biology snab
1/62
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
Myogenic
heart's ability to contract without external stimulation
test for safe dosage
test drug on healthy individuals and cell cultures
test on individuals with disease
gradual increase dose to determine safe dosage with least extreme side effects
Importance of cardiac output
increase supply of oxygenated blood to muscles
to allow aerobic respiration
provide energy and oxygen to meet demands
how adrenaline affect heart rate
adrenaline is carried in the blood made from adrenal glands on top of kidneys
acts on so sinoatrial node (SAN)
increase frequency of impulse produced by SAN
increase rate of heart contractions
effects of beta blockers
larger doses, greater decrease of heart rate
reduce heart rate reduces cardiac output
reducing supply of blood to muscle
human/animal controls
age, size, sex
body mass, level of fitness
exposure to same environmental conditions
PET
radioactive glucose
detects production of gamma rays
produces 3D image
Habituation
decreasing responsiveness result of repeated stimulation
transmission of impulses
Ca2+ ion enter presynaptic neurone resulting in neurotransmitters visible fuse with presynaptic membrane
neurotransmitter diffuses across synaptic cleft and synapse
neurotransmitter bind to receptors on post-synaptic membrane
Na+ ion diffuse into post-synaptic neurone leaving to polarisation and action potential
reduced/repeated stimulation on synapse
reduce permeability of presynaptic membrane to Ca2+ ions, fewer Ca2+ ions enter
fewer vesicles fuse with presynaptic membrane
less neurotransmitter bind to post-synaptic membrane
action potential may not occur / membrane may not be polarised
visual cortex development via visual stimulation
ocular domination column develops in visual cortex
neurone form synapse with these column cells
action potential along neurone requires to strengthen connection
stimulation in critical period needed to form connections in visual cortex
fMRI
detects blood flow in brain
increase in brain activity lead to increase demand for oxygenated blood flow for aerobic respiration
oxyhaemoglobin absorbs fewer radio waves
fMRI detects areas of less signal absorbed
risk of CT
radiation
can cause mutation in DNA muscle fibres via x-ray
Explain what a p value of 0.05 means
5% probability
The results obtained occurred by chance
Or
95% probability
The results obtained didn’t occur by chance
meaning of calculated value less than critical value (chi-squared)
observed results are not significant from observed and expected
meaning of calculated value less than critical value (t-test)
insignificant difference between 2 groups at p=0.05
use of spirometer to measure rate of aerobic respiration
add sodium hydroxide solution to dissolve CO2
Observe movement if coloured liquid in respirometer
Coloured liquid doesn’t move during anaerobic respiration and moves during aerobic respiration
state what is meant by the term Q10 temperature coefficient
The ratio of the rate of an enzyme reaction taking place at temperatures differing by 10 degrees kelvin or Celsius
Describe how flies could be gmo to produce one form of the human tau protein
Extract mRNA from one form of tau protein
Copy mRNA into DNA
Use restriction enzymes to create sticky ends
Use ligase to insert the tau dna into the vector
Introduce the vector into fertilised egg/cells
Explain how a statistical test could be used to determine if the number of shells with zero bands is significantly different in the 2 habitats
Use a statistical test such as the student t-test
If the test value is greater than the critical value at 0=0.05 the difference is significant
Explain why ions can dissolve in blood
Water is a component of blood
Ions are charged
Water has a dipole nature which therefore allows it to bind to ions
State what is meant by the term enzyme
A biological catalyst
Which livers the activation energy for a reaction
Increasing the rate of reaction
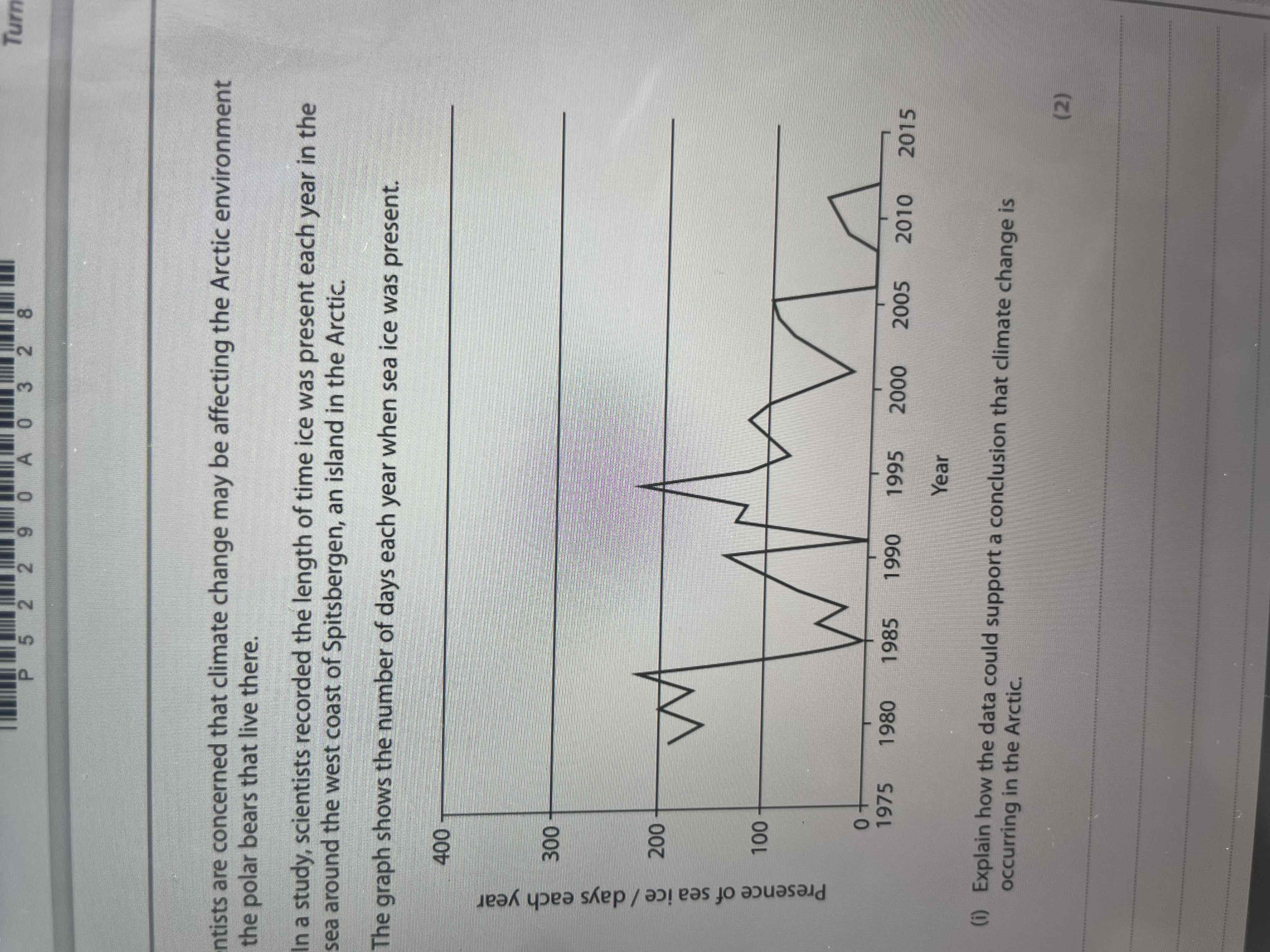
Explain how the data could support a conclusion that climate change is occurring in the the artic
Trend shows a reduction in number of days per year when sea ice is present
Sea ice melting due to global warming
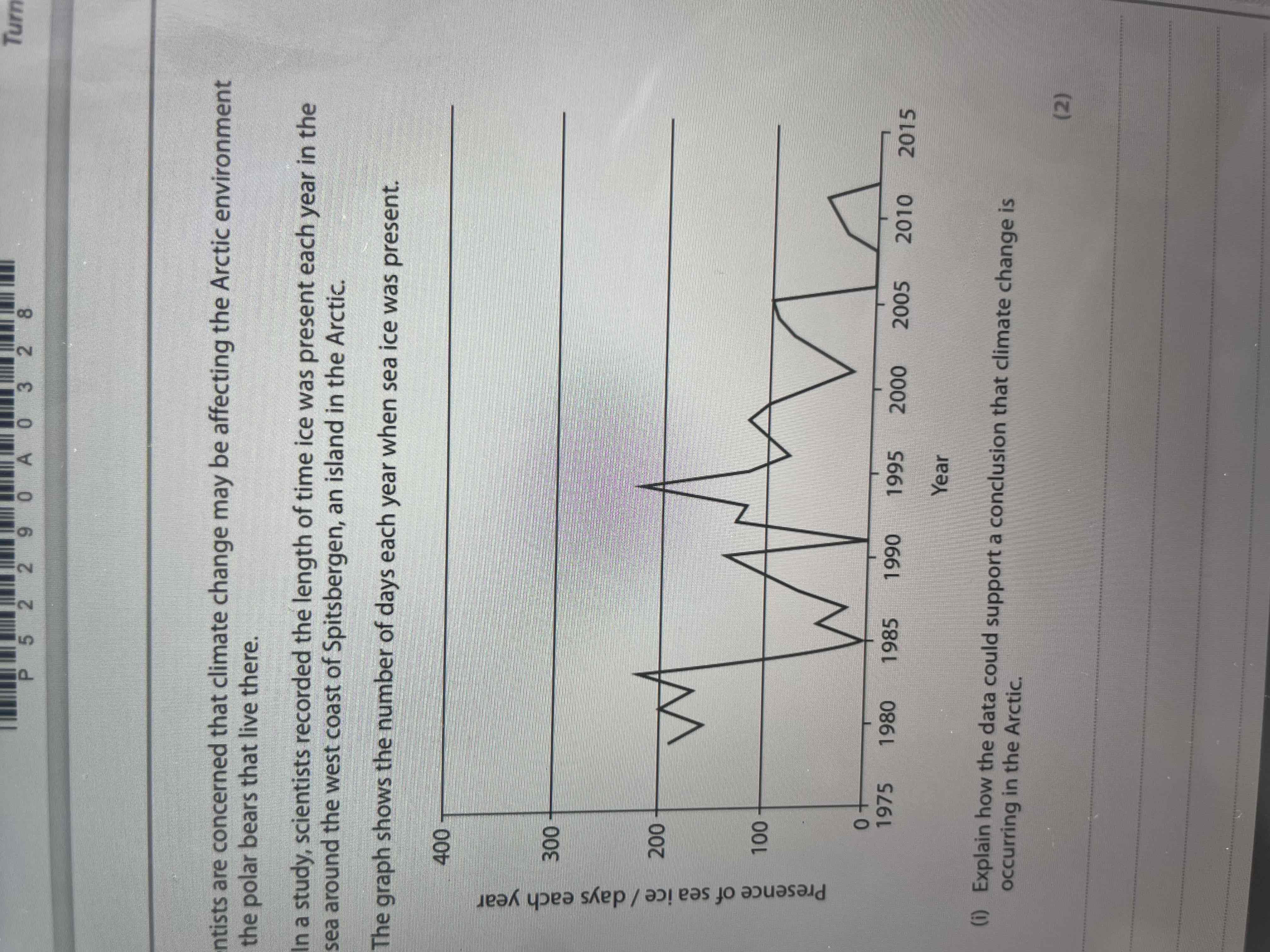
Explain why the data may not be useful for predicting future climate change
Cannot assume a trend will continue
Not enough data collected
Data from only 1 location
Data fluctuates/ no trend before 1994
Explain why the results for control ate useful in this investigation
Allows for a comparison between variables
Describe one advantage and disadvantage of using muscle fibres from the same sample of muscle
Advantage:
Controlled variable/ increases validity
Disadvantage:
May not be representative / only one muscle type tested
Give 2 reasons why there were different numbers of people in each resting heart rate group
Mid heart rate is more common in general population
Fewer people available at high and low heart rate because of other health risks
Give 2 reasons why the number of people in each resting heart rate group did not affect the validity of this investigation
Still a statistically large sample size
Wide range of heart rates considered
Percentage incidence used (rather than number)
Why are mammalian hearts needed?
To pump blood around in blood vessels
for mass transport
to overcome limitations of diffusion
myogenic
heart’s ability to contract without external stimulation
why the heart stops beating when separated from the right atrium
Sinoatrial node in the right atrium cannot send impulse to the rest of the heart for contraction
when the heart is taken out, why does it eventually stop contracting
Lack of oxygen to muscles
aerobic respiration stops
stops making ATP
phagocytosis
Engulfing/endocytosis of pathogen/bacteria
dipole nature of water in sweat
dipole allows water molecules to form hydrogen bonds with each other intermolecularly
energy is needed to break bonds between water molecules
evaporation of water causes removal of heat
how sweat mechanism to produced
homeostasis by negative feedback
thermoreceptors in the skin and hypothalamus detect a rise/ change in temperature
sends impulse from hypothalamus to sweat glands
to increase sweat production
what is myelin sheath made up of
schwann cells
role of myelin sheath in conduction of impulse
proves electrical insulation
enables saltatory conduction: jump of impulse from node to node for rapid transmission
role of ion channels in conduction of impulse
sodium ion gated channels open
sodium ion diffuses in
causing depolarisation of axon membrane
potassium ions diffuse out
causes depolarisation of membrane
how risk factors (smoking, high LDL, high fats) causes peripheral nerve cells to die
damage to cardiovascular system, development of atheroma, oedema
reduces blood flow, glucose, oxygen
insufficient aerobic respiration takes place
how a stem cell becomes specialised
due to chemical stimulus/transcription factors
activation of specific genes
transcription of those genes result in synthesis of proteins
gene mutation
change in the base sequence of DNA
how TB evade the immune system
TB survive inside macrophages due to thick waxy cell wall
remains dormant in tubercles
inhibits T-helper cells and suppresses the immune system
transcription factor
protein that controls the activation and transcription of genes
analysis of graphs
overlap of error bars: difference/effect is small
incomplete data: not enough information to draw an inclusive conclusion
caucasian ≠ cause and effect
Net productivity
NPP = GPP -R
product of light-dependent reaction
ATP
Oxygen
reduced NADP
why cells use energy in the form of ATP
contains phosphate bonds
when ATP is hydrolysed, energy is realised
energy is used to form/break bonds
ATP releases energy rapidly
how photosynthesis converts CO2 into simple organic molecules
CO2 binds with RuBP using RUBISCO
forming GP molecules
each GP is converted into GALP using ATP and reduced NADP
GALP used to form glucose
how chloroplast was adapted to their function of photosynthesis
large surface area provided by thylakoid membrane
thylakoid membrane contains chlorophyll to absorb light and enables photophsphorylation
stroma contains enzymes for light-independent reaction
stroma contains DNA and ribosomes to produce proteins involved in photosynthesis
how electrons are passed along the electron transport chain to produce ATP
via photophsphorylation
transfer of electron releases energy
used for pumping H+ into the thylakoid space/inner-membrane
proton diffuses back down concentration gradient through ATPase
forms ADP +Pi→ ATP
how change in chlorophyll molecules result in changes in wavelength absorbed
change in tertiary 3D structure, different bonds formed
changes in chlorophyll light absorbing region
changes in quantity of energy needed to excite an electron
how studying proteins and genetics used to support evolution of proteins
compare amino acid sequences
compare base sequences of DNA
in organisms from different stages of evolution
the further back in evolution, the more similar the sequence will be
allopatric vs sympatric speciation
allopatric: requires geological barriers that leads to geographical isolation result of different selection pressures
sympatric: random mutation within a population that leads to variation that stops gene flow, leads to reproductive isolation
how enzyme could tolerate to lactic acid
lactate dehydrogenase
converts lactic acid back into pyruvate
reduces H+ ion concentration
how to bring a muscle contraction
sarcolemma is depolarised causing an action potential
travels down the T-tubules
releasing Ca2+ ion into sarcoplasm
Ca2+ ion binds troponin
troponin changes shape causes troponin and tropomyosin proteins to change positions on actin filament and exposes myosin binding site on actin
myosin heads attaches to binding site forming cross-bridge
causing myosin head to change shape and hydrolysed ATP into ADP and inorganic Pi
pulling actin filament towards centre of sarcomere causes a muscle movement at a small distance shortening the sarcomere