Electric Forces (Video)
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
What are electric forces?
A type of non-contact force that can act on objects without them touching each other.
What causes electric forces?
A property of matter called “electric charge”.
Matter is made up of?
Atoms
What is an atom?
The basic unit of matter.
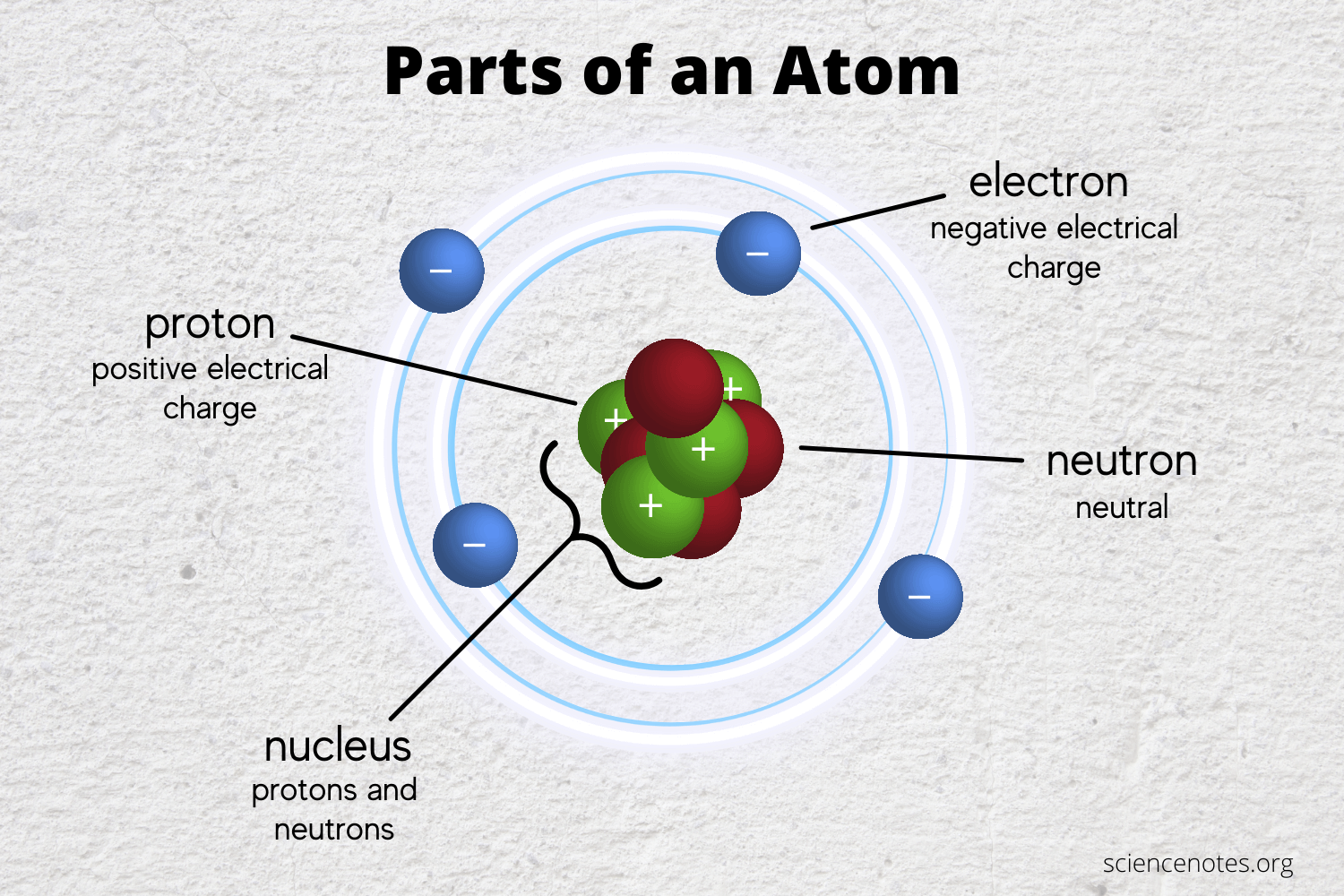
Describe the structure of an atom.
At the center of an atom is a nucleus with (positive) protons and (neutral) neutrons.
Negative electrons orbit the nucleus.
What is net charge?
The total electrical charge of an object.
What is positive net charge?
Positive net charge means an object possesses more protons than electrons.
What is negative net charge?
Negative net charge means an object has more electrons than protons.
What is neutral net charge?
This means an object has an equal amount of protons and electrons causing 0 overall charge.
What is the typical net charge of objects?
Most objects typically have neutral net charge.
What is transfer of charge?
The movement of electrons from one object to another.
What characteristics of electrons cause them to move from one object to another?
Electrons are loosely bound and lightweight compared to protons and neutrons (bound closely together and weigh more).
What are the three main causes of charge transfer?
Friction, induction, and conduction.
How does friction cause charge transfer (with example)?
Rubbing 2 objects together can cause electrons to move from one to object to the other. E.g. when you rub a balloon against your hair.
How does induction cause charge transfer?
Bringing a charged object near a neutral object can cause a separation of charges in the neutral object, even if the objects aren’t touching.
How does conduction cause charge transfer?
Bringing a charged object into physical contact with a neutral object can cause electrons to move from the charged object to the neutral object.
What causes clothing items e.g. socks and shirts, to cling to each other after putting them in a clothes dryer?
Charge transfer. The tumbling and friction inside the dryer can cause electrons to move from one item to another, e.g. from a shirt to a sock.