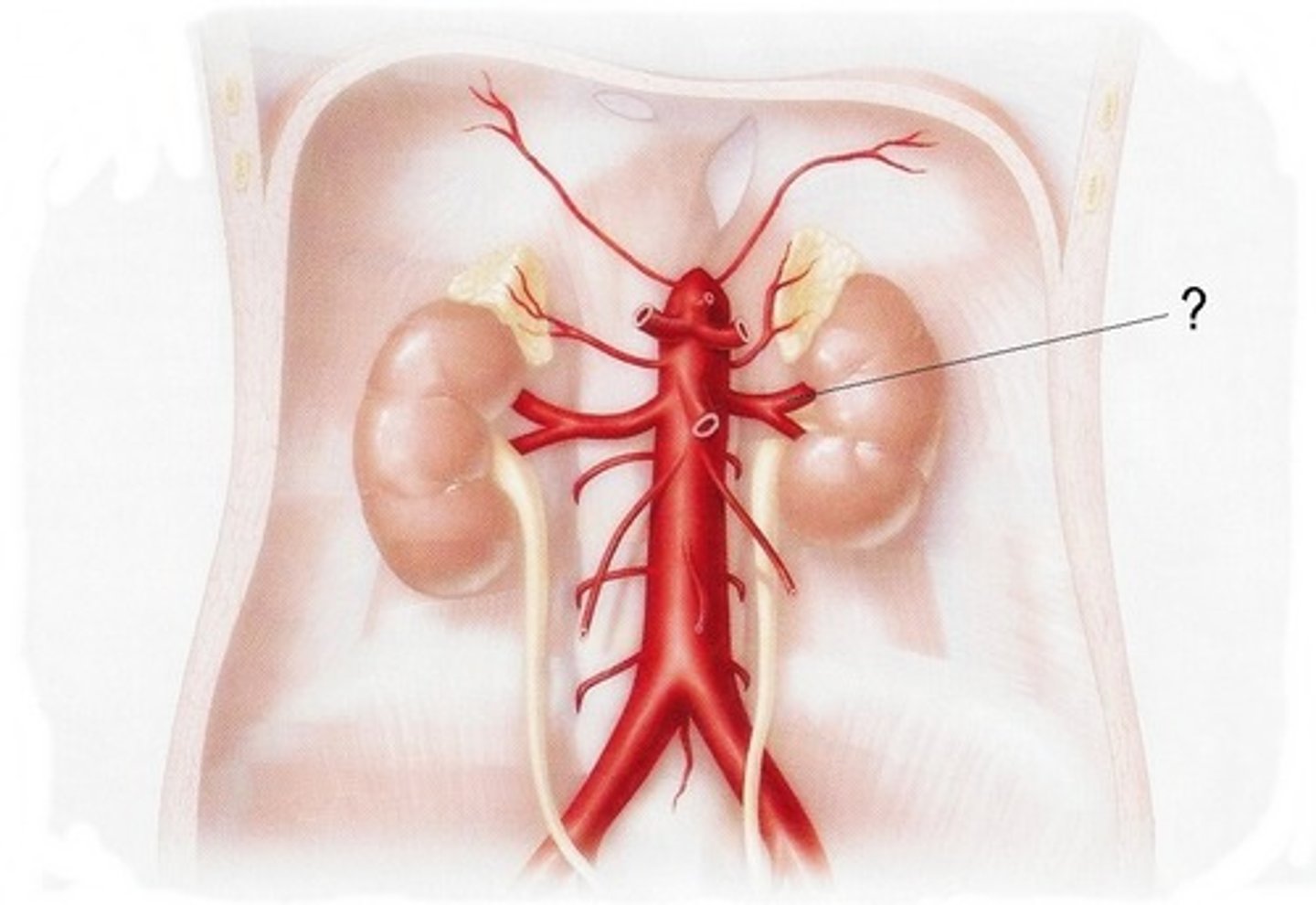
Renal Arteries
The two branches of the abdominal aorta that supply the kidneys
Superior Mesenteric Artery
large abdominal artery; feed large and small intestine
Gonadal Arteries
Serves the ovaries or testes
Inferior Mesenteric Arteries
Supply lower part of large intestine (Colon)
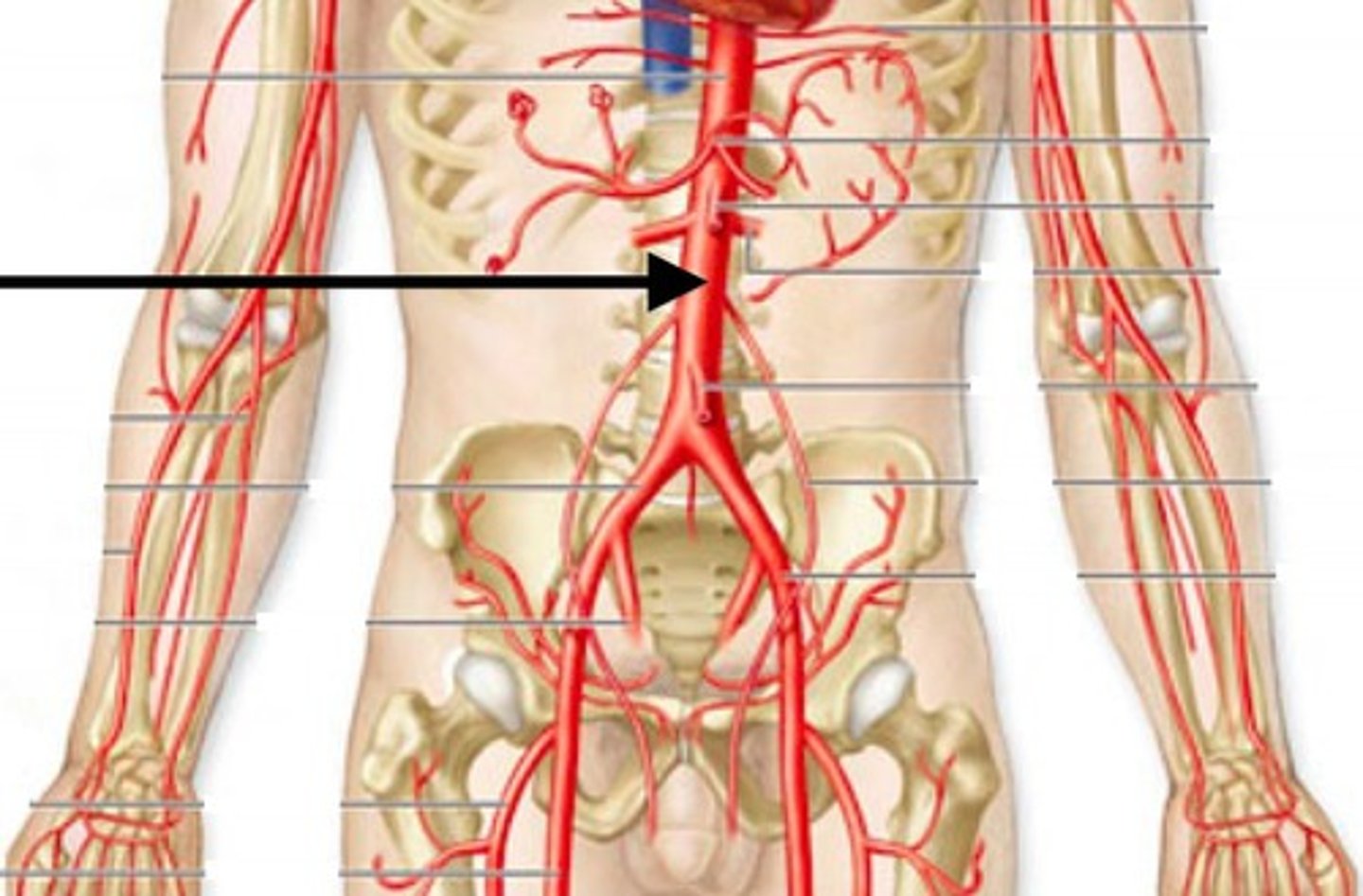
Common Iliac Arteries
supply the anterior abdominal wall, pelvic organs, and lower limbs
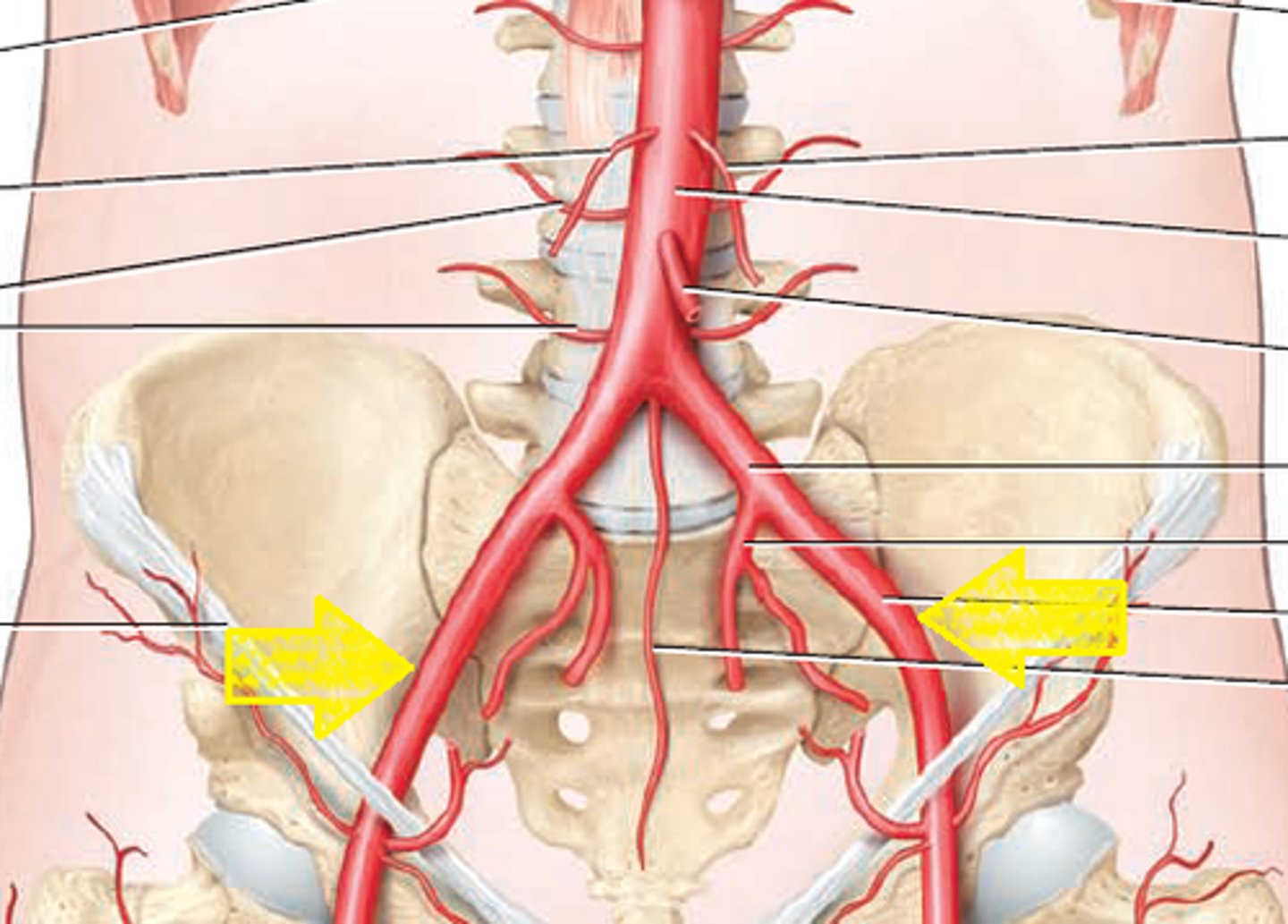
Internal Iliac Arteries
These arteries branch dorsally off the aorta, immediately anterior to the umbilical arteries. They carry blood to the pelvic region.
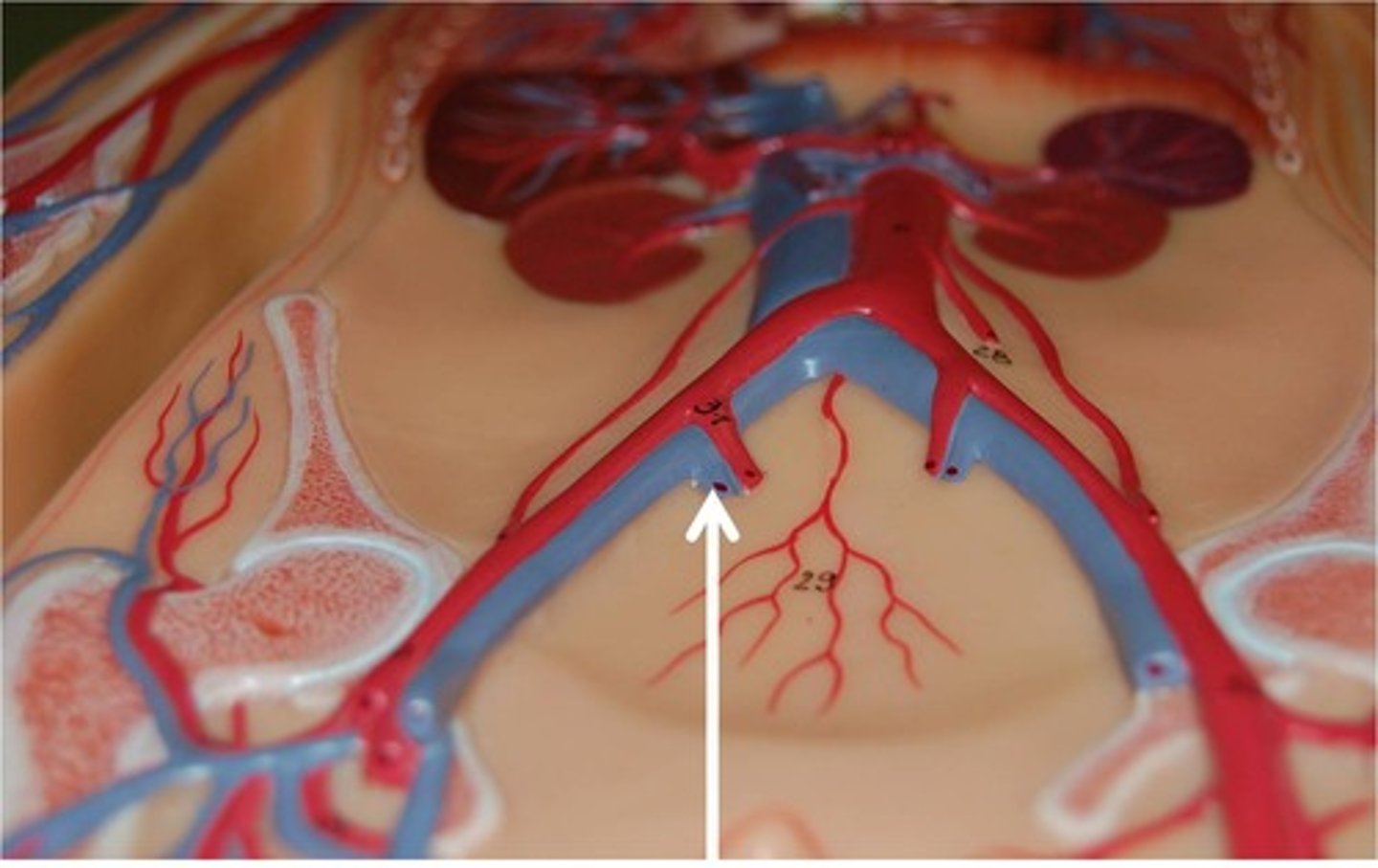
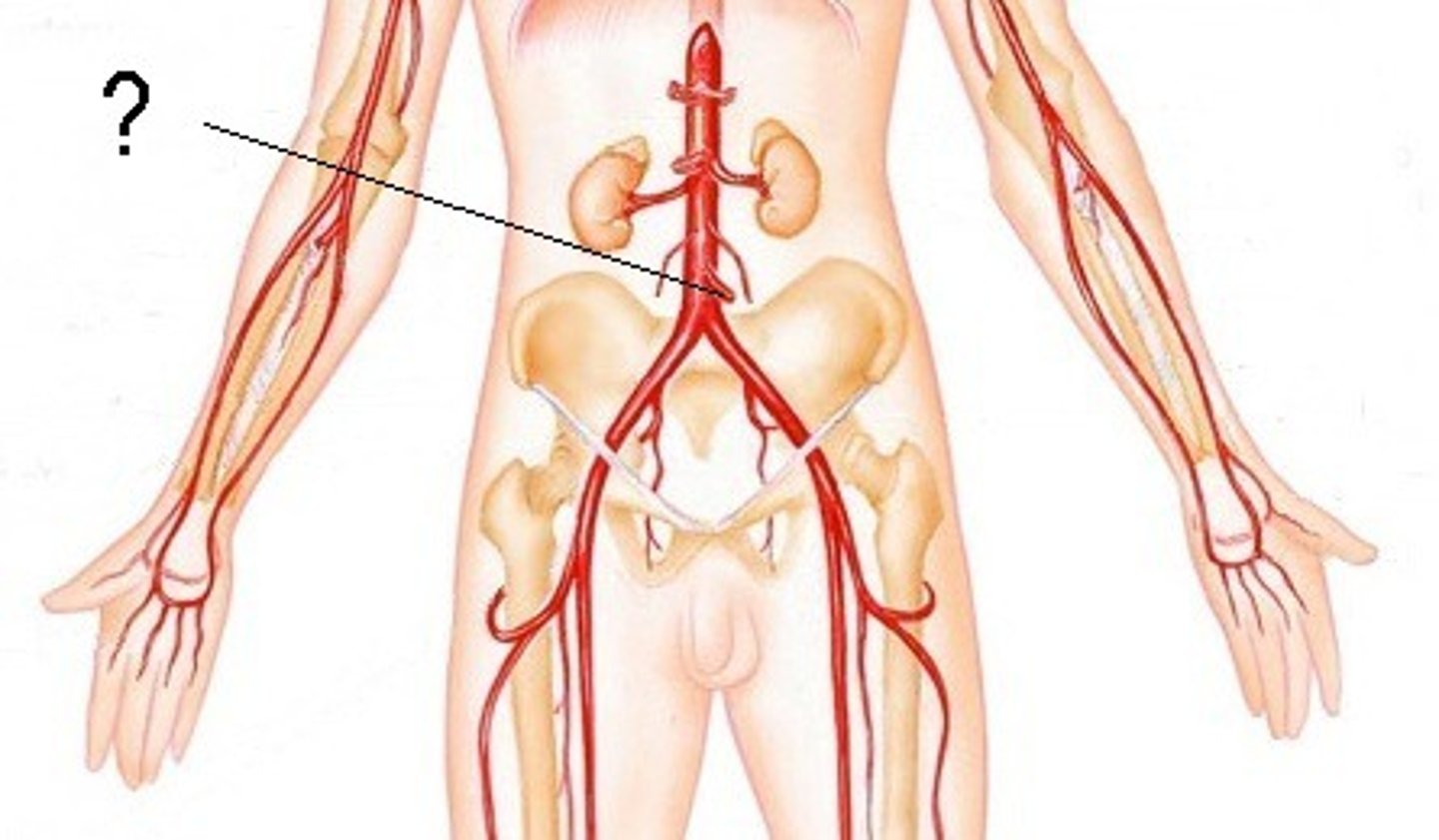
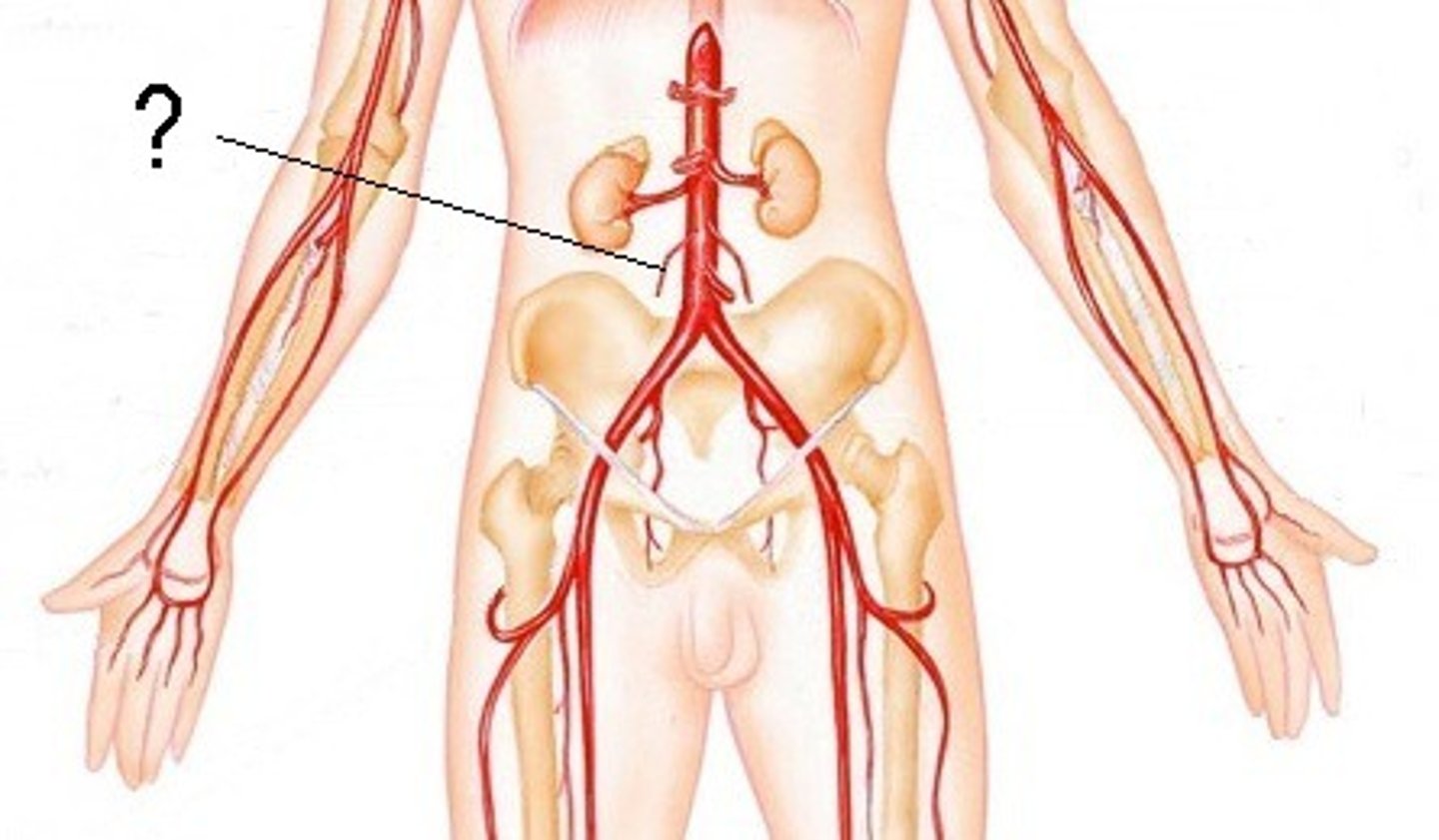
External Iliac Arteries
These arteries branch off the aorta immediately anterior to the umbilical arteries. They carry blood to the thighs and hind limbs.
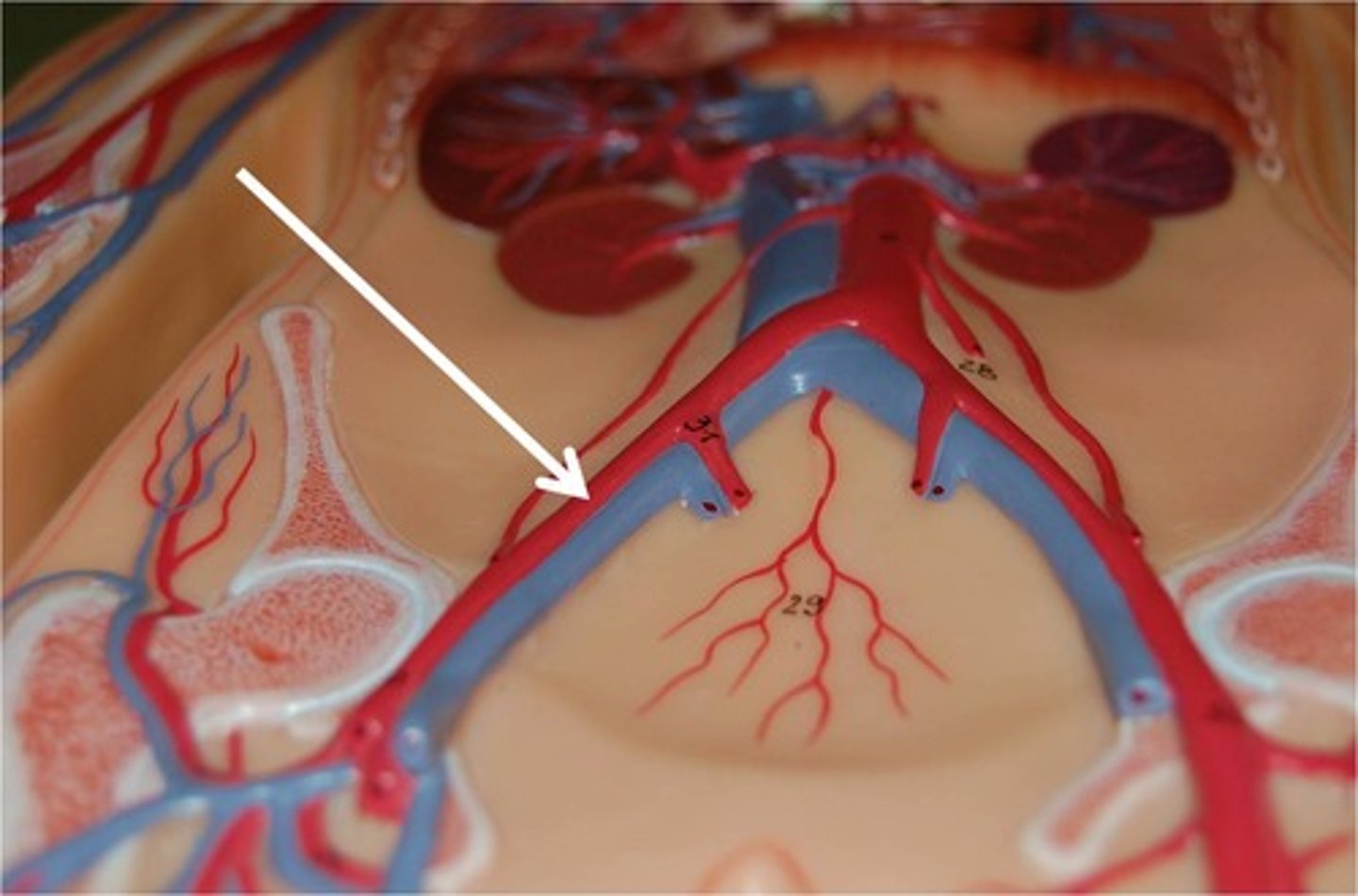
Femoral Arteries
These arteries are one of two branches of the external iliac arteries. They carry blood to the thigh and lower hind limb.
Lateral Circumflex Arteries
Supplies the anterior muscle group of the thigh, as well as the hip and knee joint
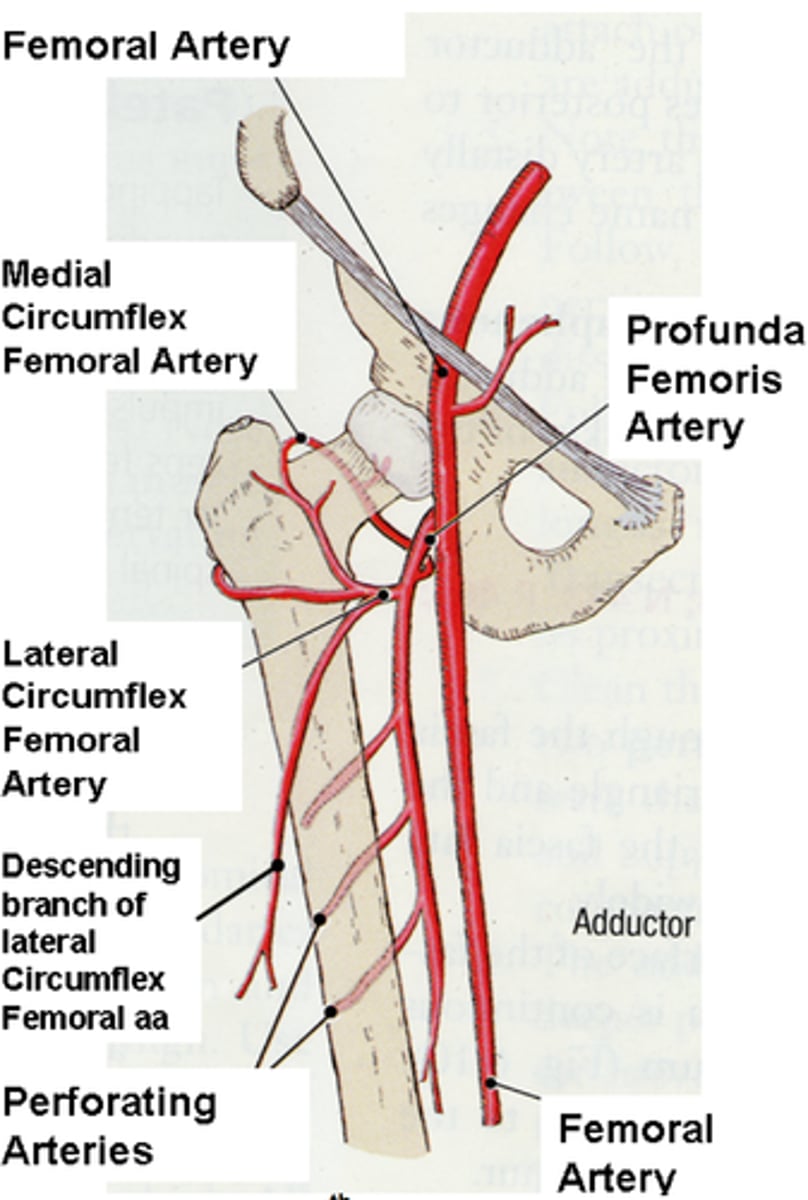
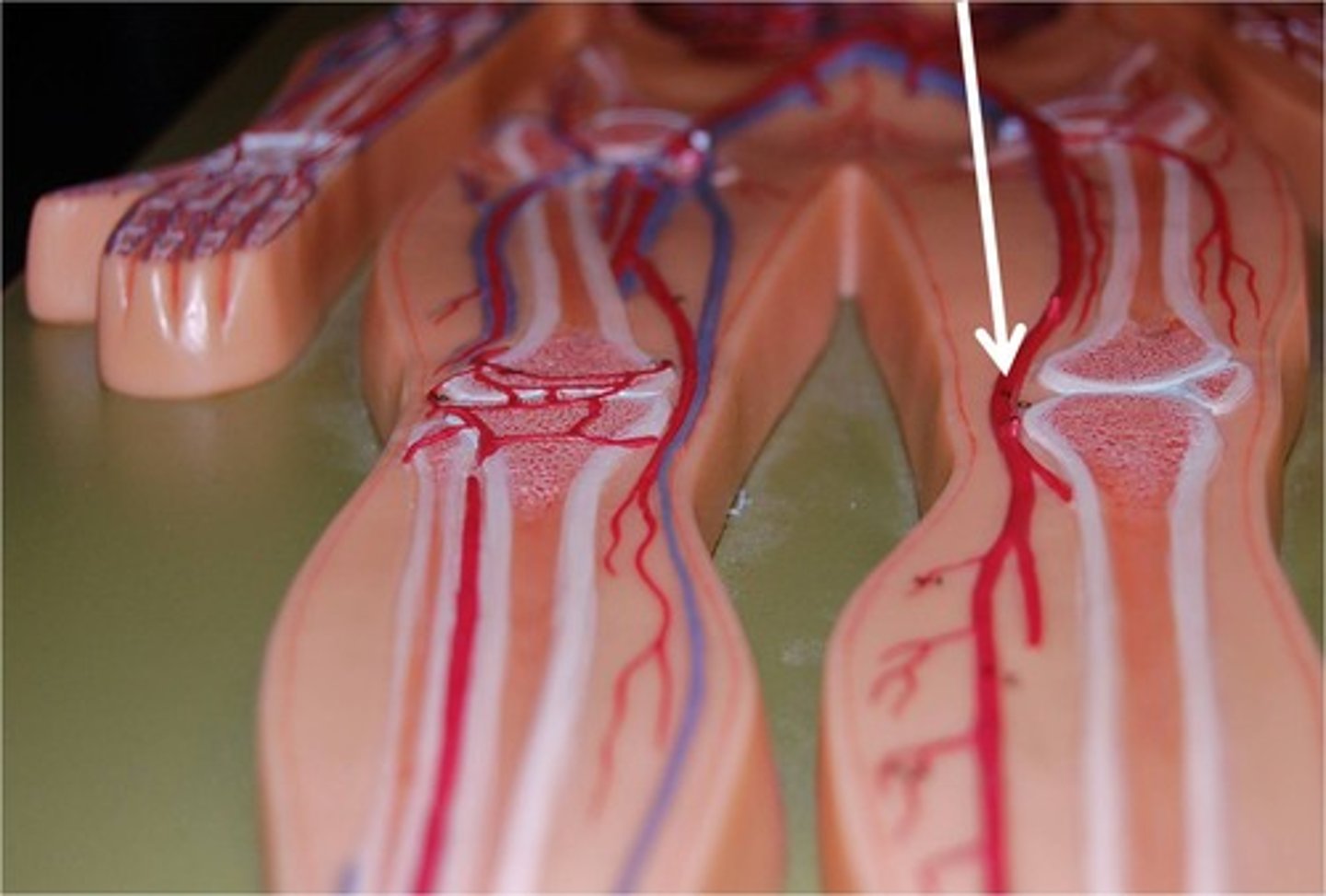
Popliteal Arteries
continuation of femoral arteries that begin in the popliteal region and end in the upper leg where they divide into the anterior and posterior tibial arteries
Anterior Tibial Arteries
A branch of the popliteal artery that supplies the anterior compartment of the leg. It becomes the dorsalis pedis artery on the dorsum of the ankle and contributes blood to the dorsal arch.
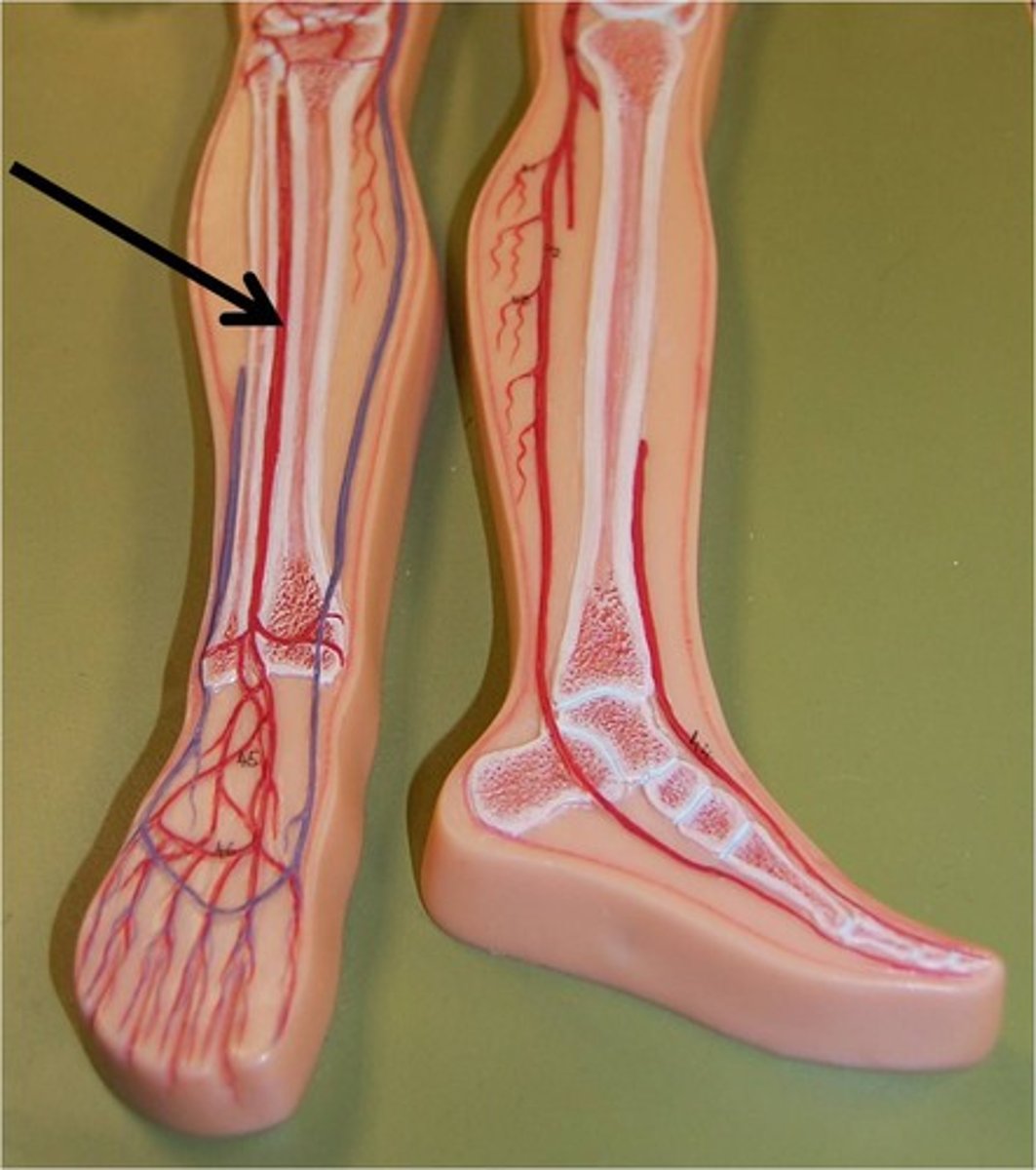
Posterior Tibial Arteries
travels from the calf to the foot
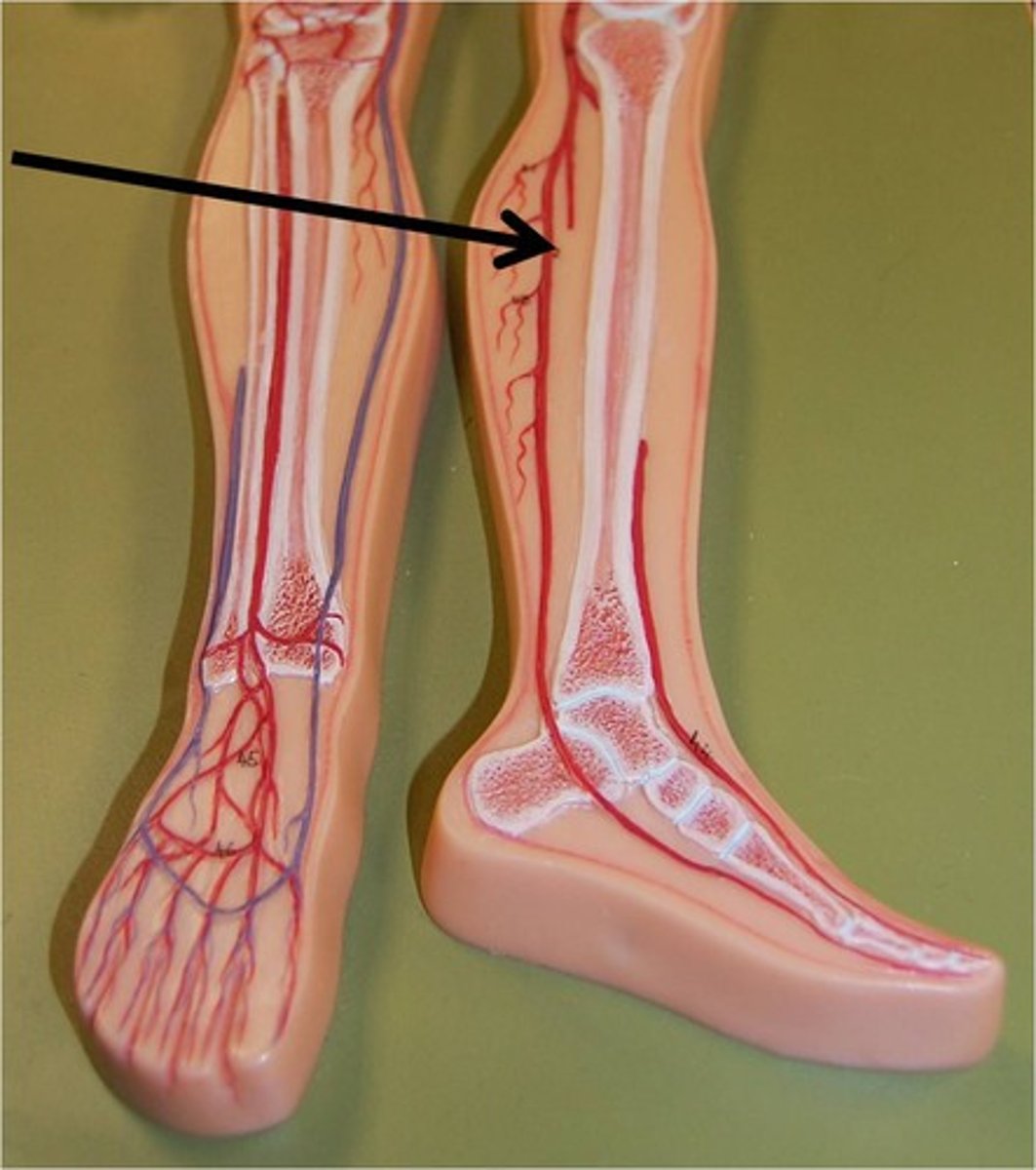
Fibular Arteries
branch off the posterior tibial artery slightly distal to the point where the popliteal artery divides into the anterior and posterior tibial arteries; descends down the lateral surface of the leg, and terminates within the foot
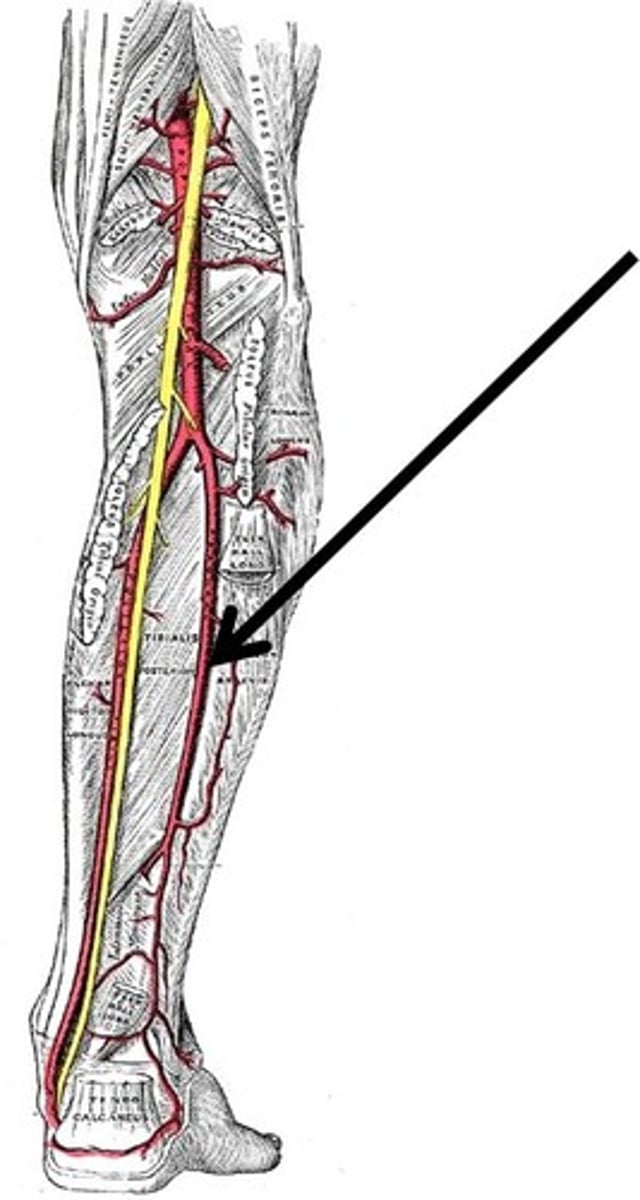
Dorsalis Pedis Arteries
the artery in the foot that can be felt on the top of the foot
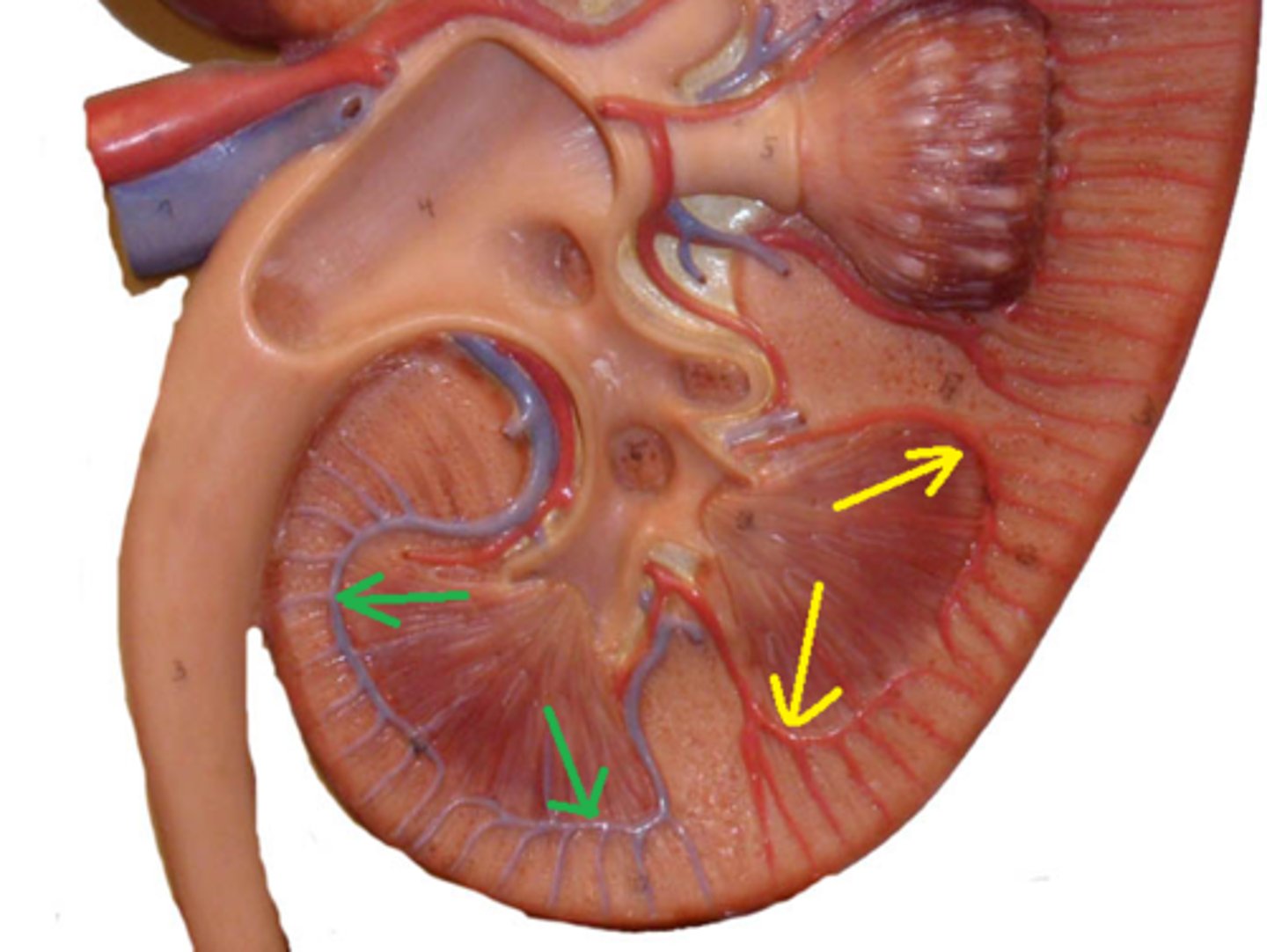
Arcuate Arteries
small vessels found at the base of the renal pyramids; appear as echogenic structures
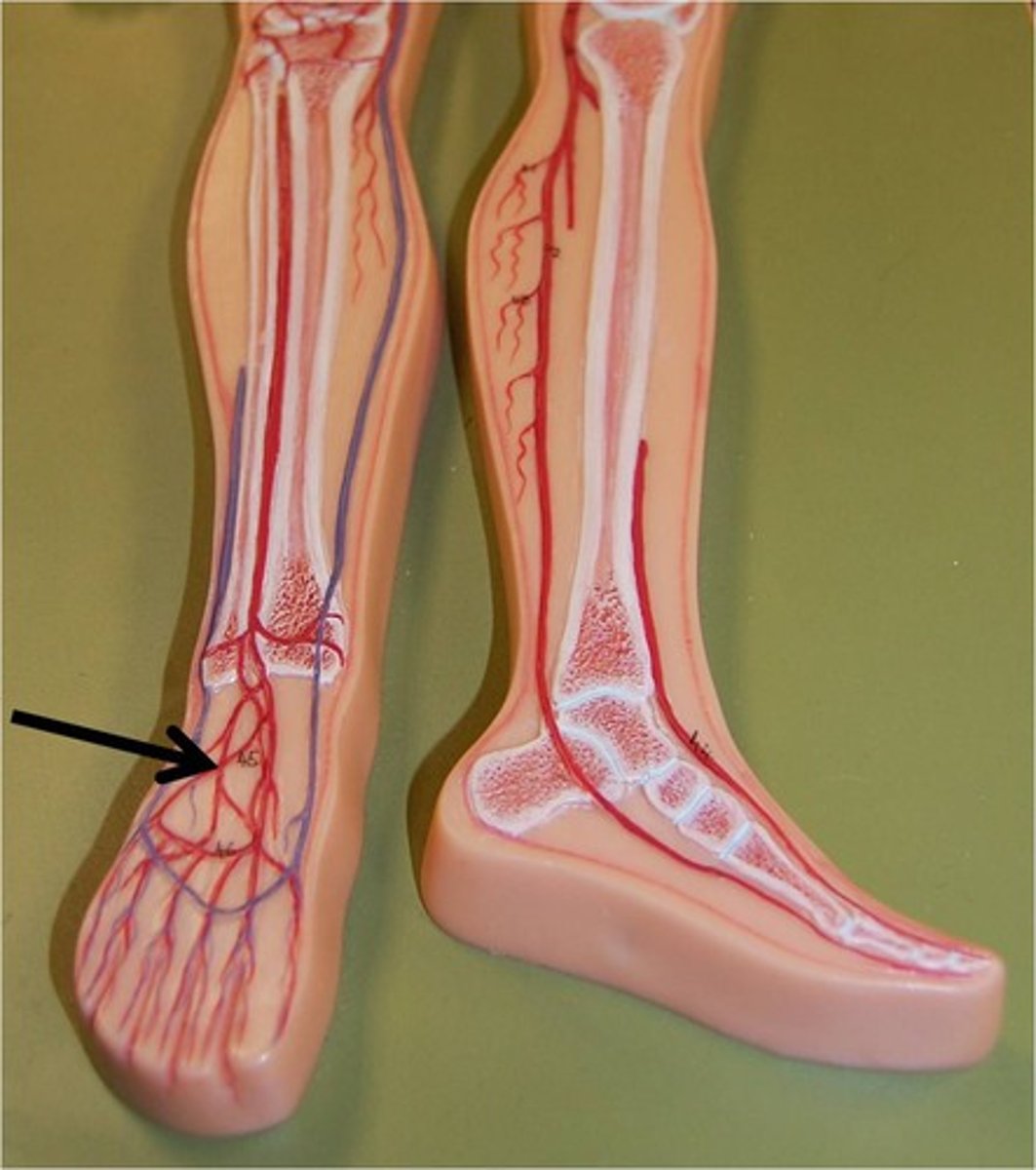
Metatarsal Arteries
Supplies foot and phalanges
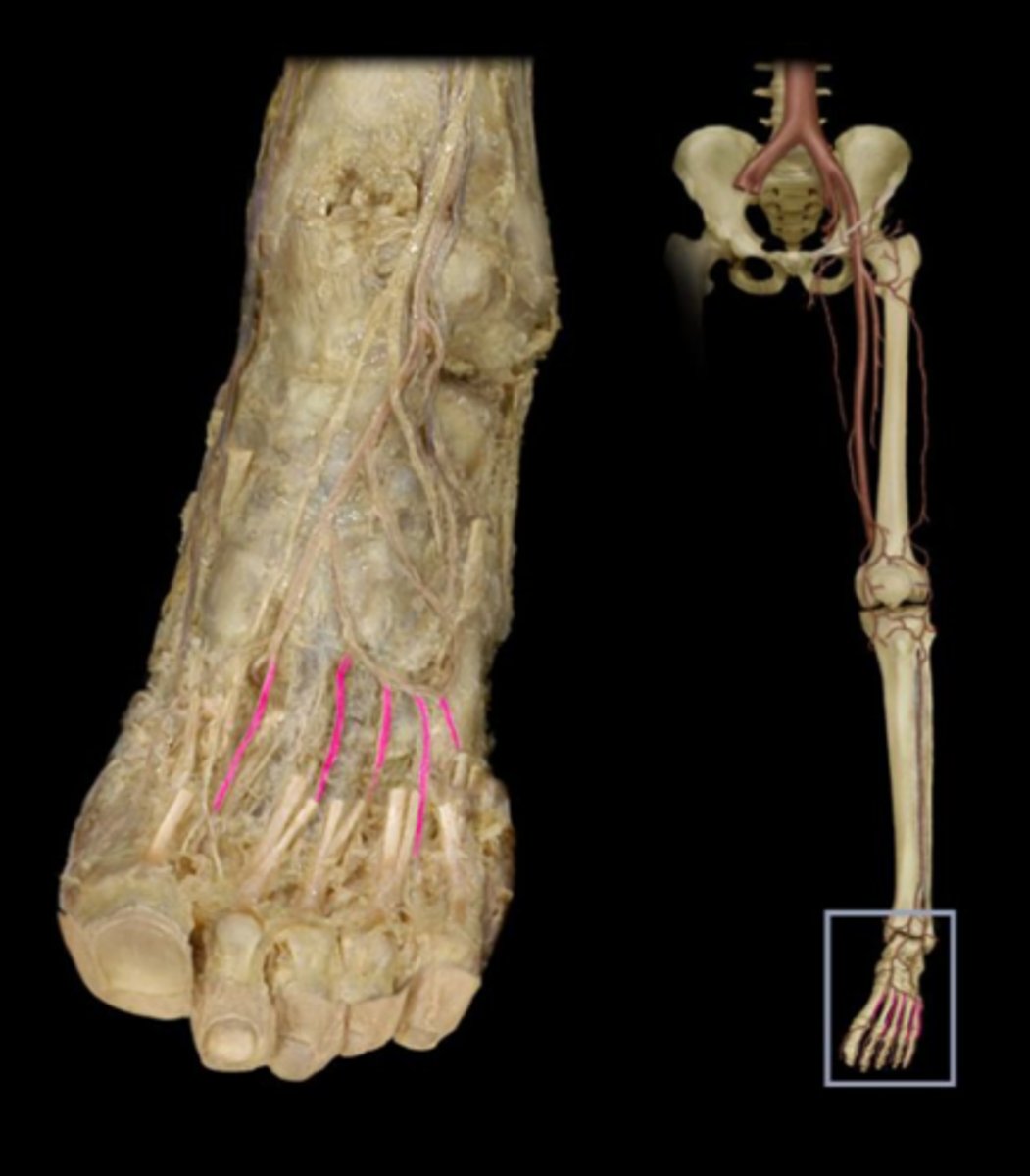
Digital Veins
drain the digits and feed into the palmar arches of the hand and dorsal venous arch of the foot
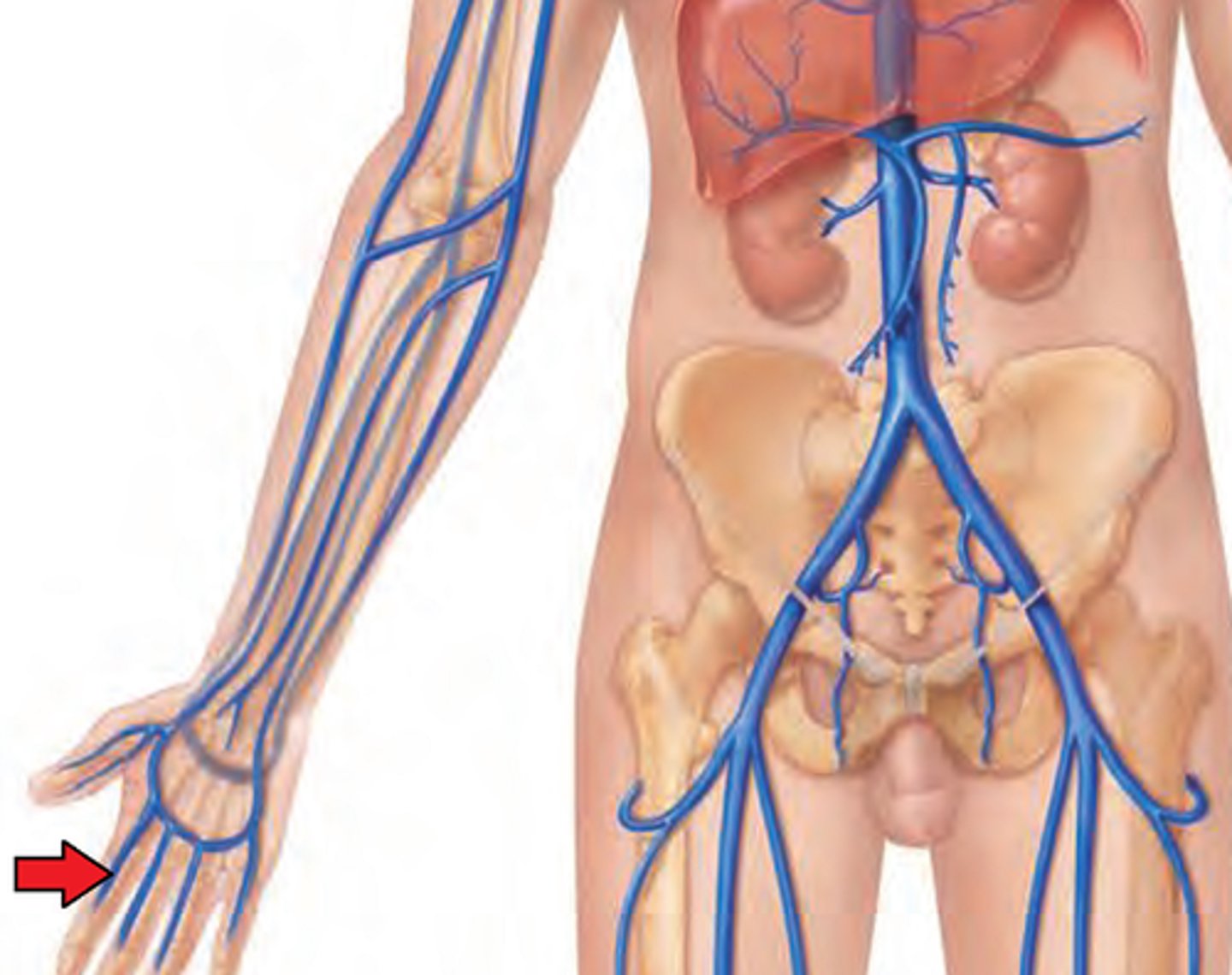
Superficial Venous Palmar Arch
Palm of hand - drains into cephalic and basilica veins
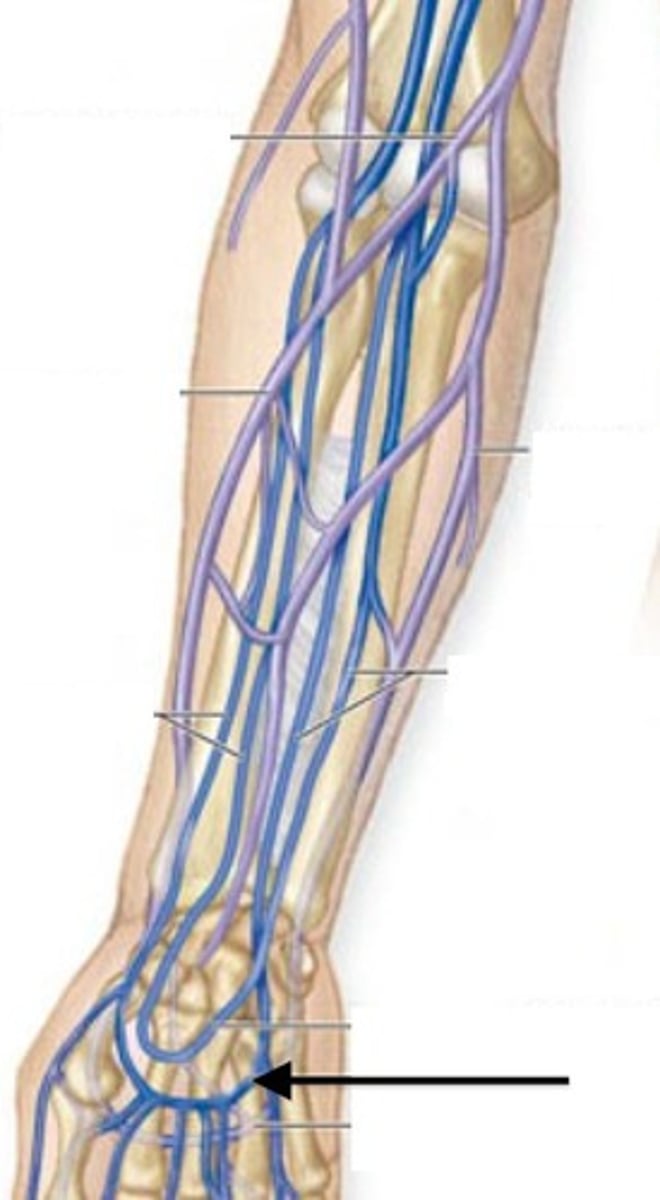
Radial Veins
Drain the palmar venous arches and forearm into brachial veins. Run along the radius.
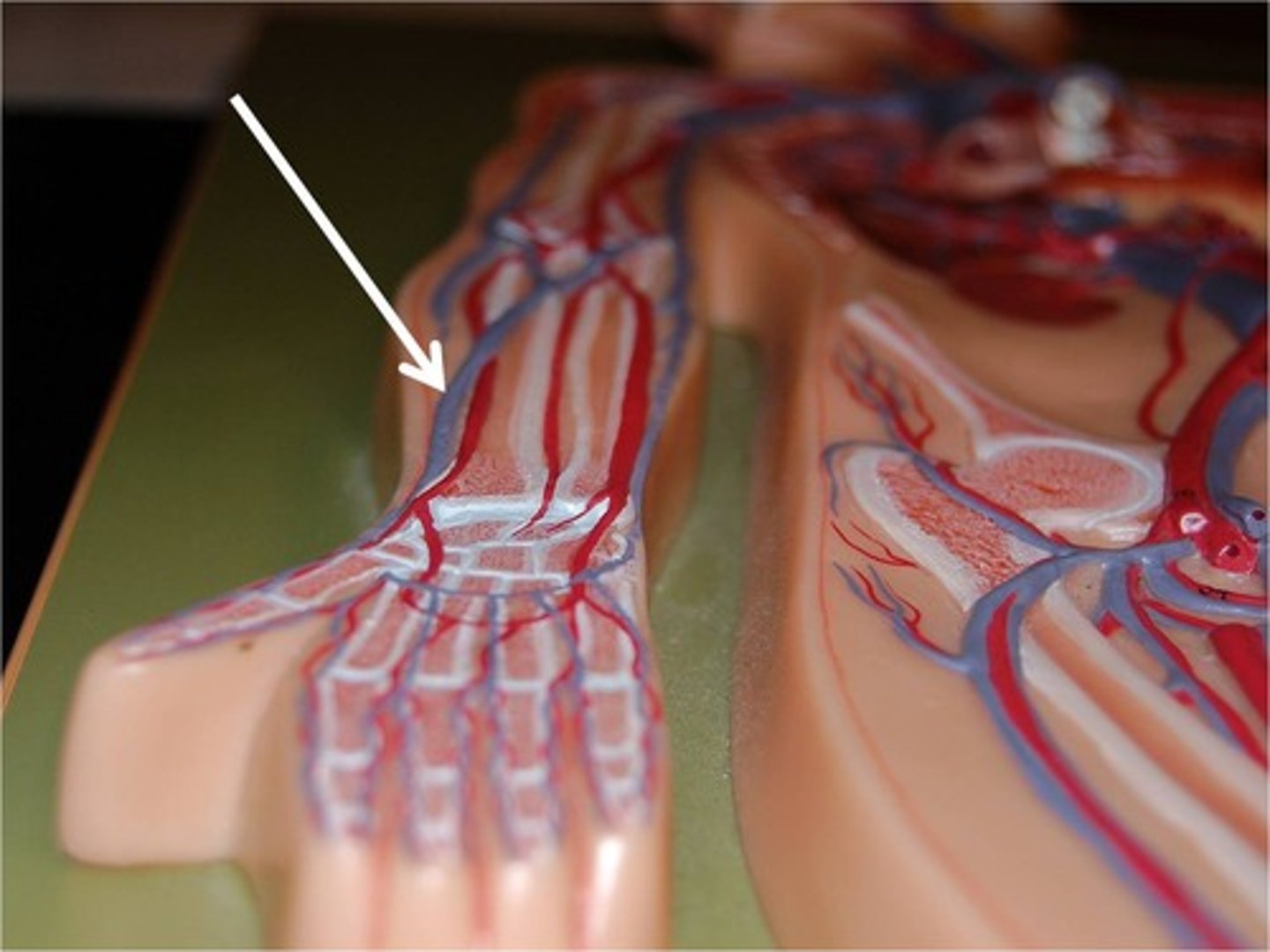
Ulnar Veins
carry oxygen depleted blood from the lower medial portion of the forearm to the brachial vein
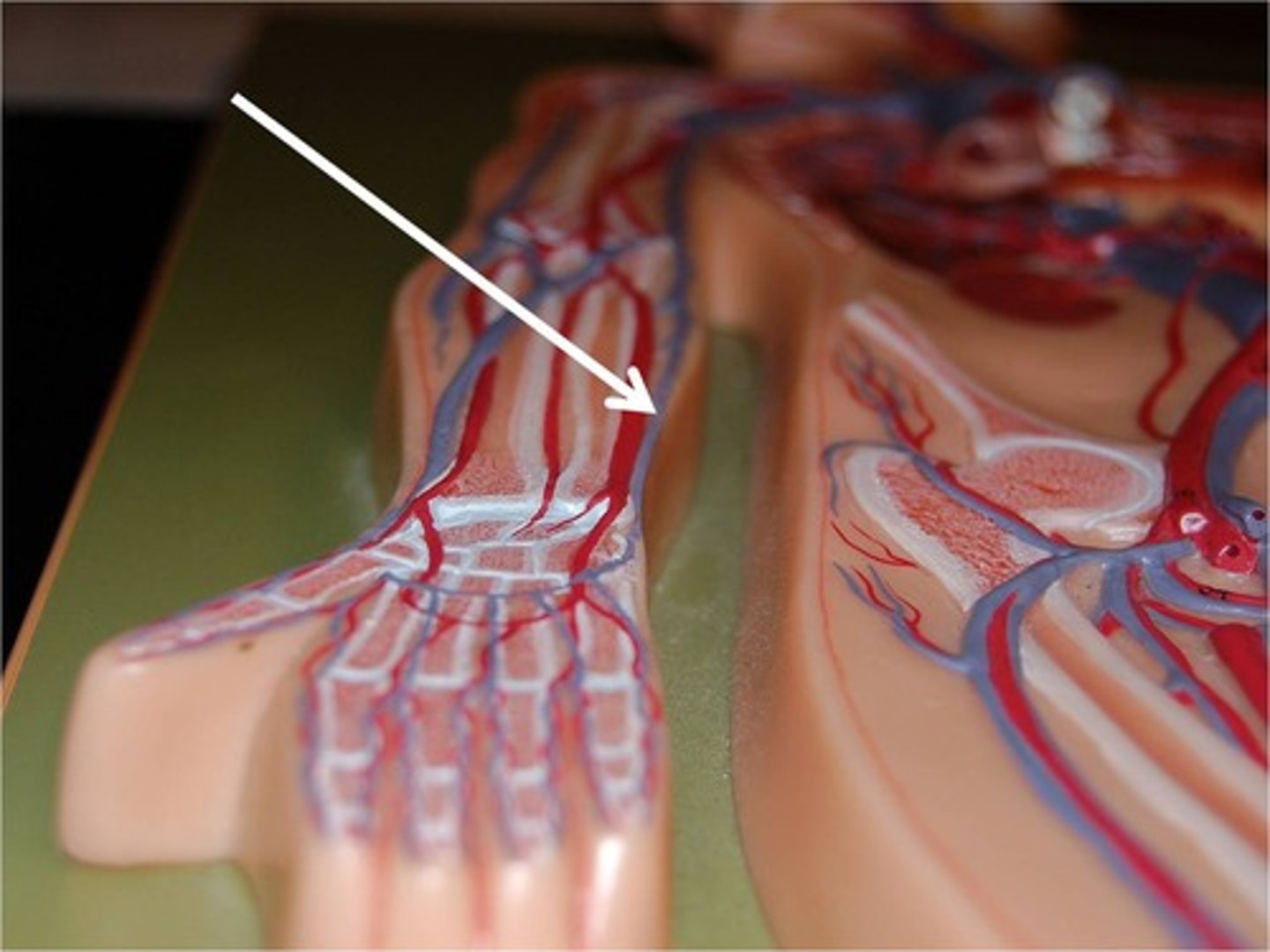
Basilic Veins
Blood vessels that drain blood back to the heart from the arms/forearms and run along the MEDIAL aspect of the arm
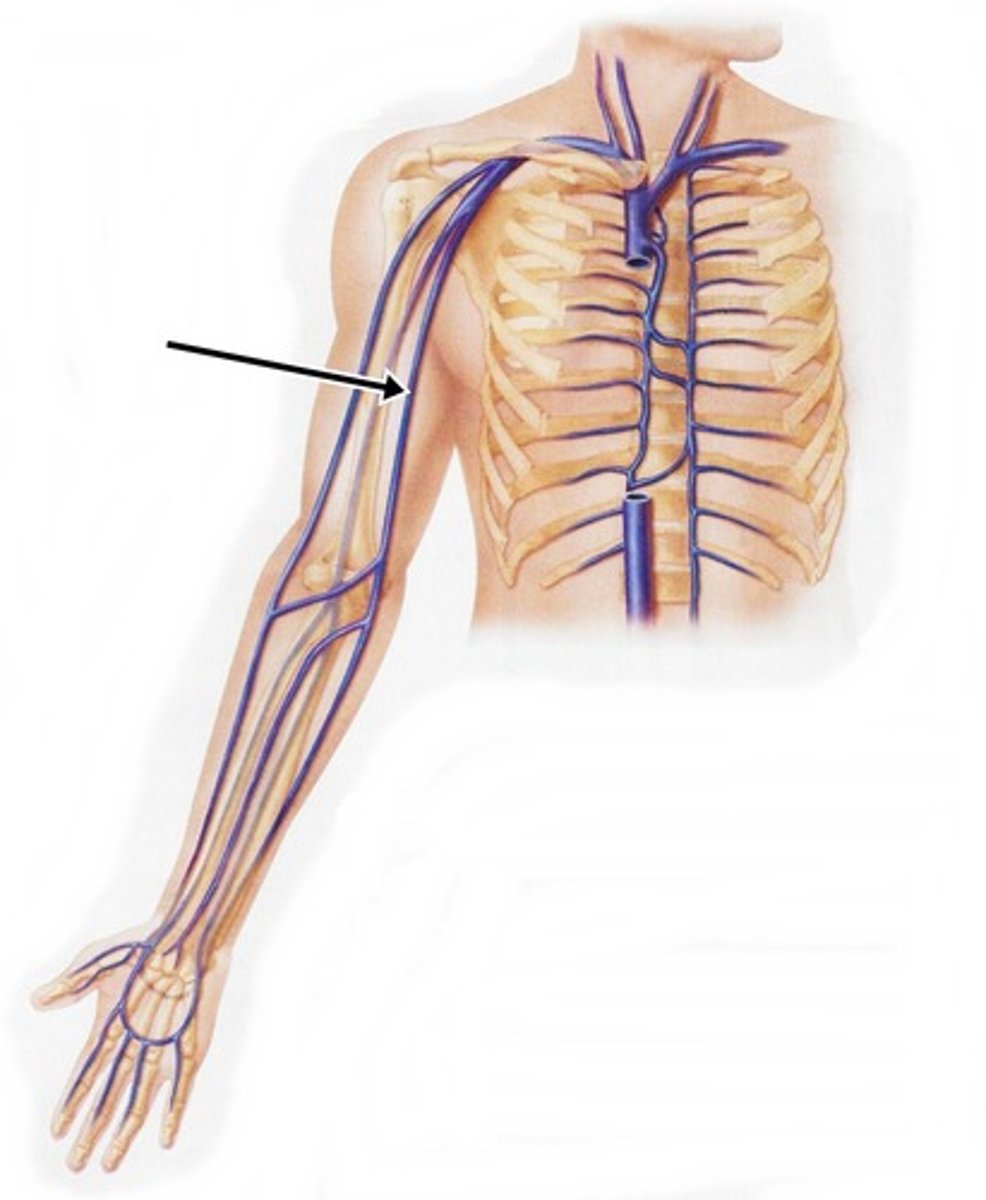
Cephalic Veins
The third vessels to emerge from the cranial vena cava, medially. These veins carry blood from the forelimb to the brachiocephalic veins.
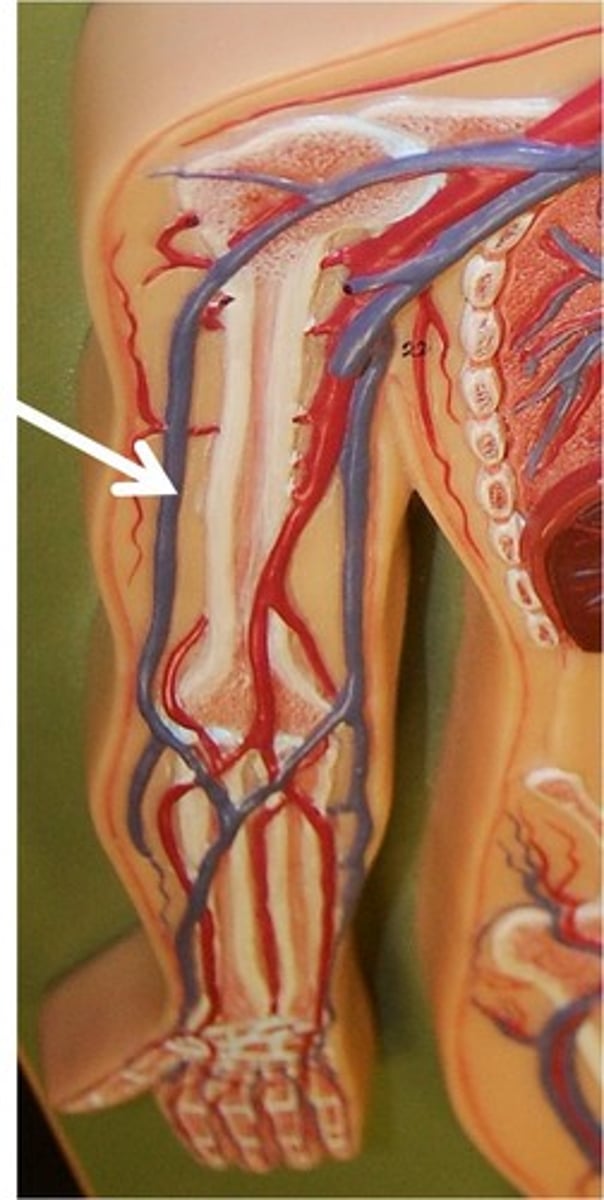
Median Antebrachial Veins
Vein that runs between the ulnar and radial veins up the forearm, terminating at the elbow by entering the basilic or cephalic vein
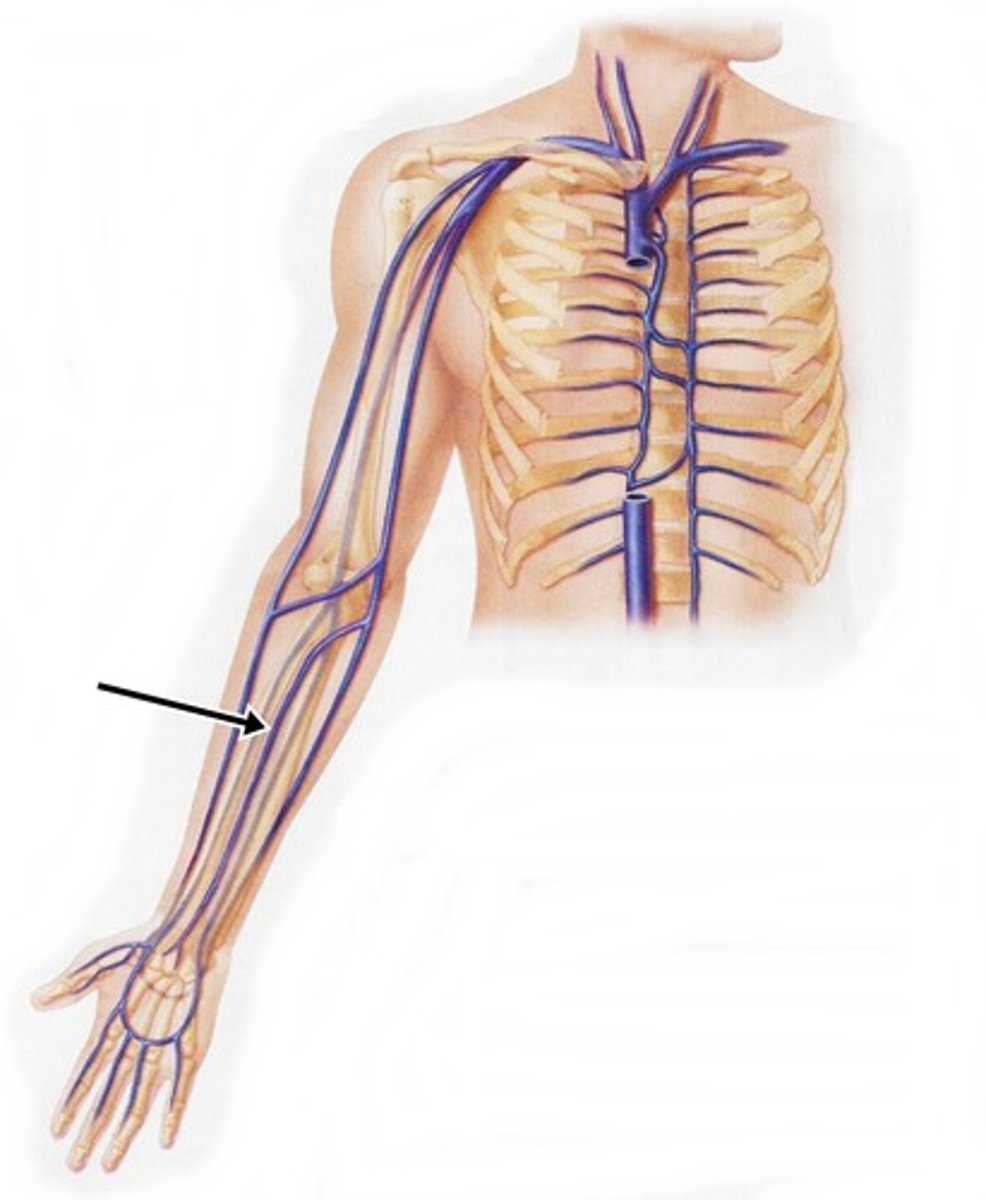
Median Cubital Veins
travel laterally across the anterior surface of the elbow to connect the basilic and cephalic veins
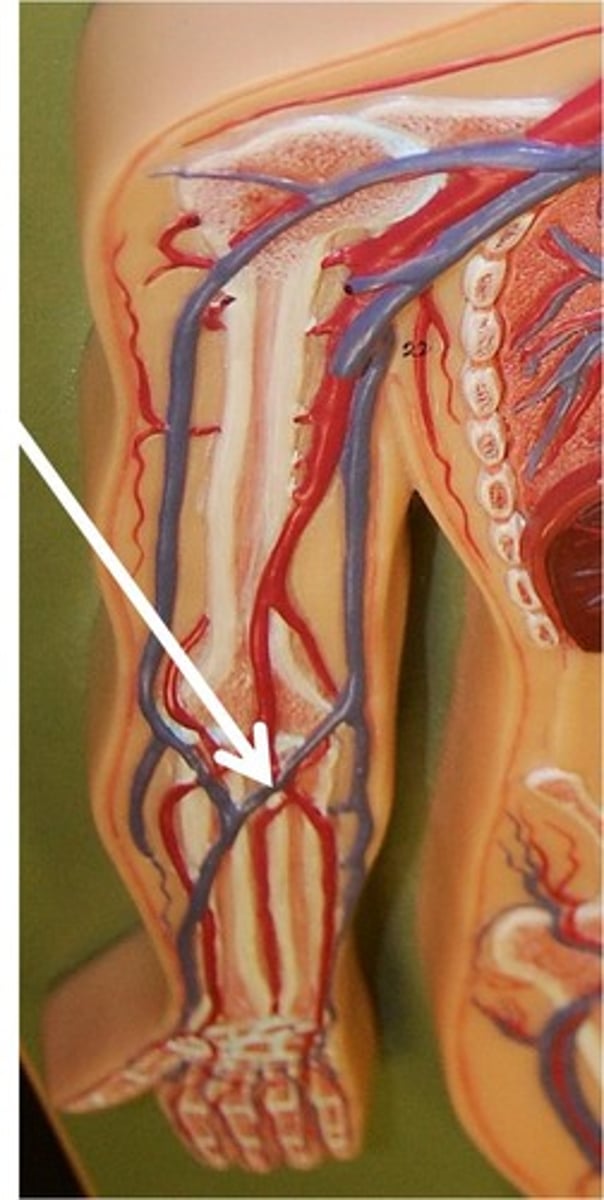
Brachial Veins
veins following the course of the brachial artery and joining with the basilic vein to form the axillary vein
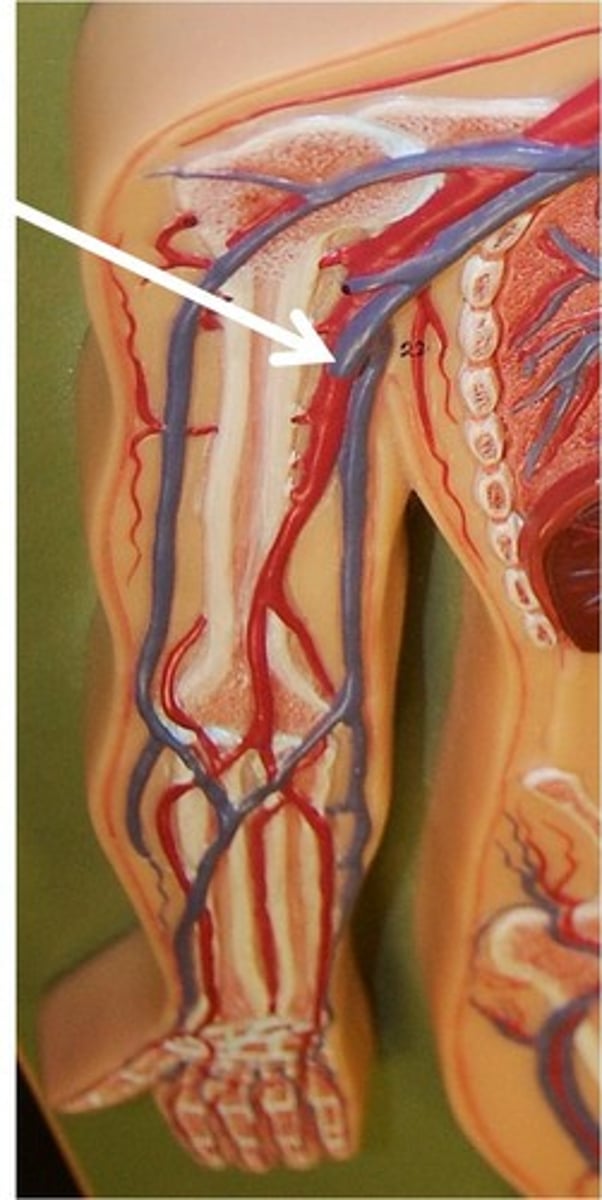
Axillary Veins
These veins carry blood from the forelimbs and join with the subscapular veins to form the subclavian vein.
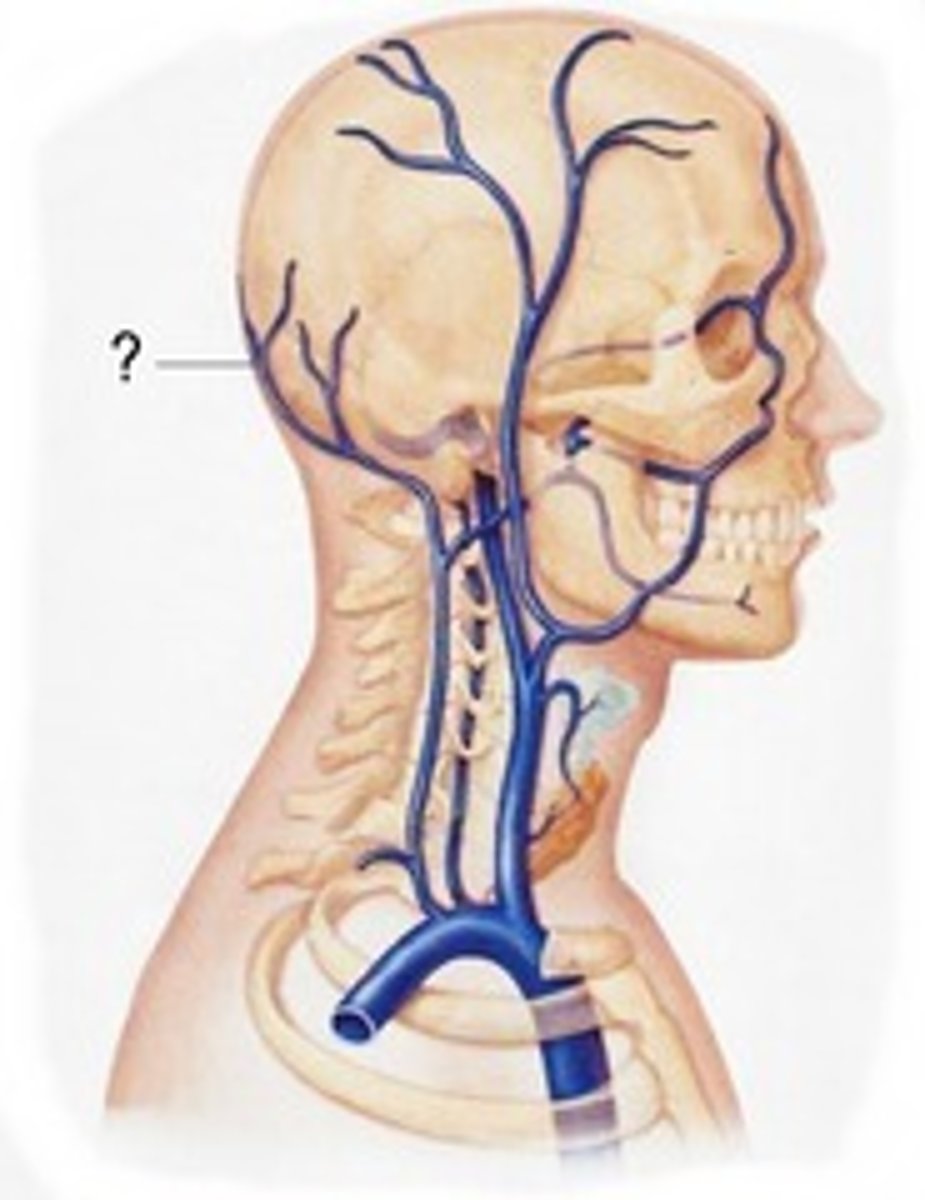
Occipital Veins
drain occipital region of scalp
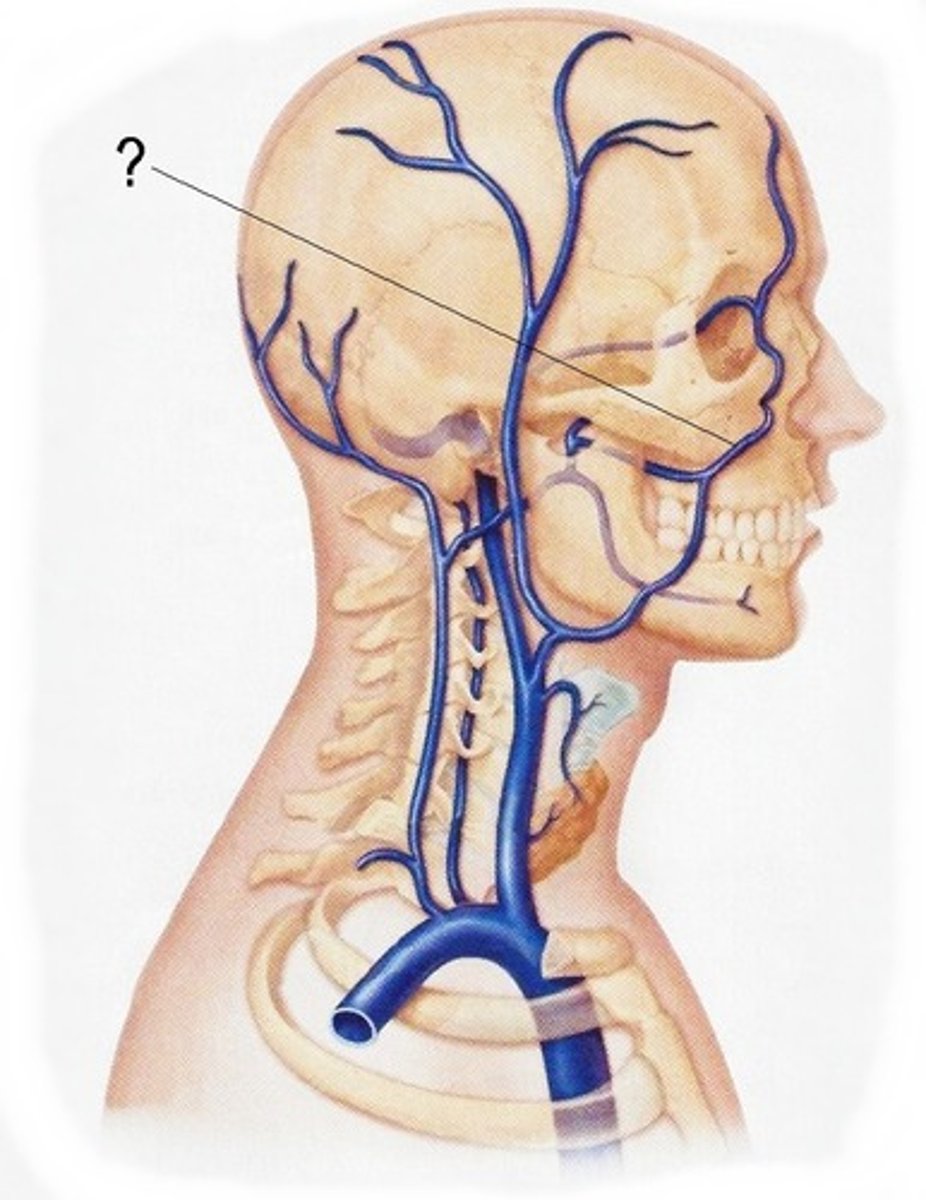
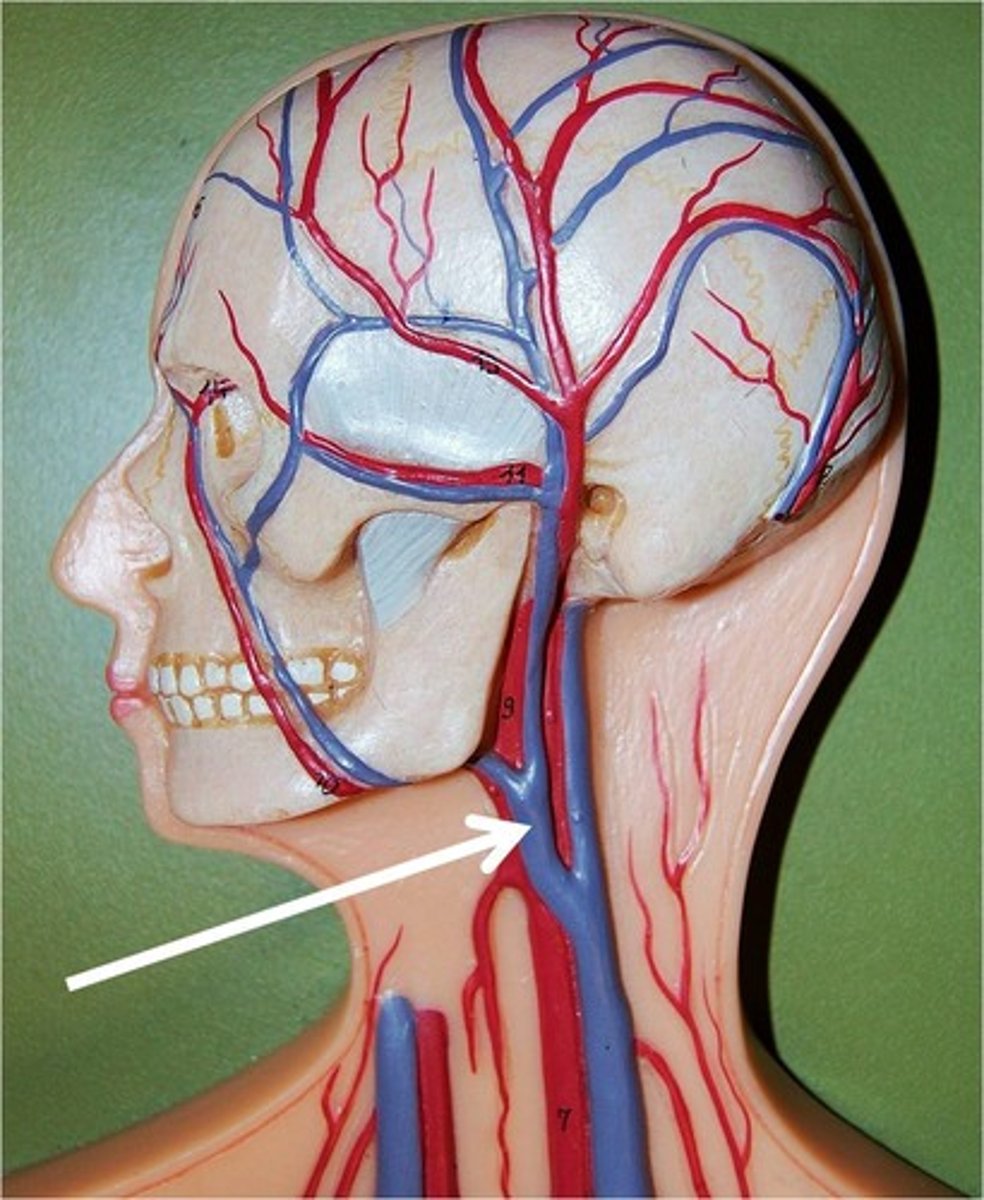
External Jugular Veins
The second set of vessels to emerge from the cranial vena cava, medially. These veins carry blood from the head to the brachiocephalic veins.
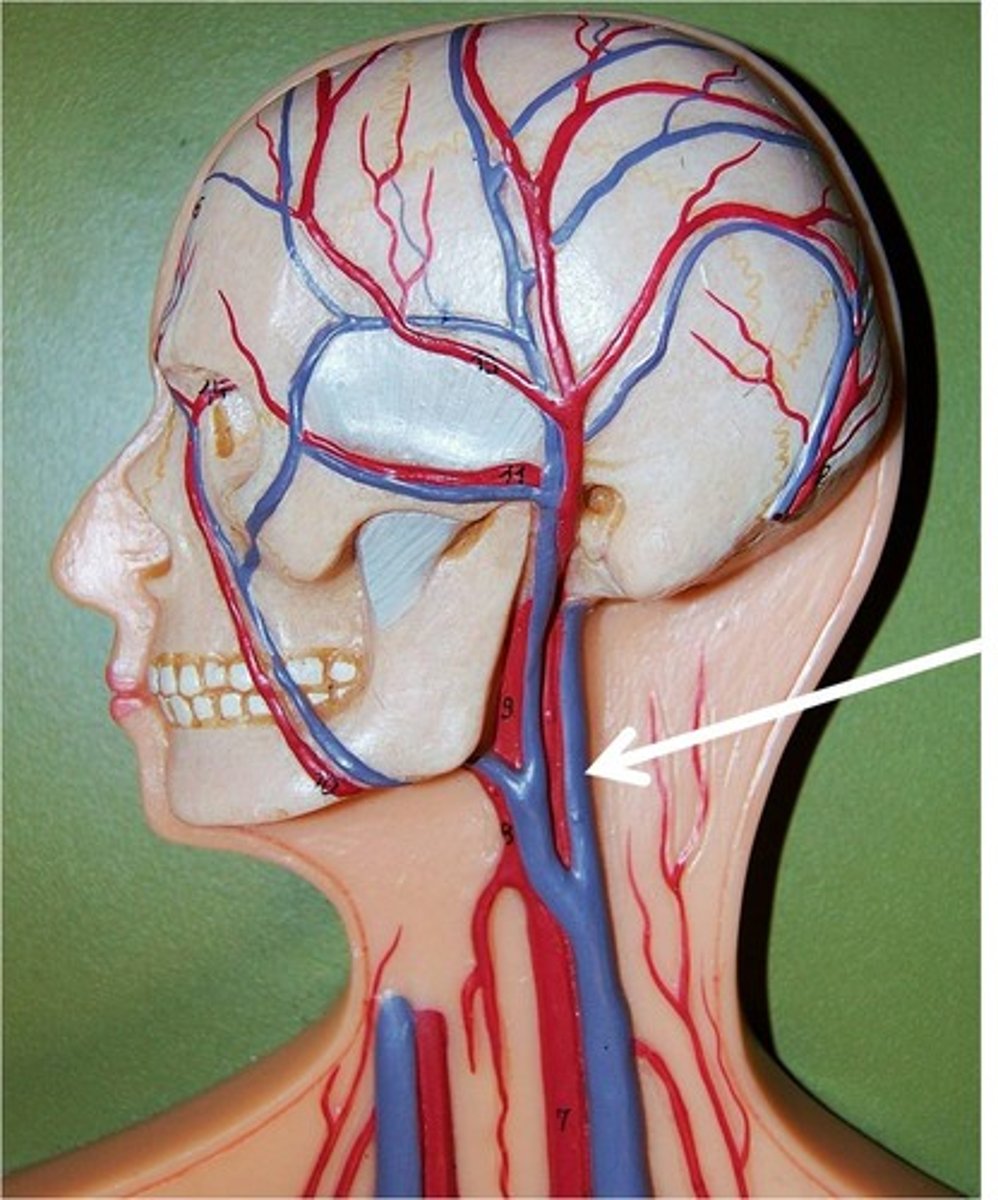
Internal Jugular Veins
The first set of vessels to emerge from the cranial vena cava, medially. These veins carry blood from the head to the brachiocephalic veins. They are located on either side of the trachea.
Subclavian Veins
The fourth set of vessels to emerge from the cranial vena cava, medially. These veins carry blood from the subscapular veins and axillary veins to the brachiocephalic veins.
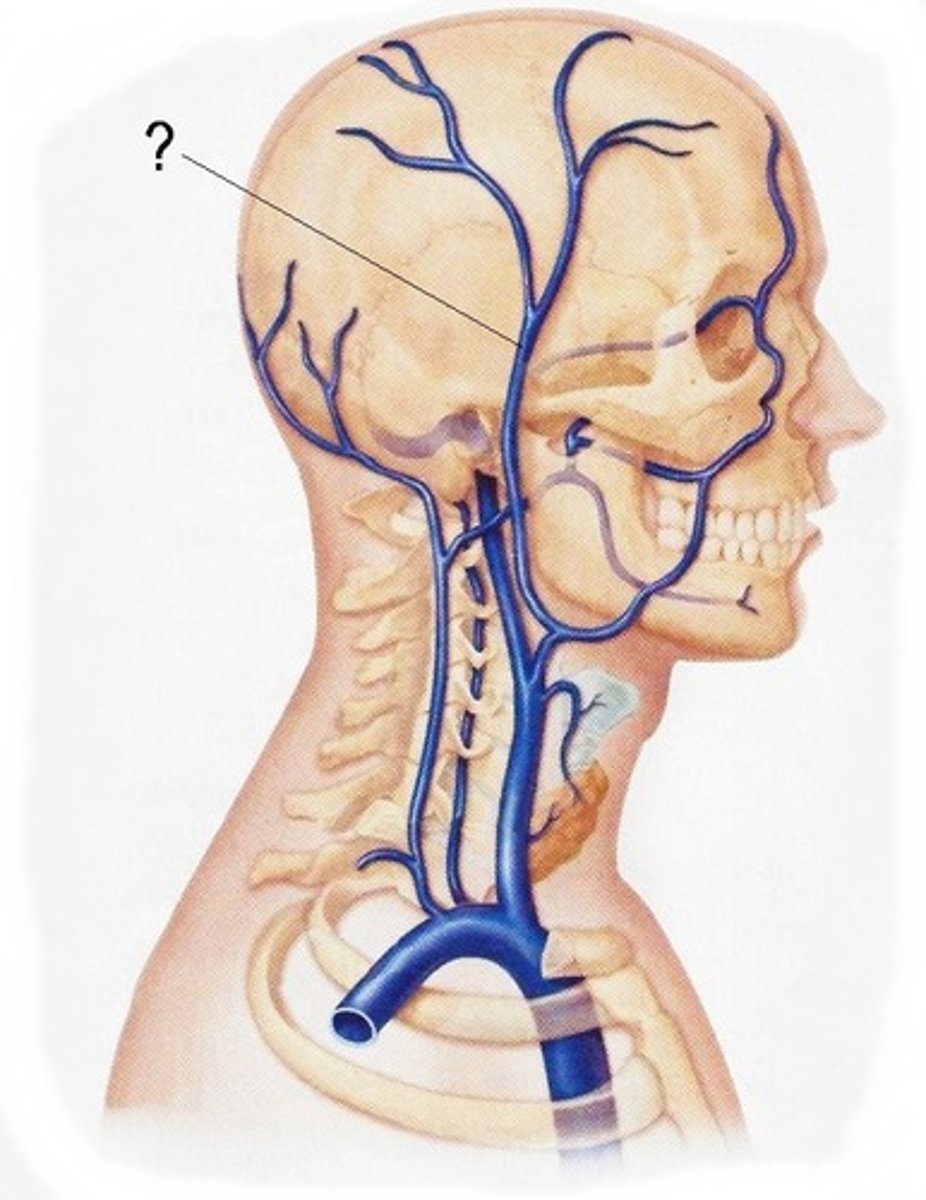
Superficial Temporal Veins
Drains the superficial temporal scalp. Gives rise to the retromandibular vein.
Ophthalmic Veins
Exit orbit through superior and inferior orbital fissures and drain into cavernous sinus
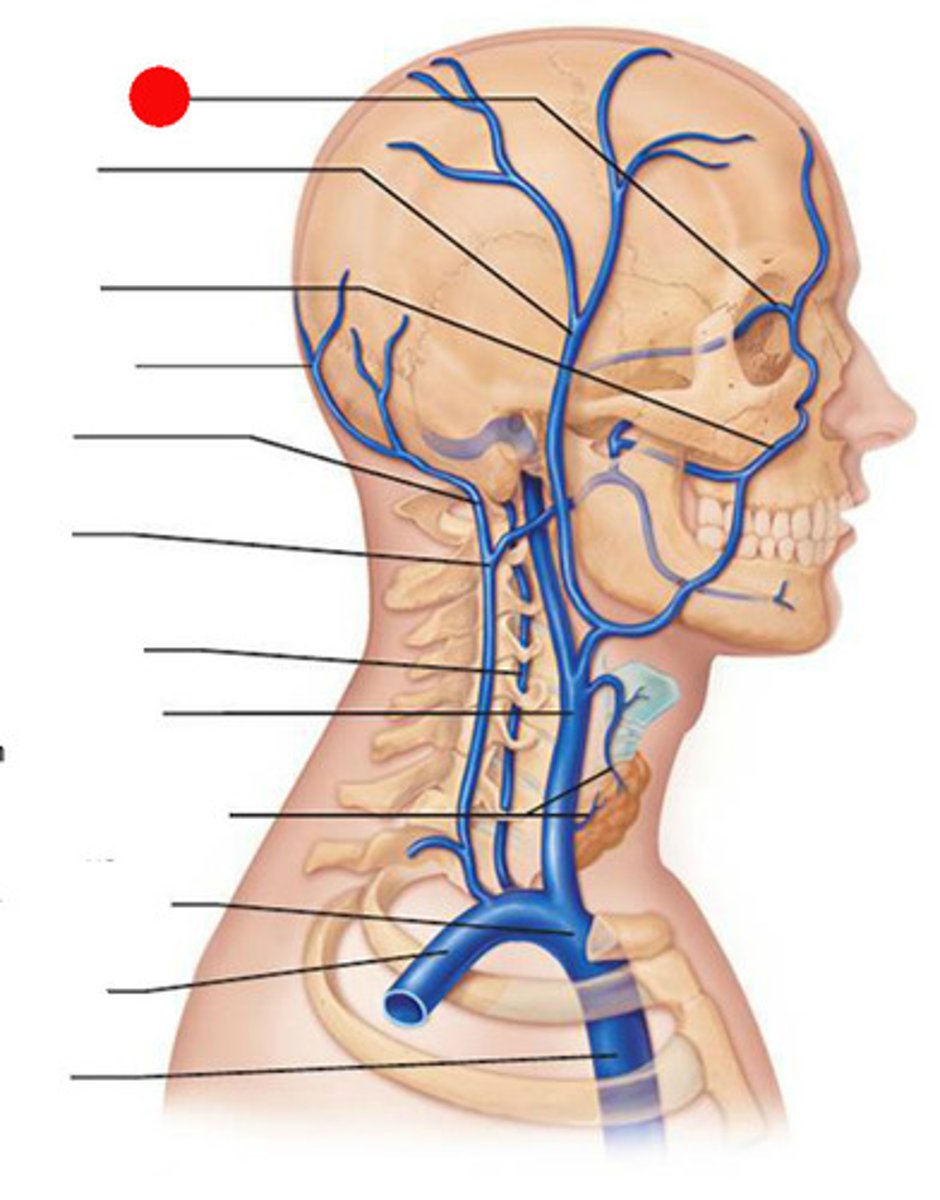
Facial Veins
Blood vessels that drain blood back to the heart from the face
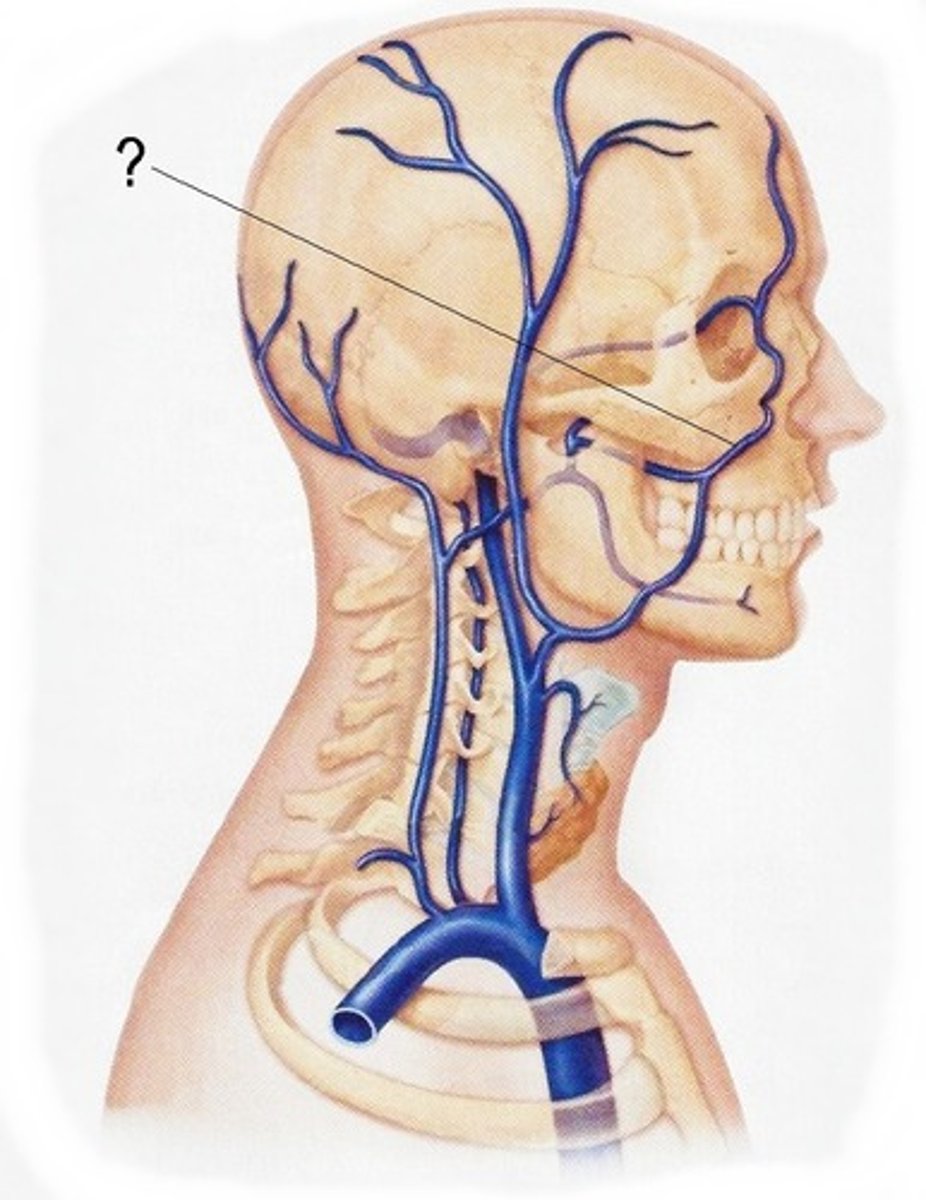
Vertebral Veins
serves posterior head, cervical vertebrae, spinal cord
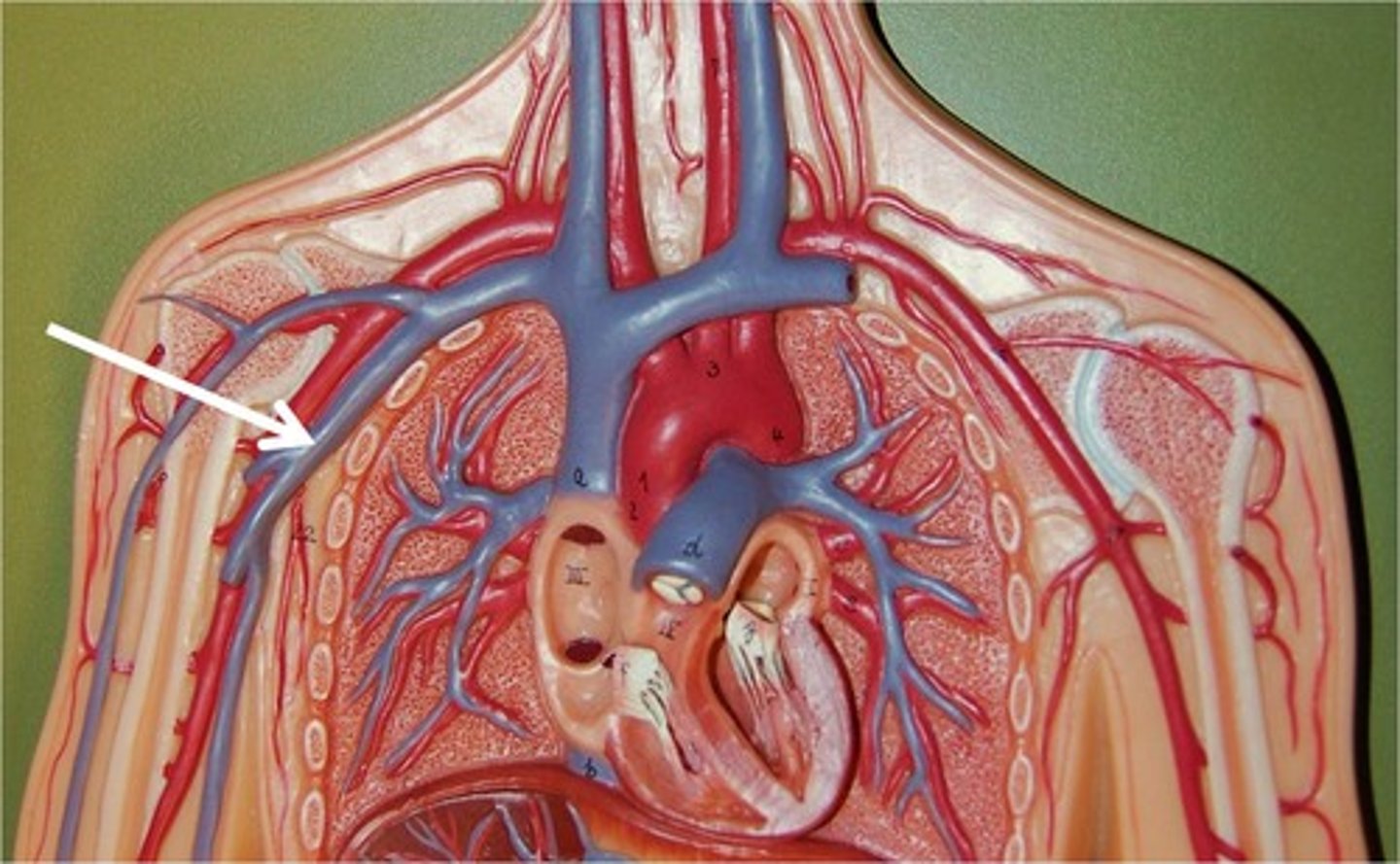
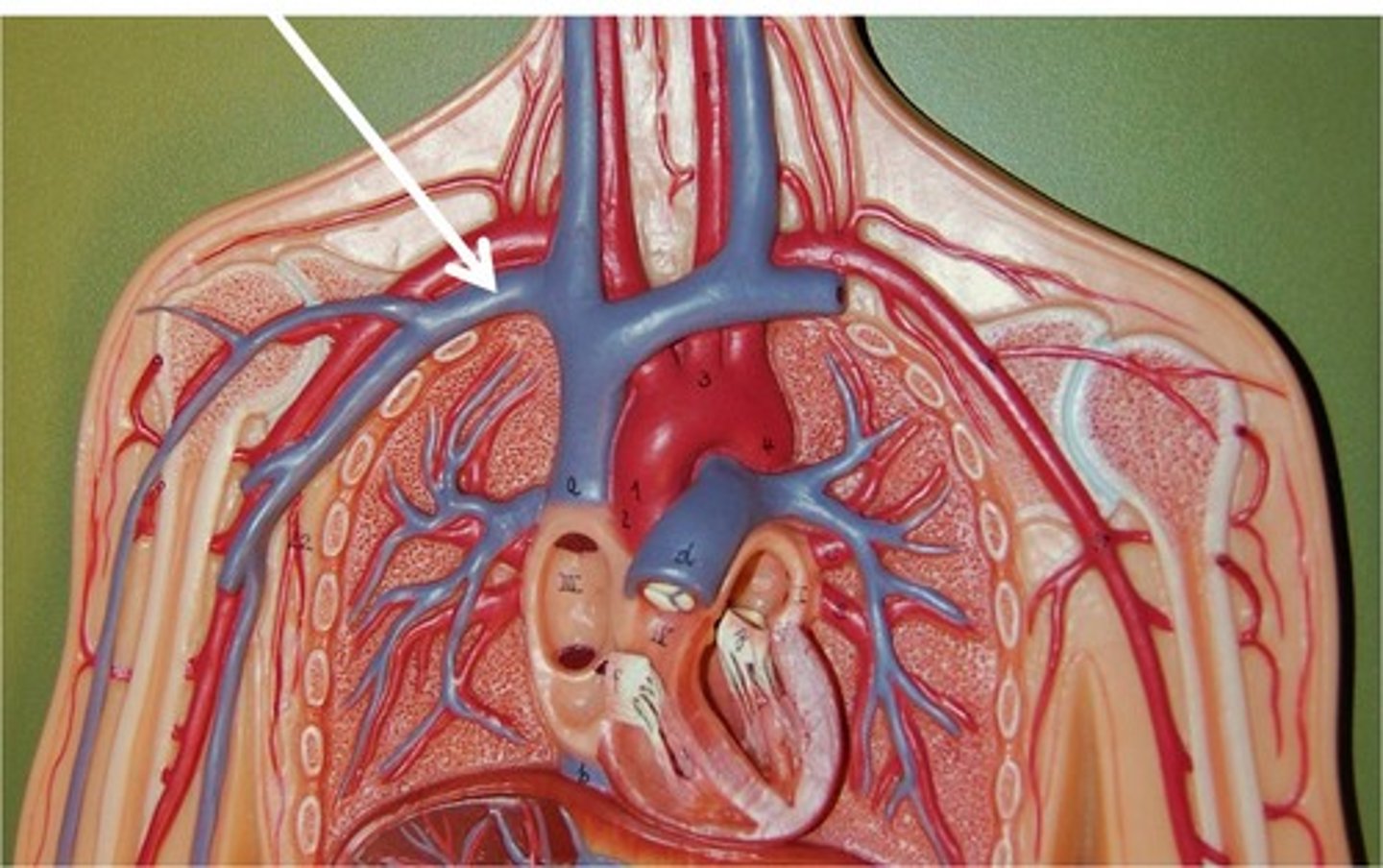
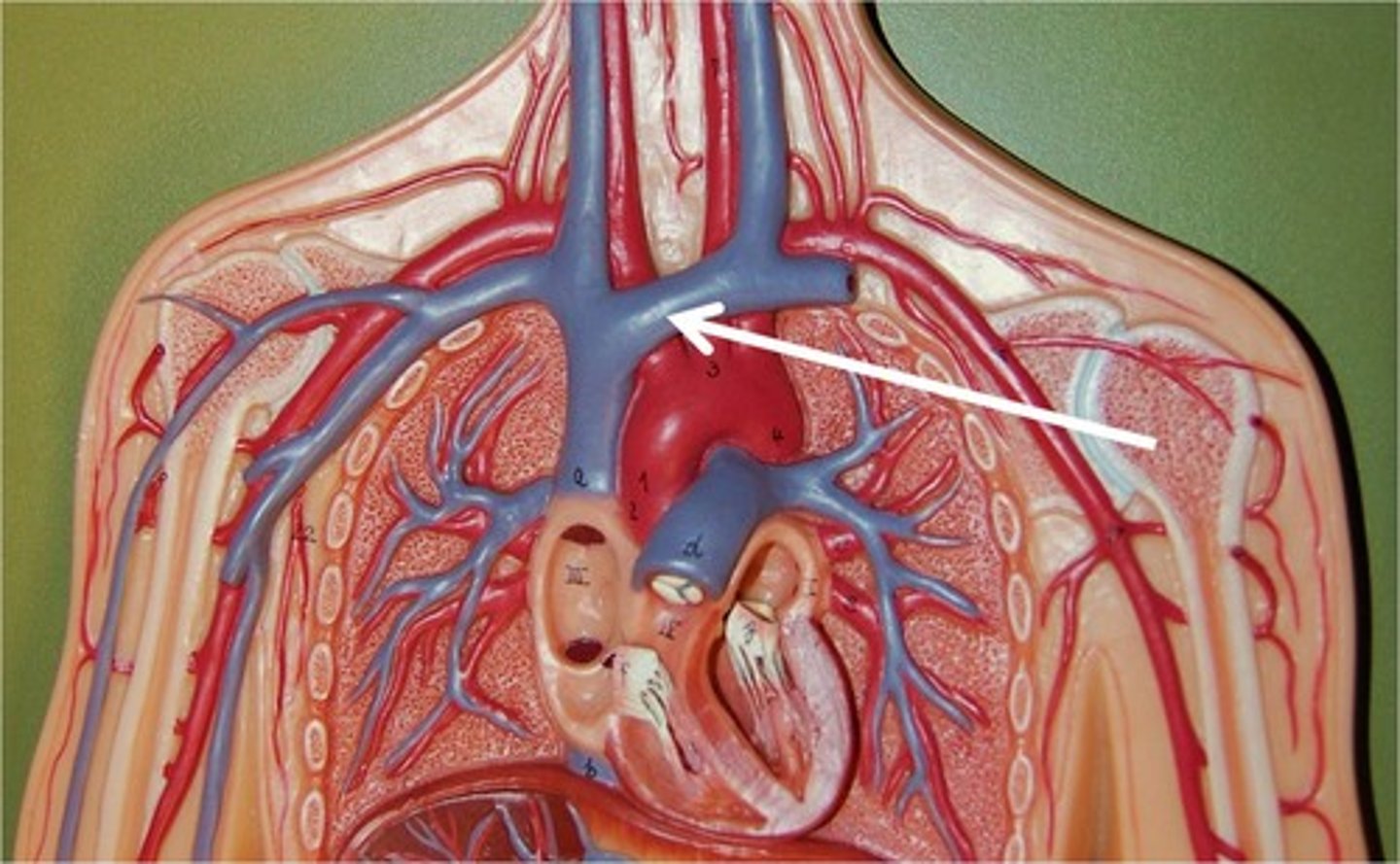
Brachiocephalic Veins
These veins carry blood from the cephalic, subclavian, and jugular veins to the cranial vena cava.
Anterior Intercostal Veins
Drain forward into the internal thoracic and musculophrenic veins
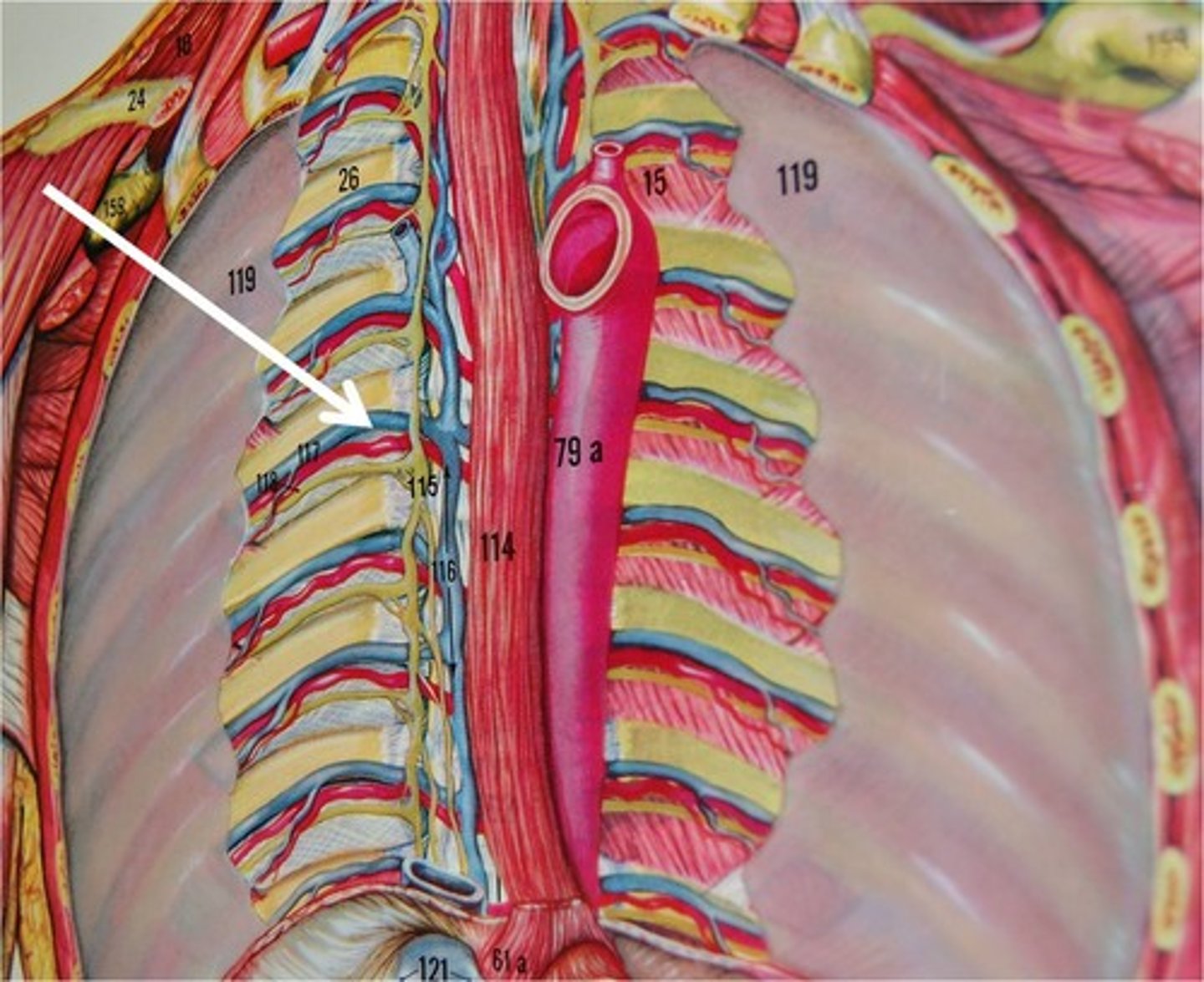
Posterior Intercostal Veins
Drains from the distal 9 intercostal spaces, anterior thoracic muscles, breast, back muscles, spinal cord, and vertebrae
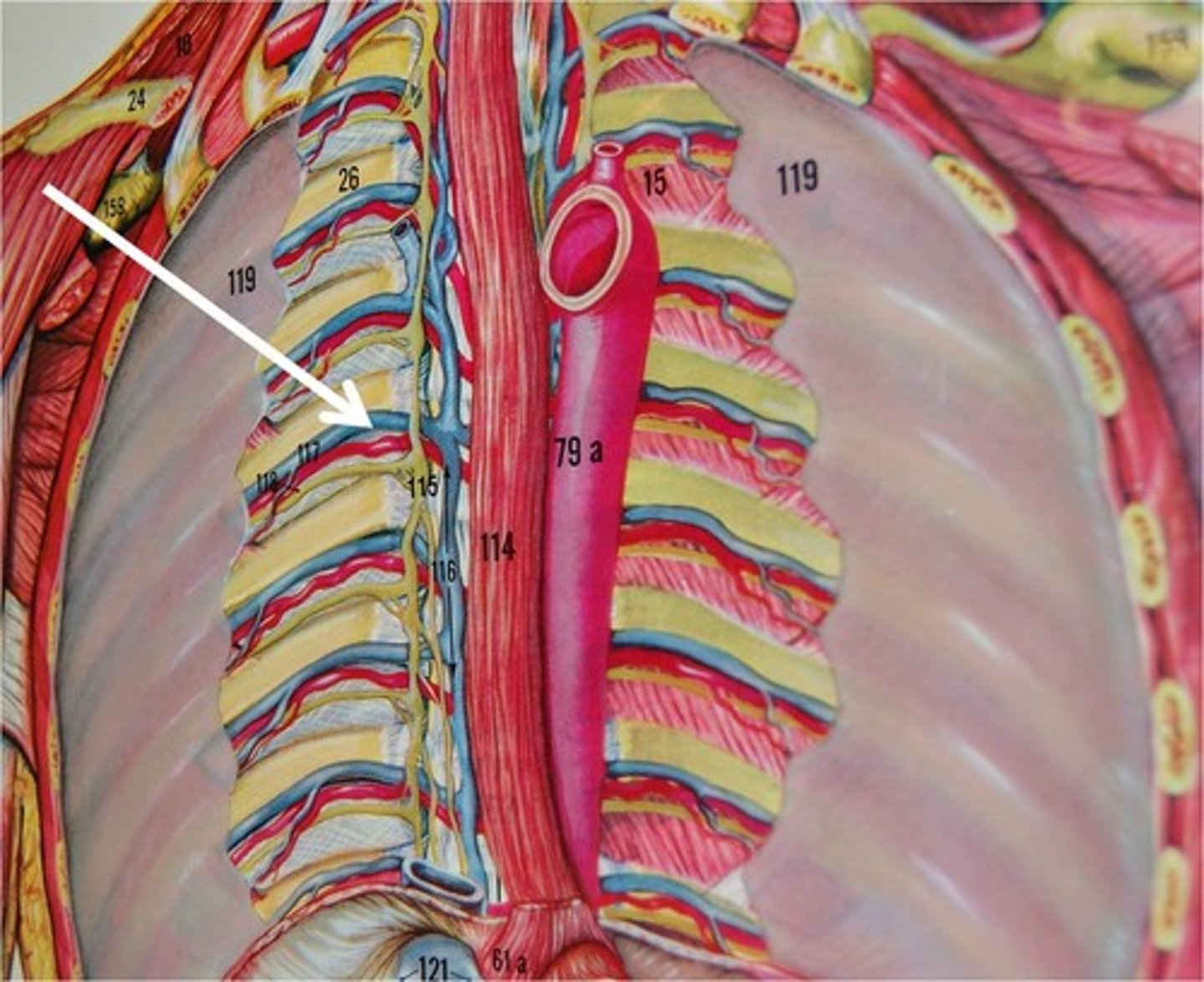
Hemiazygos Veins
Begins as continuation of left ascending lumbar vein and empties into azygos vein
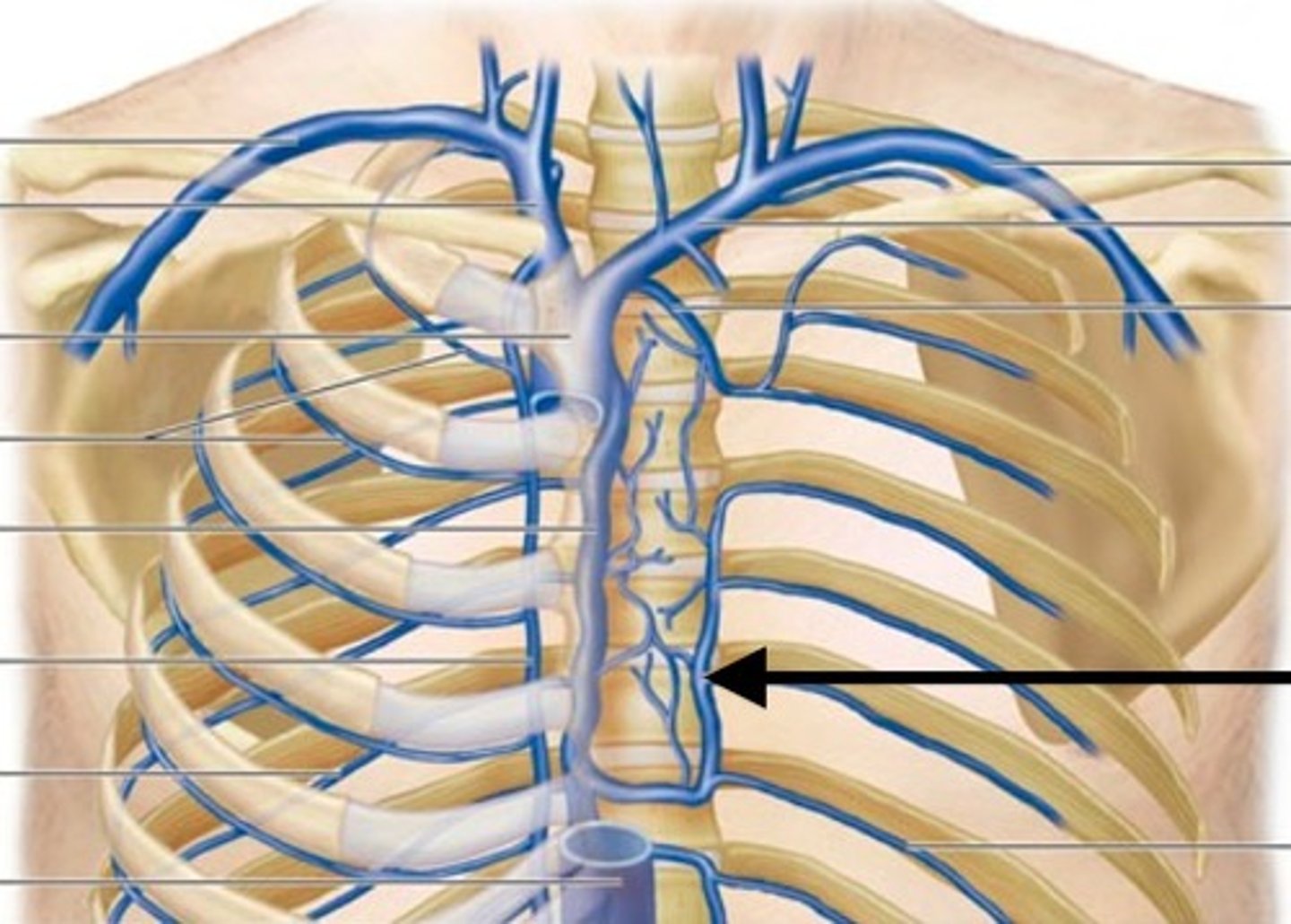
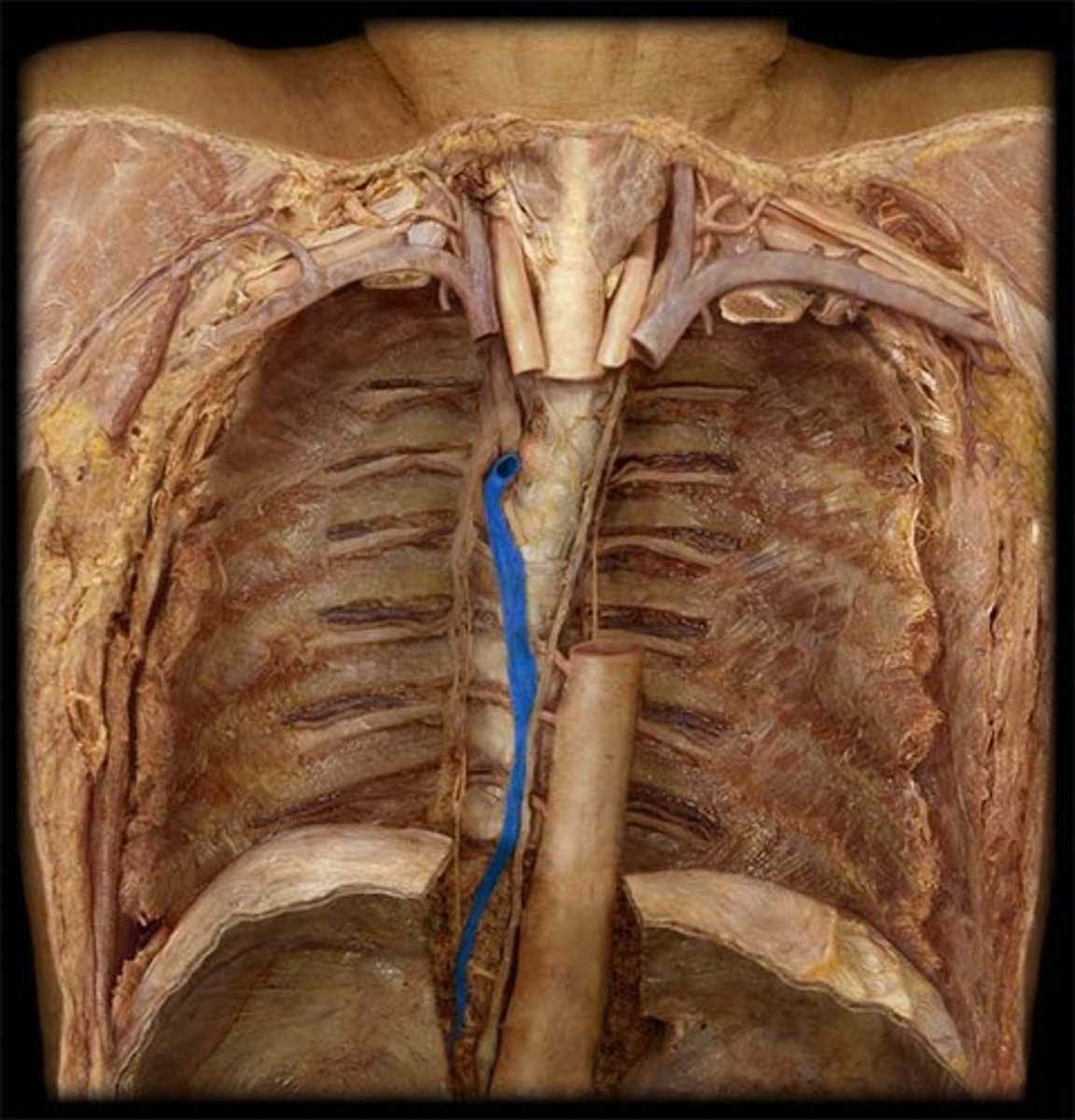
Azygos Vein
a vessel that drains blood from the chest wall and empties into the superior vena cava
Metatarsal Veins
Veins in the feet
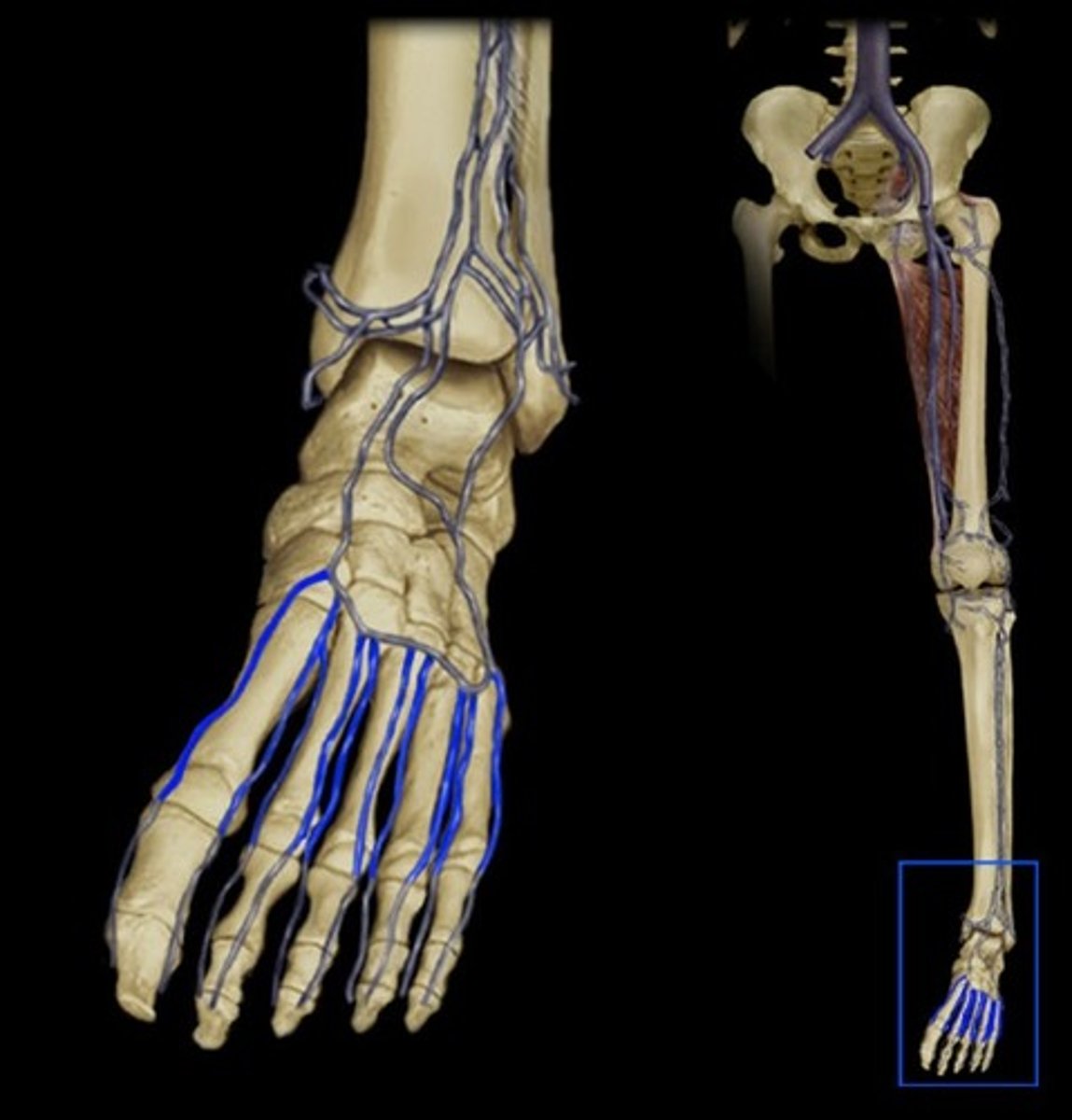
Dorsal Venous Arch
drains blood from digital veins and vessels on the superior surface of the foot
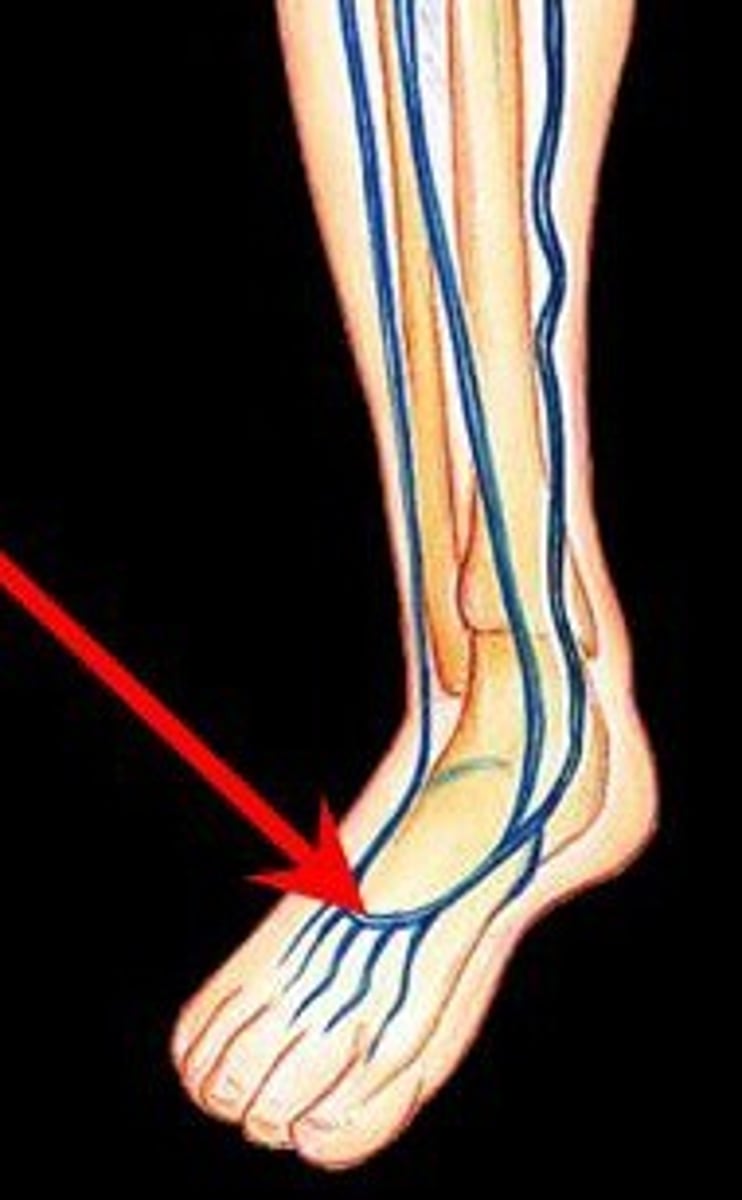
Dorsalis Pedis Veins
drains blood from the foot
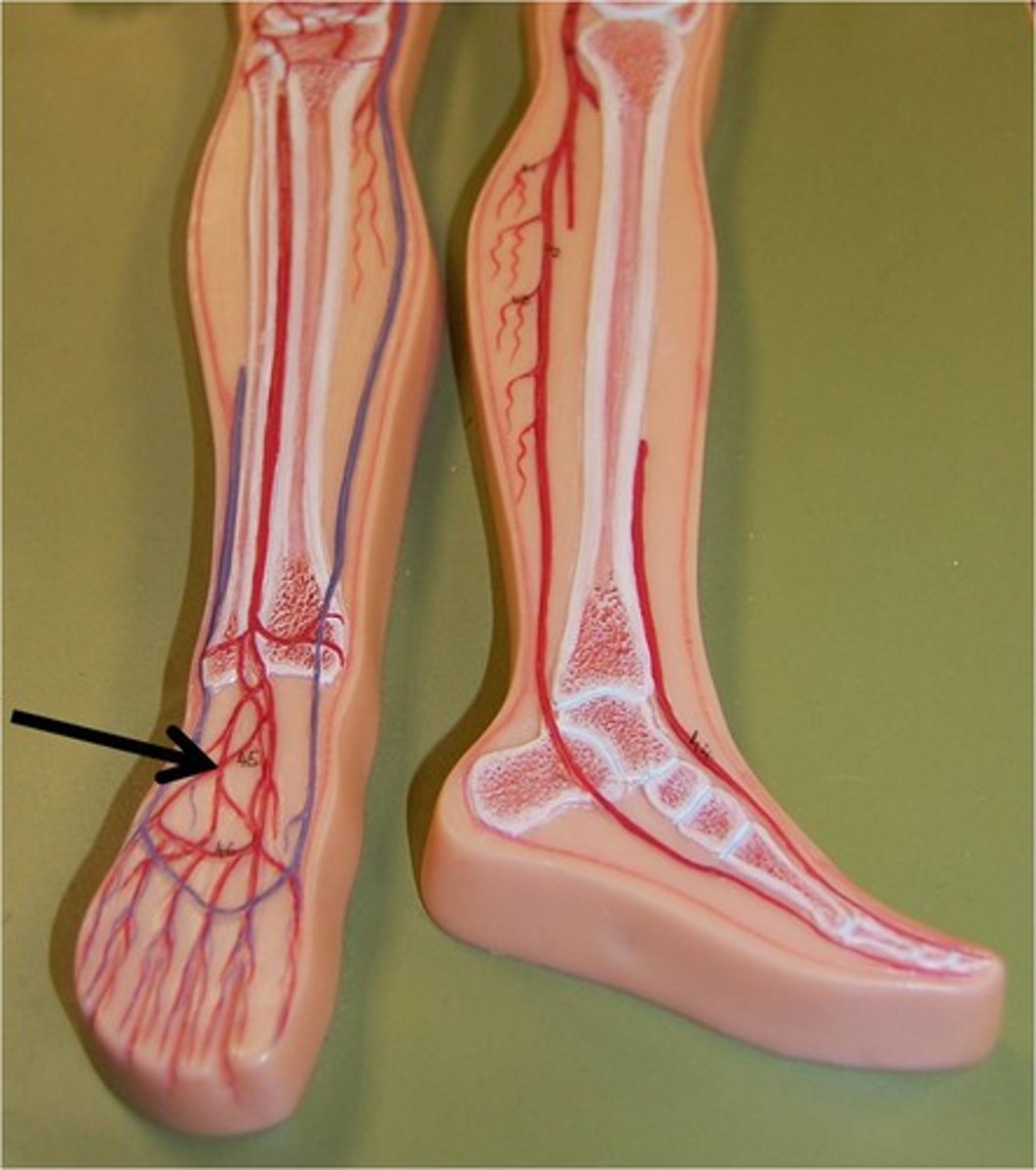
Anterior Tibial Veins
Drains the anterior lower leg. Joins the posterior tibial vein to form the popliteal vein.
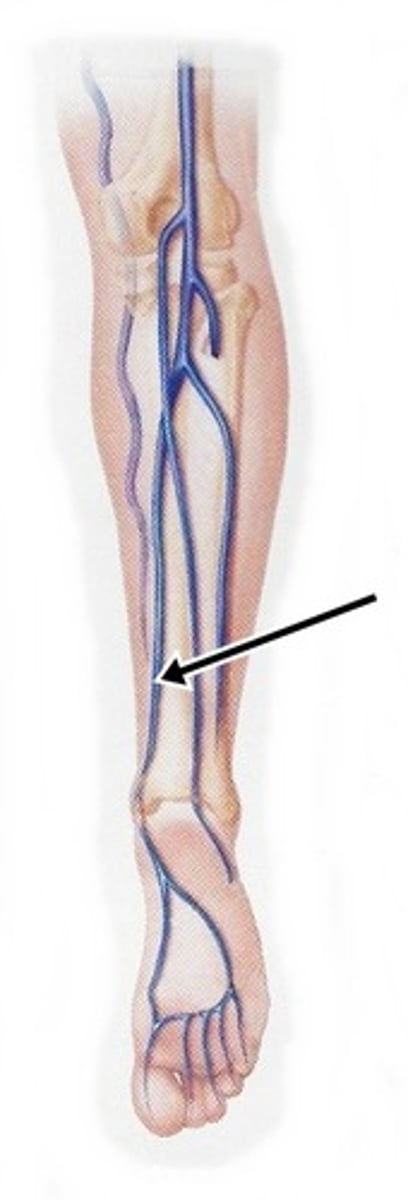
Posterior Tibial Veins
run with the posterior tibial artery, drain blood from the foot and posterior compartment of the leg
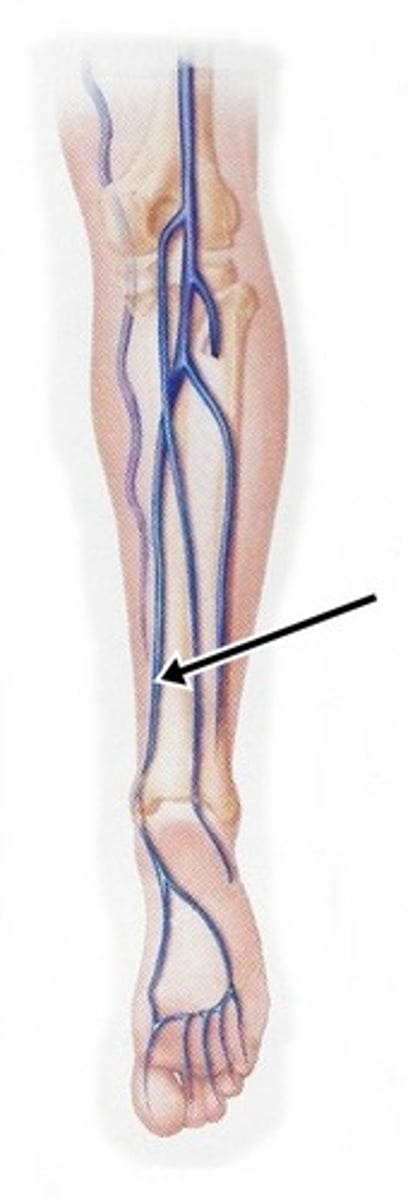
Fibular Veins
run with the fibular artery, drain blood from the lateral compartment of the leg
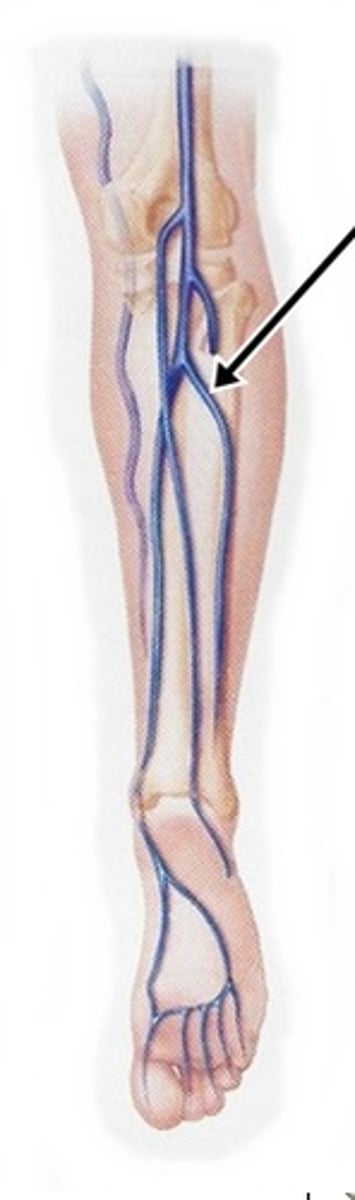
Small Saphenous Veins
superficial veins that form at the lateral end of the dorsal venous arches; run posterior to the lateral malleolus, ascend along the lateral posterior leg, and empty into the popliteal veins
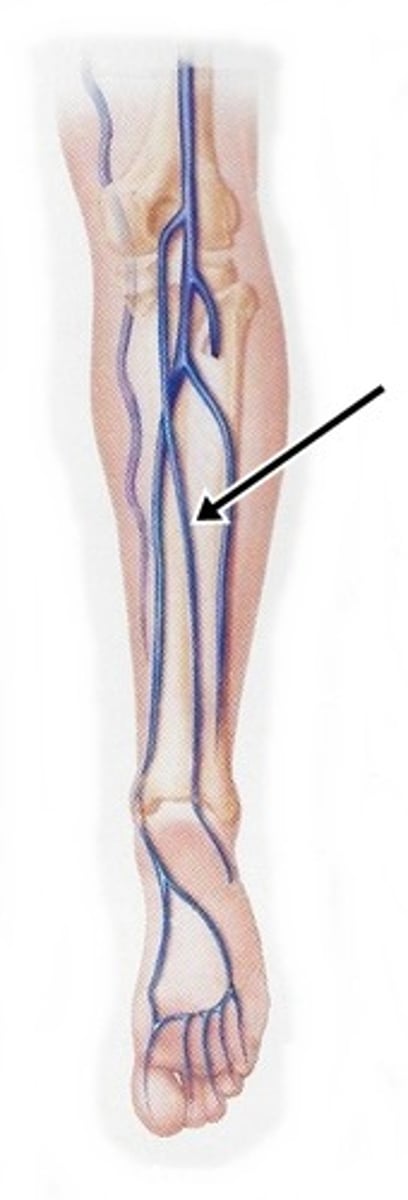
Popliteal Veins
form from the merger of the anterior and posterior tibial veins just inferior to the popliteal fossa; become the femoral veins just superior to the knee
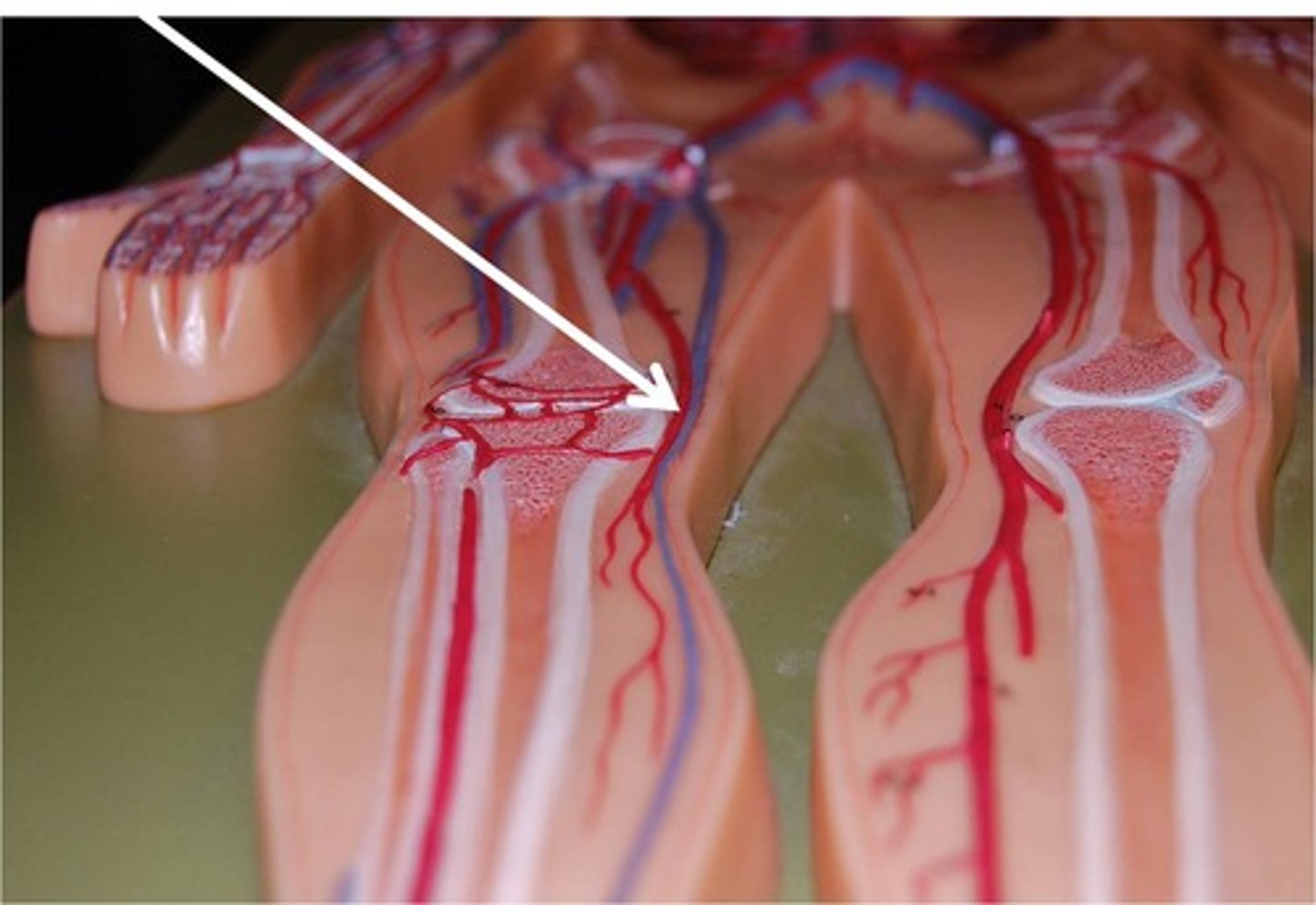
Great Saphenous Veins
The longest veins in the body. They receive the superficial drainage of the leg. They begin at the dorsal venous arch in the foot and travel up to the medial aspect of the leg to empty into the femoral vein in the thigh
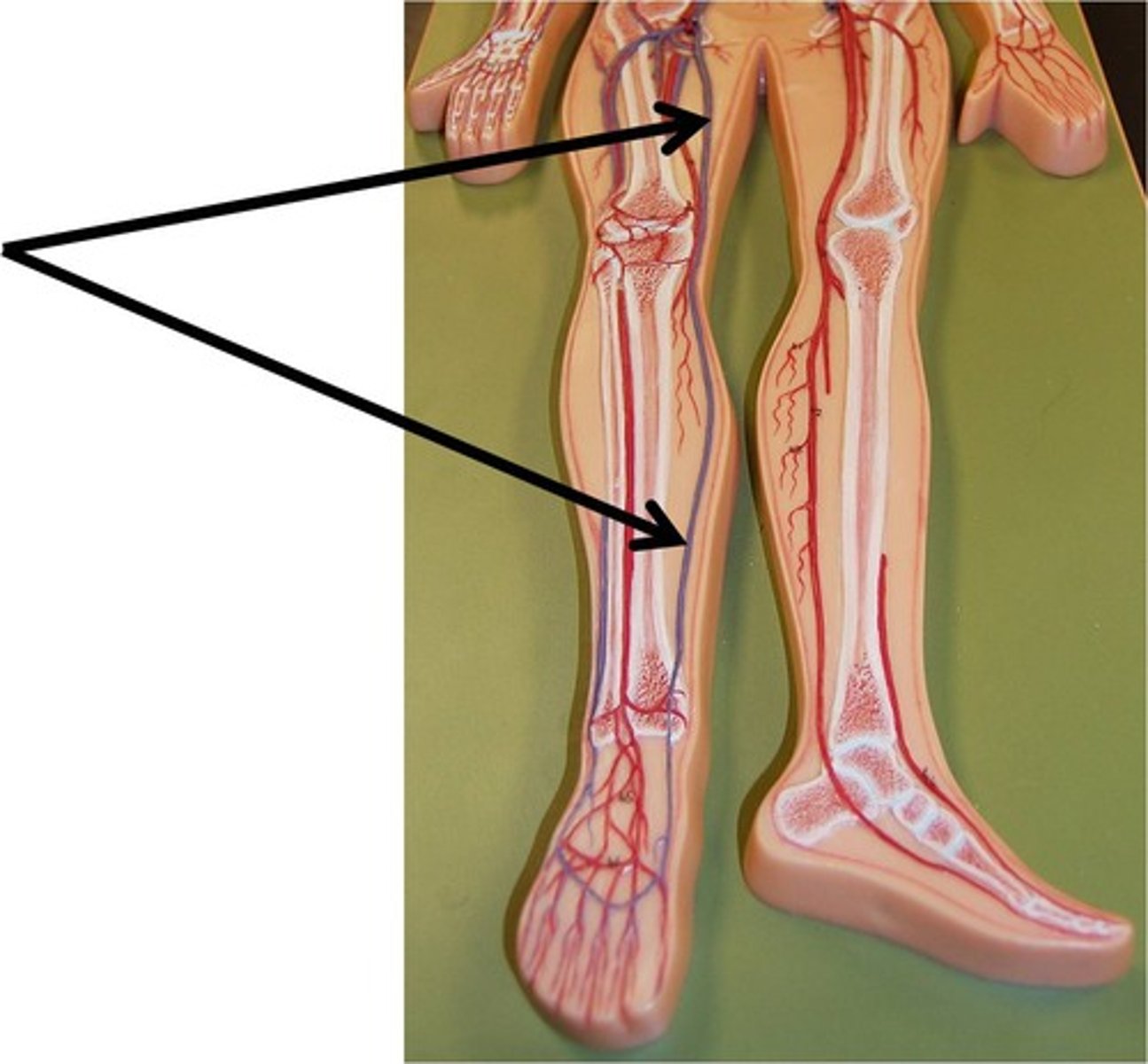
Femoral Veins
These veins carry blood from the thigh and lower hind limb to the external iliac veins.
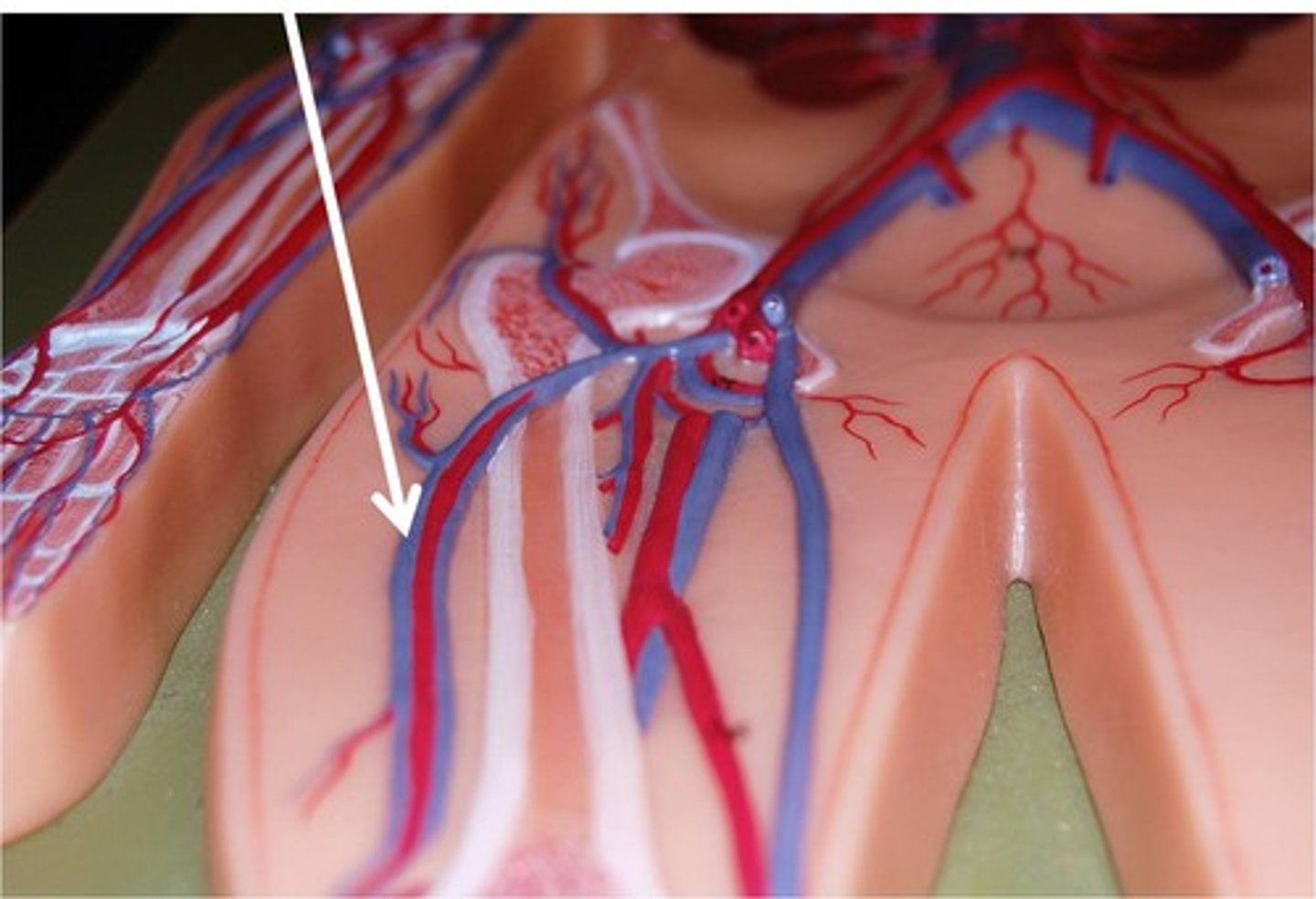
Common Iliac Veins
These veins carry blood from the external and internal iliac veins to the caudal vena cava
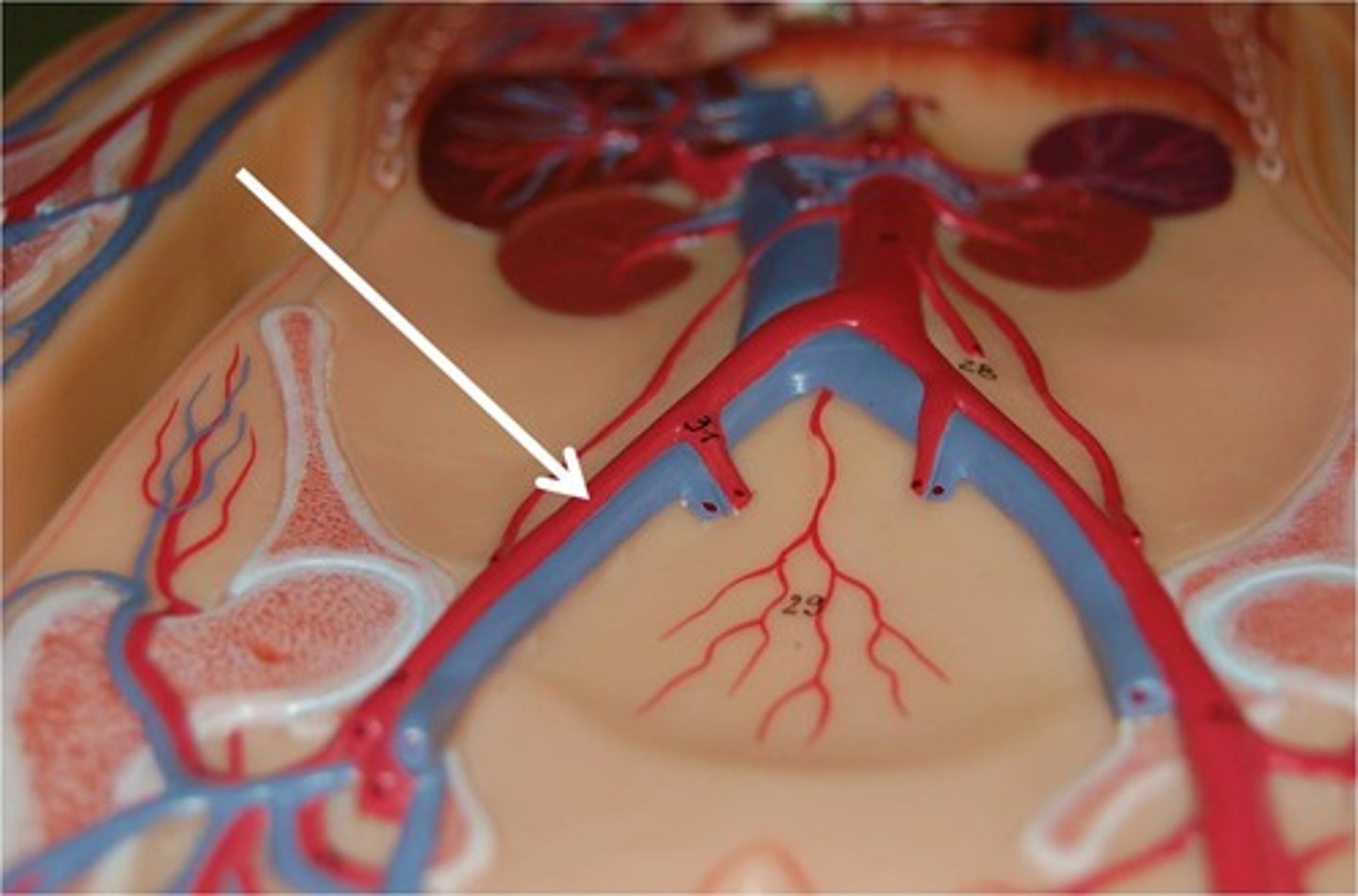
External Iliac Veins
these veins carry blood from the femoral and deep femoral veins to the common iliac veins
Internal Iliac Veins
These veins carry blood from the pelvis to the common iliac veins.
Ascending Lumbar Vein
- Branches of common iliac veins
- R. ascending joins w/ R. subcoastal vein to form azygous vein.
- L. ascending joins w/ L. subcoastal vein to for hemiazygous vein.
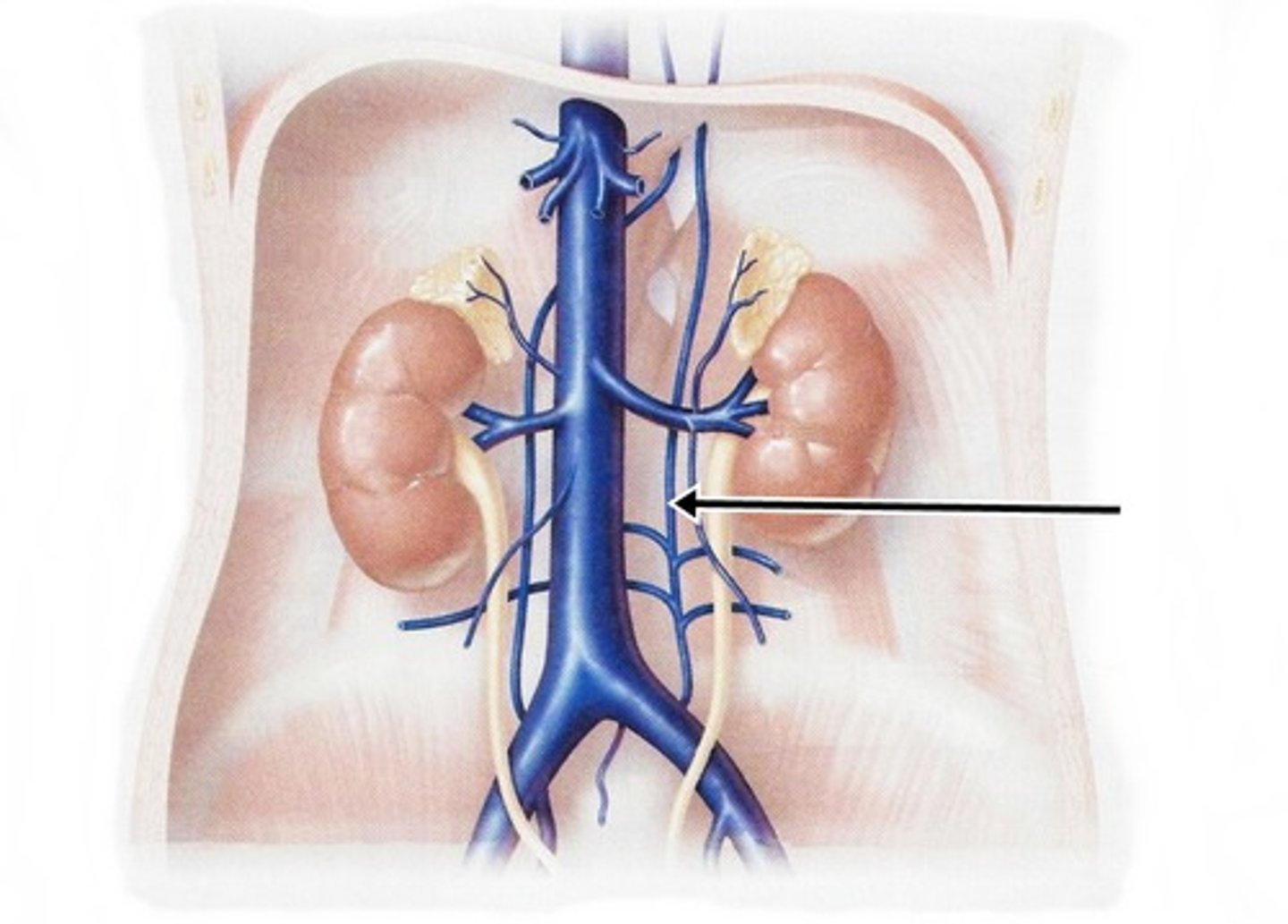
Gonadal Veins
veins that are very slender; drains either ovaries or testes
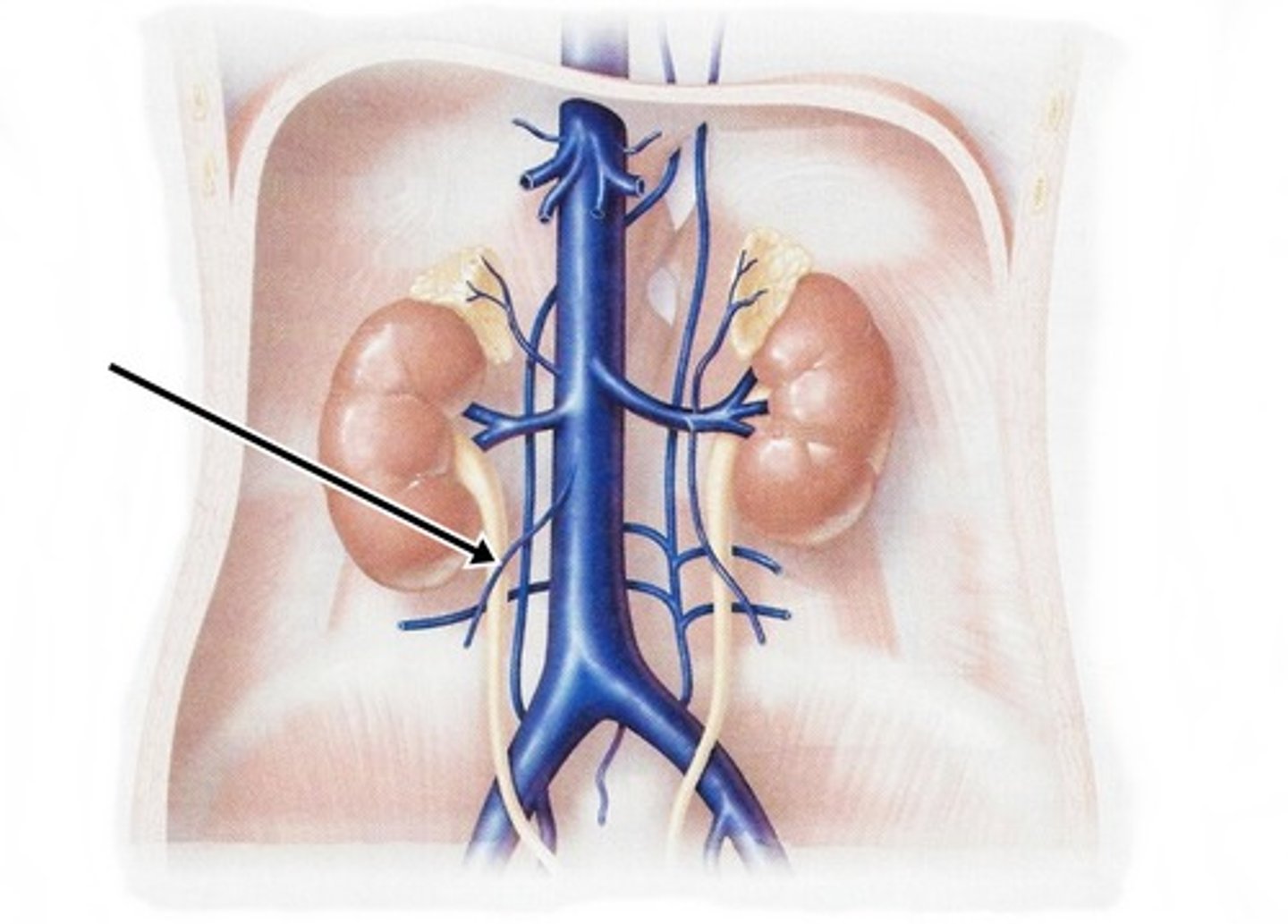
Renal Veins
Removes deoxygenated blood from the kidneys
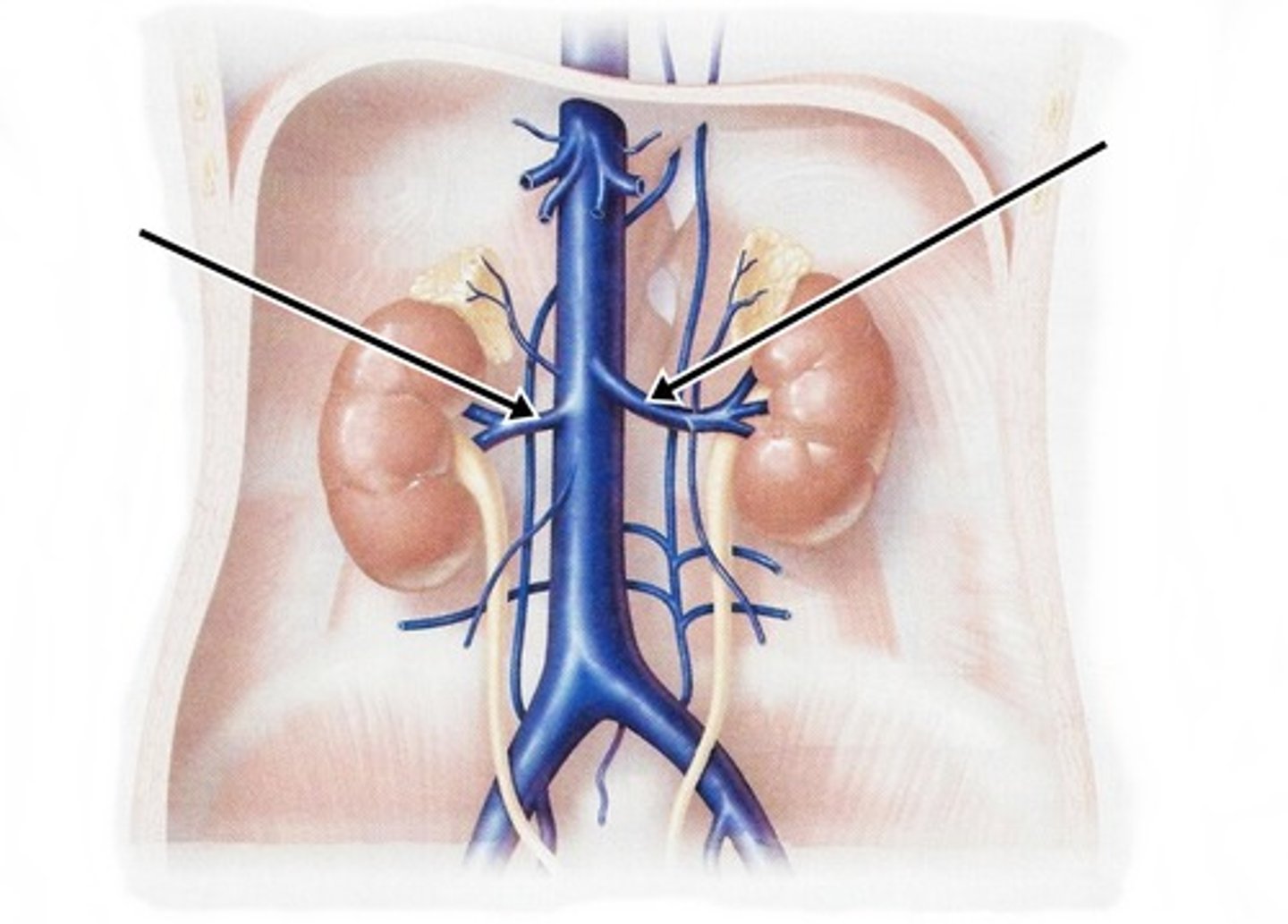
Suprarenal Veins
run adjacent to the suprarenal arteries and drain into the inferior vena cava
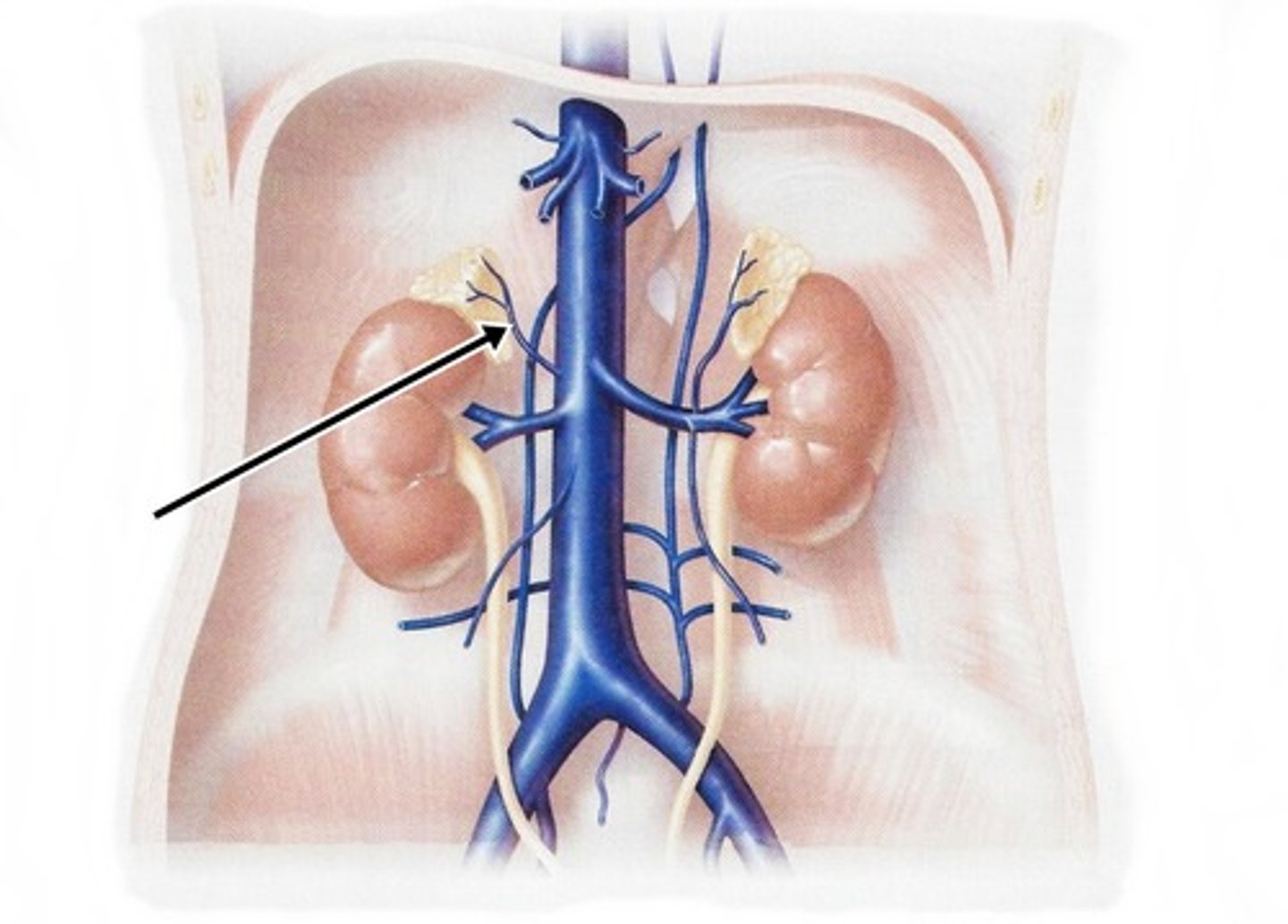
Inferior Phrenic Vein
drains: inferior diaphragm
empties into: inferior vena cava
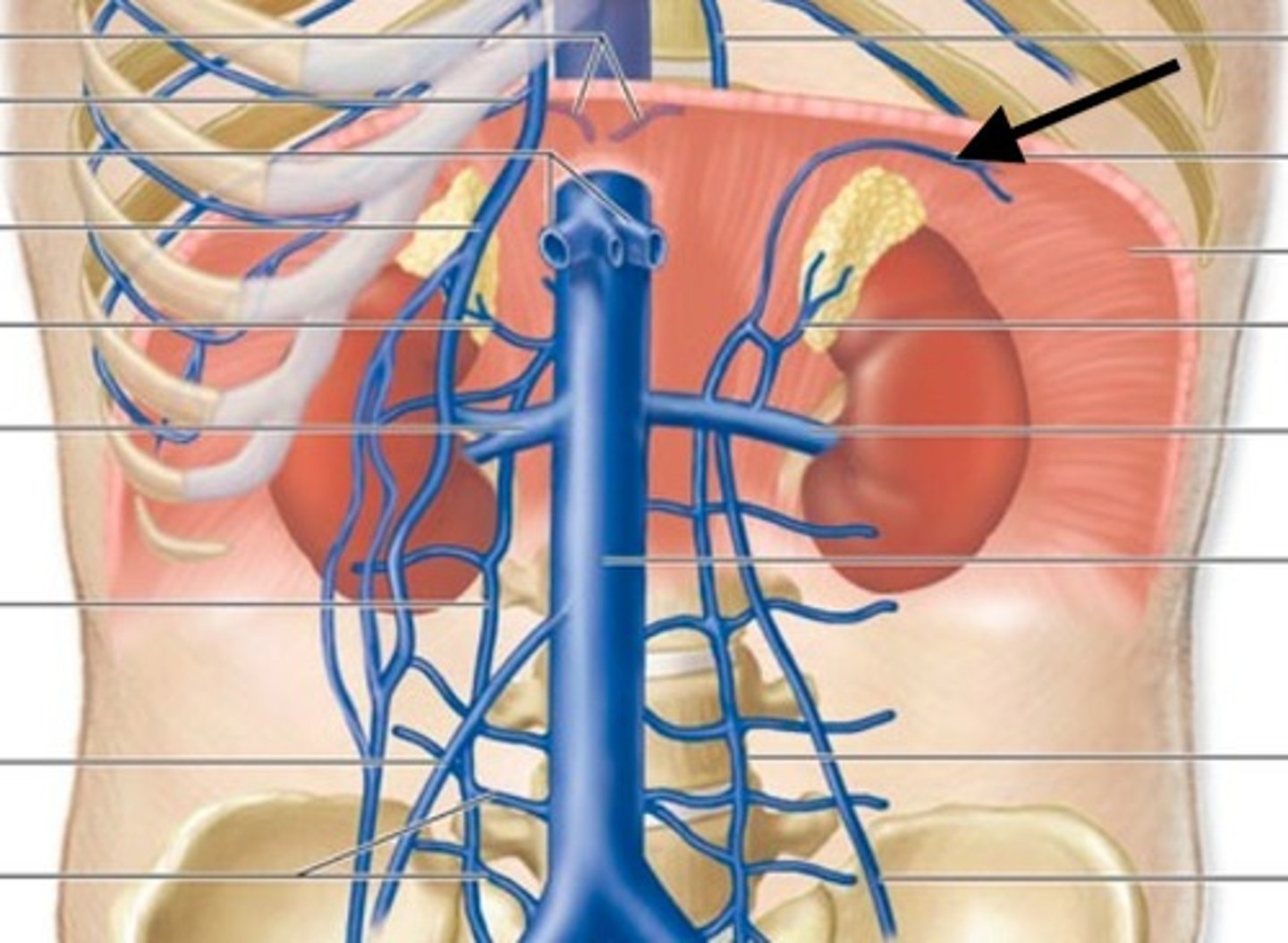
Hepatic Veins
carry blood from the liver to the caudal vena cava
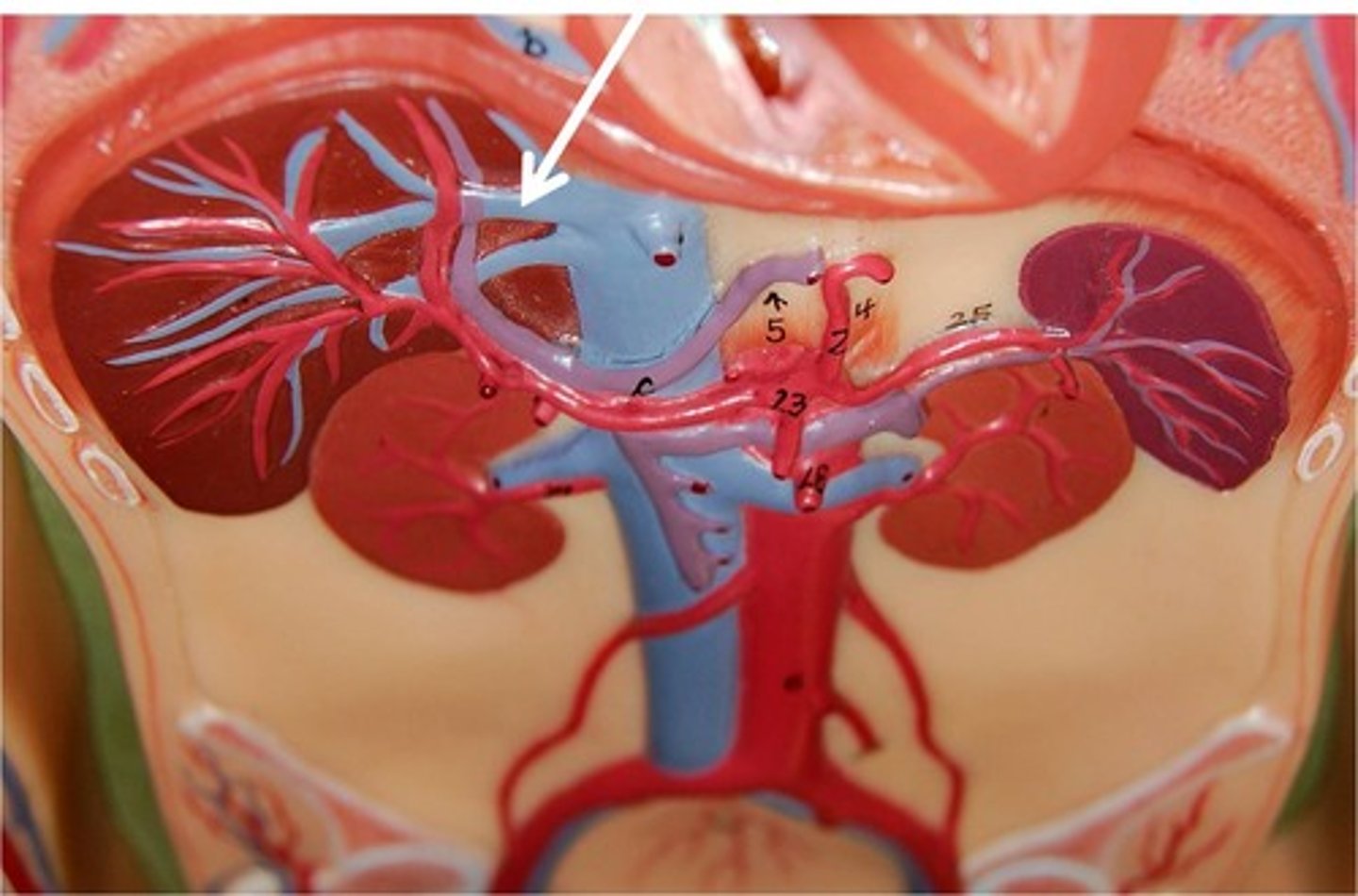
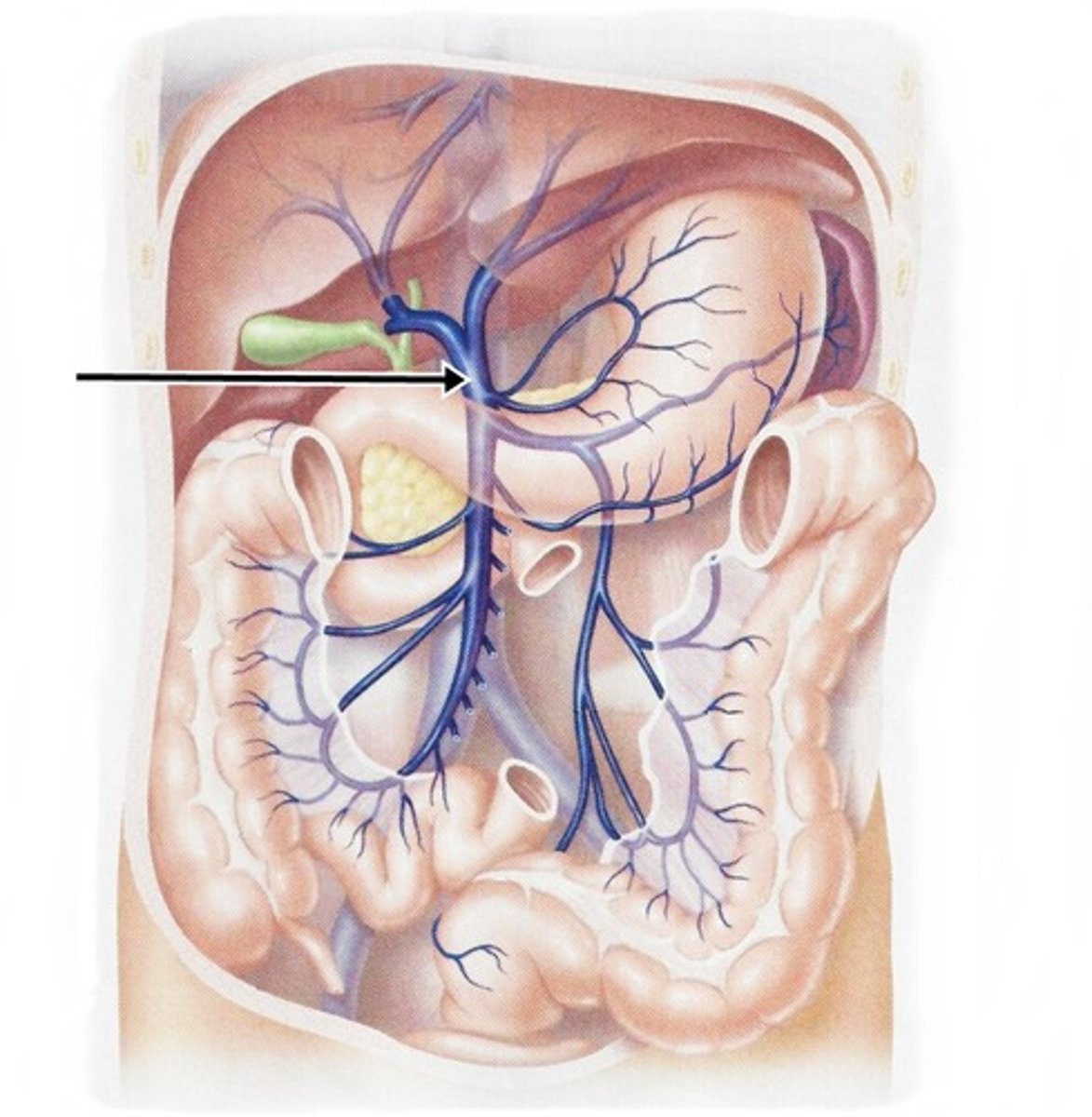
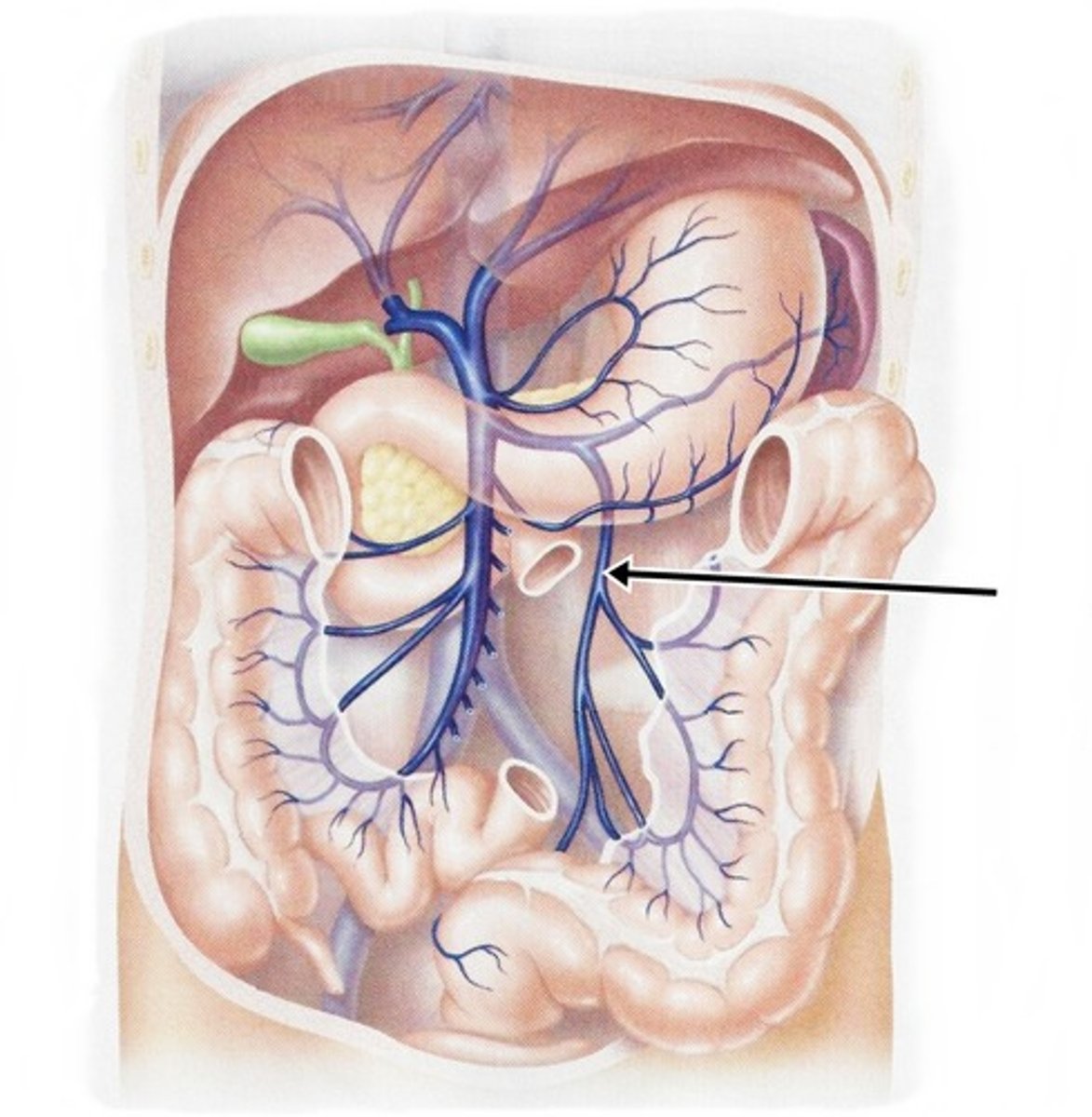
Hepatic Portal Veins
gastrointestinal tract to capillaries in the liver