Bits and Drillstring Design
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lecture 5 for drilling Van Oort
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
How do tooth characteristics differ for soft formations compared to hard formations?
Soft formations require wide, long, and sharp teeth for aggressive cutting for softer formation; hard formations require close, short, and rounded teeth that leading to Relatively Low ROP. reduce wear and maintain greater pressure.

Two types of drill bit?
Milled tooth: cutting structure milled from steel
TCI: cutting structure made of hard inserts pressed into cone
What are the three main types of roller cone bit bearings?
Which bearing type is the least expensive and relies on drilling fluid for lubrication and used on shallow-surface hole?
Unsealed roller bearings
What type of roller cone bearing uses grease or oil sealed within the bearing to achieve a longer run life? - more expensive
Sealed roller bearings
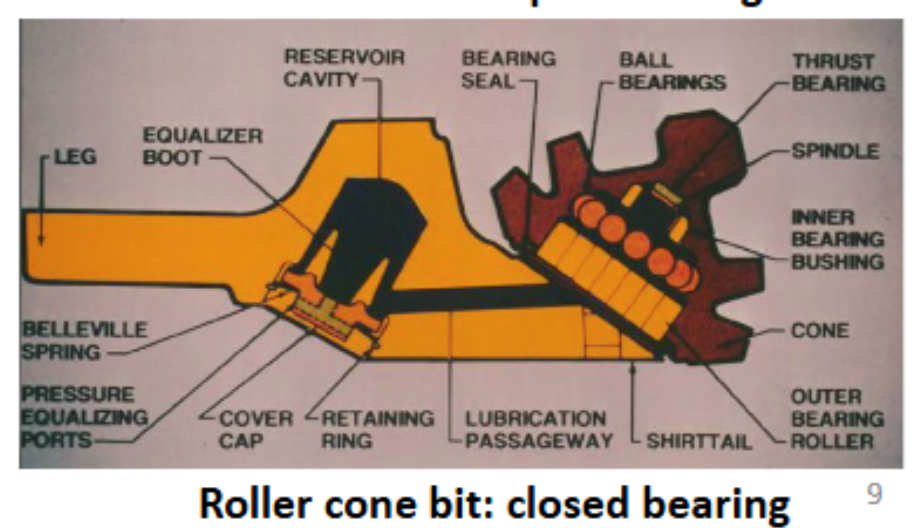
Roller Cone Bit Closed Bearings:
remeber the picture maybe
Which bearing type has the longest life and is the most expensive?
Journal bearings
Where is the oil reservoir located for Journal bearings?
In the shank - what is this
What component is primarily responsible for holding the roller cone on the shank?
The ball bearings
Name two key indications that a roller cone bearing is failing during a run
Increased and/or erratic rotary torque, increased drillstring vibrations (axial, lateral, or torsional), or sudden loss of penetration rate
What key feature gives PDC bits a main advantage over roller-cone bits?
They have no moving parts and no roller bearings, elimiate th erisk of bearing failrire common in roller cone
What are two typ of bit body types? - pDC
Steel PDC bits - machined from alloy steel, dimensionally accurate, easy to refurbish, but must be protected with hardfacing against abrasion
Matrix bits - cast from Tungsten Carbide grains, far more abrasion and erosion resistant, preferred where body failure is a risk
Name two of the four key terms used to define PDC cutter orientation.
Backrake, siderake, cutter exposure, or blade height
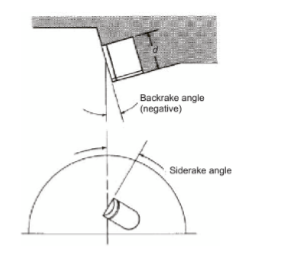
What is the trade-off associated with a low backrake angle on a PDC bit?
It increases aggressiveness (potential for higher ROP) but makes the bit more prone to impact damage.
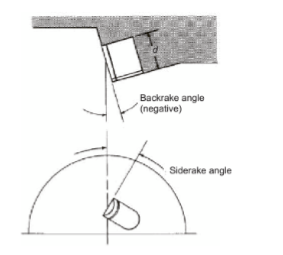
Sideracke inlfuences bit stabilty
negative siderake improves stability but may compromise bit cleaning; positive siderake improves cleaning but has no effect on stability
Cutter exposure determines how much “bite” a cutter will take
increased exposure makes bits more aggressive, depending on cutter
size
Blade height and open-face volume provide room for cuttings to peel
off the hole bottom—
without sticking to the bit’s body (global balling) or packing off on the cutters themselves (bit balling)
Why do Impregnated and Diamond Bits typically require high RPM using specialized downhole tools?
The diamonds are small, resulting in a small depth of cut, sensistive to shocks and vibrations(17)
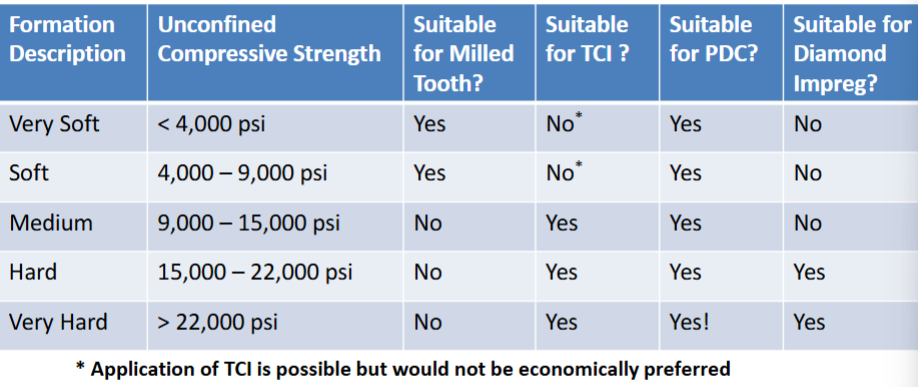
BIT Selection
PDC is preferred because of strength in every section
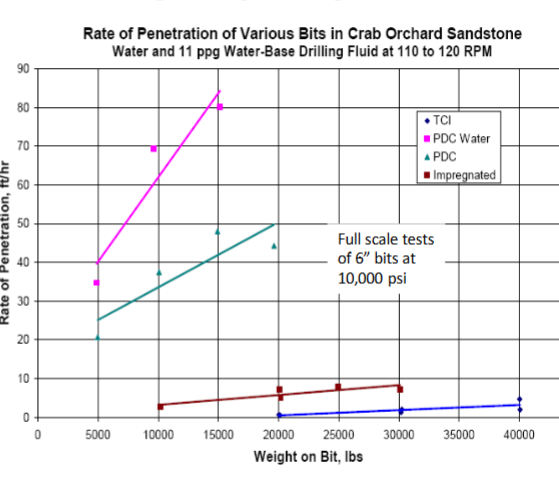
ROP (ft/hr) vs WOB
PDS is best but TCI is used for greater weight on bit
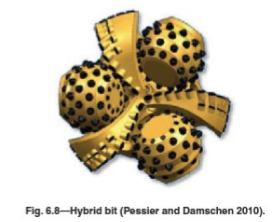
Kymera Bits
Marry essentila features of roller cones and PDC bits
LArge diamter hole in medium hard fromation, with stringers e.g chert.
Bi-center PDC Bits( extra space spinner)
i-Center bits are used within RWD (Ream-while-Drilling) systems. RWD systems, generally, are deployed in situations where a drilled borehole needs to be under-reamed, such as to facilitate tight clearance casing schemes in deepwater wells. "Bicentered reamers" are specifically listed as a type of RWD system
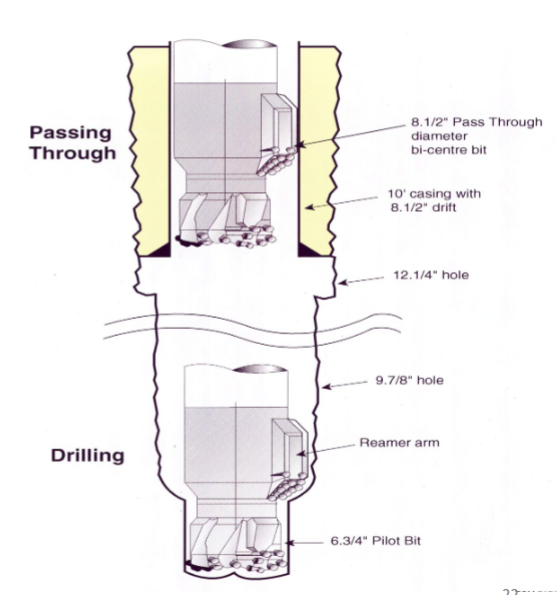
Types of RWD ( ream while drilling) - minimize pass though diameter
underreamers, roller reamers,
near-bit reamers, bicentered reamers,
RFID reamers, expandable reamers
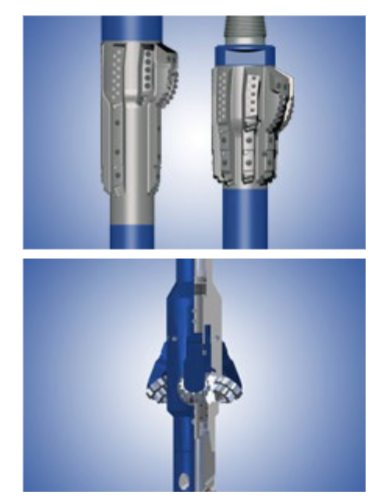
In order to make the bit work we provide what 3 ooptions
Compression loads through transferring part of the bottom hole assembly weight to the bit. Otherwise known as weight on bit (WOB)
Torque can be supplied by rotating the bit with the drill string and/or a down hole motor. Torque on bit (TOB)
Hydraulic horsepower and impact force through the circulation of the drilling fluid through the bit nozzles.
Roller Cone Bits vs Drag Bits ( Fixed Cutter/ PDC)
ask AI about this in sldies
RCB are cheaper and have moving parts(roller bearings)
But drag bits last longer and dont come apart (25-27)
Rock Failure mechanism
Crushing – compressive failure
• Grinding – compressive/shear failure
• Shearing – shear failure
• Erosion – fluid jet action
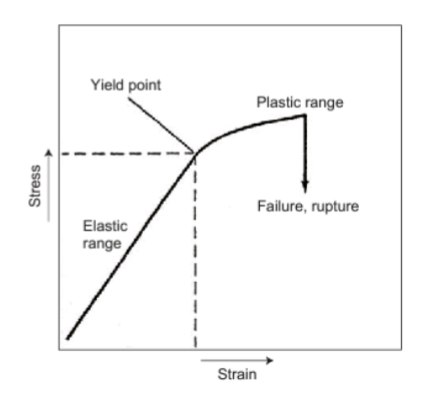
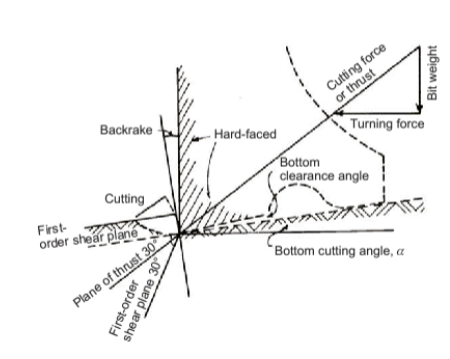
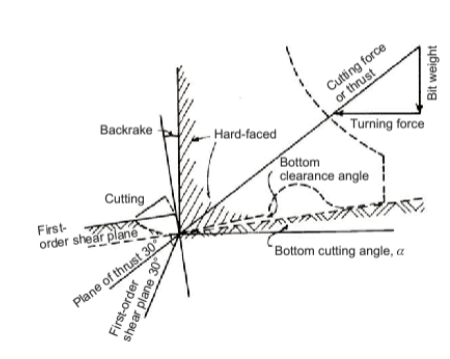
Rock Failure - PDC Bits - what does the image mean?
state of stress within a rock mass and illustrates how shear failure, the mechanism used by PDC bits, occurs even when external loads are purely compressive