Diversity of Life: Circulatory and Respiratory Systems in Mammals
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
What are the four chambers of a mammalian heart?
Right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, left ventricle.
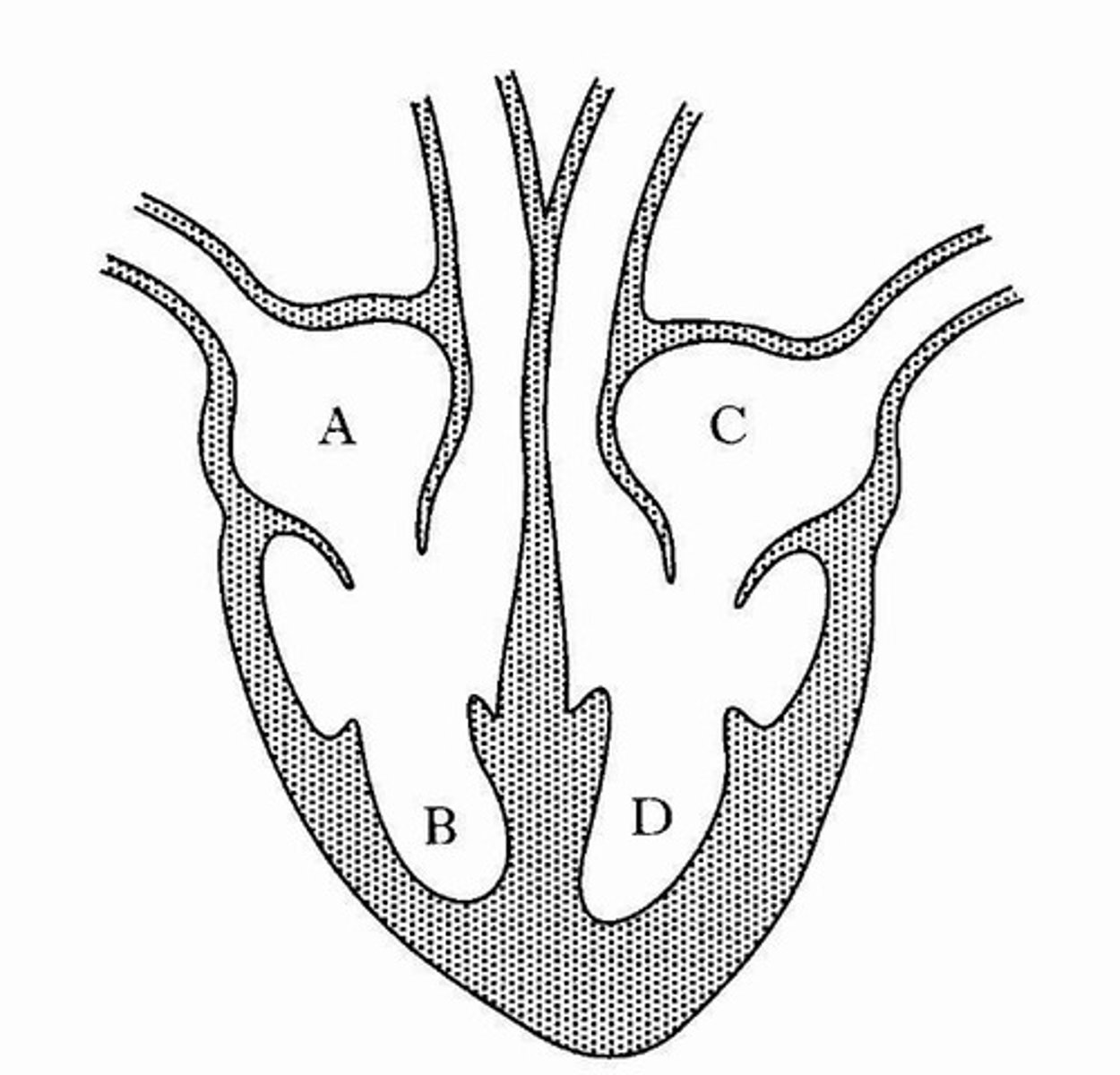
What separates the ventricles from the arteries?
Semilunar valves.
What type of blood does the pulmonary vein carry?
Oxygenated blood.
What is the main function of capillaries in the circulatory system?
To allow for gas exchange.
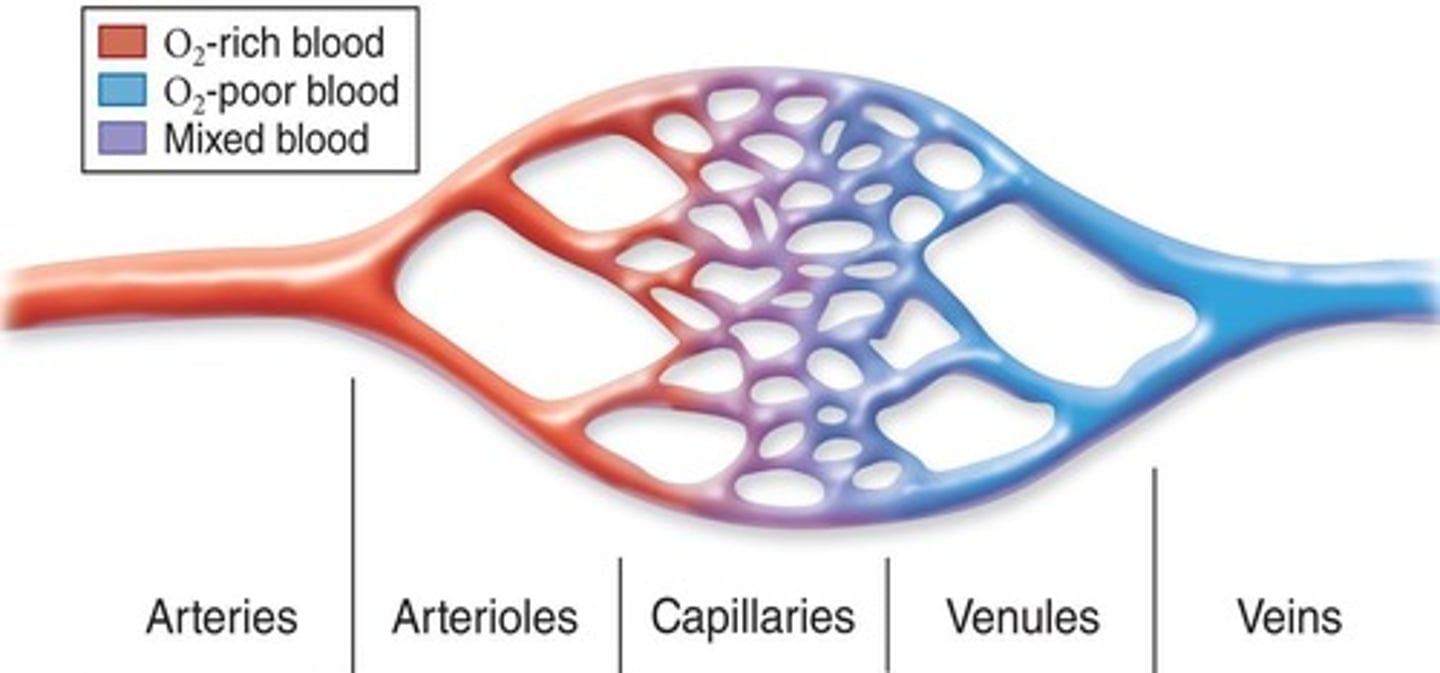
How do systolic and diastolic blood pressure differ?
Systolic pressure is the pressure during heartbeats, while diastolic pressure is the pressure between heartbeats.
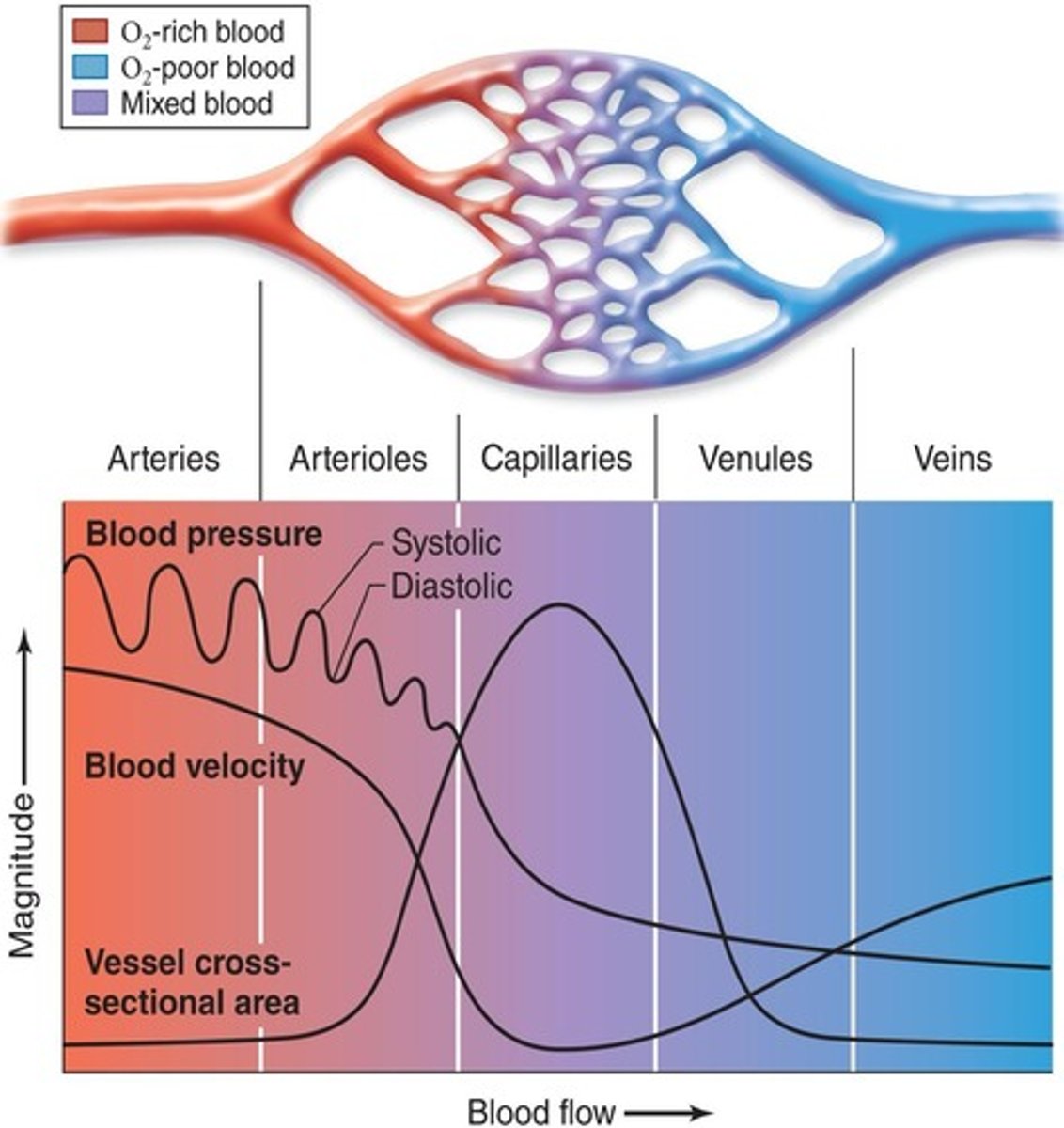
What happens to blood velocity as it passes through capillaries?
slows down to allow for gas exchange.
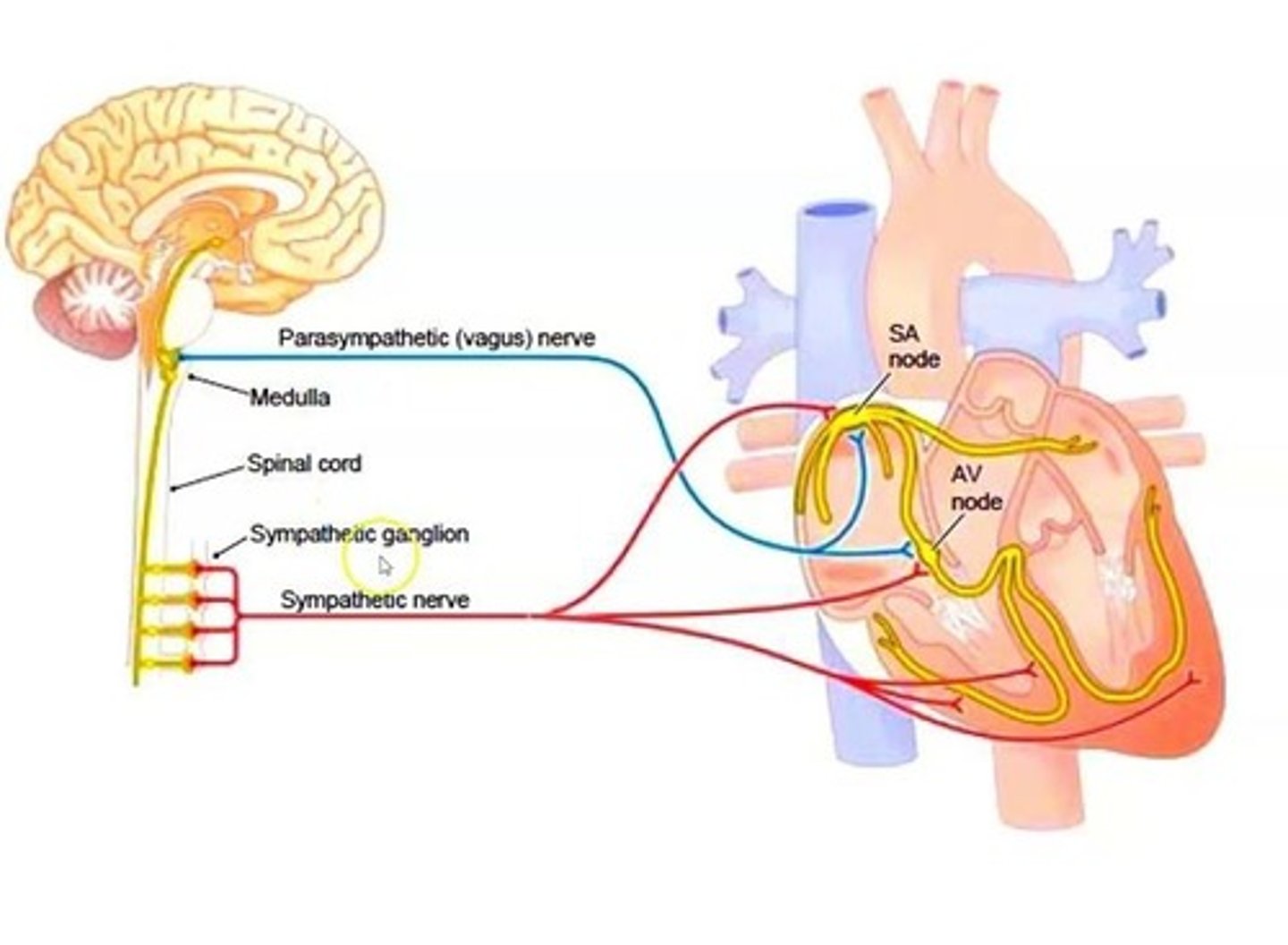
Which nervous system(s) regulate cardiovascular function?
the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems.
What role does nitric oxide play in the circulatory system?
It helps lower high blood pressure in the pulmonary circuit.
What is the consequence of left-sided heart failure?
Blood accumulates in the pulmonary capillary bed.
Which chamber of the heart would work hardest to compensate for an AV valve malfunction?
The ventricle.
What type of pressure does the heart create when it pumps?
Positive pressure.
What is the difference between positive and negative pressure in the context of the heart?
The heart creates positive pressure when pumping blood.
What happens to blood pressure in the pulmonary circuit during left-sided heart failure?
Blood pressure increases.
Which system increases heart rate if blood pressure is too low?
The sympathetic nervous system.
What cluster of cells sets the heart rate?
The SA node.
What is diastole?
when the heart relaxes and fills with blood.
What is systole?
The phase when the heart contracts and pumps blood.
What happens to blood flow into the systemic circuit if the right side of the heart fails?
Blood flow decreases.
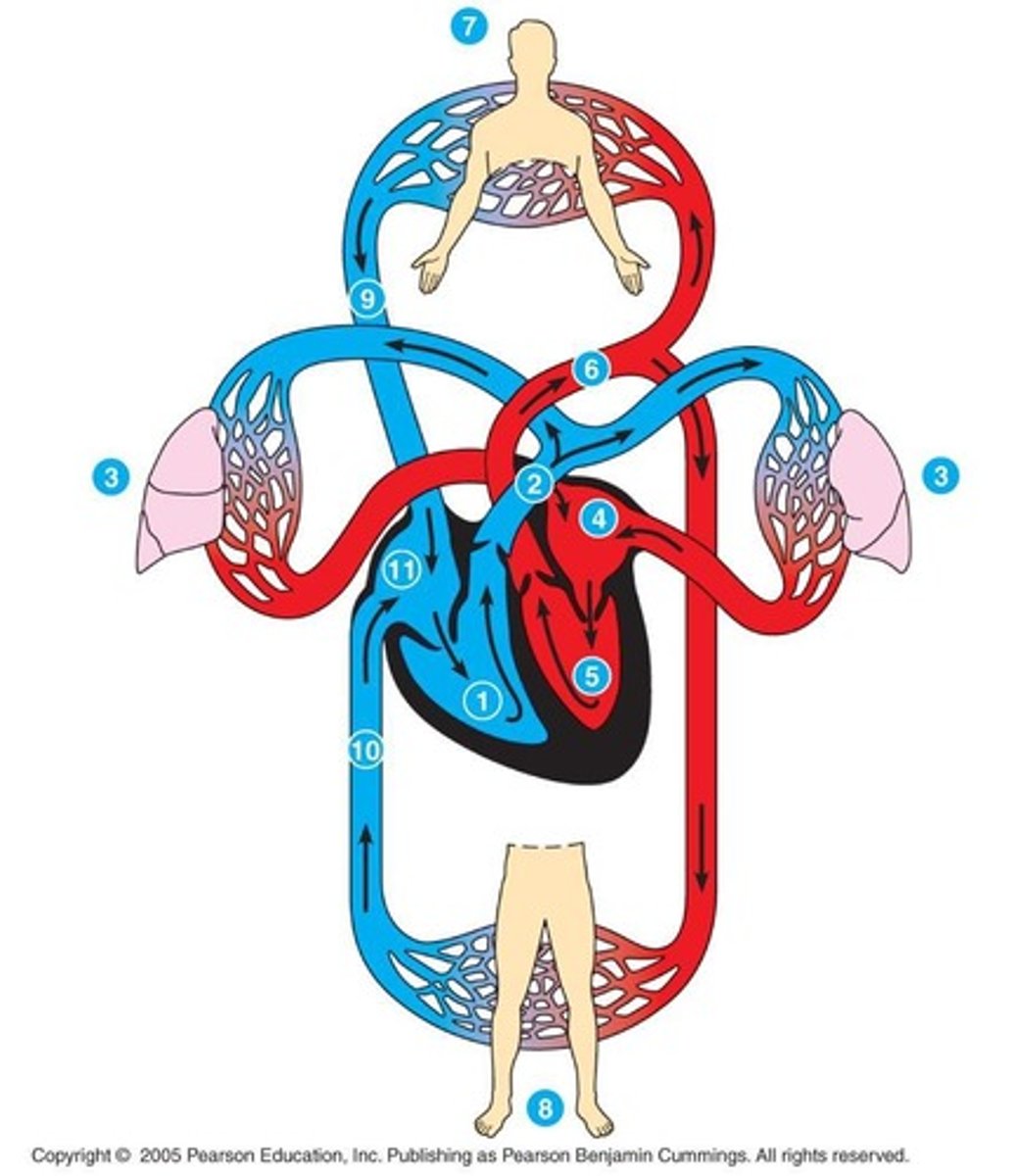
Which animals have double circulation?
Birds and mammals, including humans.
What is the total cross-sectional area of capillaries compared to arteries and veins?
Capillaries have a larger total cross-sectional area.
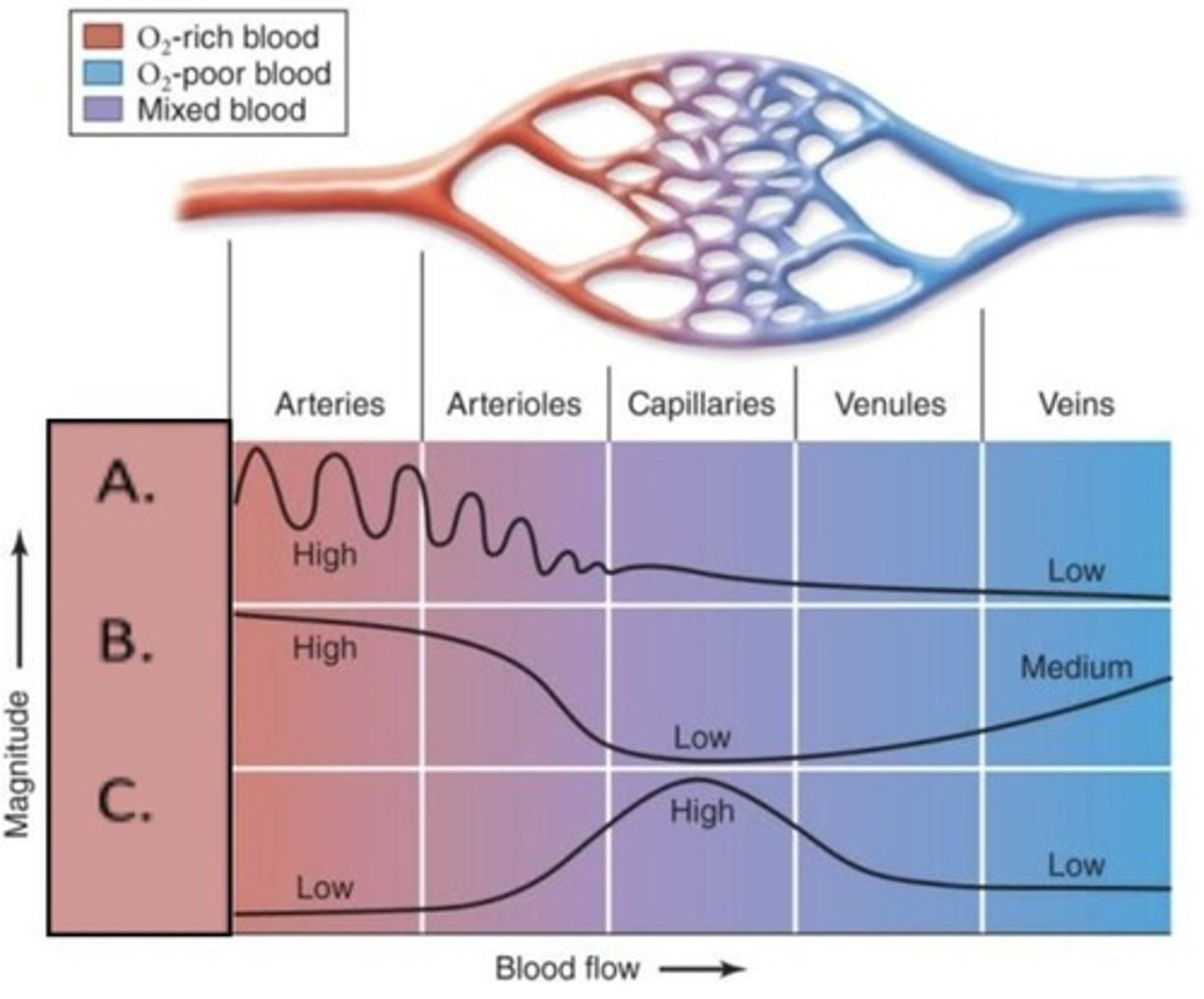
What is the primary function of arteries?
To carry oxygenated blood away from the heart, excluding pulmonary arteries
What is the primary function of veins?
To carry deoxygenated blood back to the heart, excluding pulmonary veins
What is the significance of blood pressure oscillating between systolic and diastolic levels?
It indicates efficiency and heart health
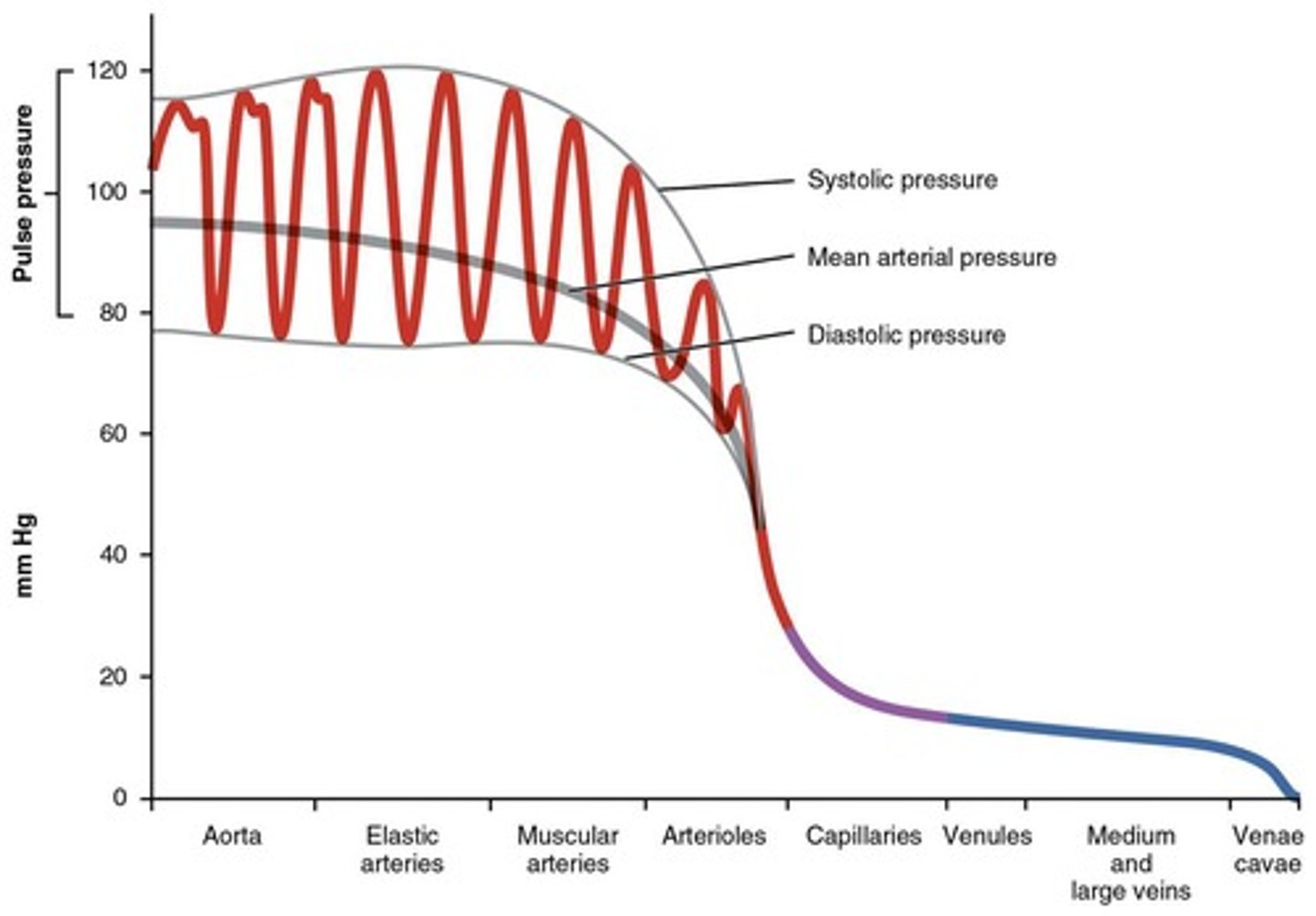
What causes the decrease in blood pressure as you move away from the heart?
The resistance of blood vessels and the distance from the pumping source.
What is the process by which organisms deliver water or air to their respiratory surfaces?
Ventilation
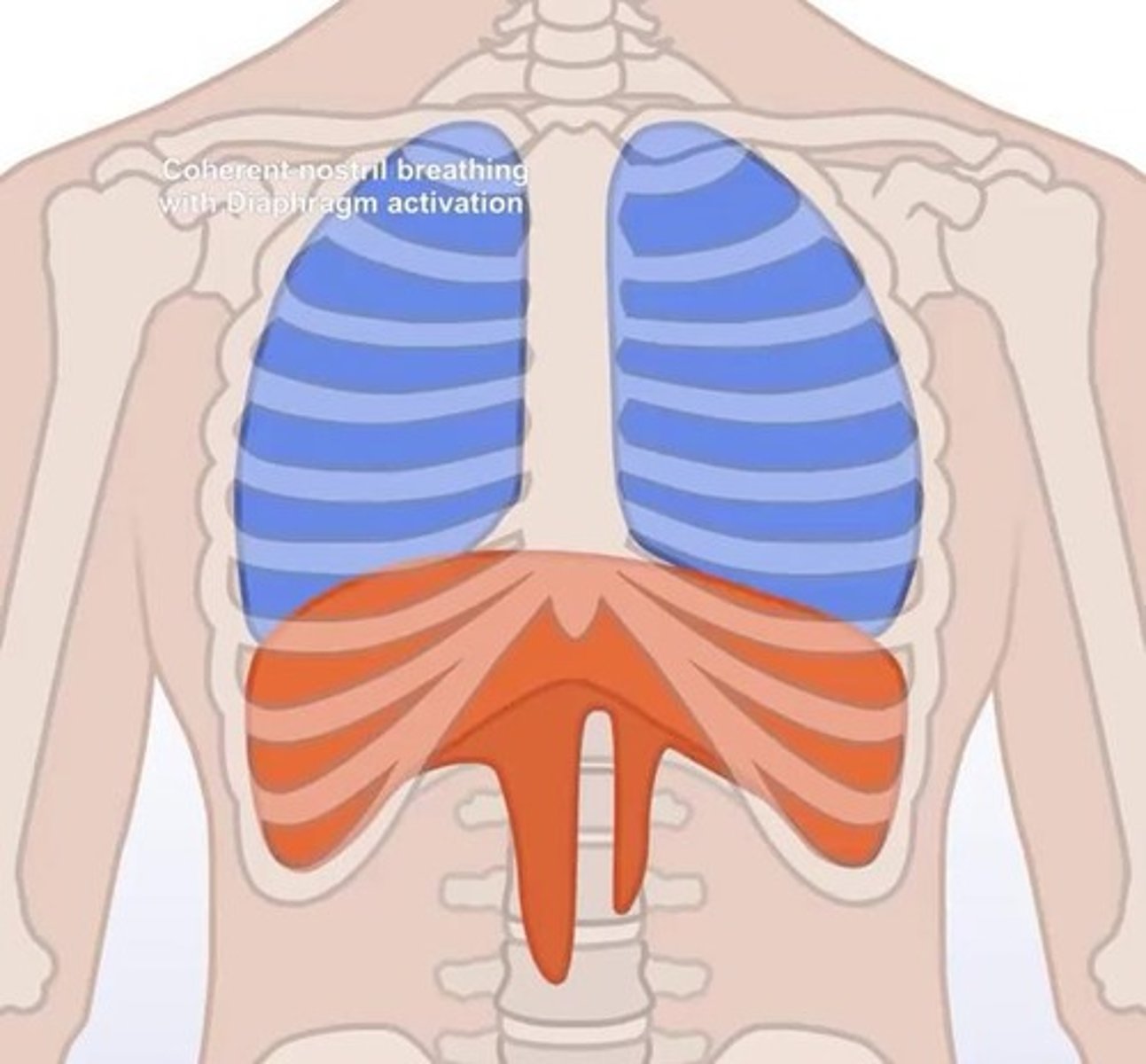
What happens to the volume and pressure of the chest cavity when the diaphragm contracts?
Volume increases and pressure decreases, resulting in inhalation.
What type of respiration brings oxygen into the circulatory system following ventilation?
External respiration
What drives the movement of oxygen during external and internal respiration?
Partial pressure gradients of oxygen
How does oxygen move from the pulmonary capillaries to the systemic capillaries?
Through transport in blood
What is the role of hemoglobin in the blood?
To bind oxygen and facilitate its transport from the lungs to tissues.
How many binding sites does hemoglobin have for oxygen?
Four binding sites
What mineral is necessary for hemoglobin to bind oxygen?
Iron
How does a decrease in pH affect hemoglobin's ability to bind oxygen?
It reduces hemoglobin's ability to bind oxygen.
What causes blood pH to lower from 7.4 to 7.2?
An increase in CO2 in the blood
What is the effect of low air pressure outside the body on oxygen concentration in the blood?
It lowers the concentration of oxygen in the blood.
What is the significance of Charles' high PO2 but low % O2 saturation of hemoglobin?
Carbon monoxide binds to hemoglobin with a much higher affinity than oxygen
What is the primary malfunction in Charles' condition of low % O2 saturation of hemoglobin?
Pulmonary ventilation
What physiological factors influence the rates of external and internal respiration?
Respiratory and metabolic rates
What happens to the heart's workload if oxygen were only found in blood plasma?
The heart would have to work much harder to move oxygen.
What is the relationship between CO2 concentration and blood pH?
More CO2 leads to lower pH-acidic
What is the effect of a small increase in temperature on hemoglobin's rate of oxygen loading?
It decreases the rate of oxygen loading.
What is the expected outcome if blood pH rises from 7.2 to 7.4?
It would indicate a decrease in CO2 concentration.
What is the primary function of internal respiration?
To exchange gases between the blood and the interstitial fluid in systemic tissues.
What is the effect of a decrease in pH on hemoglobin's oxygen saturation at a given pO2?
It decreases the oxygen saturation percentage.
What is the expected result of Charles' blood gas analysis showing elevated CO levels?
he has impaired oxygen transport due to CO's high affinity for hemoglobin.
What are the two types of respiration involved in gas exchange?
External respiration and internal respiration
What is the role of the diaphragm during inhalation?
It contracts to increase the volume of the chest cavity, decreasing pressure.
How does the body regulate respiratory rate?
Through negative feedback control involving CO2 levels.