Parasitology exam 1 Simplified
1/226
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
227 Terms
Symbiosis
Parasitism is a type of ________
Phoresis
To carry
No physiologic dependency
Mutualism
two organisms living together in a situation that benefits both
Obligatory mutualism
Both organisms are metabolically dependent on each other
Ex. Rumen Microbes
Commensalism
Relationship in which the commensal benefits from an association with a host where the host is passive to there relationship
metabolic needs
Habitat
Parasites depend on the host for
Parasitism
one organism lives in or on another organism at the expense of the host
Organism = yes, (+) positive effect
Host = no, (-/0)
Parasitism
Physiologic dependence (organism to host) = ?
Effects on participants?
Helminths
Multi-cellular
Roundworms, flatworms, thorny headed worms
Protozoa
Single celled
Amoebae, flagellates, ciliates, apicoplexans
Arthropods
Multicellular
Fleas, ticks, mites, flies, mosquitoes, ets
Endoparasite
any parasite that lives in the internal organs of animals
Ectoparasite
Any parasite that lives on the exterior of animals
Infection
The entry and development or multiplication of an infectious agent within the body of an animal
Infestation
The lodgement, development, or reproduction of parasites on the surface of the body or superficial tissue
obligate parasite
must live a parasitic lifestyle or die
Facultative parasite
opportunistic parasite that can survive without the host
Definitive host
Host in which a parasite reaches maturity and if applicable reproduces sexually
intermediate host
a host in which a parasite goes through its larval or developmental stages
Paratenic host
a host in which the parasite remains viable but does not undergo any further growth or development
Direct life cycle
Requires a definitive host but not an intermediate
Parasite infects new definitive host Via the environment
Direct
Describe the lifestyle in the image

Indirect life cycle
Requires >1 intermediate host(s) in addition to a definitive host to complete its cycle
Indirect
Indirect or Direct?
Fasciola spp.
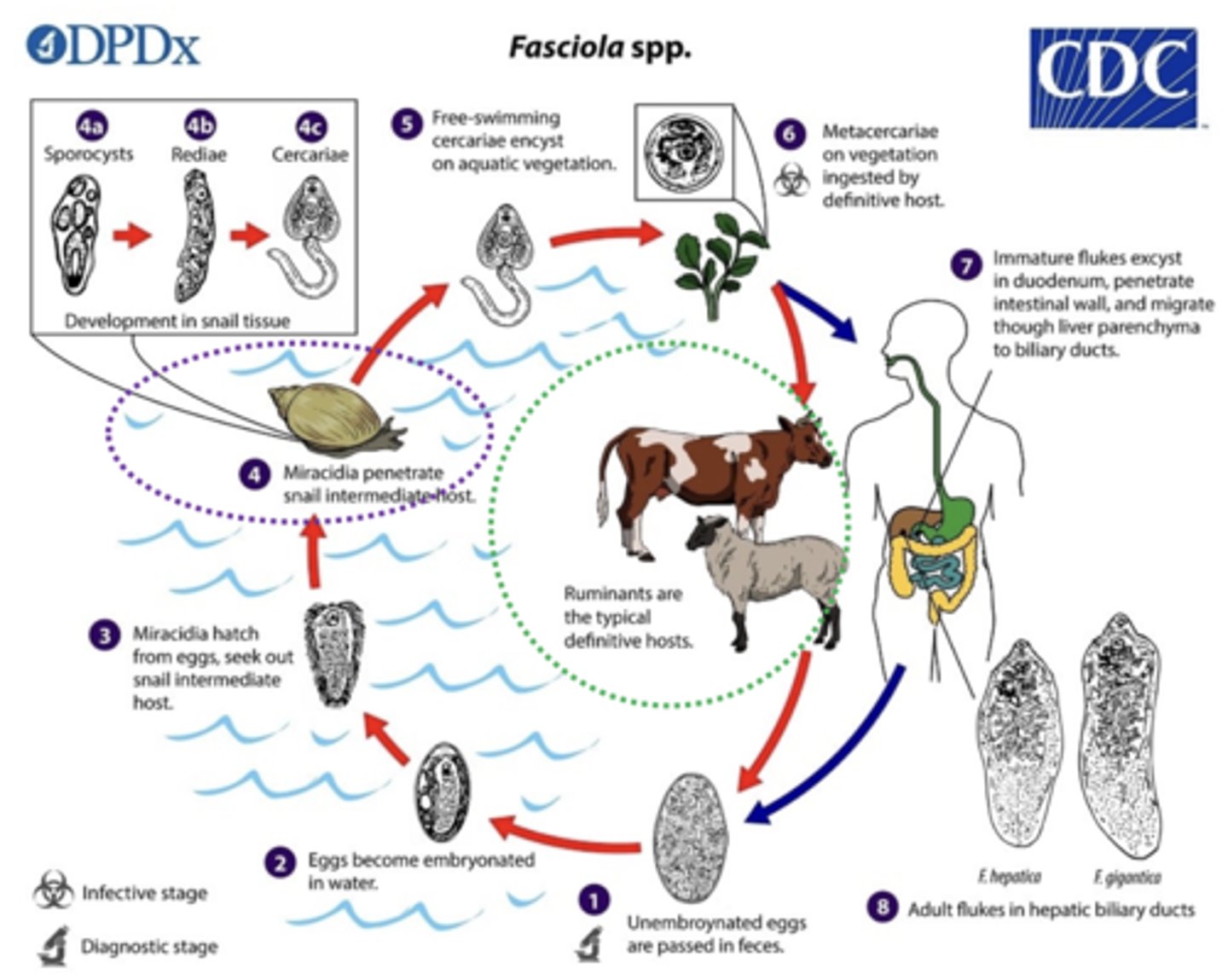
Direct
Note= can involve a proteinic host too
Indirect or Direct?
Toxocara spp.
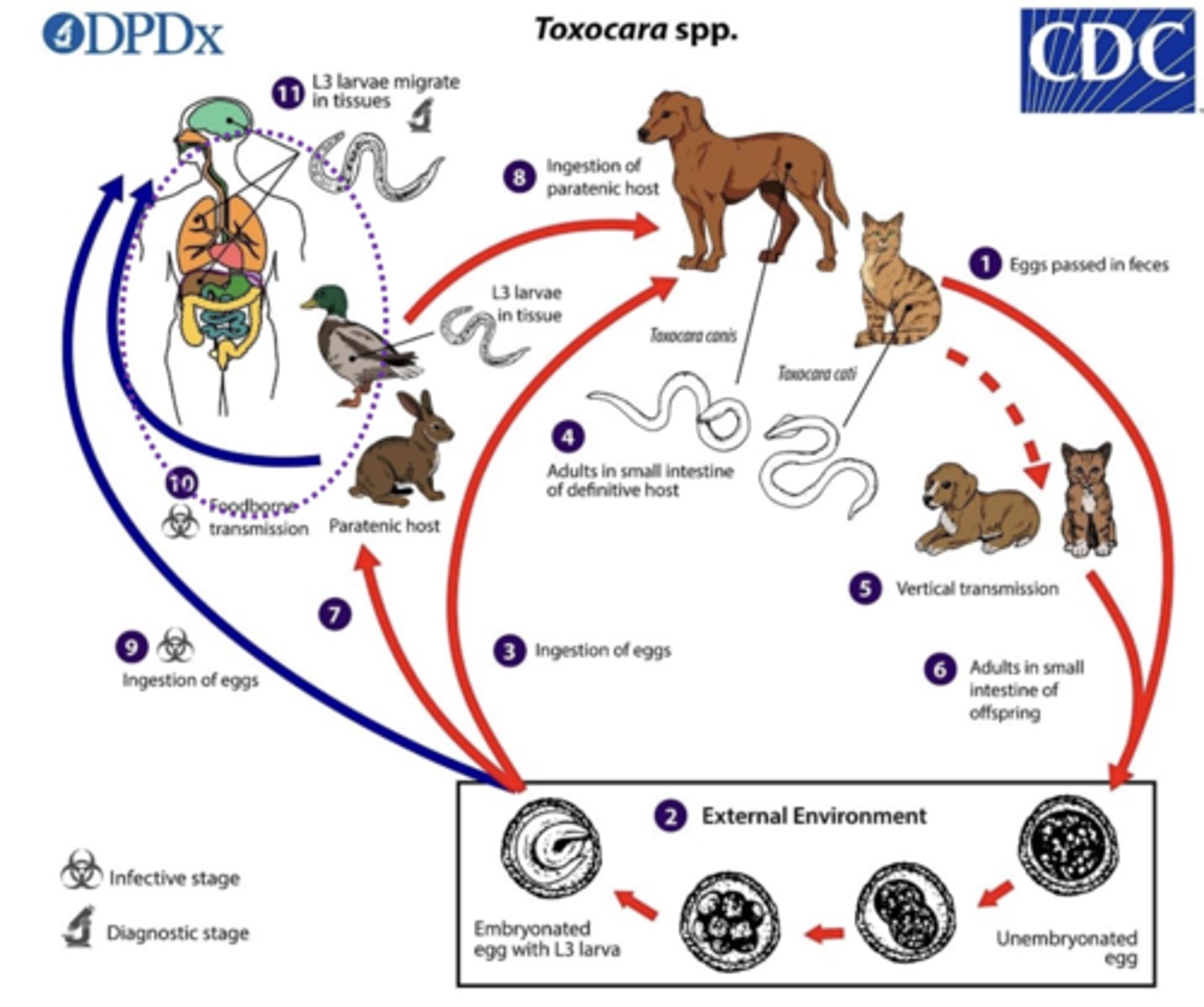
accidental parasite
a parasite that invades an organism other than its natural host
aberrent parasite
Parasite wanders to wrong site within host and cannot complete life cycle
pseudoparasite
any object or organism that resembles or is mistaken for a parasite
spurious parasites
Parasites that pass through the GI tract of a non-host species and are mistaken as parasites of the non-host
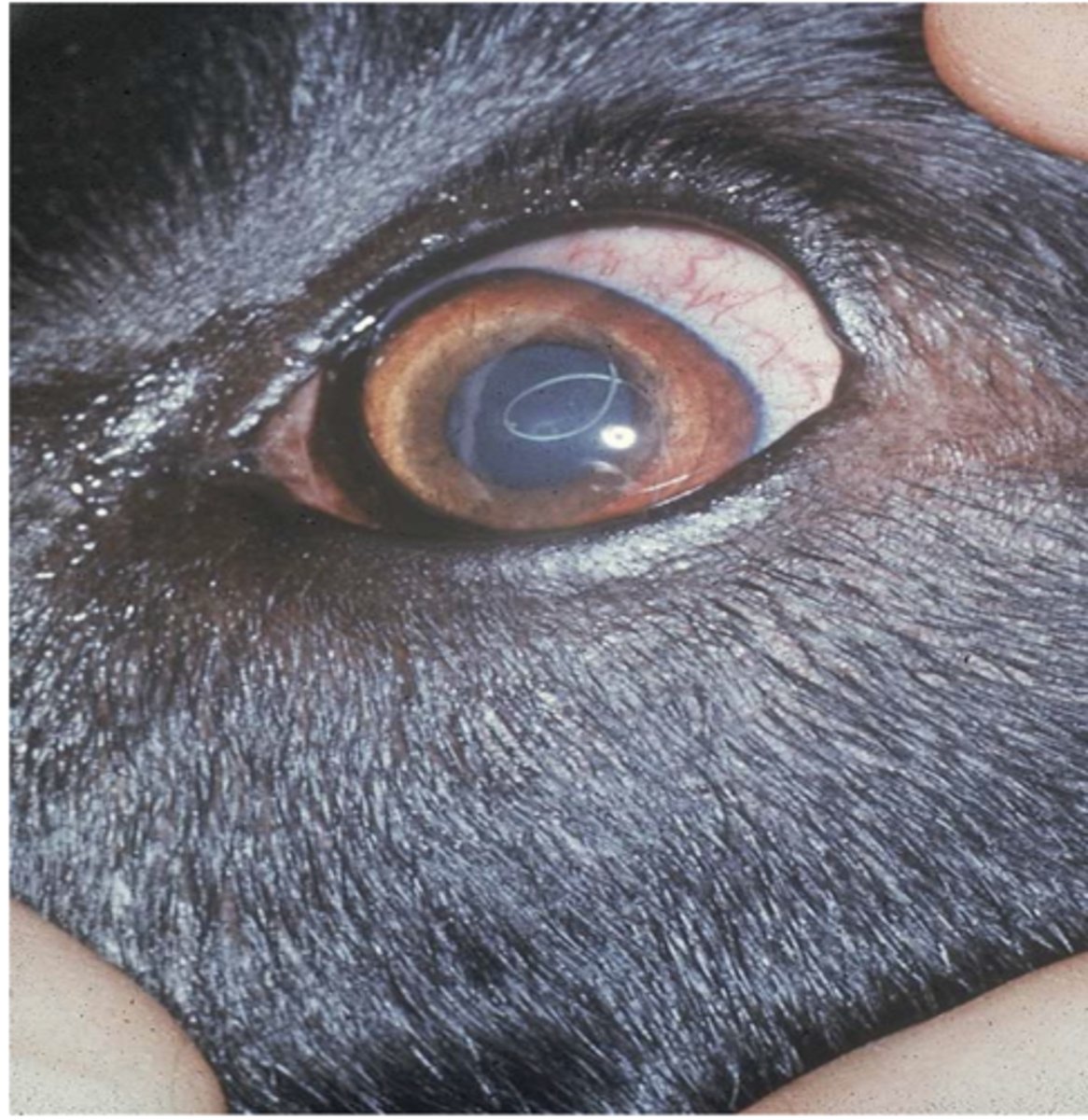
aberrant
Heartworm in the eye of a dog
Aberrant or accidental parasite?
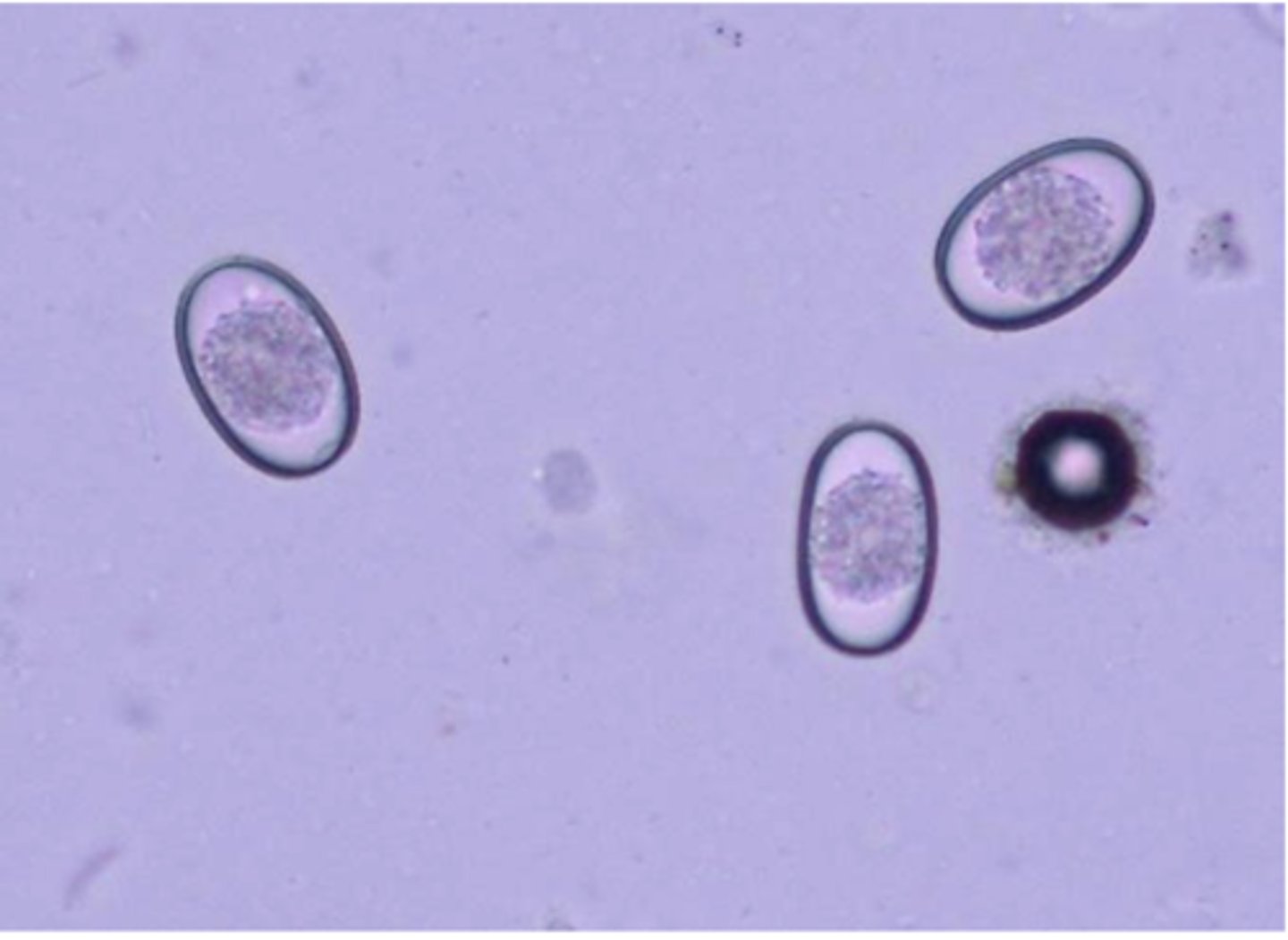
spurious
SPURIOUS PARASITE OR PSEUDOPARASITE?
Eimeria from an herbivore; found in dog feces
Incubation period
time interval between entry of an infectious organism into a host and the first appearance of clinical signs of disease in the host.
Pre-patent period
time interval between entry of an infectious organism into a host and the first time we can detect the organism in the host.
Oviparous
Female lays eggs with an undeveloped embryo
Ovoviviparous
female lays an egg that contains first stage larvae
Viviparous
Female gives birth to larvae instead of laying eggs
Lifecycle of Nematodes
1. Pre-parasitic stages occur outside host
2. Stage exiting the host is usually an egg or L1
3. Stage infecting host is most ofter an L3
4. Parasitic stages occur inside host
Blood worms, red worms
Common names for true strongyles include:
Ingestion of L3 larvae
How does Strongylus vulgaris enter the body?
Equids
Species affected by strongylus vulgaris/ large strongyles?
Yes, Penetrate intestinal wall and migrate to the cranial mesenteric artery
Do strongylus vulgaris migrate within the body of the horse?
Cecum and colon
Where do adult strongylus vulgaris live?
Larval migration
The pathology of the strongylus species is ____
Strongylus vulgaris
Thromboembolic colic / Verminous
arteritis ==> infarction
Verminous arteritis
Acute disease of strongylus vulgaris
Colic
Anemia
Arteritis
Thrombosis
infarction of gut wall
altered intestina motility
Symptoms associated with strongylus vulgaris?
Strongylus Vulgaris
The only nematode with larval development in the arterial system of horses?
Ingestion of L3 Larvae
How do strongylus edentatus enter the body?
Yes, L3 penetrate the intestinal wall and migrate to the liver via the bloodstream. from the liver they migrate to the peritoneal cavity
Is there migration within the host of strongylus edentatus?
Cecum
Where do adult strongylus edentatus live?
Fecal float/FEC
ID adults at necropsy, look for lesions
Test to ID Strongylus species
Liver
Peritoneum - peritonitis
gut wall - adhesions
What kind of damage do strongylus edentatus cause?
Strongylus vulgaris
Strongylus edentatus
Strongylus Equinas
What strongyles belong to "Large Strongyles"
False, all strongyle type eggs look the same
T/F You are able to tell "Strongyle-type" eggs apart in the feces
Equids
Definitive host of cyathostomes
(60-120) x (35-60)
small Strongyle type eggs can be ___ x ____ in size
True
T/F Small strongyle eggs cannot be differentiated from large strongyles
cecum/ colon lumen
Adults of cyathostomes can be found in
Larval = Synchronous emergence of arrested larvae
-Non responsive diarrhea, hypoproteinemia, edema, weight loss, seasonal
Chronic = normal maturation/life cycle
-Poor hair coat, weight loss, loose stool, pot belly
Describe the difference between Larval cyathostominosis and chronic cyathostominosis
Arrested development of L3
Larval cyathostominosis
Direct life cycle
Describe the development of small strongyles
Cyathostomes
Small strongyles are also considered
Quantitative float
What is the method to test for small strongyles/ cyathostomes
Selective therapy
Describe the best method of treatment for small strongyles?
Parasites are unevenly distributed (overdispursed)
Strongyle egg shedding is consistent over time (in adult horses)
Selective therapy relies on what two observations:
Control populations in order to avoid clinical signs
Control/slow the development of resistance
Reduce eggs on pasture
Goals of selective therapy
Binomial negative distribution
80% of the worms
carried by 20% of the population
Describe the 80/20 rule
Refugia
Untreated/ non dewormed animals are ________
Fecal egg count reduction tests annually
No anthelmintic will eliminate all parasitic stages from a horse
Continue using fecal egg counts once or twice a year
Deworm all horses at a baseline rate (once or twice a year) and target selected horses more often based on FEC
Important AAEP guidelines
Oesophagostomum spp.
What parasite would you expect to see a cervical vesicle and shallow buccal cavity
reinfection that produce lesions of localised immune-mediated reaction around larvae in mucosa
The pathology of Oesophagostomum spp. is unique in that they can cause ________
Oesophagostomum spp
Nodular worm
Ruminants and swine
Oesophagostomum spp are known to affect what species of animals
Primary infection can be harmless but enteritis can emerge if a large number of larvae emerge from mucosal cysts
Pathology of oesophagostumum spp
Many drugs can kill adult worms, none target encysted larvae, this results in reinfection
What is unique about the treatment of Oesophagostum spp
Stephanurus Dentatus
Swine kidney worm
stongyle type eggs in Fresh urine
How can one detect the eggs of stephanurus dentatus?
yes, but the eggs cannot survive the cold and dry
Can pigs raised outside get Stephanurus dentatus
True
T/F Pigs can get stephanurus dentatus from Parentenic host: earthworms that penetrate the skin, ingestion of larvae, or ingestion of infected earthworms
Haemonchus
Ostertagia
Trichostrongylus
Cooperia
HOTC
Haemonchus cortortus
Barber pole worm
Haemonchosis
Haemonchus contortus can cause the clinical condition _________ in Sheep, goats, camelids
Haemonchus cortortus
The most important parasite of sheep, goats, and camelids
Haemonchus Placei
Cattle Wireworm
Haemonchus Placei
This abomasum cattle worm can be found worldwide and also infect sheep primarily in warmer locations
Haemonchus spp
Both sexes are blood suckers
Strongyle type eggs
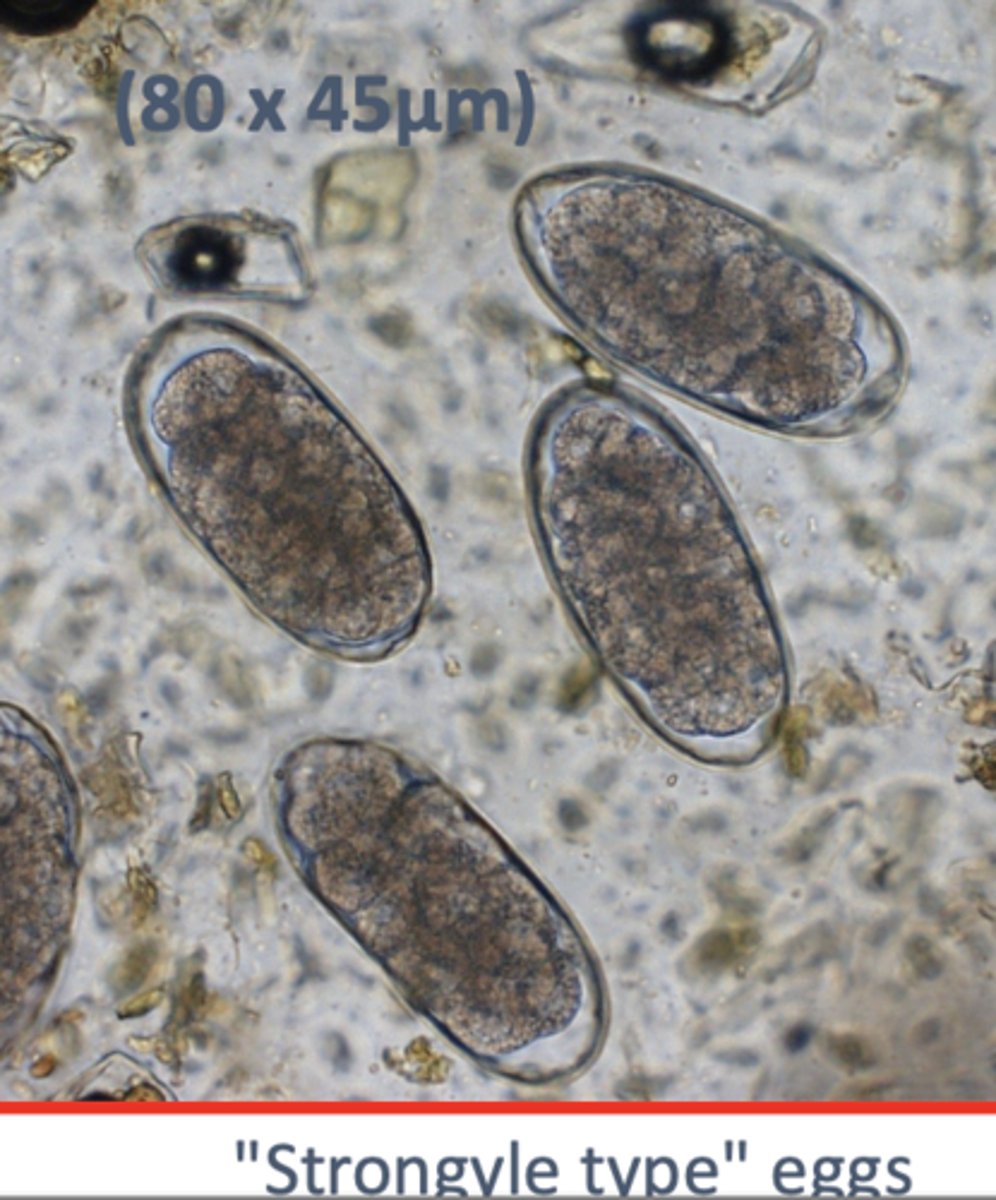
Haemonchus spp.
The pathogenesis of this worm can cause Voracious/ Excess blood loss resulting in decreased RBC's and proteins
Hypopreteinemia
decreased oncotic pressure
Haemonchus spp
Unless mixed with other strongyles, diarrhea is generally not a feature of infection unless mixed with other strongyles
Anemia and dependent anemia
FAMACHA
Younger animals
Quantitative fecal can be helpful
The best test and indication of Haemonchus spp
Ostertagia ostertagi
This is historically the most important economically helminth parasite in cattle in the US although its distribution is worldwide
Ostertagia ostertagi
Brown stomach worm
Hypobiosis of L4 is seasonal and emerge in the next season
Ostertagia ostertagi is unique lifecycle in that
Morocco leather of cobblestone appearance of the abomasal mucosa
Changes to mucosa
Change in abomasal pH
The pathogeneis of Ostertagia ostertagi shows
Type 1 ostertagiasis: No developmental arrest - no hypobiosis
Type 2 ostertagiasis: Developmental arrest - hypobiosis
The difference between type 1 and type 2 ostertagiasis
True strongyles
Hookworms
Trichostongyles (mostly)
Direct lifecycles, eggs/freeliving L3
meningeal worm
Indirect lifecycles with snail/slug intermediate host
Lungworms
Some direct life cycle, eggs with larva; some indirect lifecycle with snail/slug intermediate host
Trichostrongylus axie
stomach hair worm
Erosion of the abomasal epithelium +/- haemorrhage
Horse: hyperemic gastritis
Pathogenesis of trichostrongylus axei
Diarrhea, weight loss, anorexia
Clinical signs of trichonstrongylus axei
Cooperia spp
What small intestine trichostrongylus is extremely hard to kill with macrocyclic lactones?