Cell Parts Midterm Study
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
What is a cell?
The basic unit of life
What did Robert Hooke do?
He was the first to use a compound microscope to look at "cells", therefore discovering/naming it for the first time.
What did Anton van Leeuwenhoek do?
He used a single-lens microscope (simple microscope) to look at pond water where he observed small organisms moving
What did Anton van Leeuwenhoek name the small organisms he observed?
"animalcules"
What did Schleiden, Schwann, and Virchow contribute to?
They helped create the "cell theory"
What did Scheiden do?
He concluded that all plants were made of cells (plant cells)
What did Schwann do?
He concluded that all animals are made of cells (animal cells, Schwann sounds like Swan which is an animal)
What did Virchow do?
He discovered that all cells come from other or preexisting cells and go through the process of mitosis. (saw cell division)
What are the 3 aspects of the "original cell theory"?
All living things are made of cells
Cells are the basic units of structure and function
All cells are produced by existing cells
What are some modern additions to the cell theory?
Cells contain hereditary info that is passed from cell to cell during cell division
All cells are similar in chemical composition
All chemical reactions for energy flow & metabolism occur within cells
What are the 2 types of organisms?
unicellular and multicellular
What is the main difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
Prokaryotes do not have a true membrane-bound nucleus while Eukaryotes have a membrane-bound nucleus
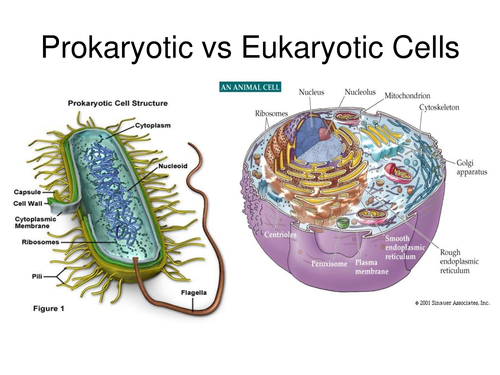
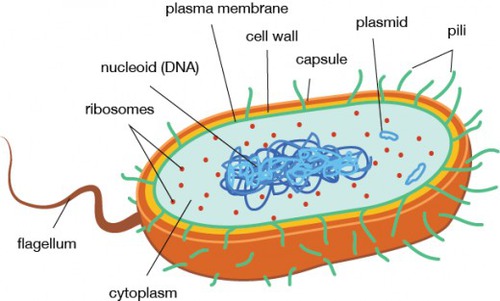
What is a prokaryotic cell?
A cell without a nucleus (DNA is not bound by a membrane)
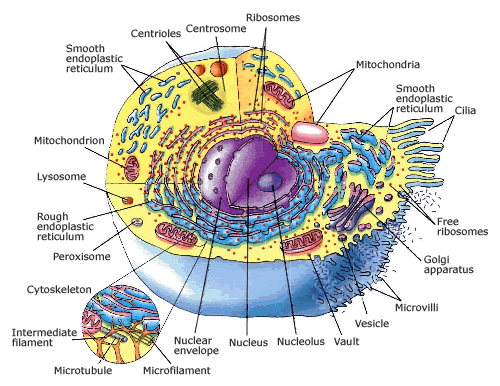
What is a eukaryotic cell?
Cell with a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles (DNA is bound within nucleus, contains organelles)
Prokaryotic cells are ________ (simpler and smaller / more complex and bigger) than eukaryotic cells.
simpler and smaller
Which cell came first: prokaryotic or eukaryotic?
Prokaryotic
eukaryotes can be ____ or ____
unicellular or multicellular
What is an organelle?
Membrane-bound structures that act like individual organs within a cell
What is a cytoplasm?
The area between the nucleus and cell membrane that is composed of water, protein, carbs, and salt
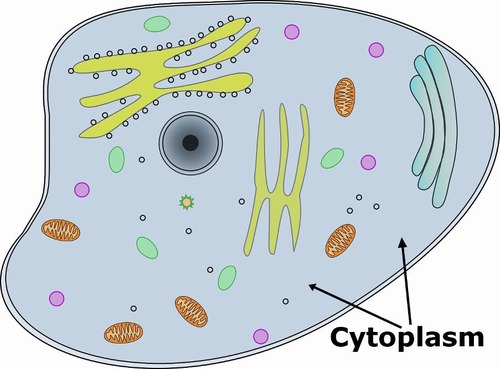
What is the function of the cytoplasm?
It is where most chemical reactions take place in the cell. It also acts as an insulation barrier.
What is the nucleus of a cell?
It is where the genetic information(DNA) is stored and is the cell's control center.
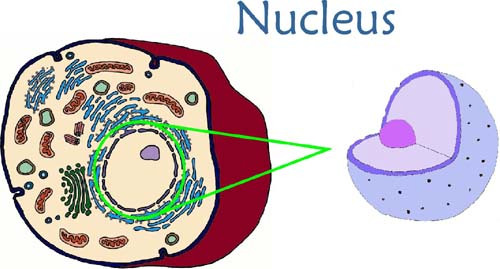
What is the funciton of the nucleus?
The nucleus stores genetic information(DNA) and regulates the activity of the cell. It also generates ribosomes.
What is the nucleolus?
It is the darker/dense center region of the nucleus where ribosomes are made
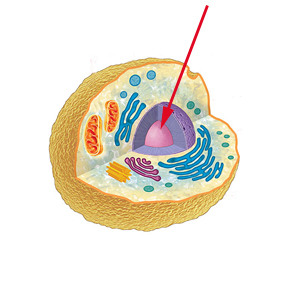
What is the function of the nucleolus?
It makes ribosomes
What is the nuclear envelope/membrane?
It is a double-membrane layer (double lipid layers) that surrounds the nucleus.
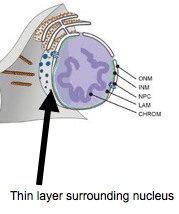
What is the function of the nuclear envelope/membrane?
It surrounds and protects the nucleus and allows for the passages of materials in an dout such as RNA and ribosomes.
What are ribosomes?
Small particles made of RNA and protein found inside the cytoplasm or attached to the rough ER
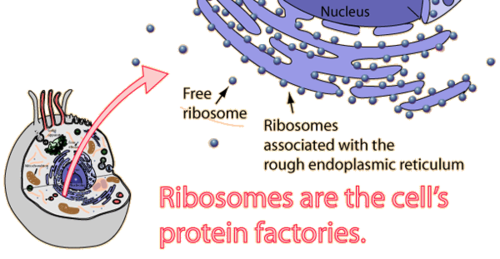
What are the functions of ribosomes?
Ribosomes produce proteins using information contained within DNA.
What are the 2 types of endoplasmic reticulums?
rough and smooth
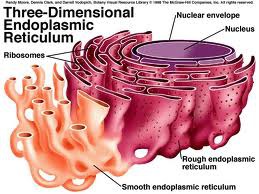
What is the rough endoplasmic reticulum (Rough ER)?
A highly folded organelle that is covered in ribosomes (rough)
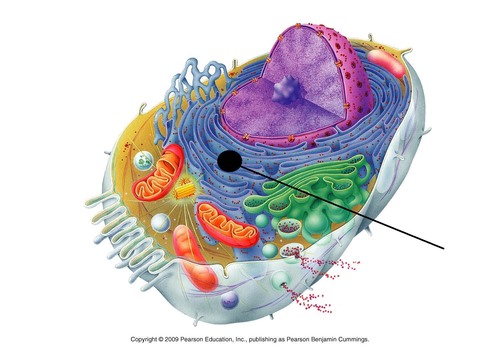
What is the function of the rough endoplasmic reticulum (Rough ER)?
It is a system of passageways that produces and transports proteins throughout the cell
What is the smooth endoplasmic reticulum (smooth ER)?
It is a coral-like organelle that doesn't have any ribosomes attached to it. It can either be attached to the rough ER or floating by itself in the cytoplasm.
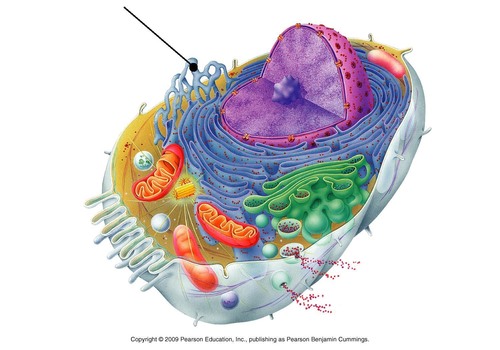
What is the function of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum (smooth ER)?
It is responsible for producing lipids and steroids/hormones. It is also responsible for the detoxification of drugs and other harmful metabolic byproducts.
What is the Golgi apparatus/body?
a complex of vesicles and folded membranes within the cytoplasm of most eukaryotic cells
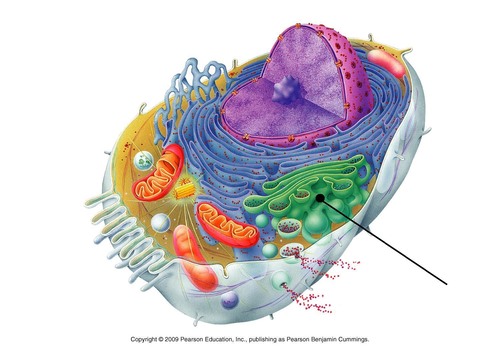
What is the function of the Golgi apparatus/body?
It modifies/packages proteins before they are secreted to the outside of the cell or used within the cell itself (puts the "finishing touches" on proteins)
What are lysosomes?
They are small organelles filled with digestive enzymes
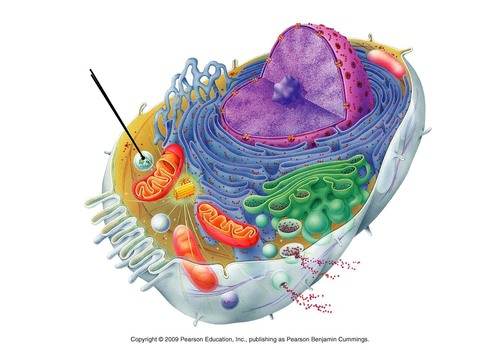
What are the functions of lysosomes?
They break down food molecules (lipids, carbs, proteins) that can be used by the cell. They also break down waste products.
What are peroxisomes?
They are specialized metabolic compartments bounded by a single lipid bilayer that contain enzymes similar to lysosomes
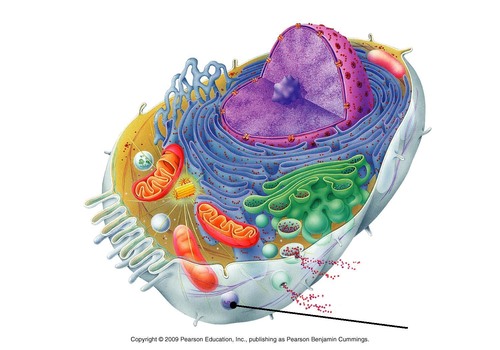
What are the functions of peroxisomes?
They break down toxic substances such as hydrogen peroxide and alcohol. They also aid in the production of fatty acids and proteins.
What are vacuoles?
Vacuoles are membrane-enclosed saclike structures that store materials such as water, salts, proteins, and carbohydrates.
What are the functions of vacuoles?
Vacuoles store materials like water, salts, proteins, and carbohydrates, which is very important in water storage for plants.
What is the mitochondria?
The "powerhouse of the cell" that is enclosed by 2 membranes (outer and inner). It is actually a bacterial cell we have formed a symbiotic relationship with (still has their own DNA and ribosomes).
What are the functions of the mitochondria?
It converts chemical energy stored in food (glucose) into ATP for the cell to use for energy.
What are chloroplasts?
Membrane-bound organelles found in plant cells only (also known as PLASTIDS) that contain certain pigments used in photosynthesis
What are the functions of chloroplasts?
They capture the light energy from the sun and convert it into glucose (photosynthesis)
What is a plastid?
any of a class of small organelles, such as chloroplasts, in the cytoplasm of plant cells, containing pigment or food.
What is the cell membrane?
A phospholipid bilayer that surrounds the cytoplasm
What is the function of the cell membrane?
The cell membrane serves as a protective boundary for a cell. It also controls what can enter and leave a cell.
What is the cell wall?
It is a rigid protective layer found outside the cell membrane in bacteria, plants, and fungi. It is composed of the polysaccharide cellulose.
What is the function of the cell wall?
It provides a protective layer to the cell and helps prevent cell stress due to the changing water pressure (gives it structure basically)
What is the cytoskeleton?
a network of fibers extending throughout the cytoplasm
What are the 3 major components of the cytoskeleton?
Microtubules, microfilaments, and intermediate filaments
What are microtubules?
Makes up flagella, cilia, and centrioles
What are microfilaments?
Twisted chains of actin (protein) that cause "contractual" movement in a cell
What are intermediate filaments?
anchor and hold the organelles in place
What are centrioles?
An organelle only found in animal cells that help cell division
What is the cilia?
Thin, hair-like microtubule structure that aids in cell or water movement
What is the flagella?
A large tail-like microtubule that enables some bacteria and eukaryotes to swim
Only plant cells have:
Cell walls and chloroplasts
Only animal cells have:
lysosomes (debated whether or not plant cells have them as well) and centrioles
What is the protein production process?
RNA to Ribosome (in rough ER or cytoplasmic)
The protein made by the Ribosome goes through rough ER and travels to Golgi Apparatus
Protein packaged by Golgi is released into a vesicle
Protein gets used within the cell or secreted through the cell membrane
True or False: Bacteria also have a cell wall like plant cells
True