ECON2105 Chap. 2
CHAPTER 2
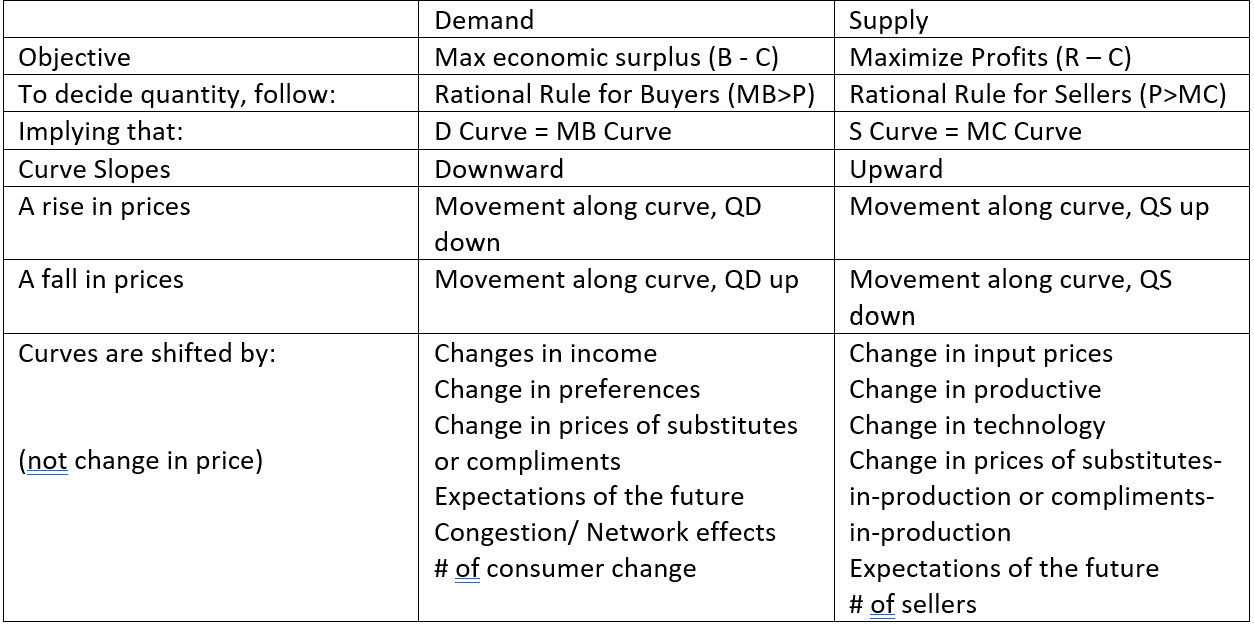
Individual Demand:Law of Demand: When the price rises, Qd decreases. When price falls, Qd increases.
Price is the MC
First 3 principles: MP, C-B, OCP
Market Demand: Aggregating all of the demand (for a single market).
Demand is shifted with interdependence
Individual Demand Curve: Graph plotting the quantity of an item someone is willing to buy at each price.
The MB curve is your Demand curve
Diminishing Marginal Benefit the reason MB is downward sloping
Estimating Market Demand:
Survey a small part of your customers
Add up the total quantity
Apply that to the population
Plot it
Changing price causes movement along the demand curve
Network effect: If more people buy a product, your demand for it increases. Ie: social media
Congestion effect: If more people buy a product, your demand for it decreases. Ie: Chick-Fil-A Line
Supply:
Law of supply – the higher the price, the higher the quantity supplied.
Individual Supply Curve is for a single business,
MC curve is supply curve; MB curve is demand curve
As sellers experiment, they follow the core principles of economics
Survival of the fittest weeds out bad managers
Input prices
Technology
Prices of related goods – substitutes in production (making new stuff) or complements in production (selling a byproduct of your good)
Expectations
Number of sellers only shifts market supply