Border Gateway Protocol
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
What does the BGP do?
allows subnet to advertise its existence, and the destinations it can reach, to rest of Internet
What does BGP Provide each AS as a means to?
obtain destination network reachability info from neighbouring ASes (eBGP)
determine routes to other networks based on reachability information and policy
propagate reachability information to all AS-internal routers (iBGP)
advertise (to neighbouring networks) destination reachability info
What is a BGP Session?
two BGP routers (“peers”) exchange BGP messages over semi-permanent TCP connection
advertising paths to different destination network prefixes
What are some BGP Messages?
OPEN - opens TCP connection to remote BGP peer and authenticates sending BGP peer
UPDATE - advertises new path (or withdraws old)
KEEPALIVE - keeps connection alive in absence of UPDATES; also ACKs OPEN request
NOTIFICATION - reports errors in previous msg; also used to close connection
What is a BGP Advertised Route?
prefix + attributes
prefix - destination being advertised
attributes - AS-PATH - list of ASes through which prefix advertisement has passed ,NEXT-HOP - indicates specific internal-AS router to next-hop AS
What is Policy Based Routing?
gateway receiving route advertisement uses import policy to accept/decline path (e.g., never route through AS Y)
AS policy also determines whether to advertise path to other neighbouring ASes
What is Path Advertisment?
AS2 router 2c receives path advertisement AS3,X (via eBGP) from AS3 router 3a
based on AS2 policy, AS2 router 2c accepts path AS3,X, propagates (via iBGP) to all AS2 routers
based on AS2 policy, AS2 router 2a advertises (via eBGP) path AS2, AS3, X to AS1 router 1c
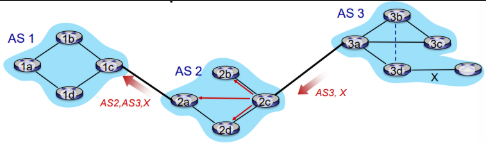
What is Hot Potato Routing?
2d learns (via iBGP) it can route to X via 2b or 2c
choose local gateway that has least intradomain cost (e.g., 2d chooses 2c over 2b)
What is the process for Route Selection?
select the route with the highest local preference value: (the local preference is configured by an AS to implement local policy decisions)
if two routes have the same local preference, then select the one with the shortest AS-PATH
if there is still a tie (same local preferences and same AS-PATH lengths) then choose the closest NEXT-HOP router: hot potato routing
Why does a Router selects one Inter-Domain Route per Destination?
avoiding forwarding loops - using multiple unrelated AS paths risks creating inter-domain forwarding loops because BGP lacks the consistency guarantees of intra-domain routing
stability and convergence - selecting a single best path prevents oscillations and ensures fast, stable convergence