Chemistry~ 4.1 predicting chemical reactions
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
What are the properties of group 1, alkali metals?
shiny, good conductors. softer and denser as you go down the group, less denser than water, low melting point(that decrease as you go down)
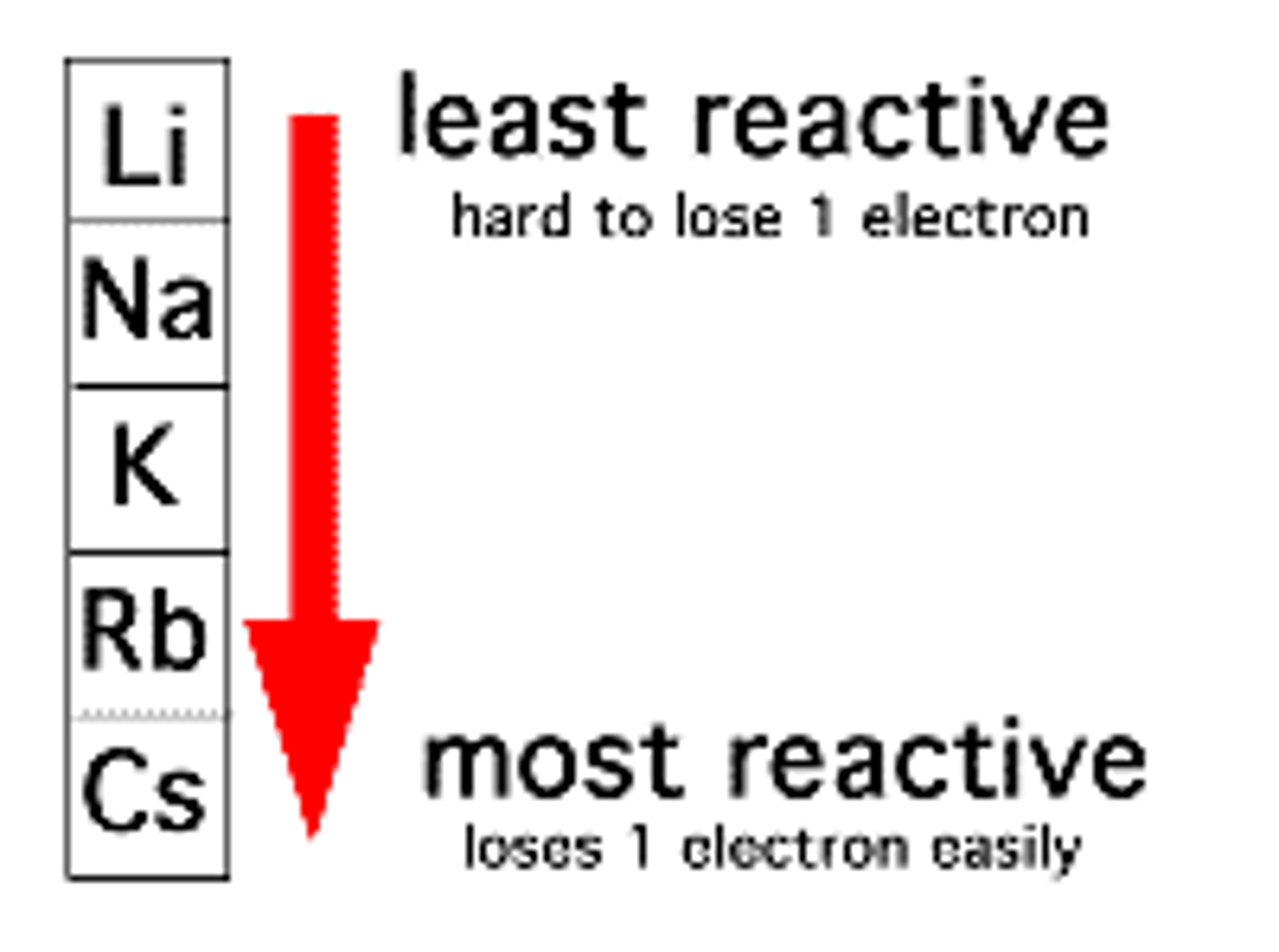
Why are group 1, alkali metals stored in oil?
Because they react quickly with water and oxygen
Metal + water → _____ + _____
metal hydroxide + hydrogen
Lithium reaction with water
Fizzes steadily, gradually disappears

Sodium reaction with water
melts into a silver ball, fizzes vigorously, disappears more quickly

Potassium reaction with water
Ignites (burns) with a lilac flame, disappears very quickly

What colour would you expect universal indicator to be in potassium hydroxide solution?
blue, contains OH- ions
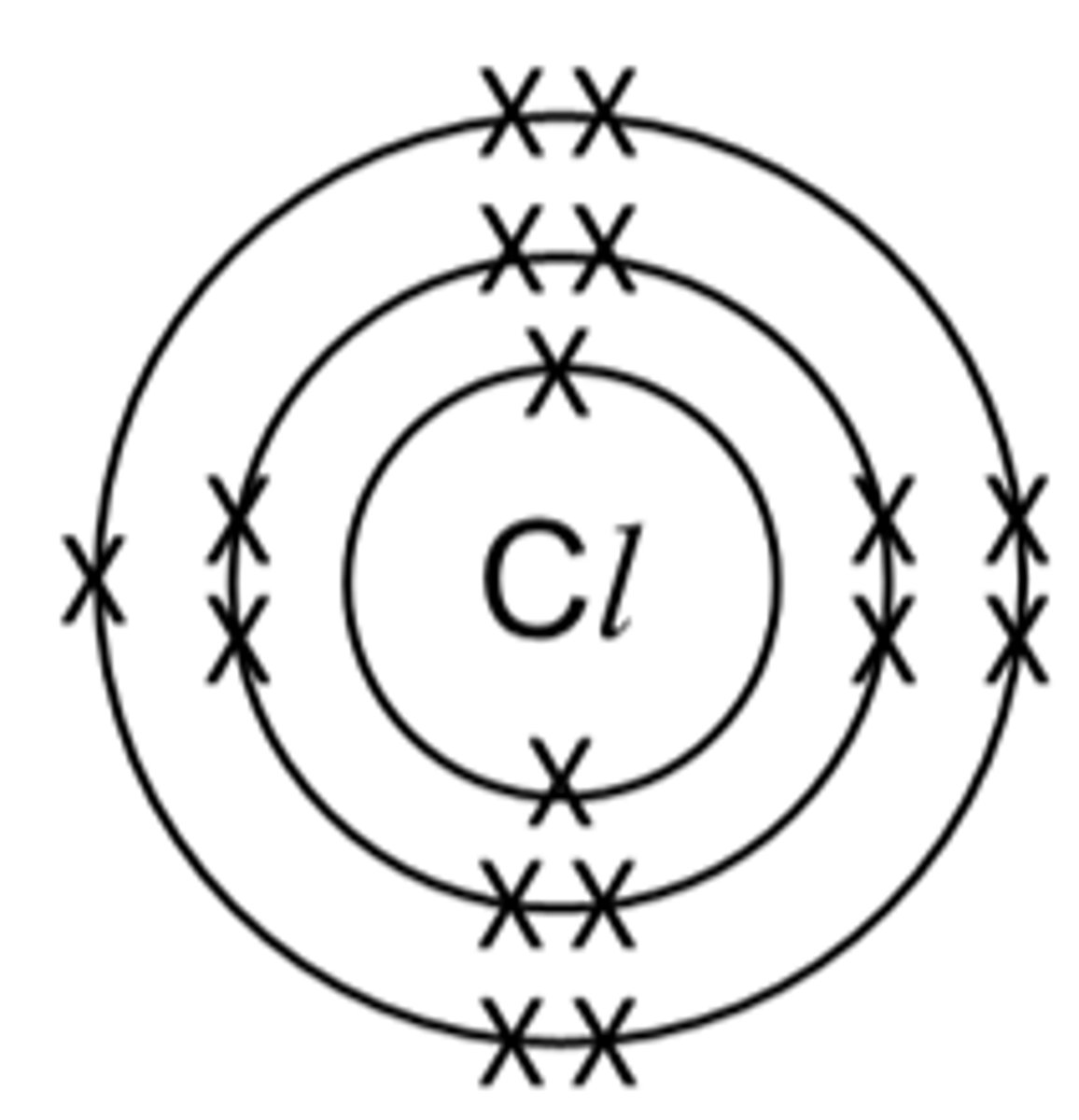
What are the properties of the group 7, halogens?
brittle in solid state, poor conductors, exist as diatomic molecules /w weak intermolecular forces, coloured/form coloured vapours, exist at different states at room temperature
fluorine (F₂) colour
pale yellow gas

chlorine (Cl₂) colour
green gas

bromine(Br₂) colour
orange-brown liquid that vaporises easily

Iodine(I₂) colour
shiny grey-black crystalline (ordered structure) solid that sublimes(s-g) to form purple vapour

What are the trends of group 7 elements going down the group?
density increases, melting and boiling point increase
metal + halide → ____ ____
metal halide
general ionic equation for a halogen
X₂ + 2e¯ = 2X¯
The easier it is for a halogen atom to gain an electron...
the more reactive the element is
Explain shielding with an example (chlorine)
Chlorine atoms are bigger (3 shells), this means the outer electron shell is further away from the nucleus and is shielded from its pull by the inner shells making it harder to gain an electron
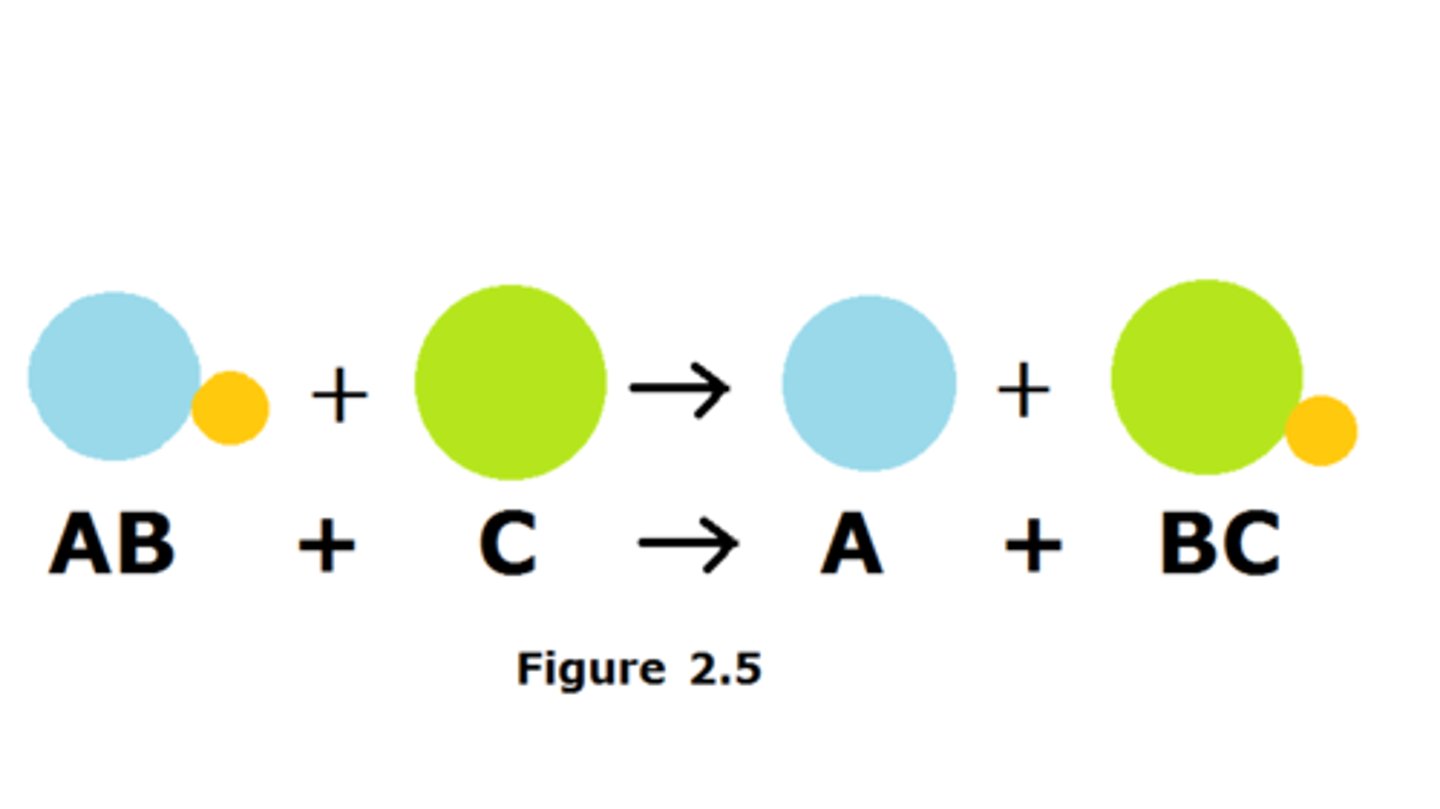
How do displacement reactions work?
A more reactive metal can replace a less reactive metal from a compound.
EG of displacement reaction: bromine + potassium iodide =
iodine + potassium bromide
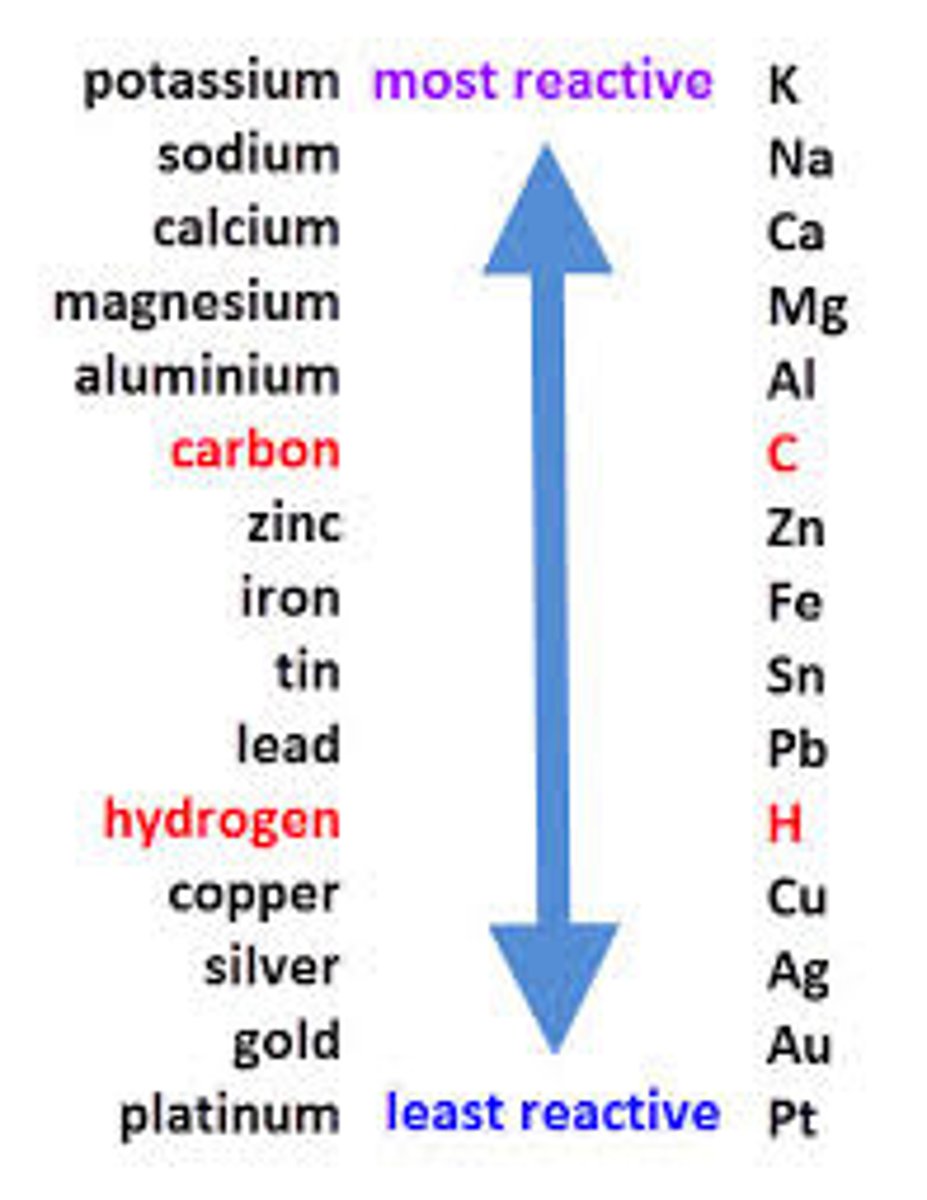
Reactivity series order :
Potassium, Sodium, Lithium, Calcium, Magnesium, (carbon), Aluminium, Tin, Lead, Iron, (hyrdogen), Copper, Silver, Gold, Platinum
What are the trends and properties of transition metals?
from more than one stable ion (EG: iron(II) and iron(III)), traditional metals, form coloured compounds, good catalysts
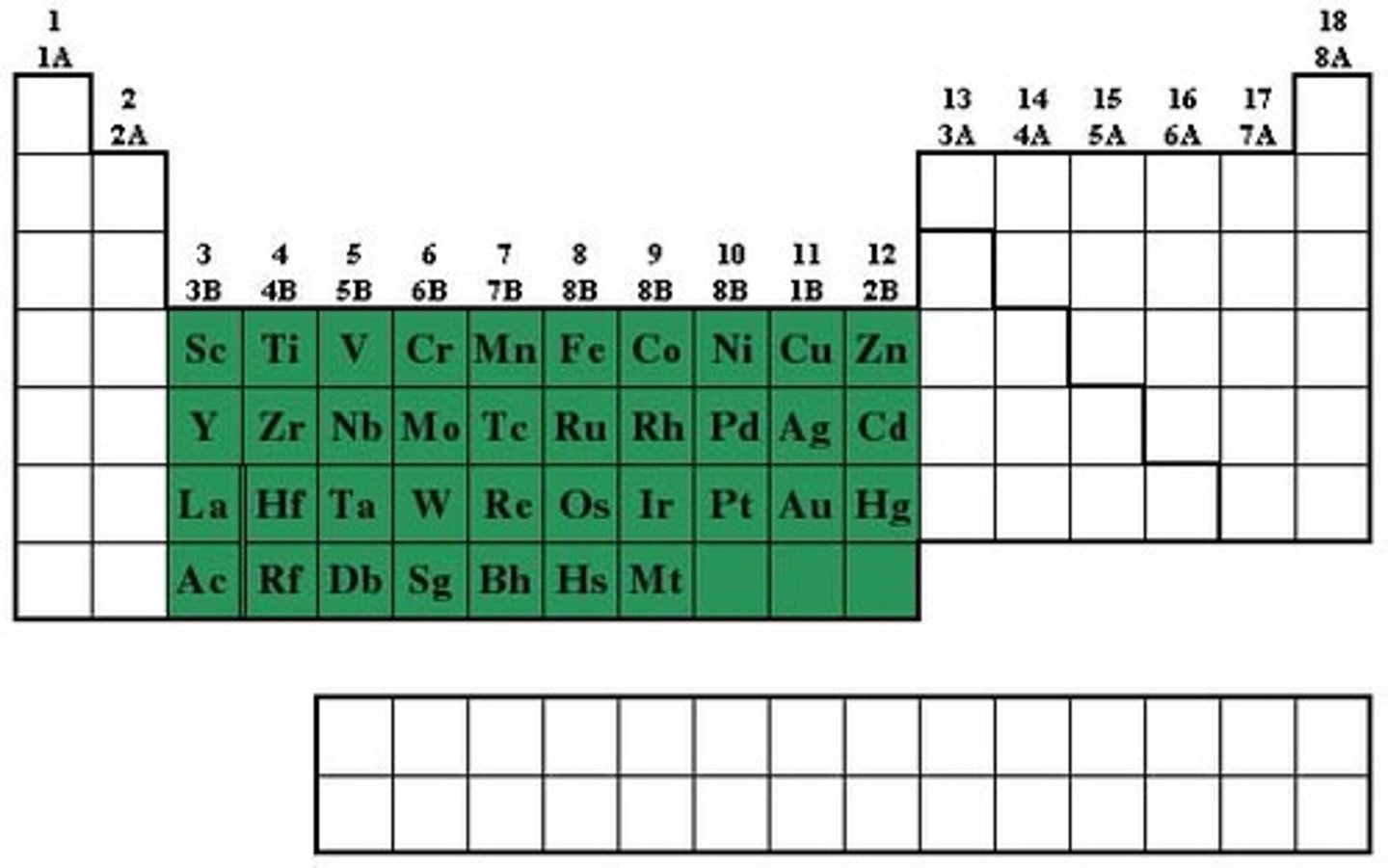
Metal + oxygen → ____ ____
metal oxide
metal + acid → ____ + ____
salt + hydrogen
What are the trends and properties of group 0, noble gases?
gases, monoatomic, unreactive/inert, density and boiling point increase as you go down the group, glow with different colours when electricity is passed through them, larger atomic molecules have stronger intermolecular forces
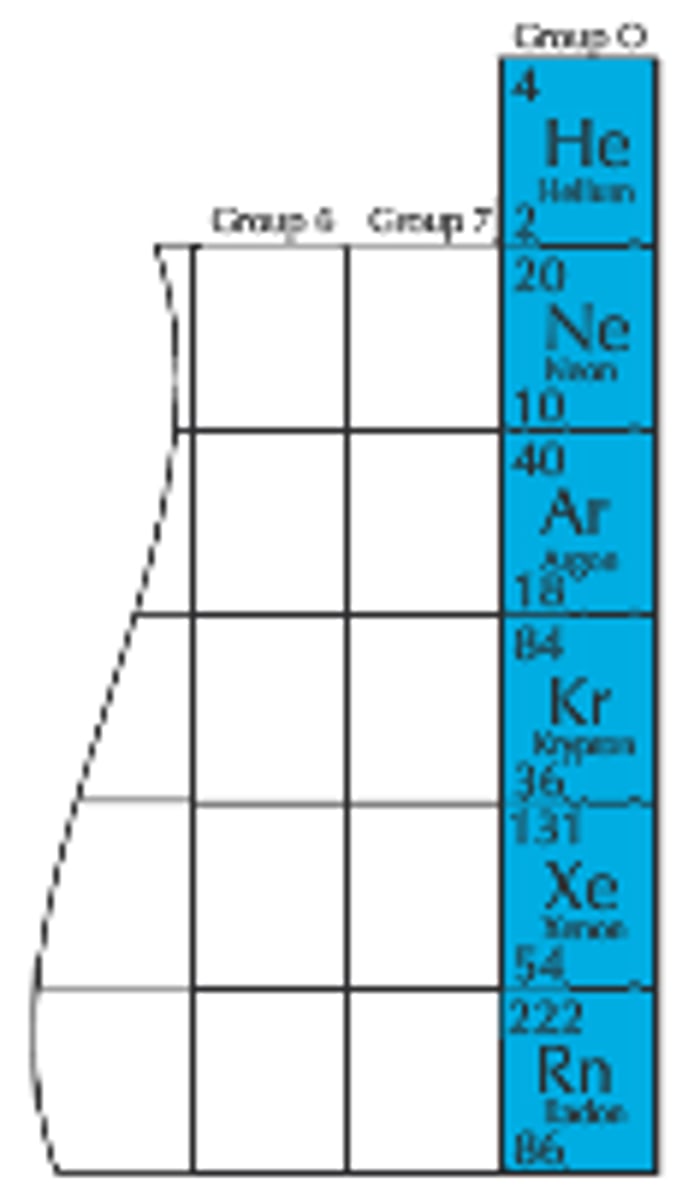
uses of noble gases?
MRI scanner, light bulbs, carrier gas (in gas chromatography)