psych unit 3: sensation and perception
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
sensation
the stimulation of sensory receptors, info sent to brain

perception
concious experience of the enviornment

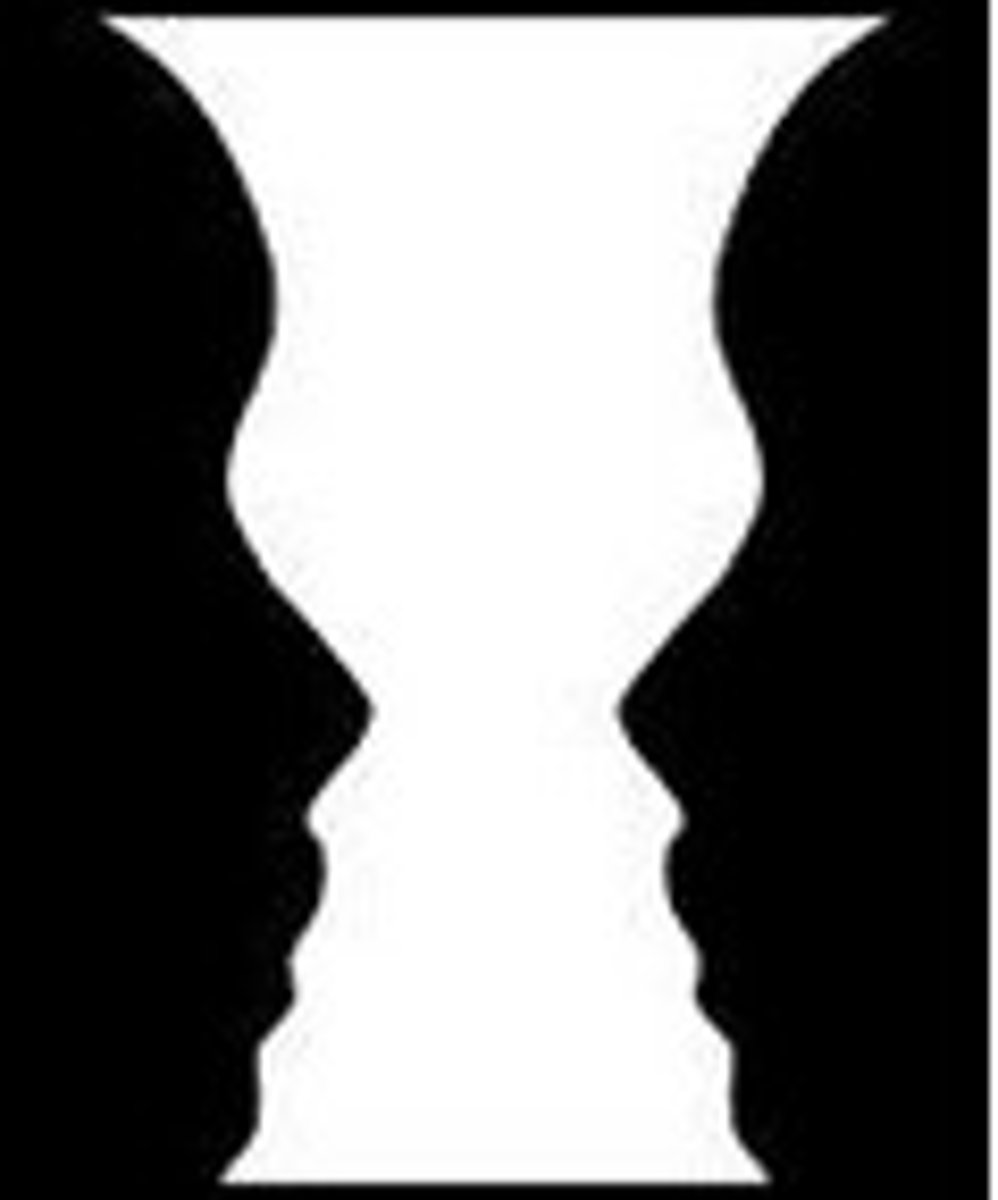
illusion
when sensation and perception DONT MATCH
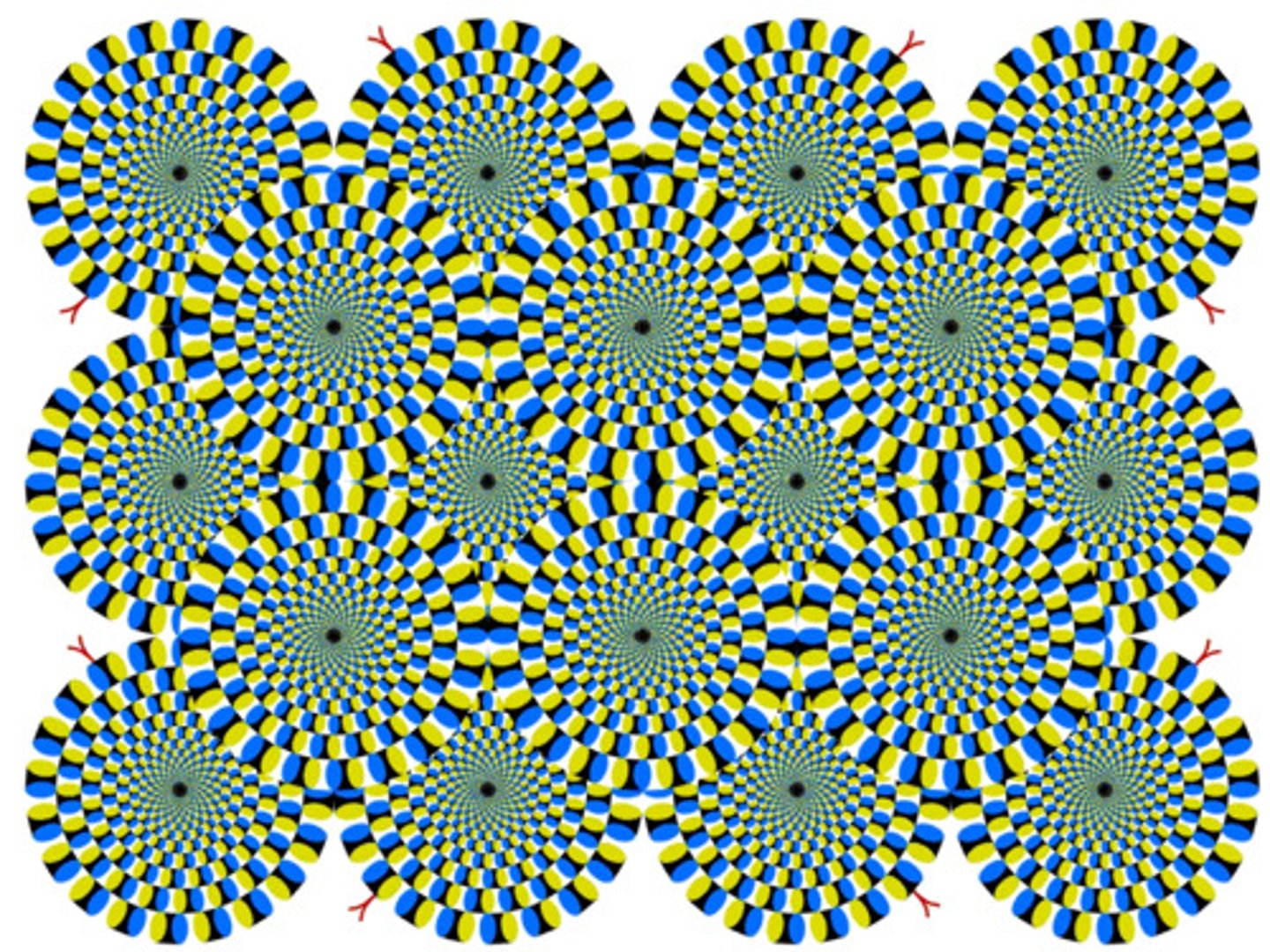
bottom-up processing
Processing that starts with information received by the receptors. This type of processing is also called data-based processing.
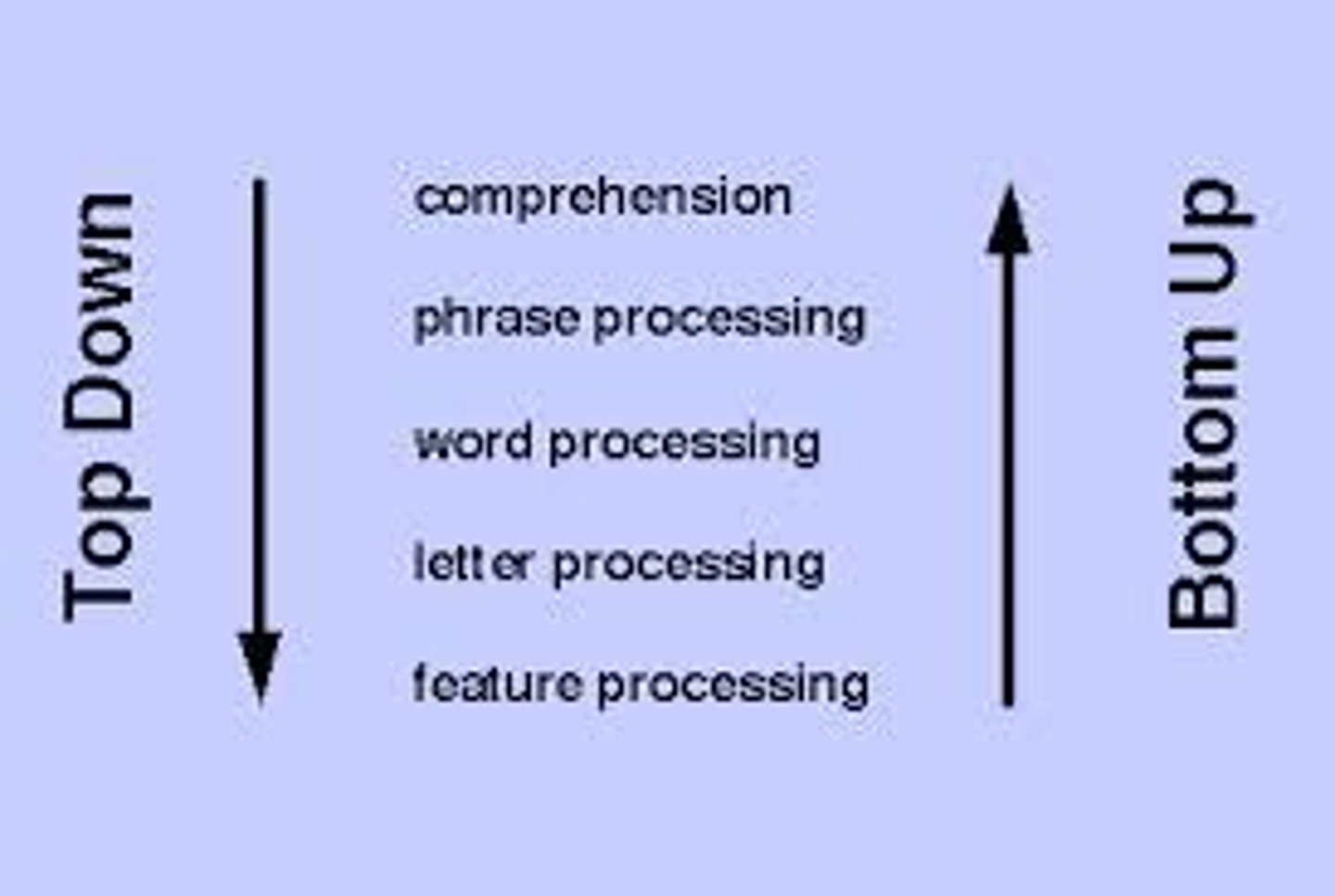
top-down processing
the use of preexisting knowledge to organize individual features into a unified whole
steps from sensation to perception
detect stimuli,transduction, send to brain to organize
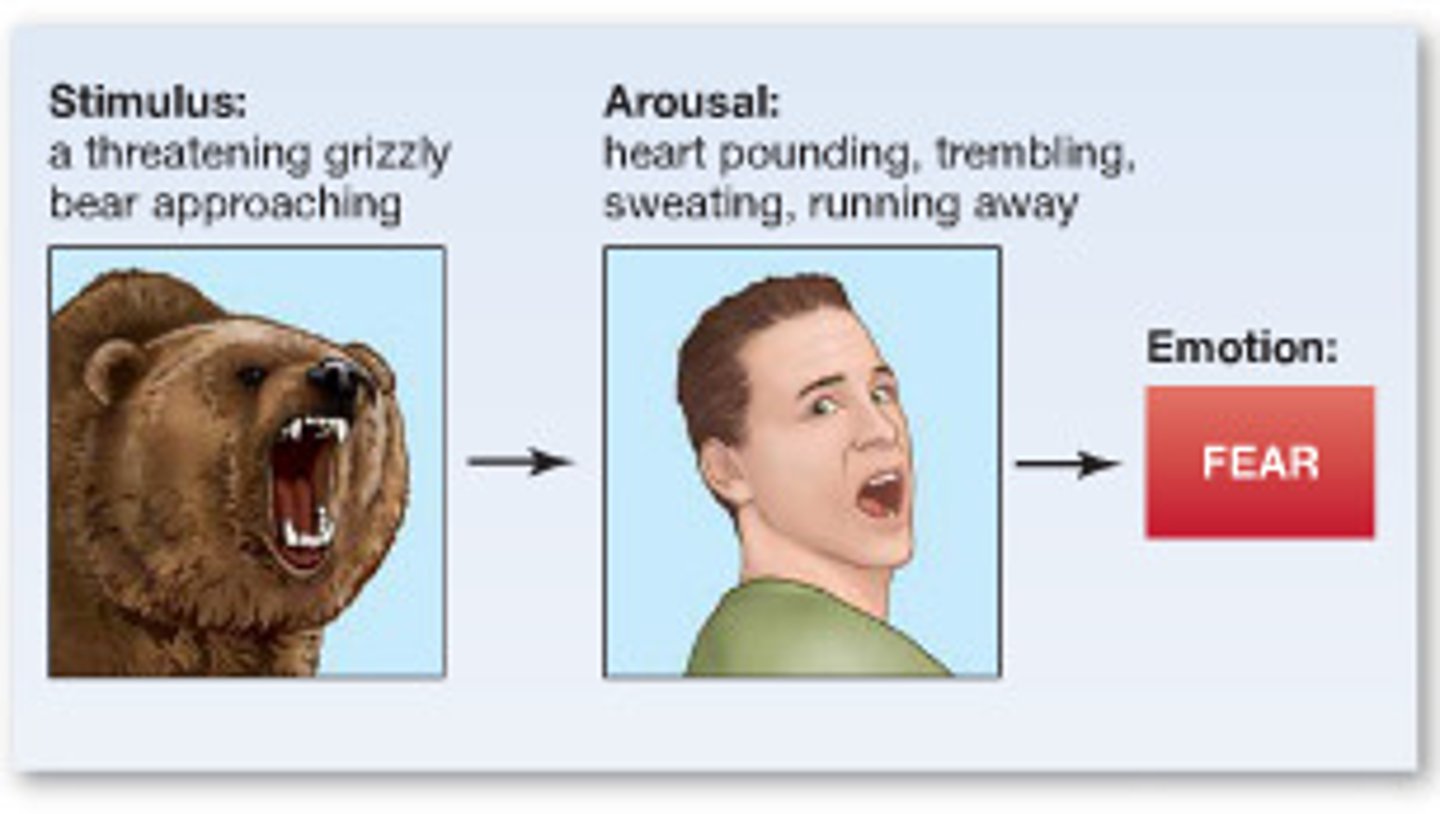
Transduction
transforming physical energy into neural impulses in receptors which can then be sent to the brain to be processed
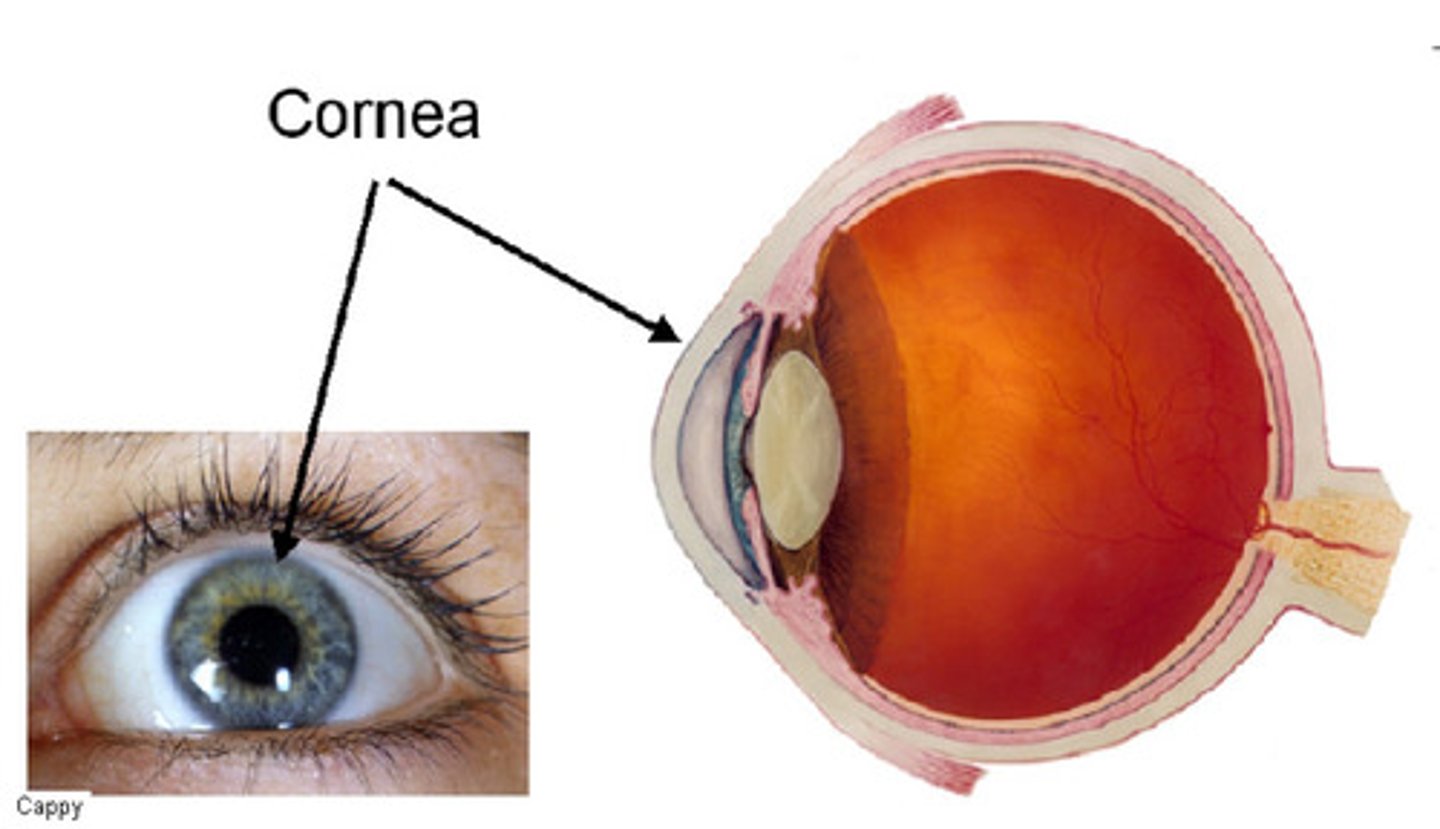
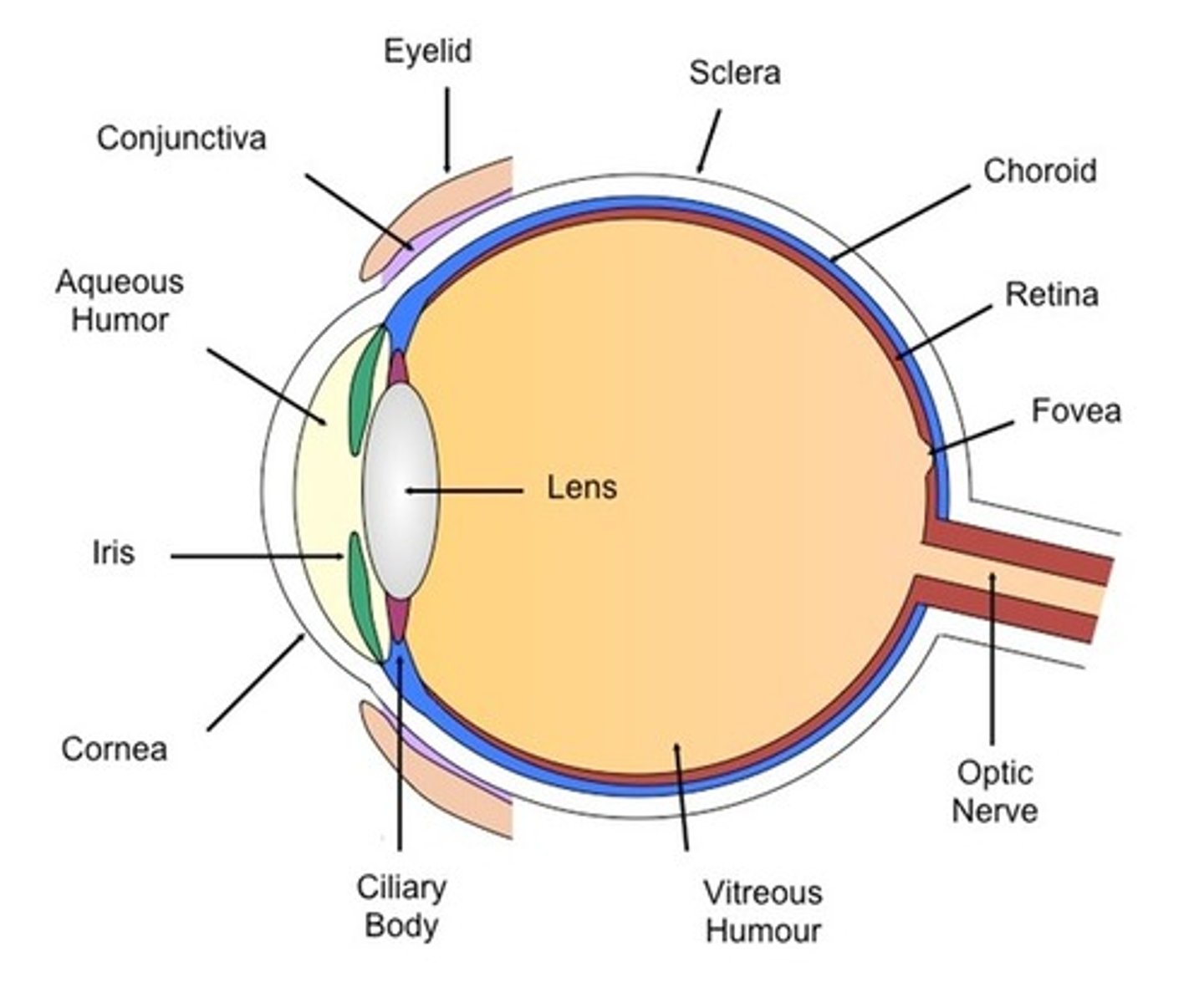
cornea
-the transparent outer covering of the eye
-protects you from dust and foreign objects
-80% of light is focused through the cornea
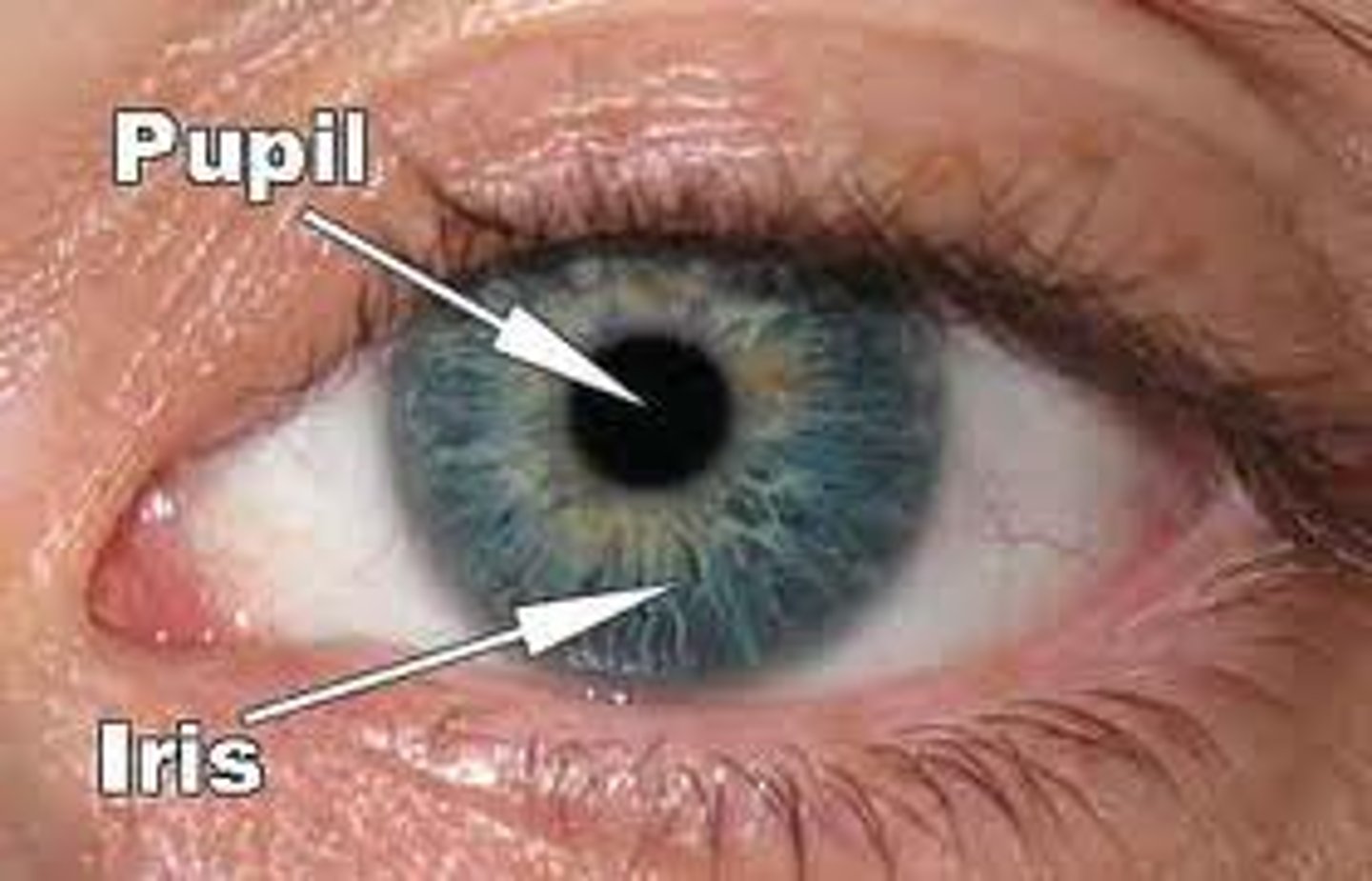
iris
colored muscle that changes shape to let light into the pupil.
Pupil isn't actaully changing shape, your iris is
lens
-focuses 20% of light
-changes shape depending on if you need to see close or far
accomodation
the process by which the eye's lens changes shape to focus near or far objects on the retina
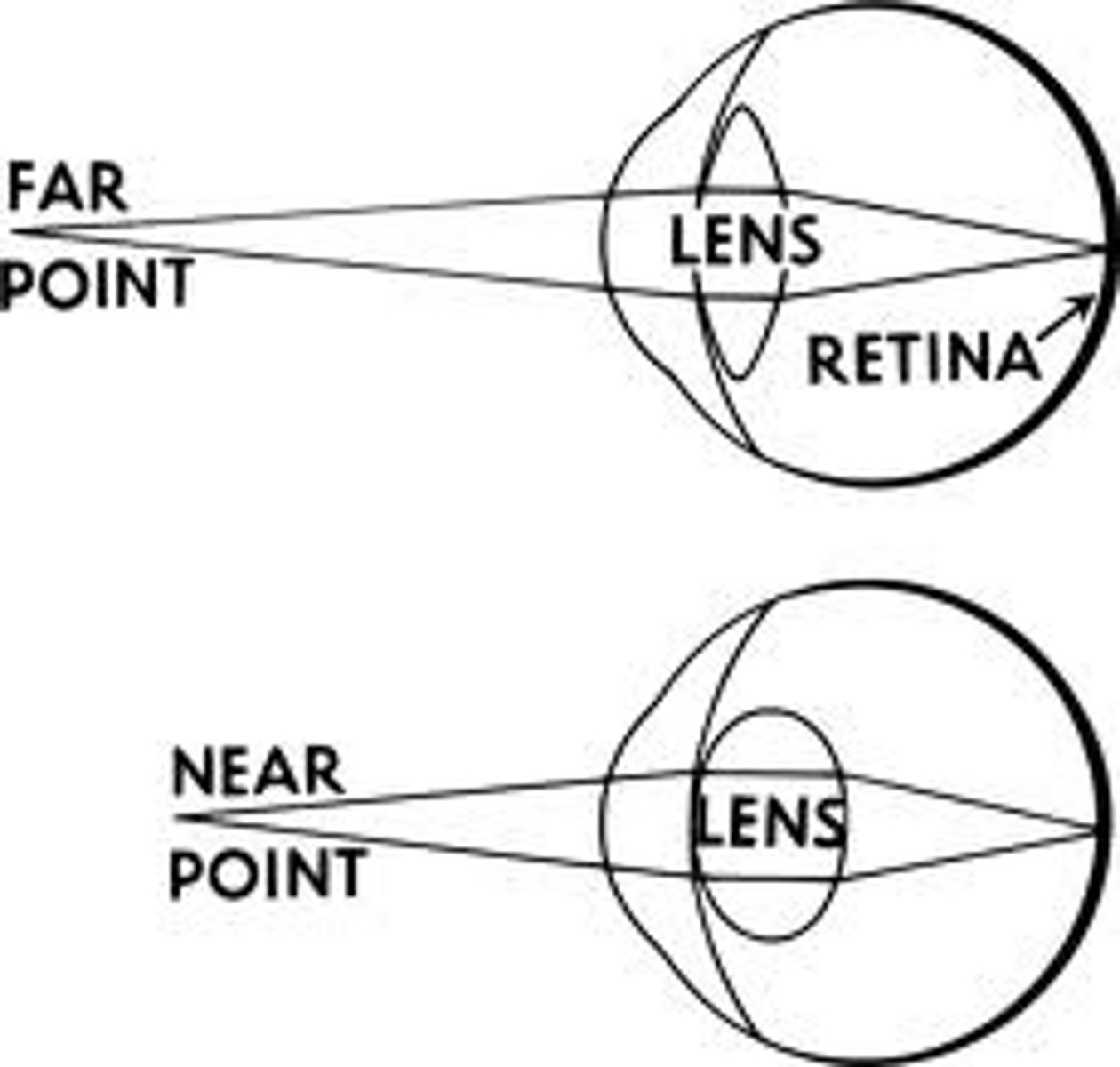
Presbyopia
the lens stifens over time, making it hard to see at different distances

fovea
the central focal point in the retina, around which the eye's cones cluster
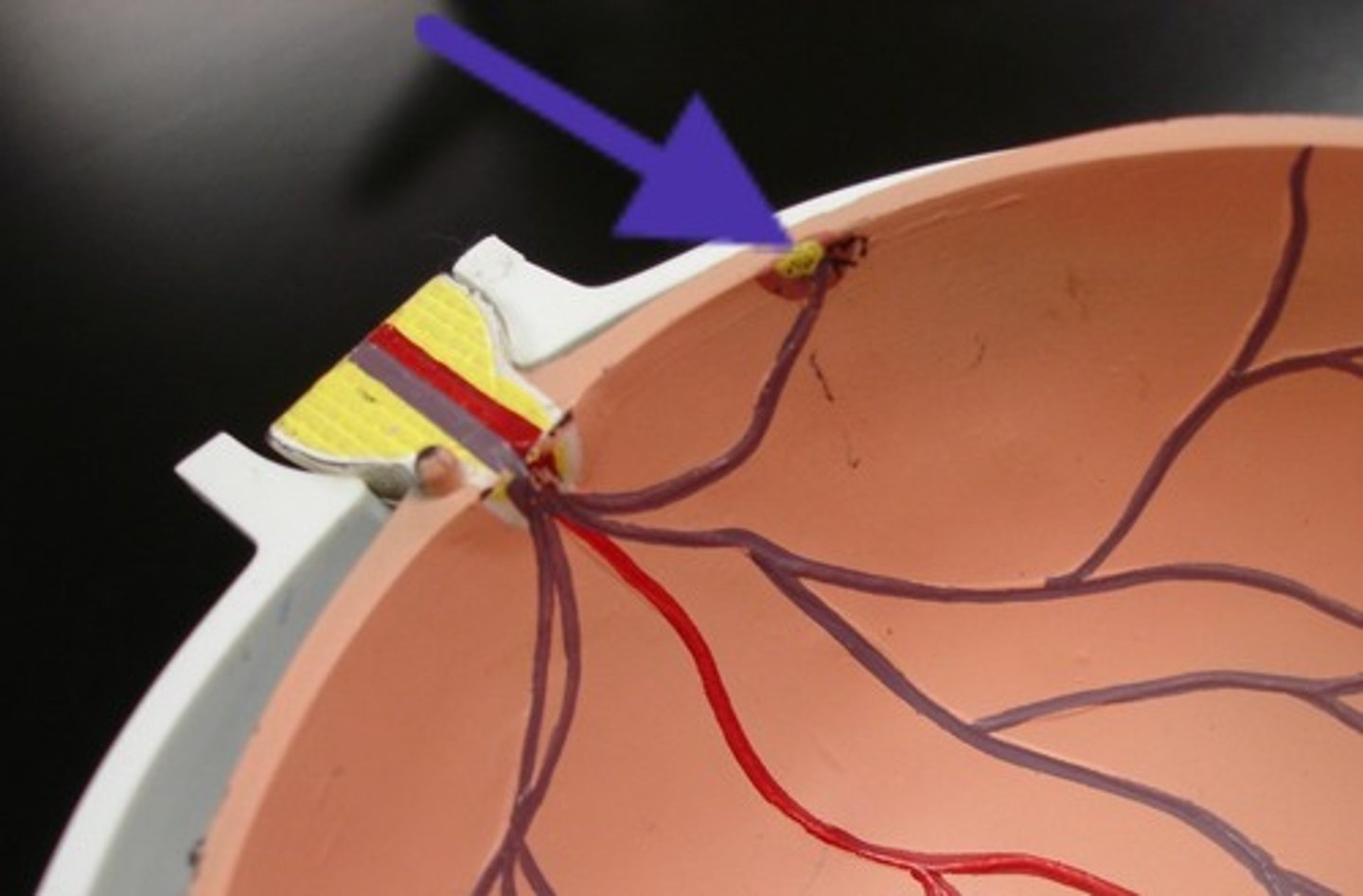
transduction in the eyes
1. first light goes past the rows of other cells to the rods and cones in the back
2. occurs in the rods and cones, where light waves become neural impulses
3. Neural impulse goes back through cells to ganglion cells
4. travels from ganglion to optic nerve, then to the visual cortex(in the occiptital lobe)
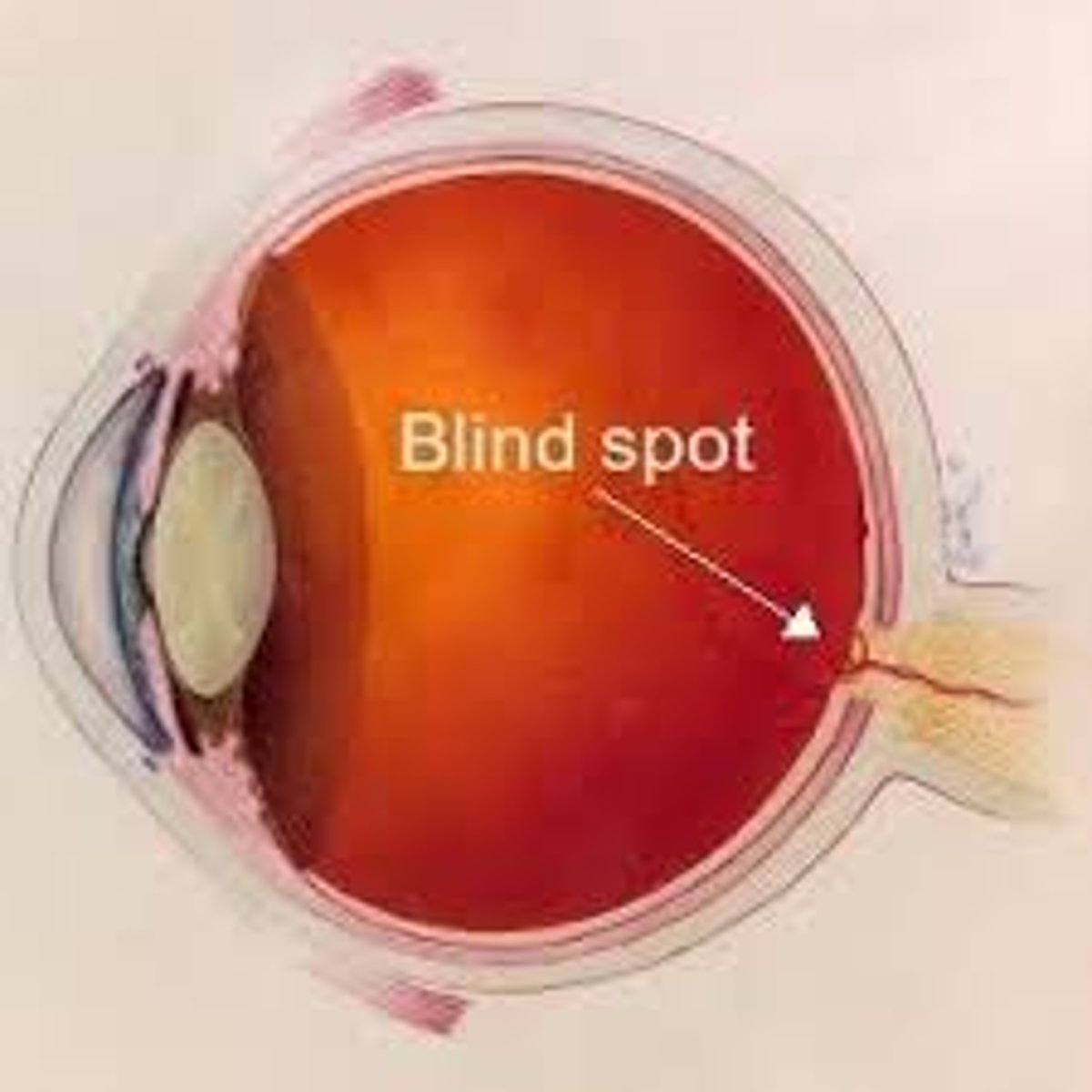
blind spot
the point at which the optic nerve leaves the eye, creating a "blind" spot because no receptor cells are located there
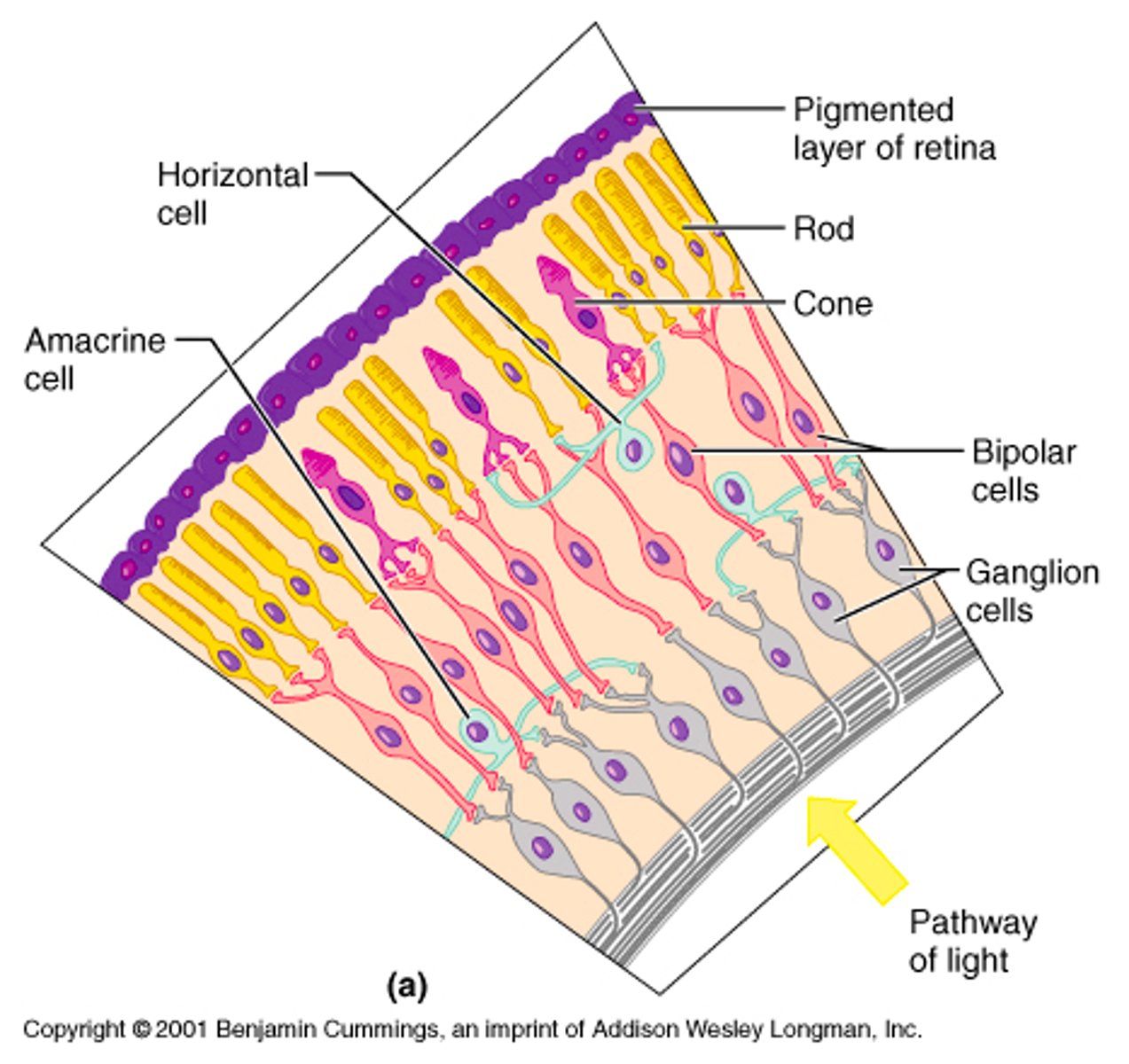
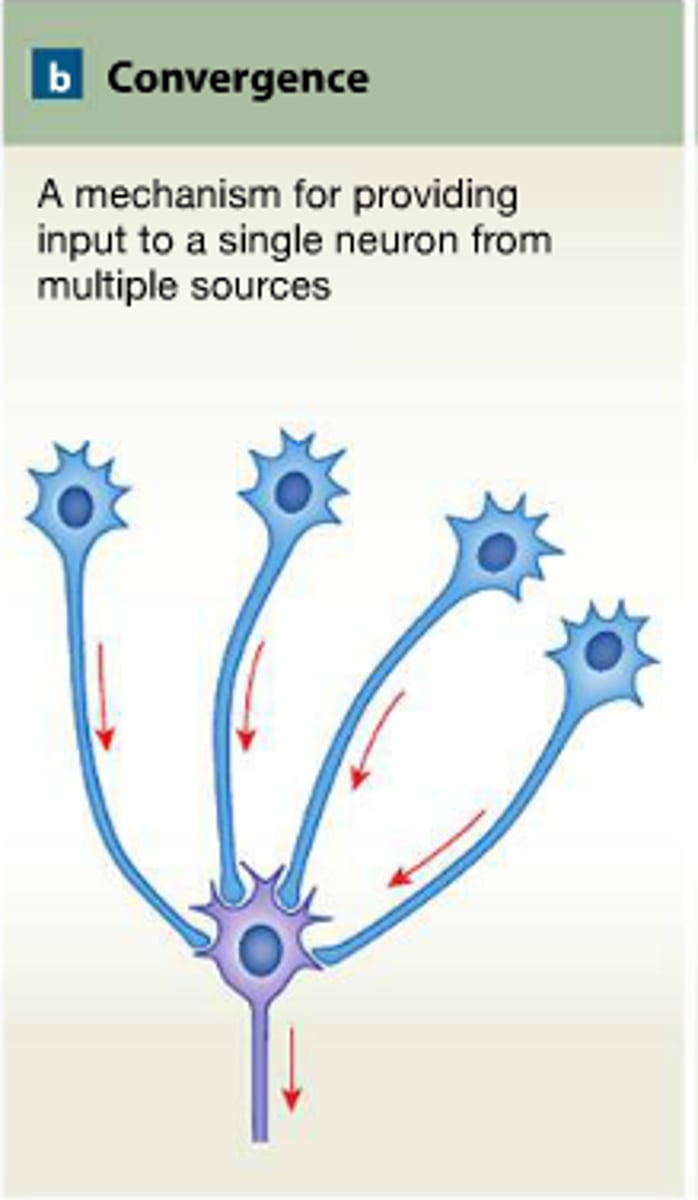
convergence
Several rods combine together and converge onto a gangleion cell.
Ex: if a ganglion cell needs 10 units to fire but its dim and the cones are only getting 3 units each, it won't fire. However, 2 units per rod combined will get a ganglion cell to fire
properties of cones
Color, visual acuity(better at seeing details), located in the fovea
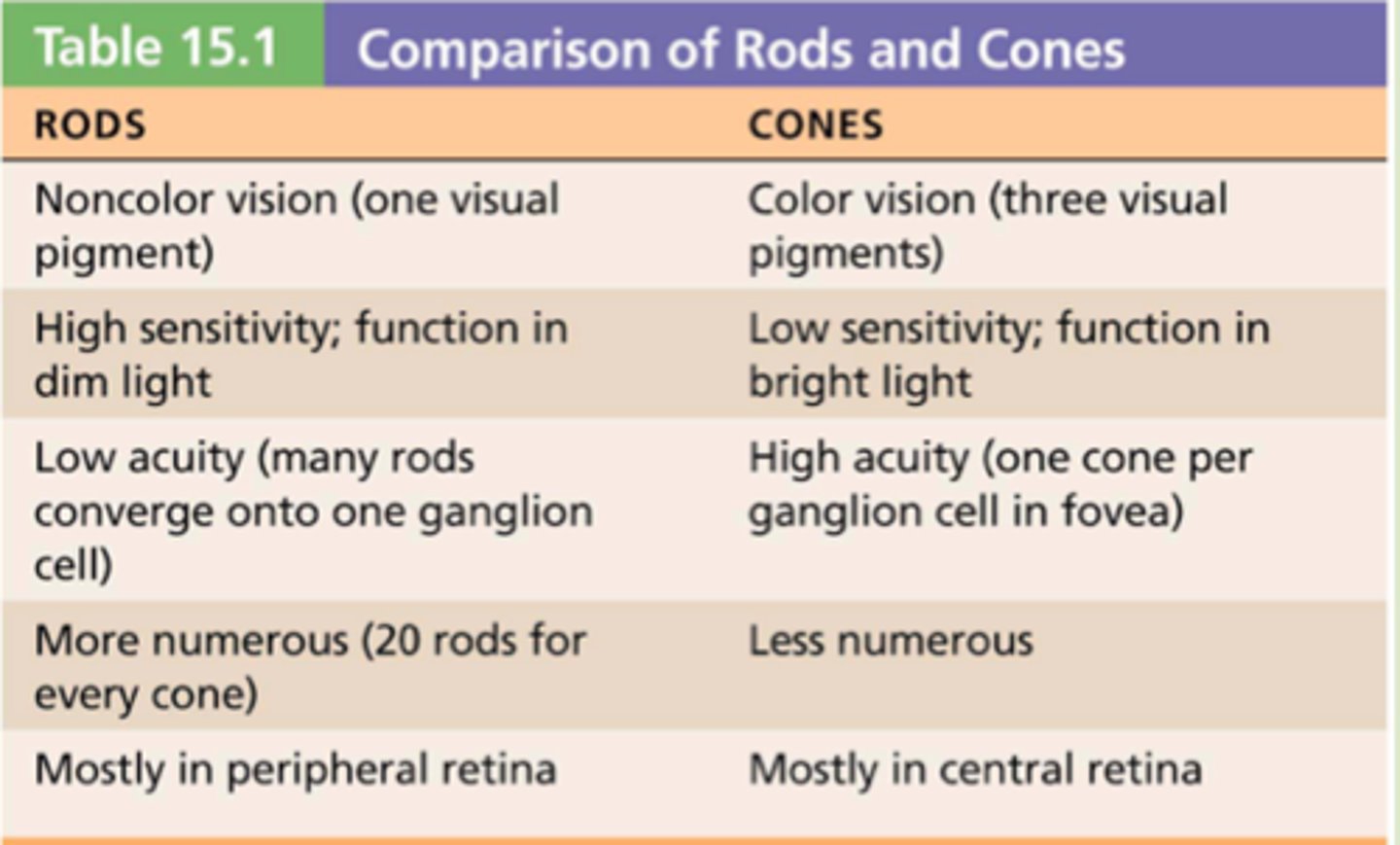
properties of rods
more sensitive to dim lighting, periphery
attention is:
the glue that binds things together
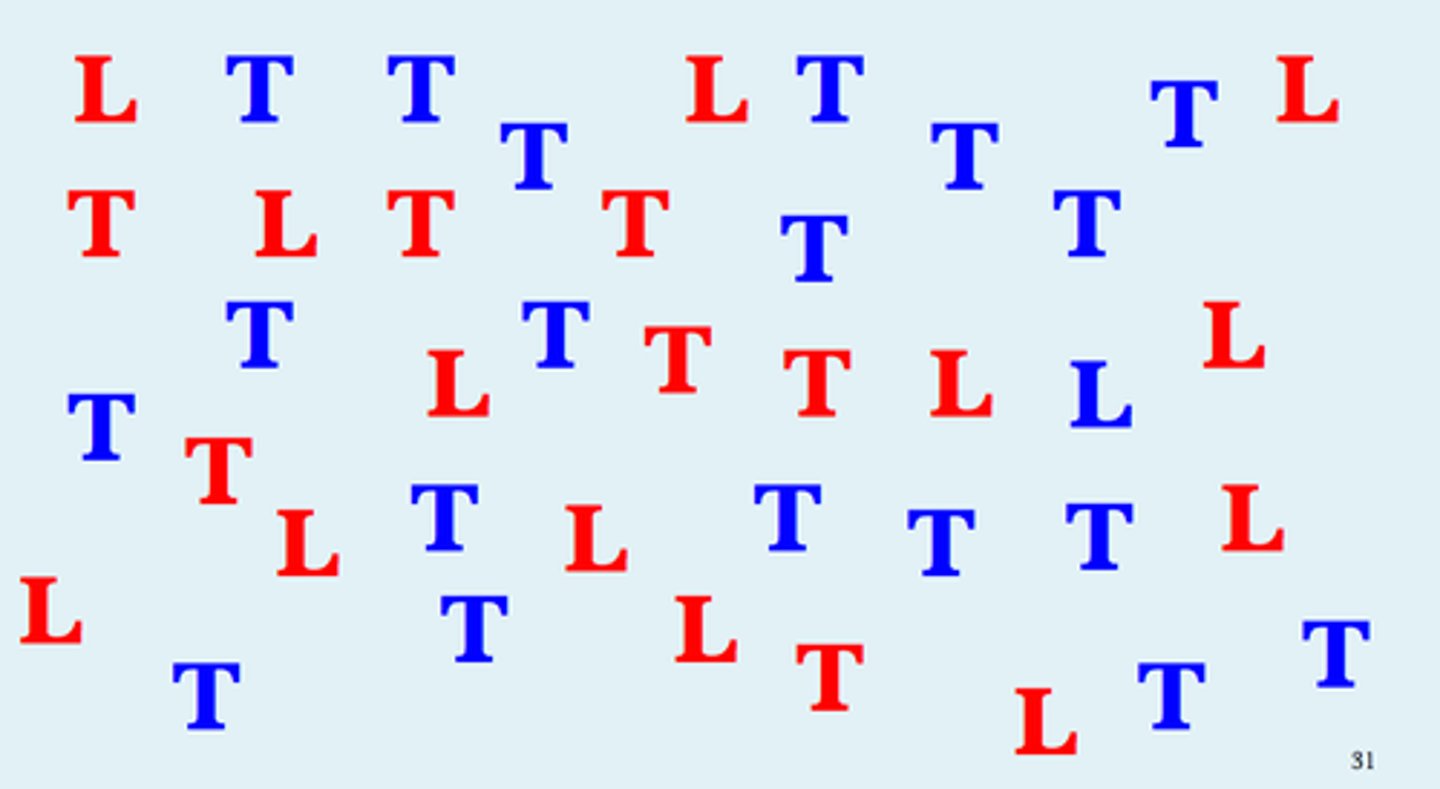
conjunction search
search for a target defined by the presence of two or more attributes
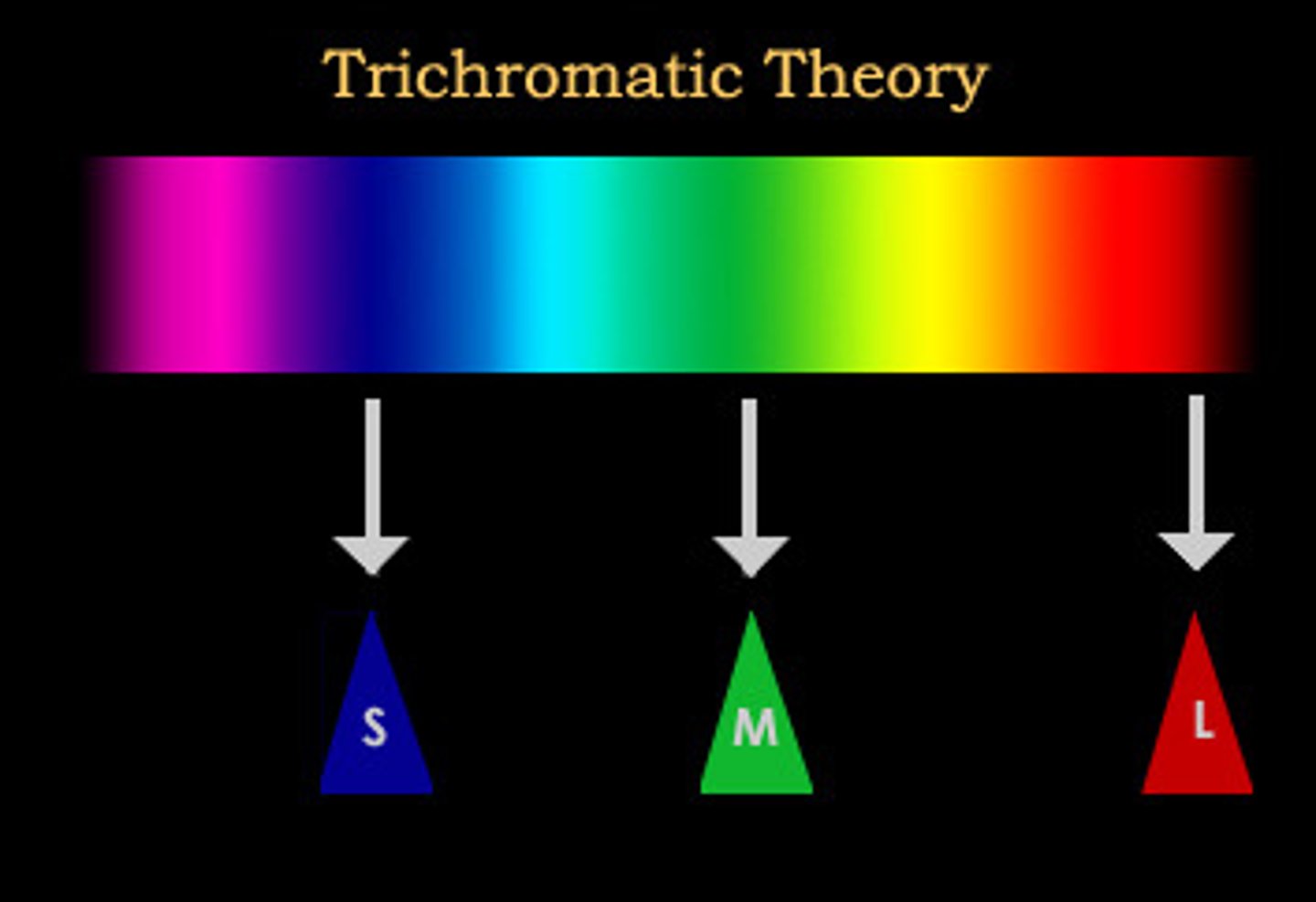
trichromatic theory
-3 cones sensitive to different wavelengths
-s cones fire for shorter wavelengths, l cones for longer
- if multiple cones are activated you will perceive the combo of their activation
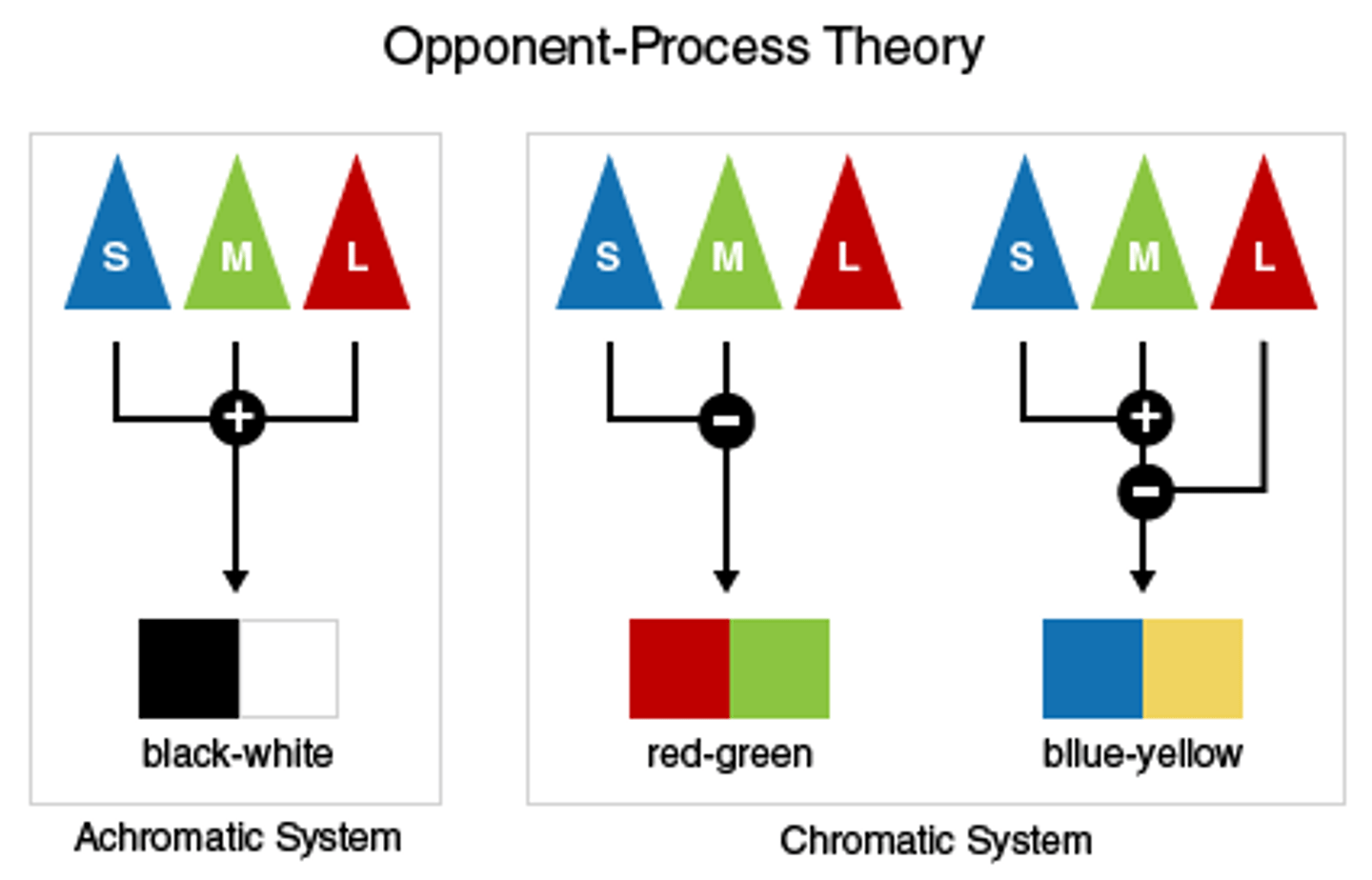
opponent process theory
in additon to our rods and cones, further in the visual cortex, we have opponent cells. If one is firing it negates the other.
ex: when yellow fires it inhibits the blue
after image
if we stare at a color to long and then at white. The cells of the color we just looked at get tired and we only see its complementary color

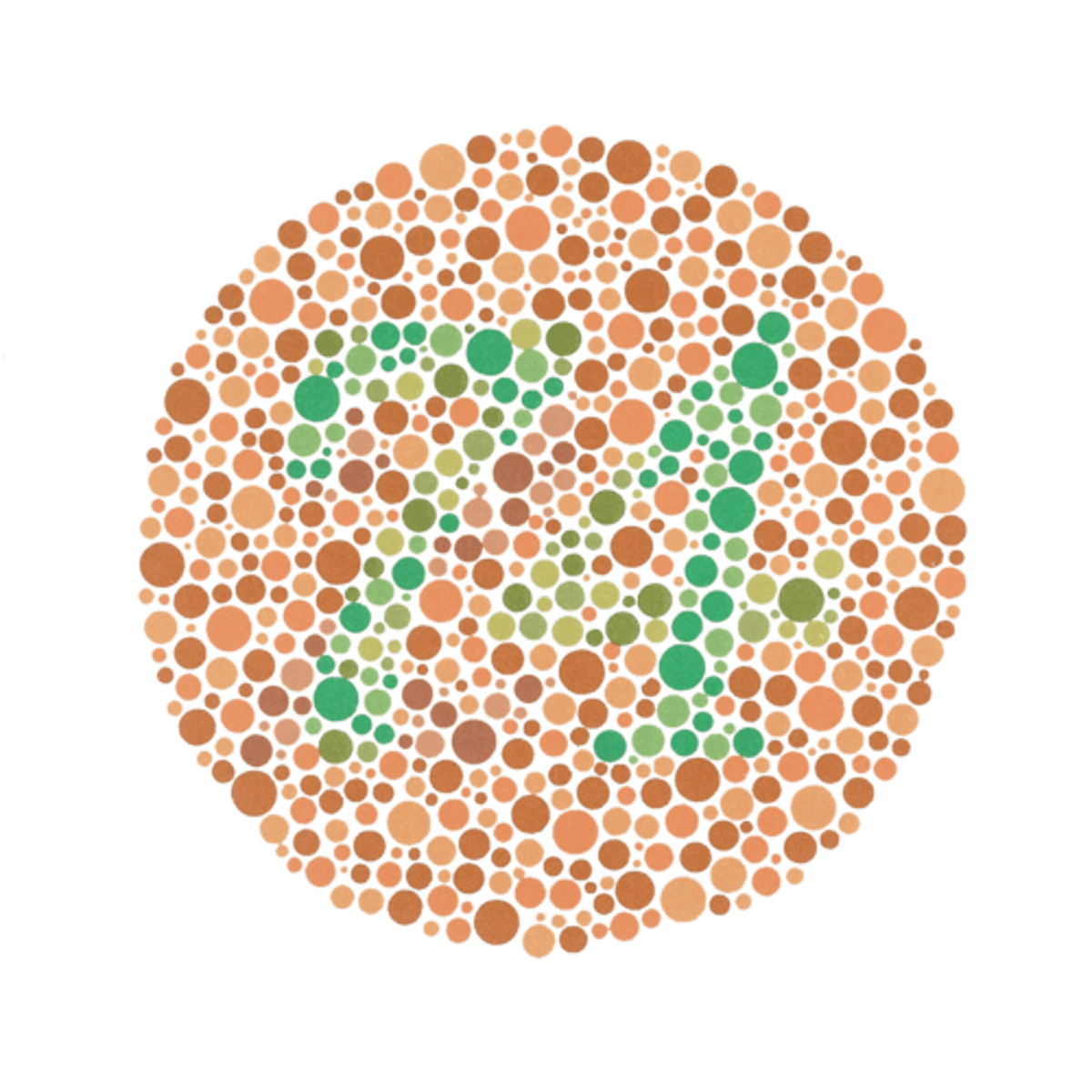
color blindness
trait found on x chromosome when you are missing the M cone or its not functioning properly
monocular cues
depth cues available to either eye alone
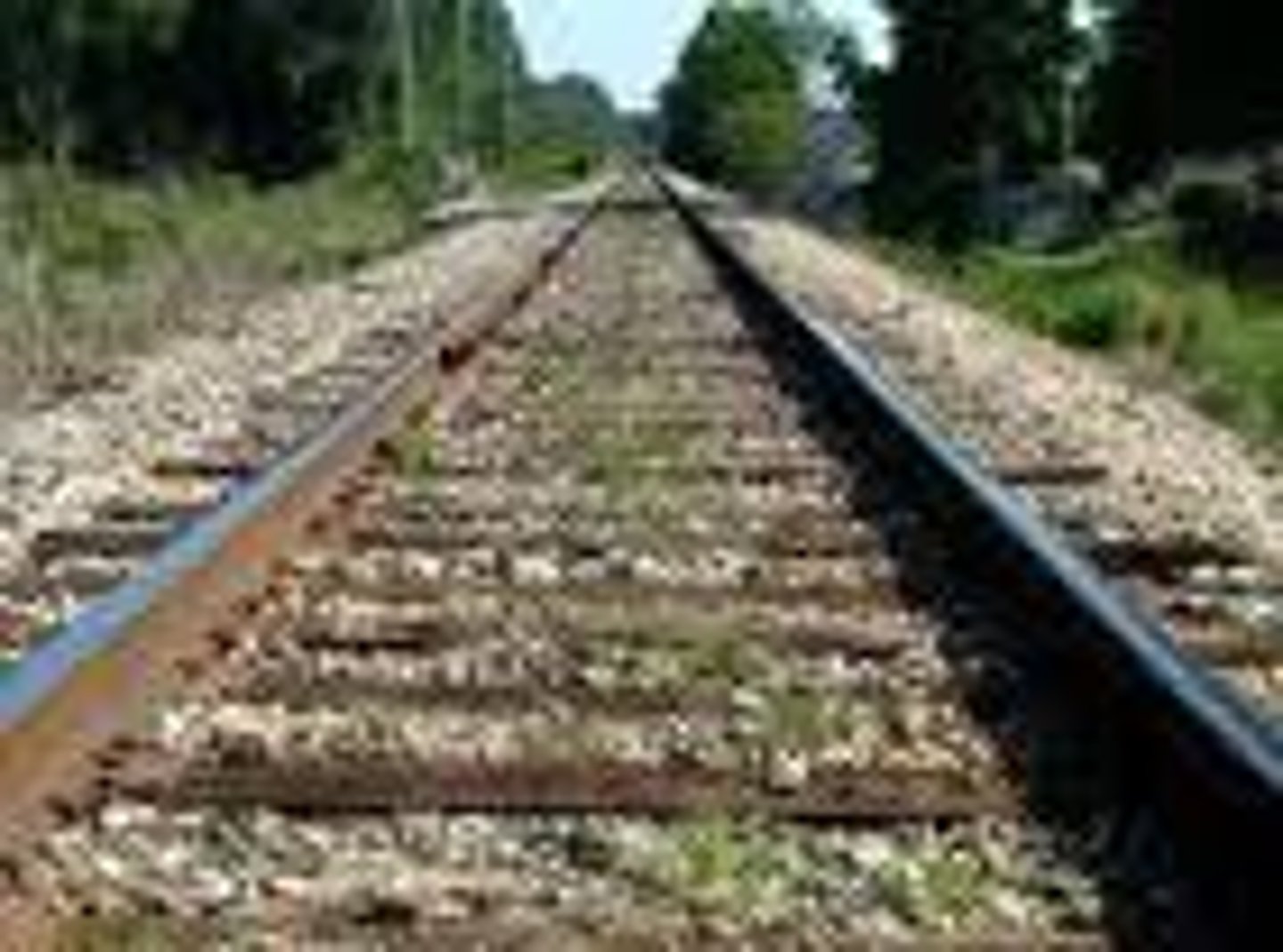

texture gradient
things appear more closely packed in the distance
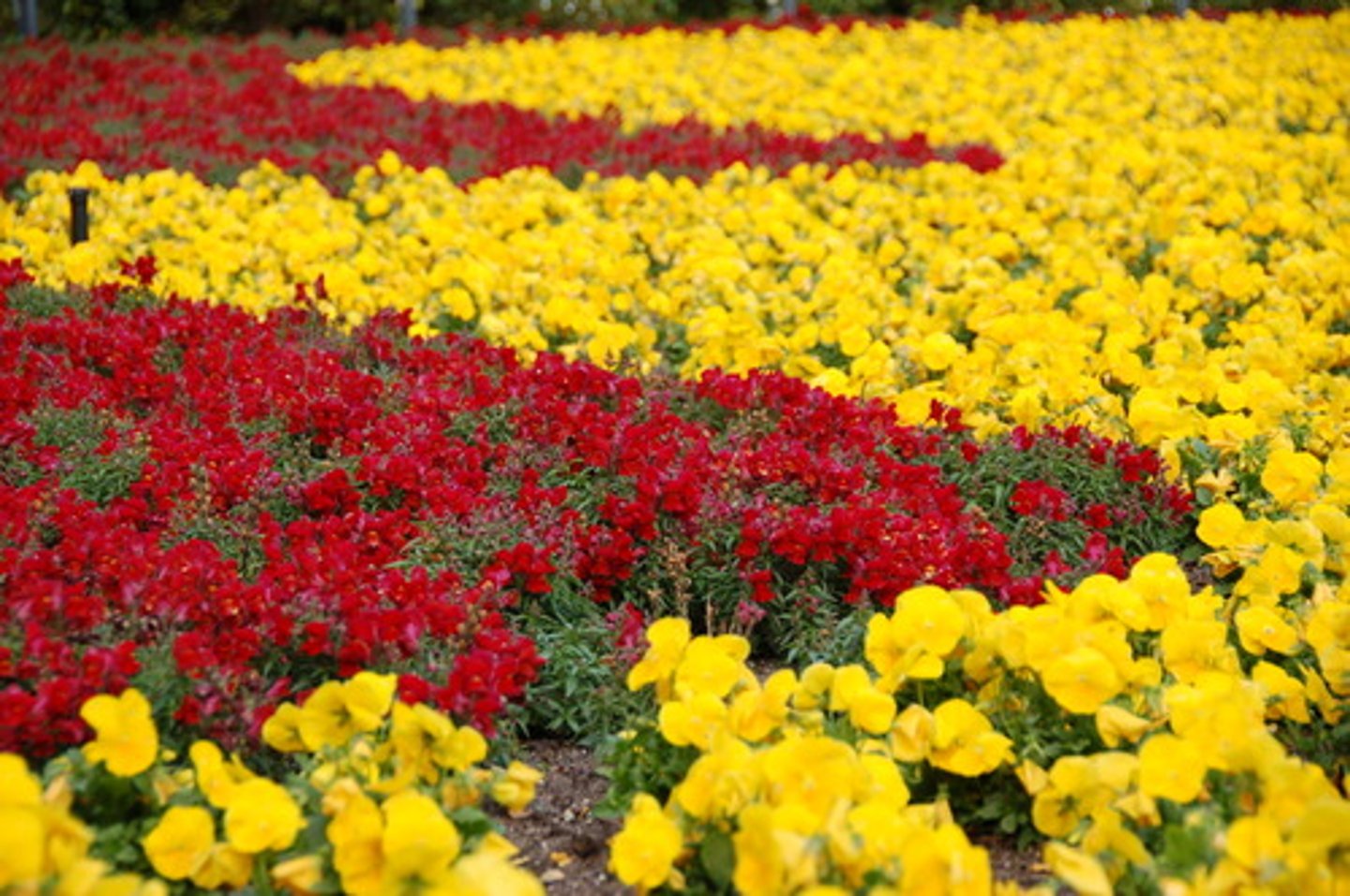

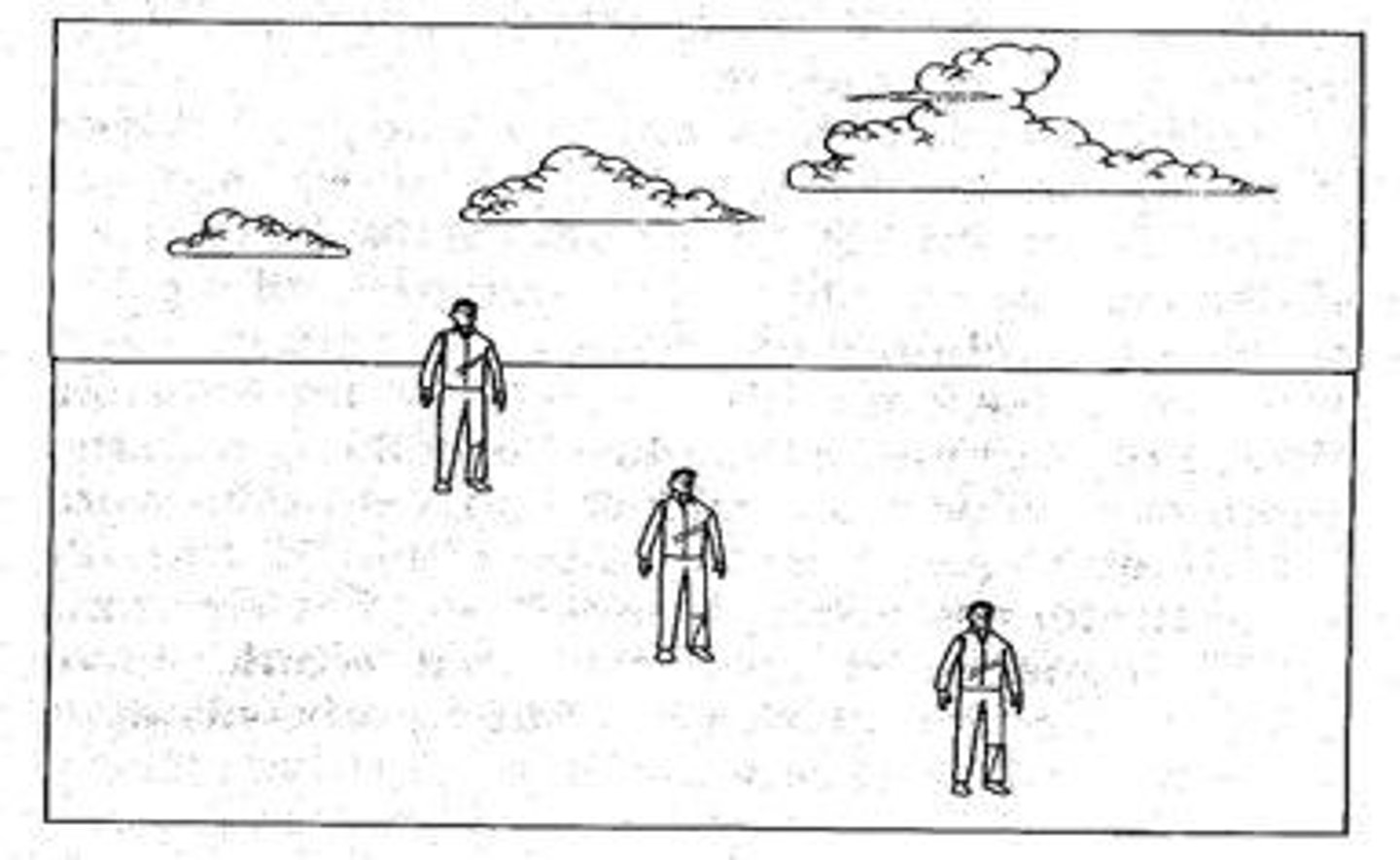
relative size
if something in a photo is bigger, it appears closer to you

relative height
if something is farther it appears closer to the horizan
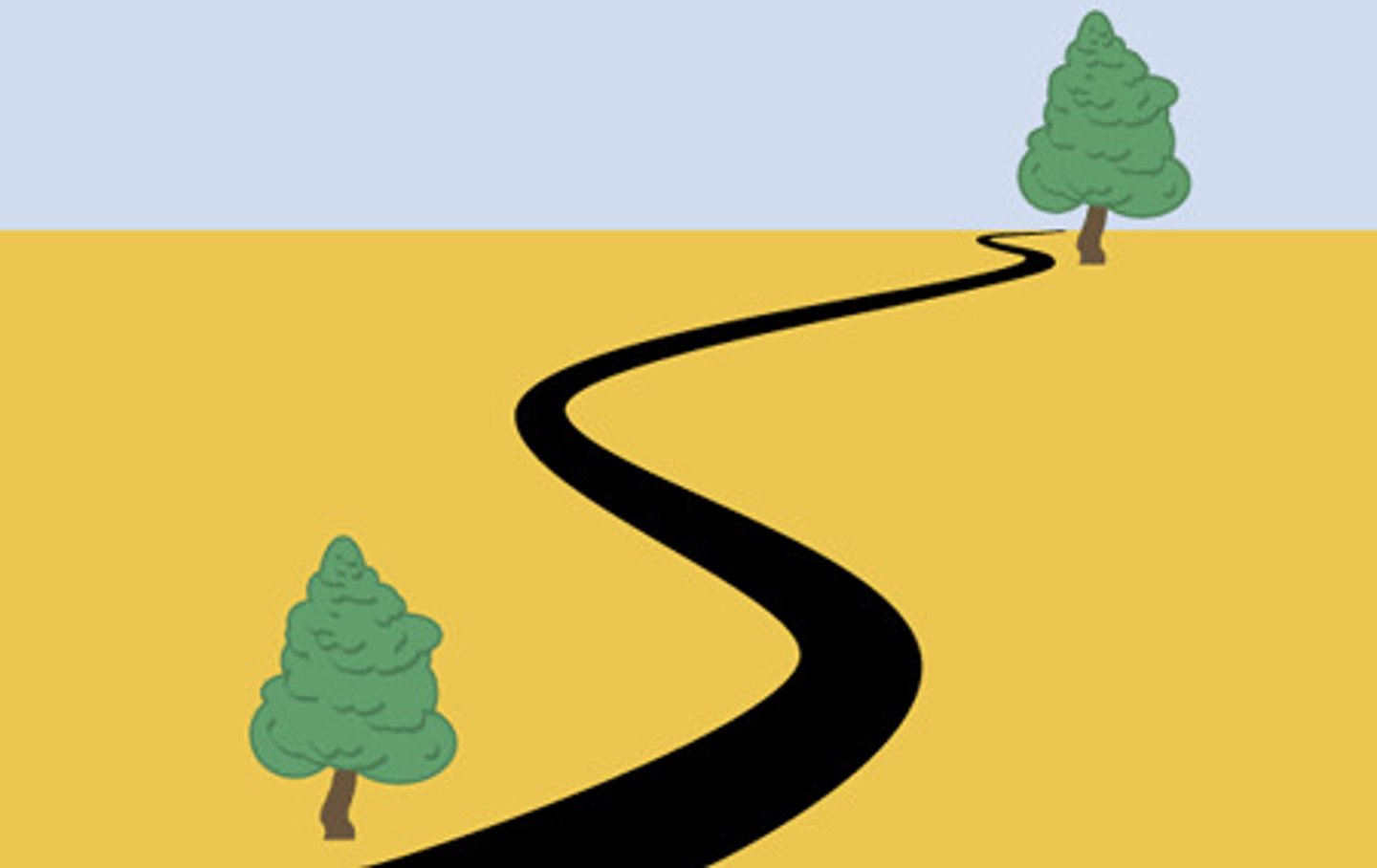

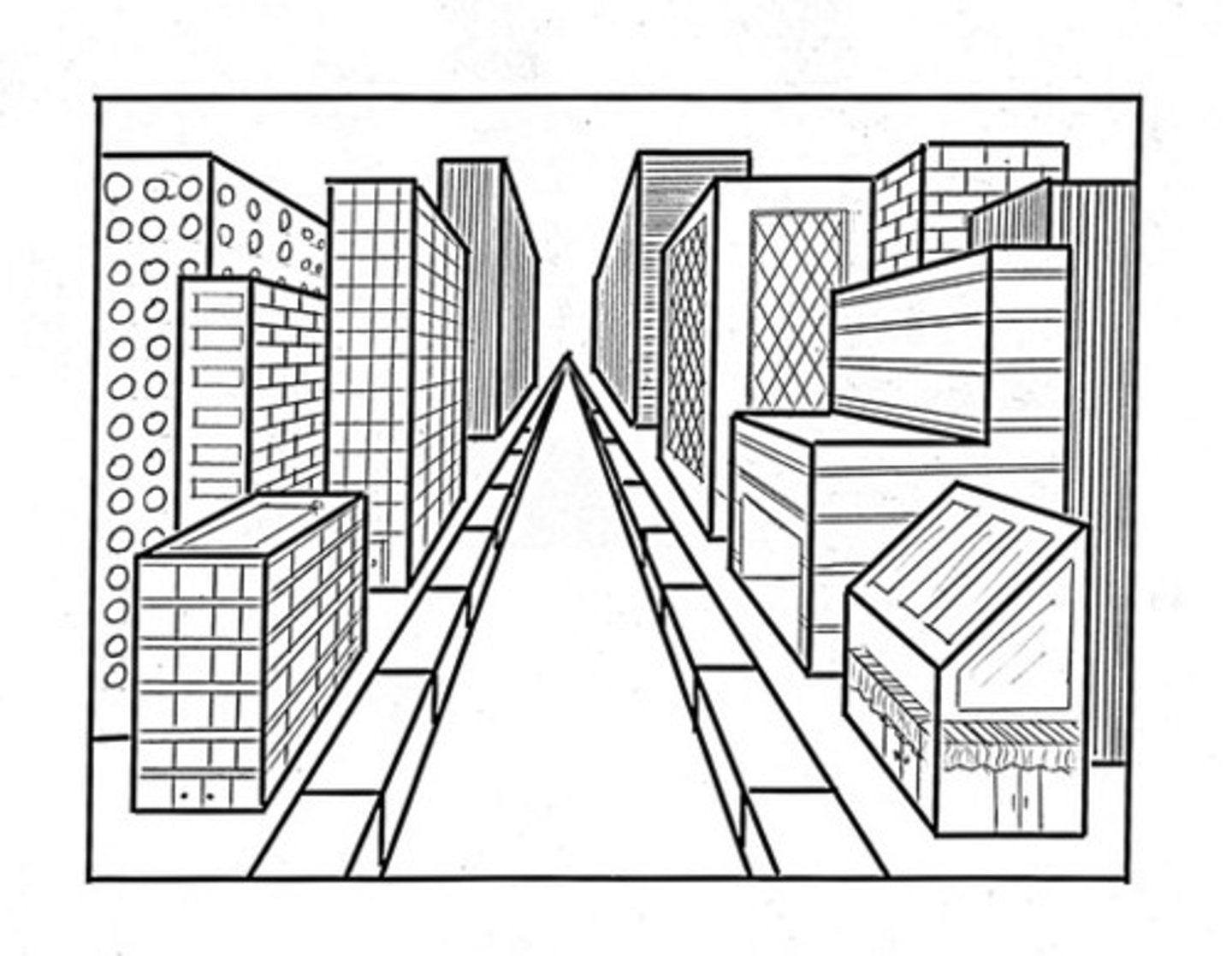
linear perspective
as parallel lines extend into the distance, they appear to meet together
occlusion
if an object is blocking something then it appears closer
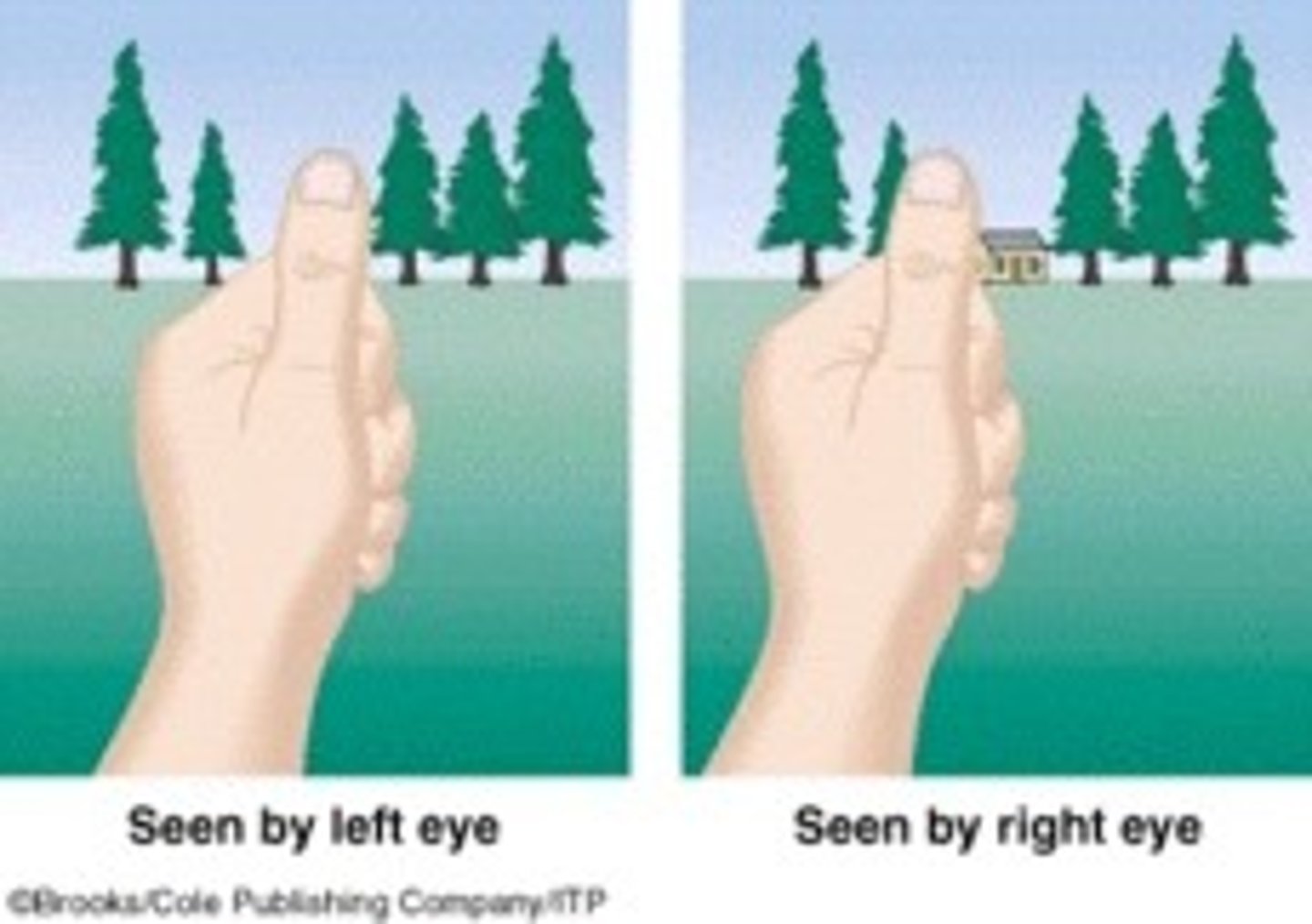
binocular cues
depth cues, such as retinal disparity,that depend on the use of two eyes
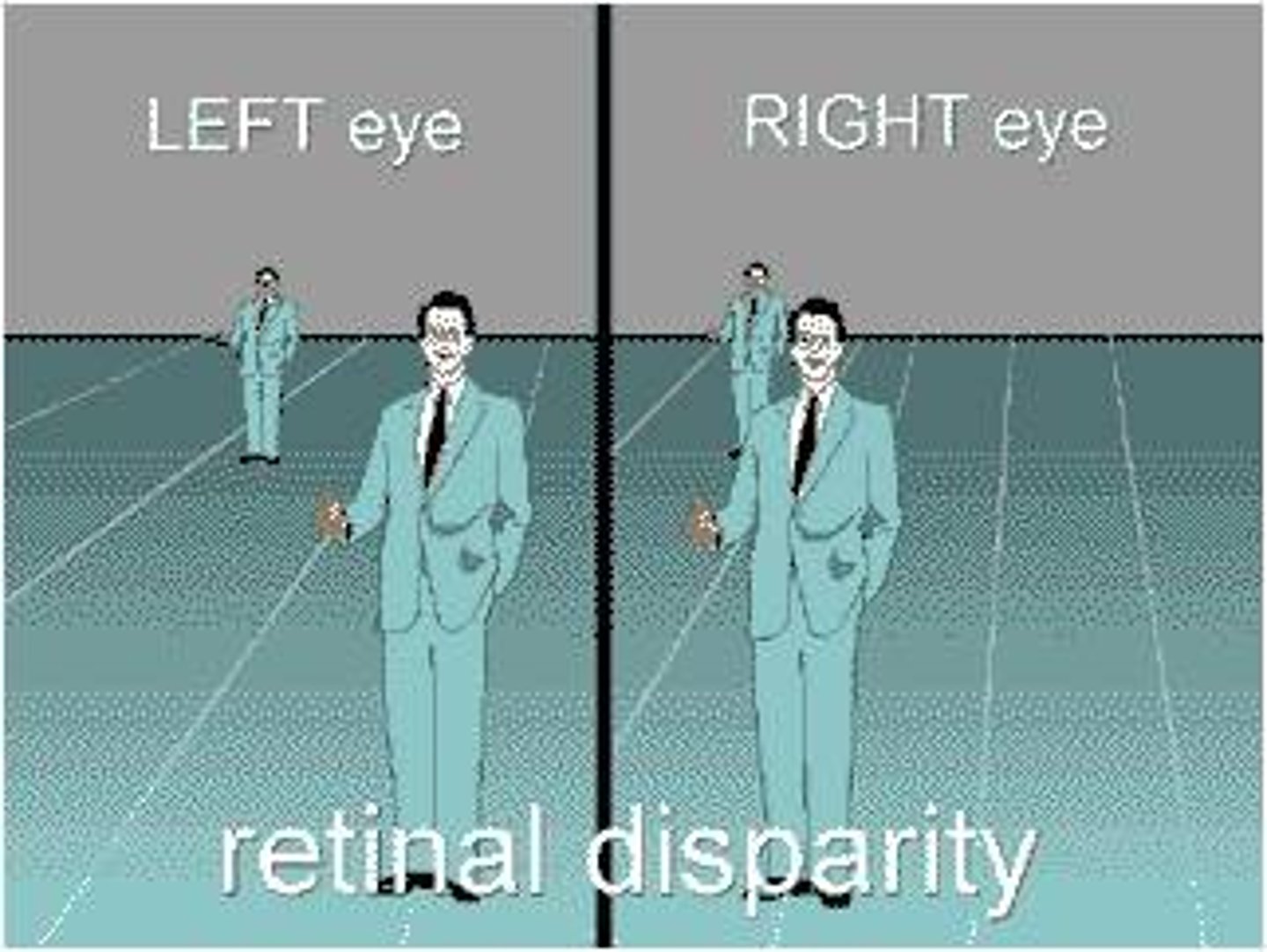
retinal disparity
a binocular cue for perceiving depth by comparing images from the retinas in the two eyes, the brain computes distance—the greater the disparity (difference) between the two images, the closer the object.
structuralists
believe you cannot perceive something that isn't there because perception arises from sensation
Gestalt Psychology
disagrees with structuralists because they believe in an organized whole. Gestalt psychologists emphasized our tendency to integrate pieces of information into meaningful wholes.

max berheimer
one of the first gestalt psychologists who discovered phi movement: the illusion that lights that are actually stationary seem to be moving
Gestalt Principles
Describe the top-down processing that organizes sensory information into distinct forms.
continuity,closure,simmilarity,proximity,figure, common fate
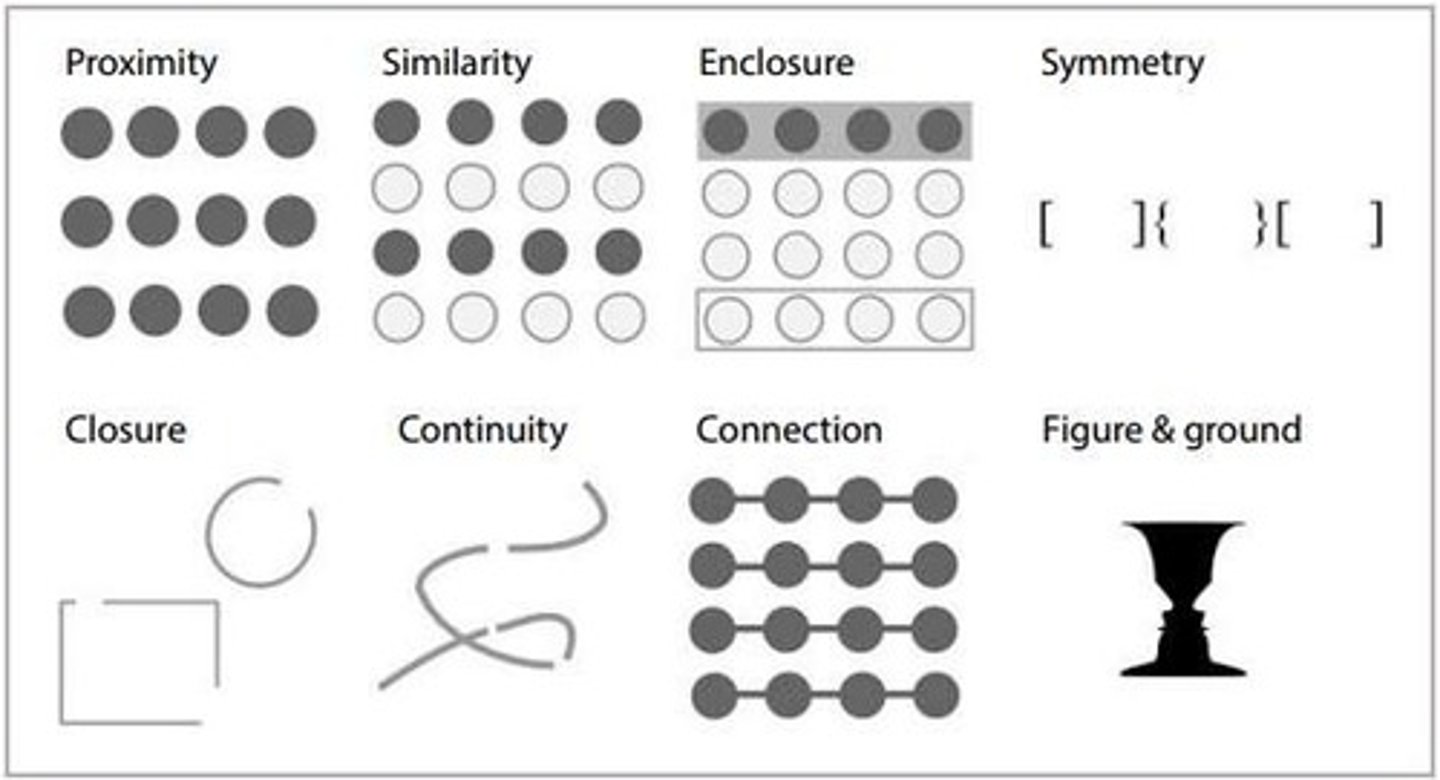
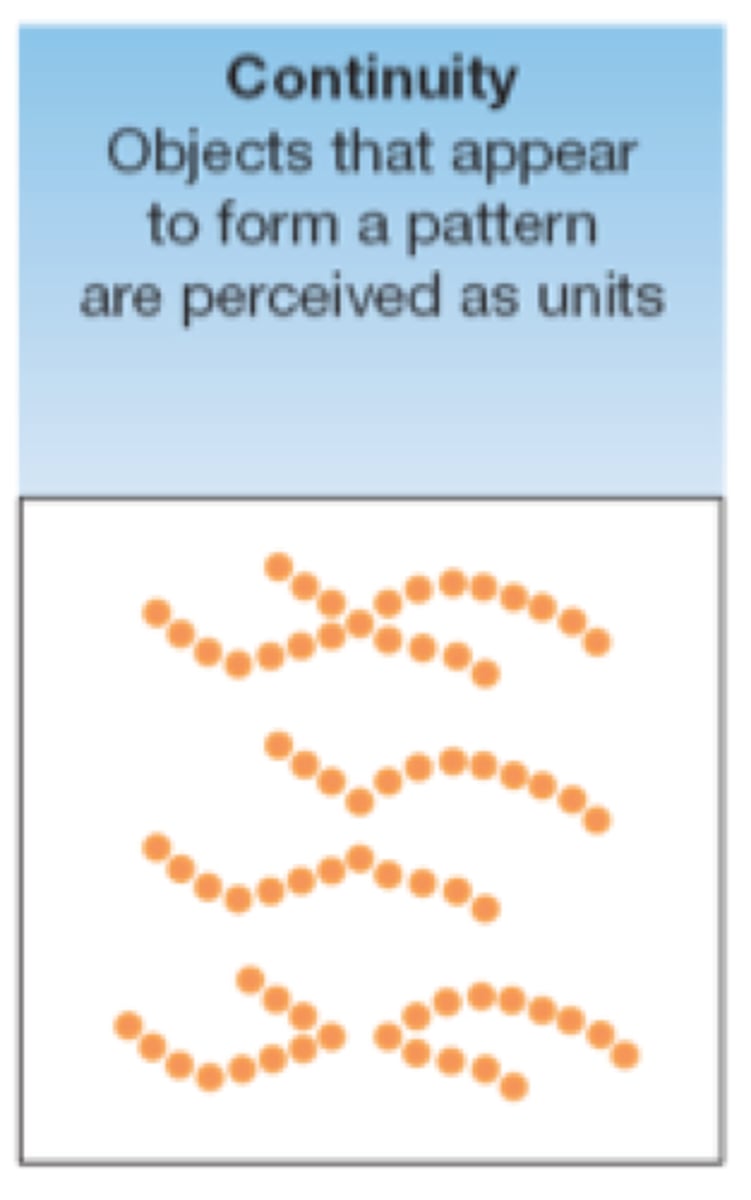
continuity
we perceive smooth, continuous patterns rather than discontinuous ones
Closure
the tendency to complete figures that are incomplete

similarity
the tendency to perceive things that look similar to each other as being part of the same group
proximity
more likely to group things that are closer together

figure
the perception of figures against a background
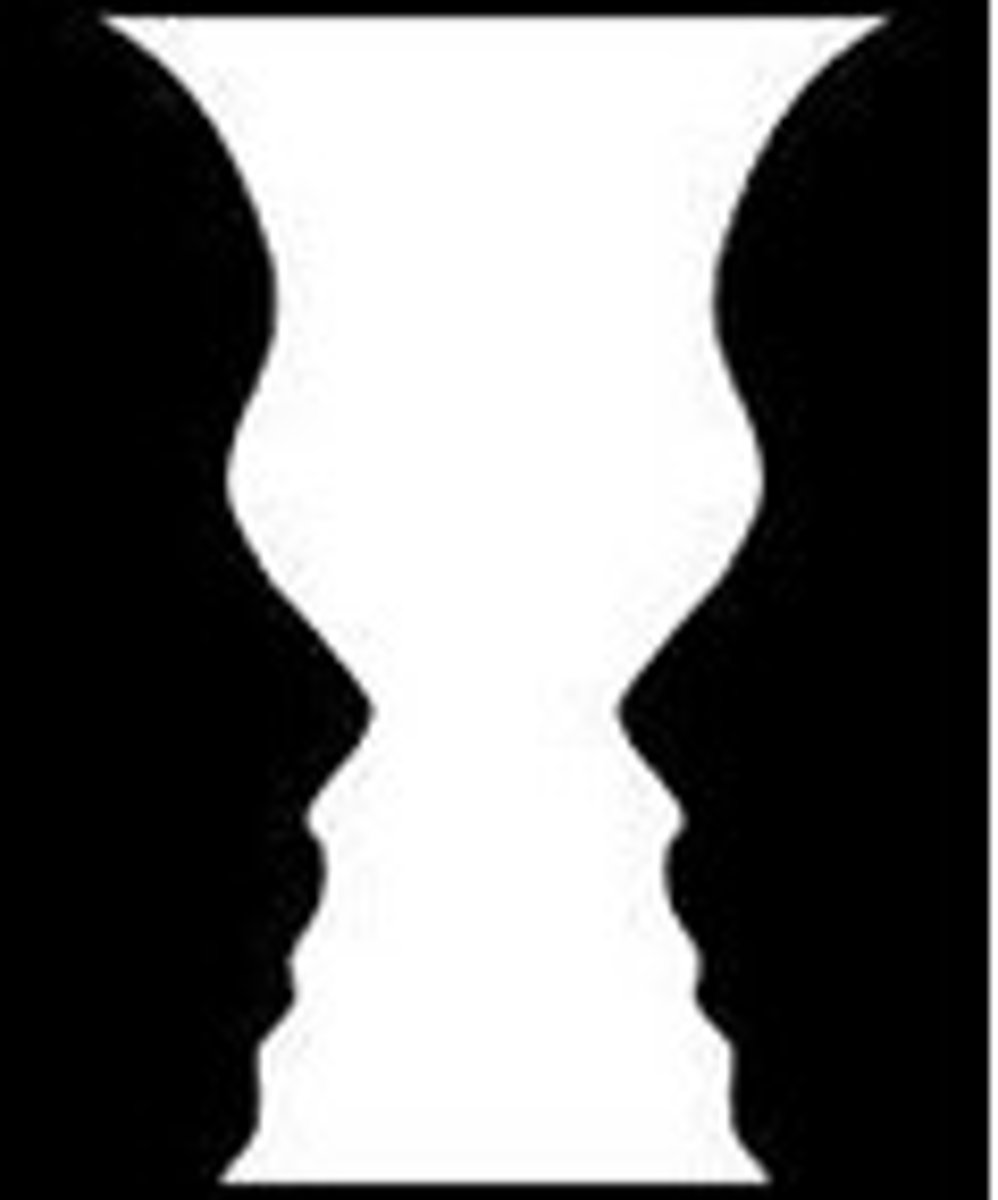

common fate
the tendency to perceive objects that are moving together as belonging together
dogs are __________ times more sensative to smell than humans
10,000
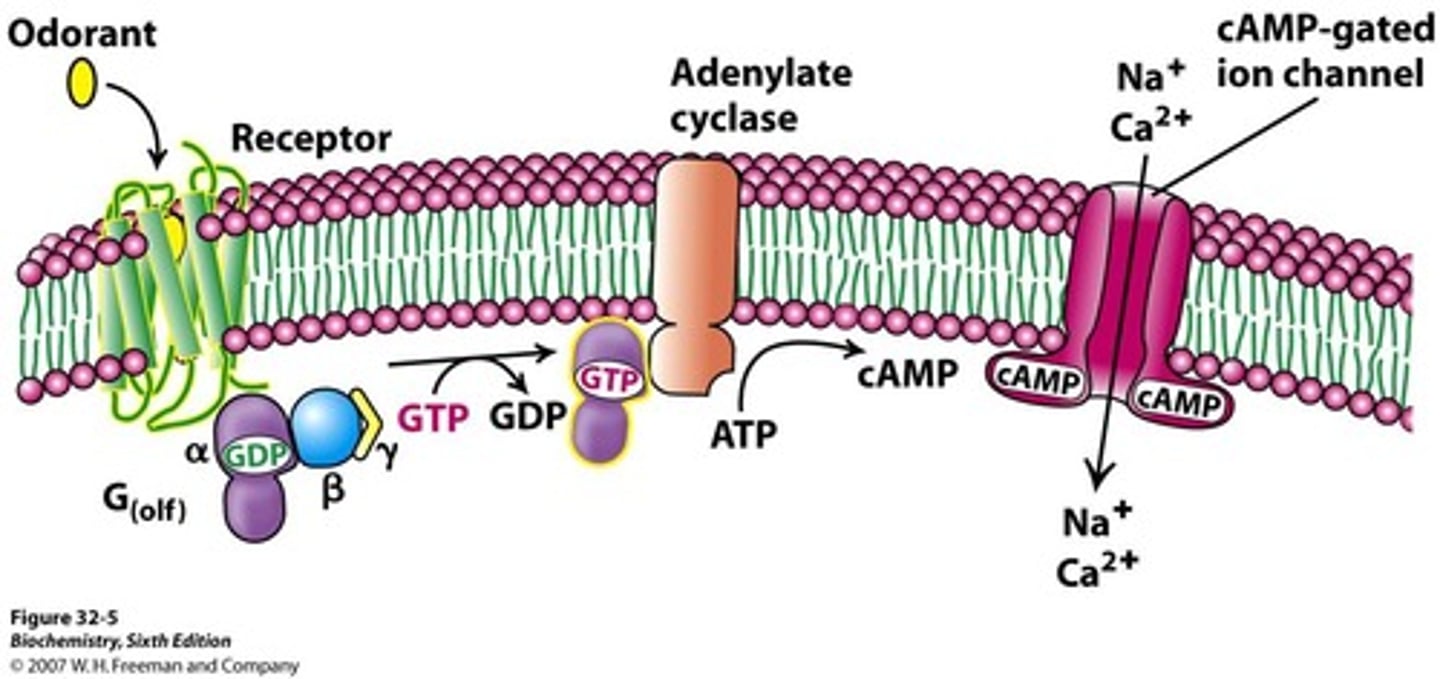
olfactory epithelium
400 types of olfactory receptors found in the back of the nasal cavity
The infinite smells we detect are made up of_______
different odorants that can be detected by many different receptors
women have_____ percent ________ neurons in their olfactory bulb than men
50,more
linguistic variation
explains why some cultures have more words to describe specific scents than other
chemical senses
smell and taste because receptors are detecting specific chemicals
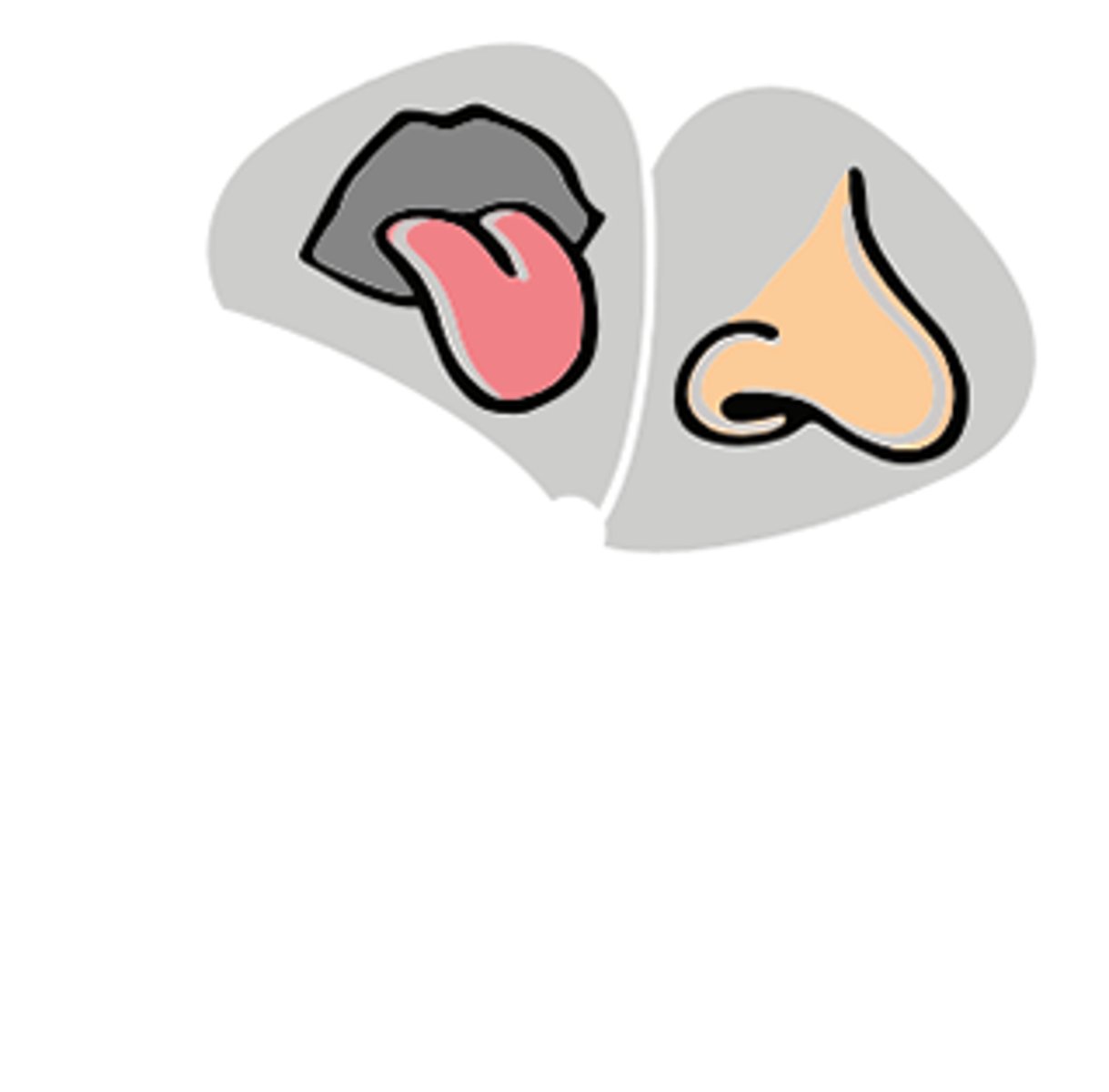

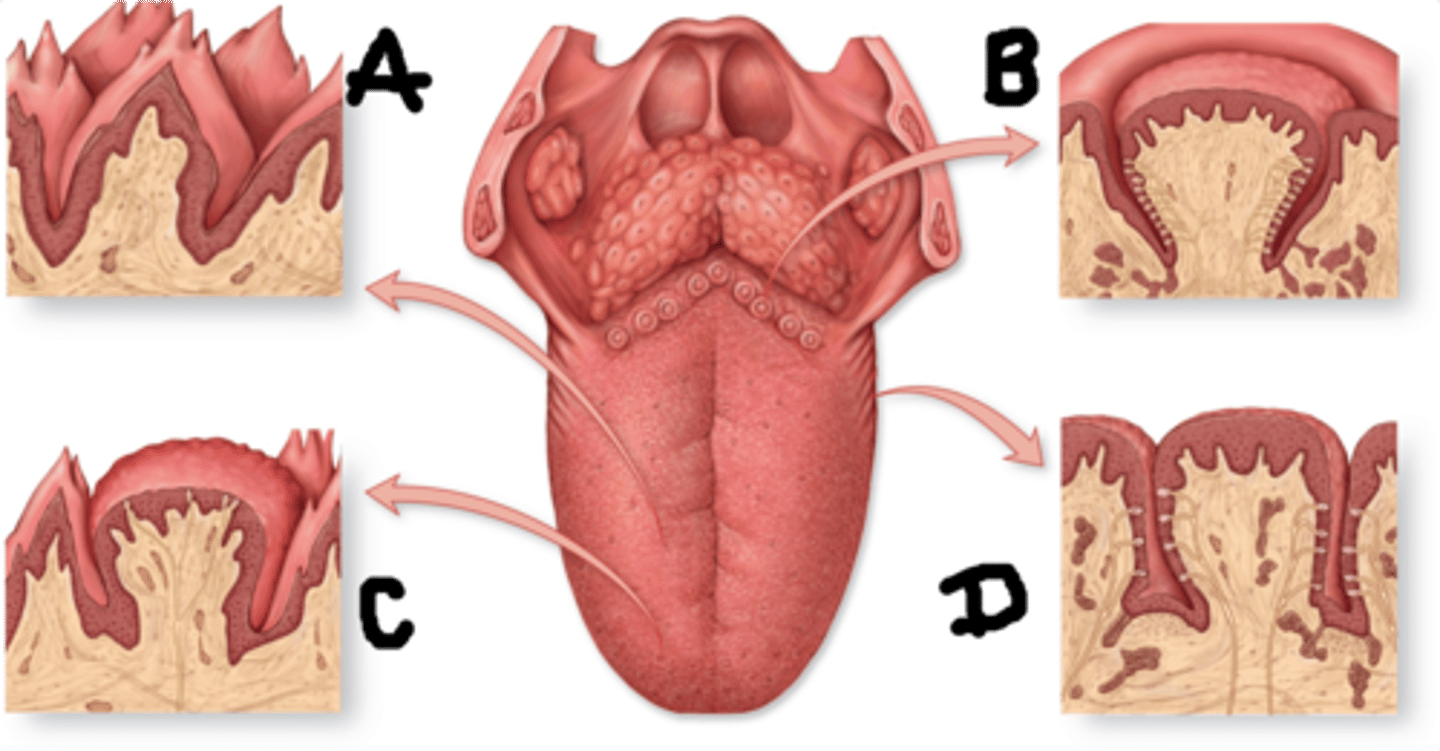
Papillae
bumps on our tongue where taste buds lie between
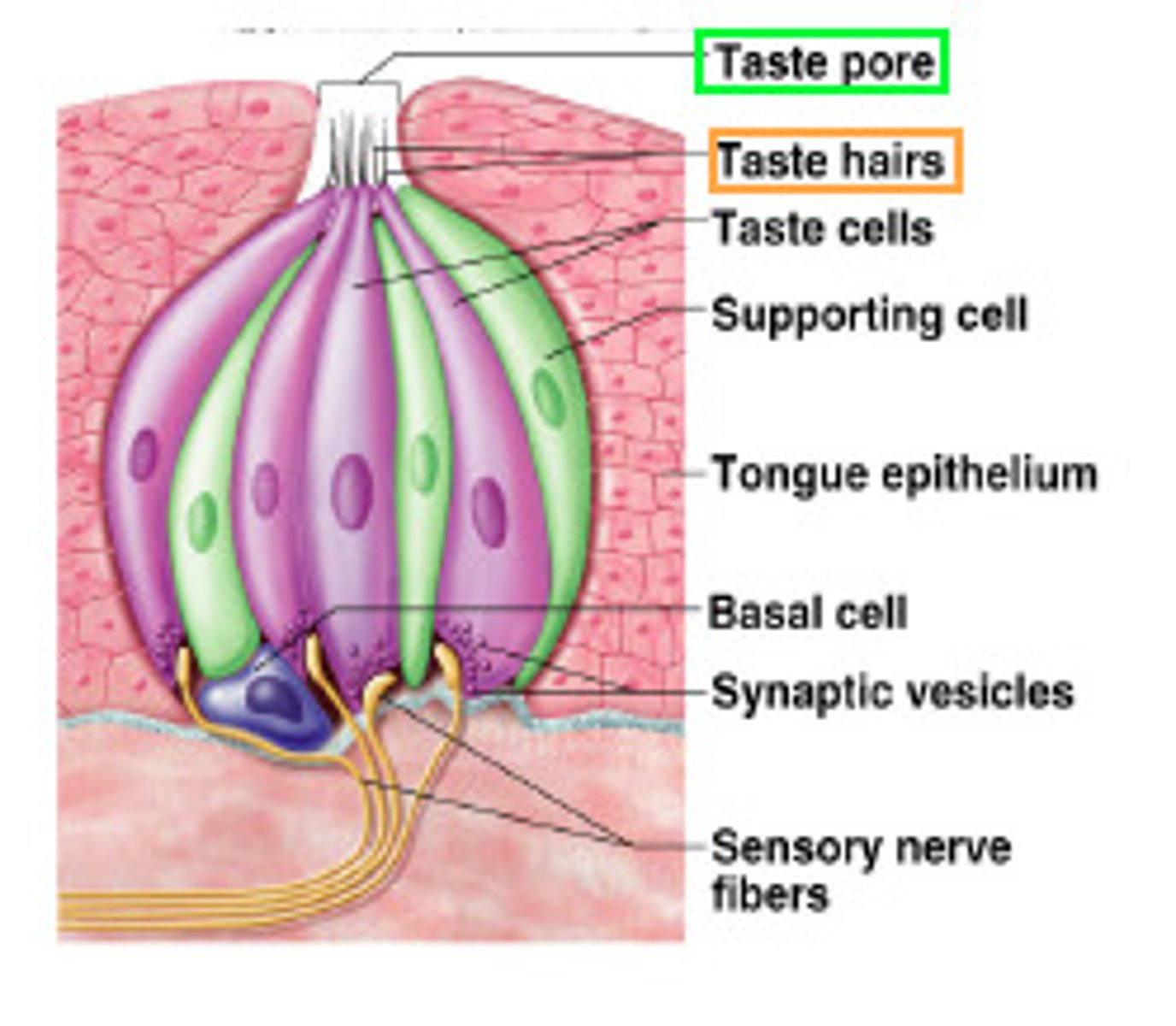
taste buds
receptor cells for taste where transduction occurs
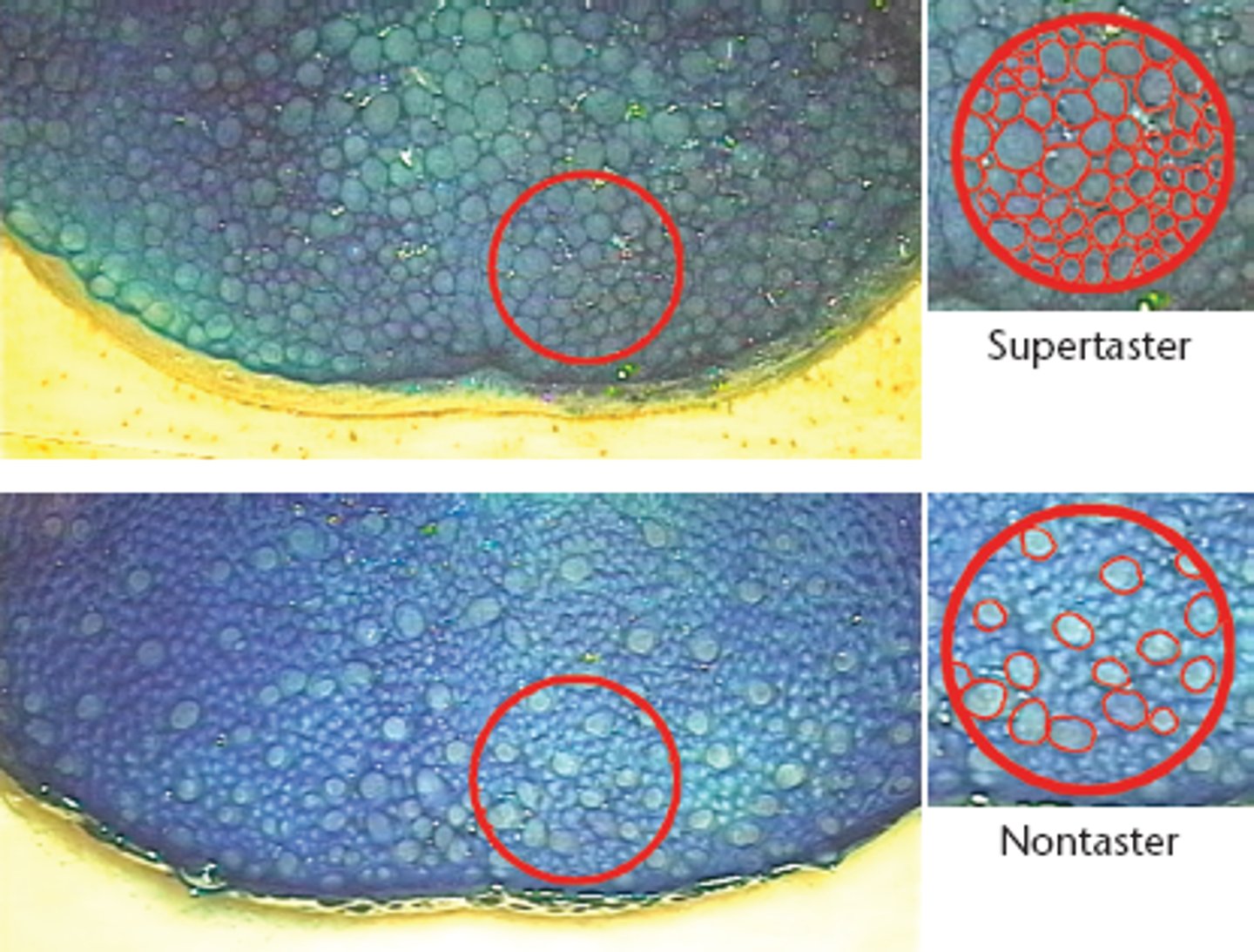
supertaster
has more than 35 paplilae in a hole punch
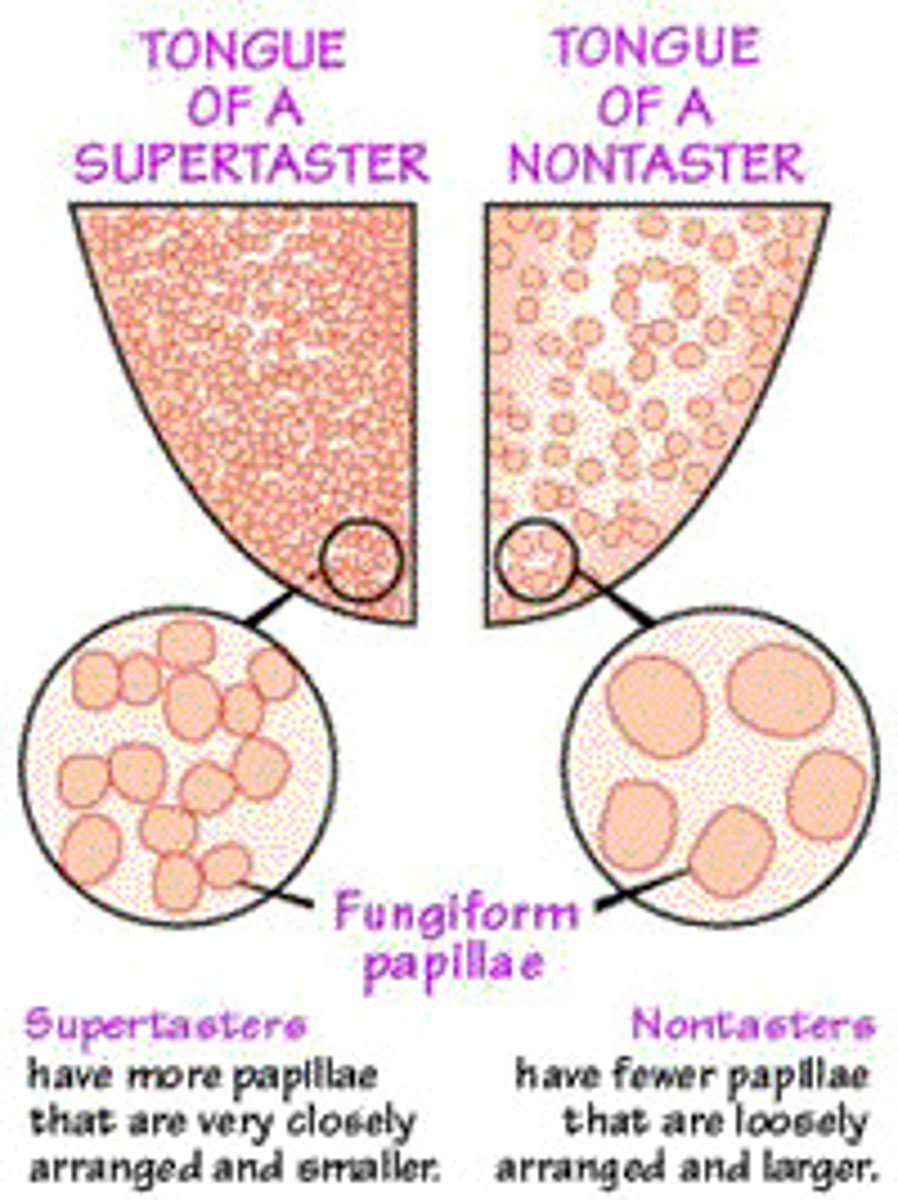
nontaster
has less than 15 papilae in a hole punch circle. Correlation with smoking and obesity
somatic senses
also known as tactile senses: touch, pressure, temperature, pain. controlled by motor cortex and sensory cortex.
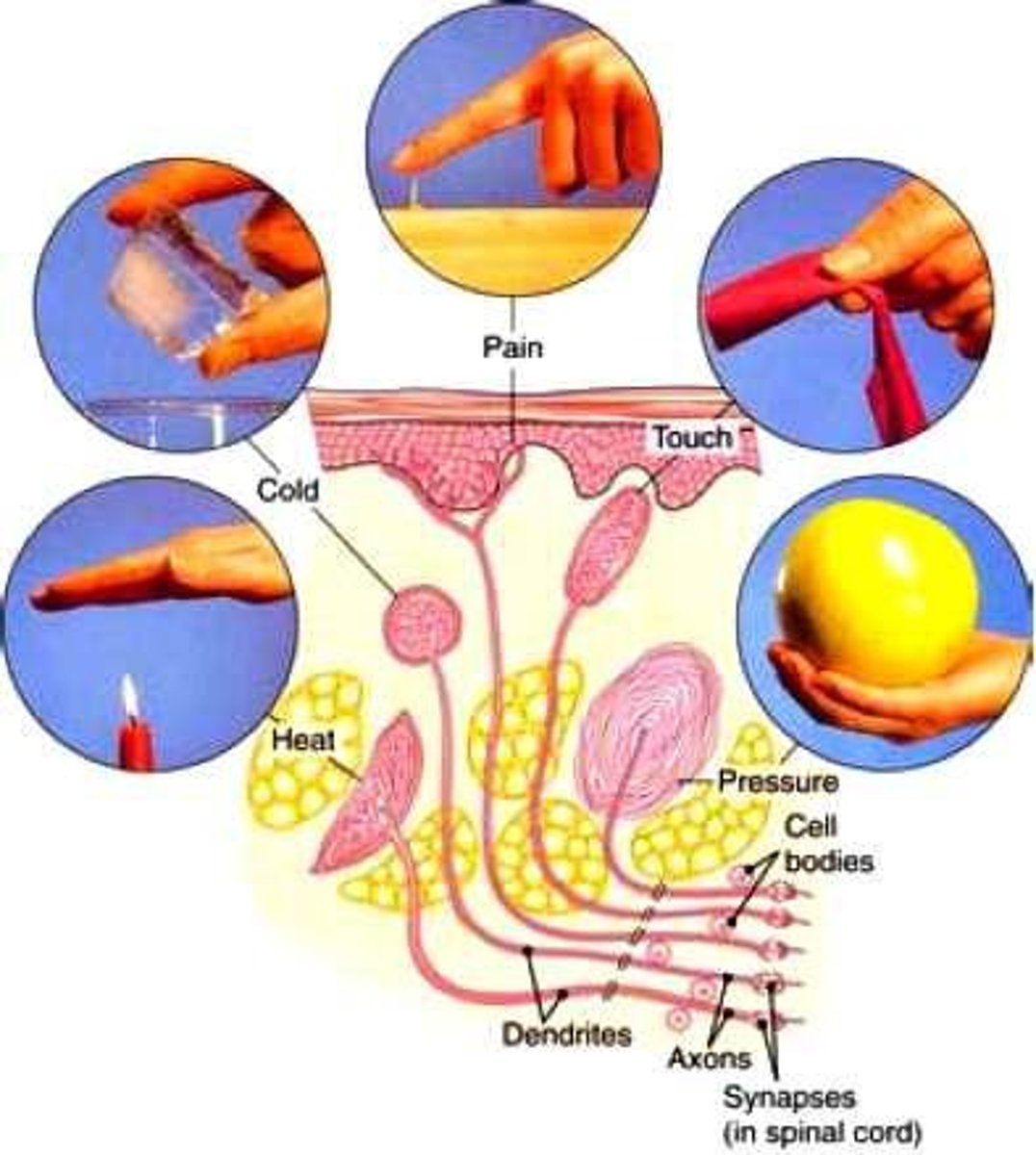
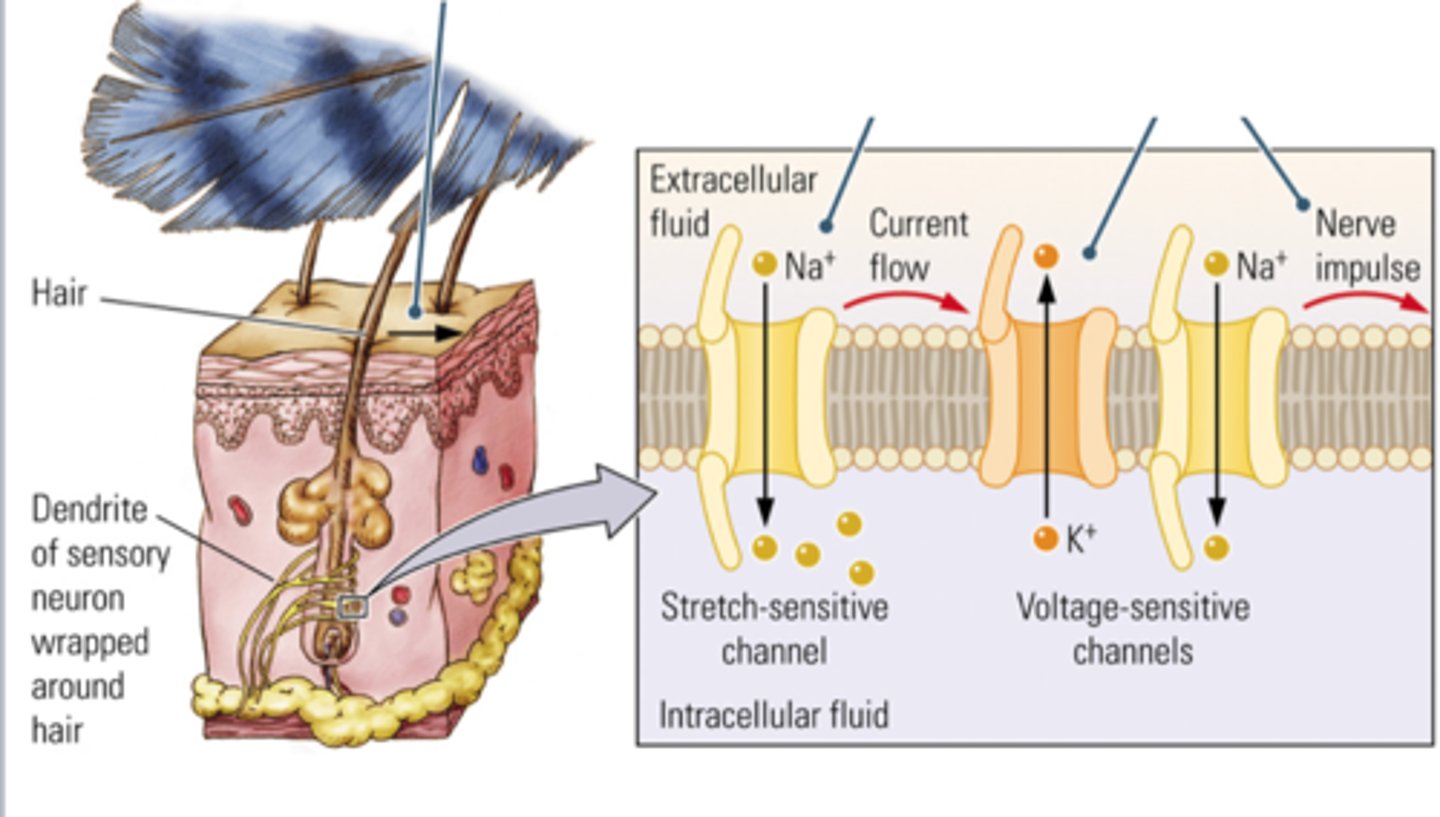
haptic receptors
in our skin all over our body that respond to temperature,pressure,and pain
endorphins
natural, opiate-like neurotransmitters linked to pain control and to pleasure

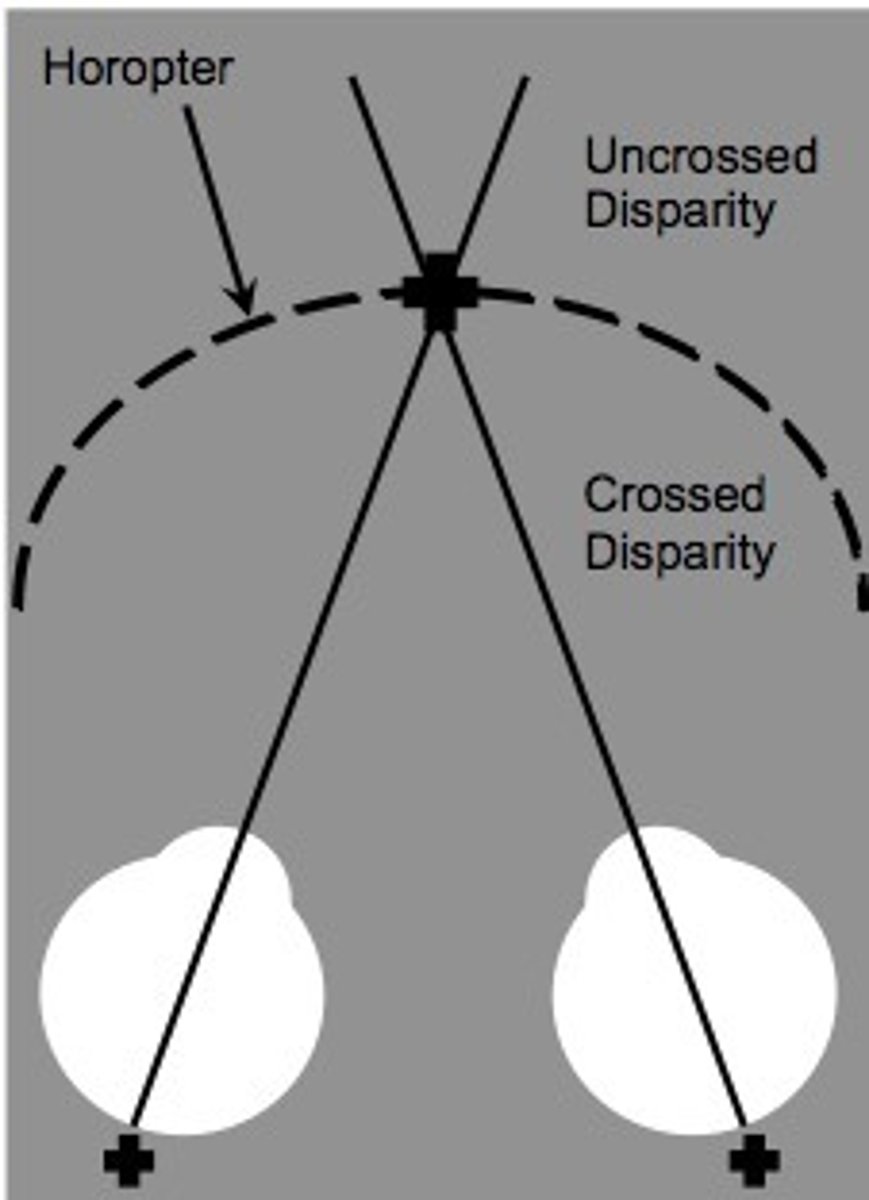
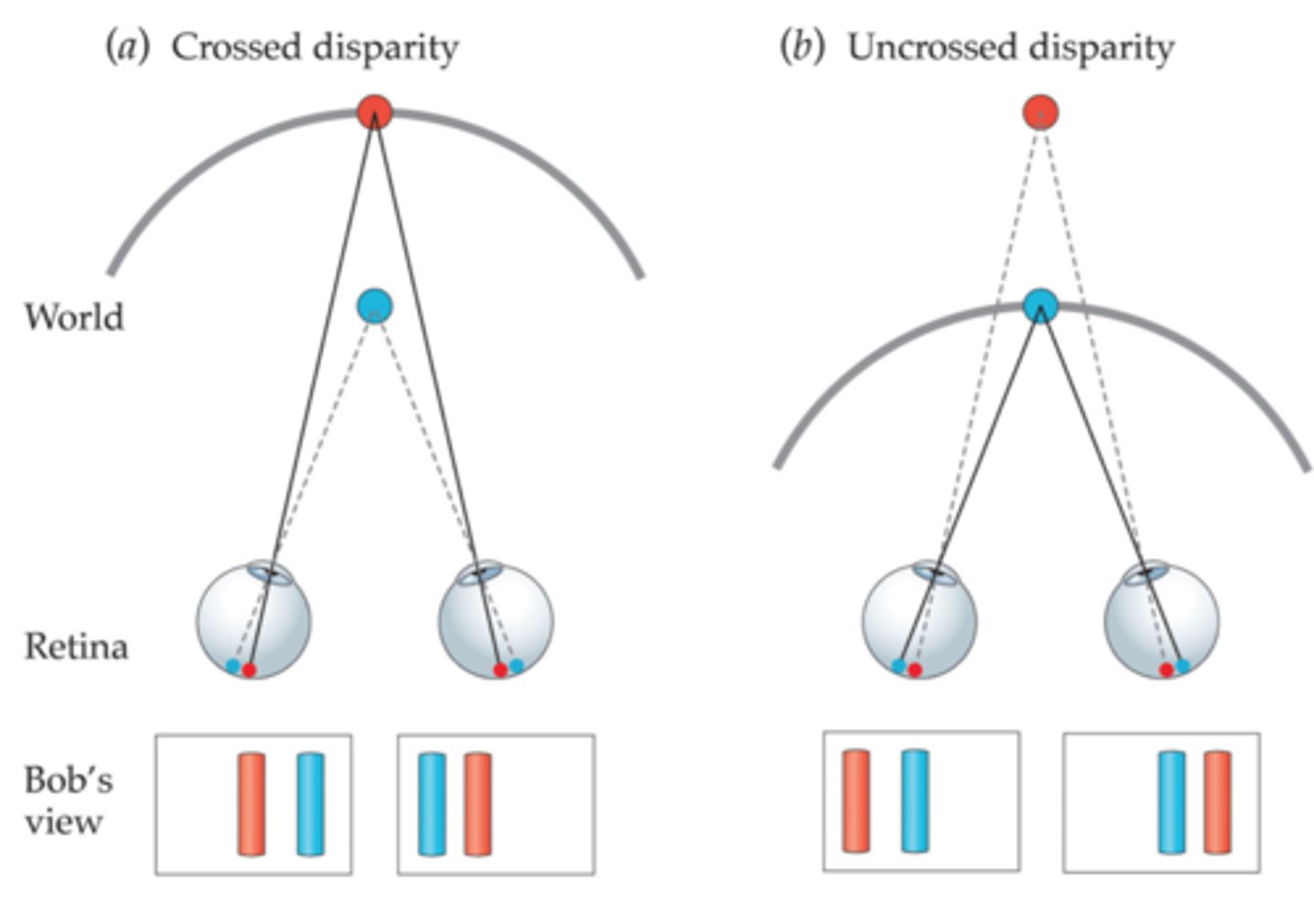
horopter
An imaginary surface that passes through the point of fixation. Images caused by a visual stimulus on this surface fall on corresponding points on the two retinas.
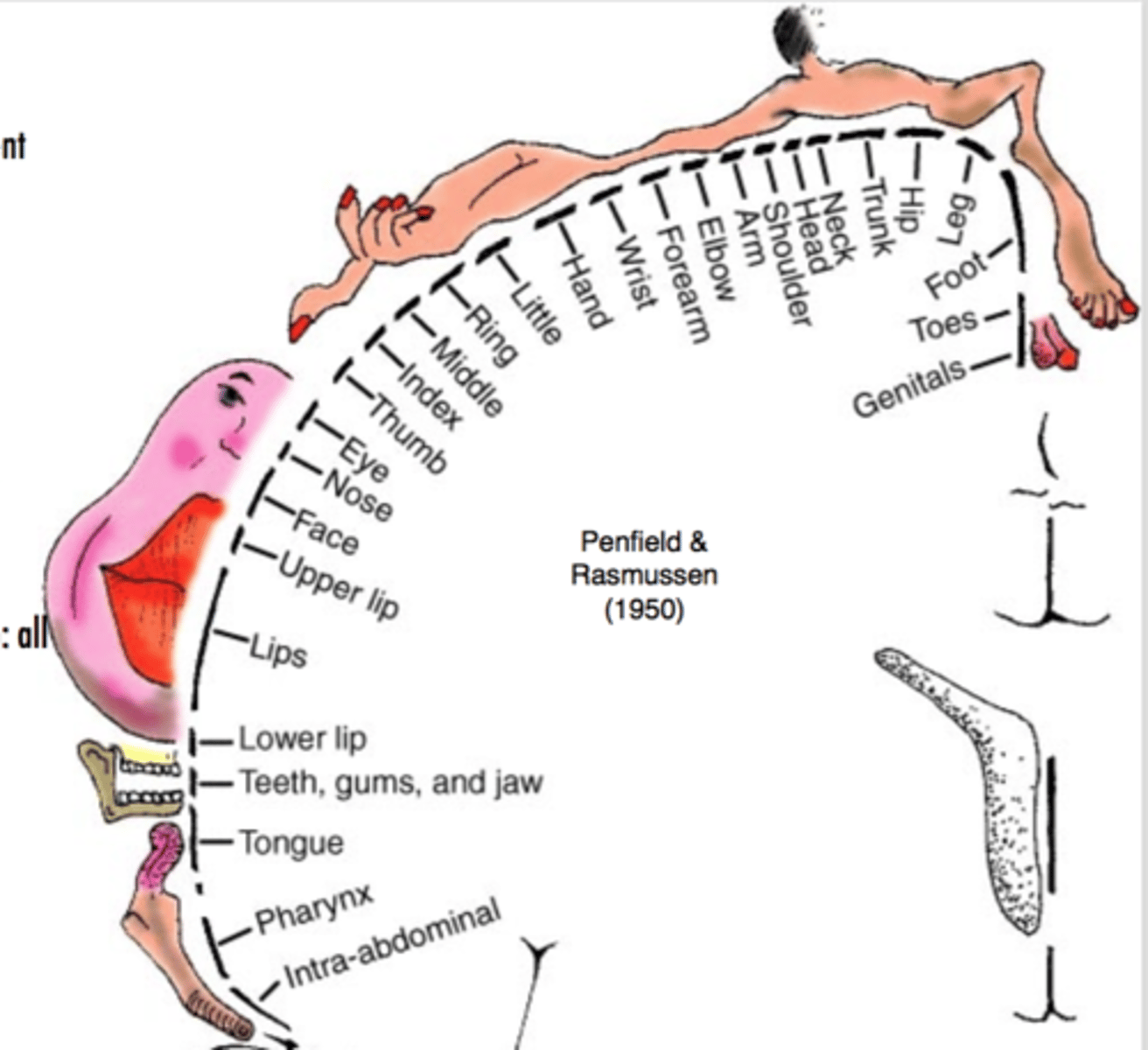
cortical magnification
The amount of cortical area (usually specified in millimeters) devoted to a specific region (e.g., 1 degree) in the visual field.
crossed disparity
image is closer than the horopter so images move to the temporal side
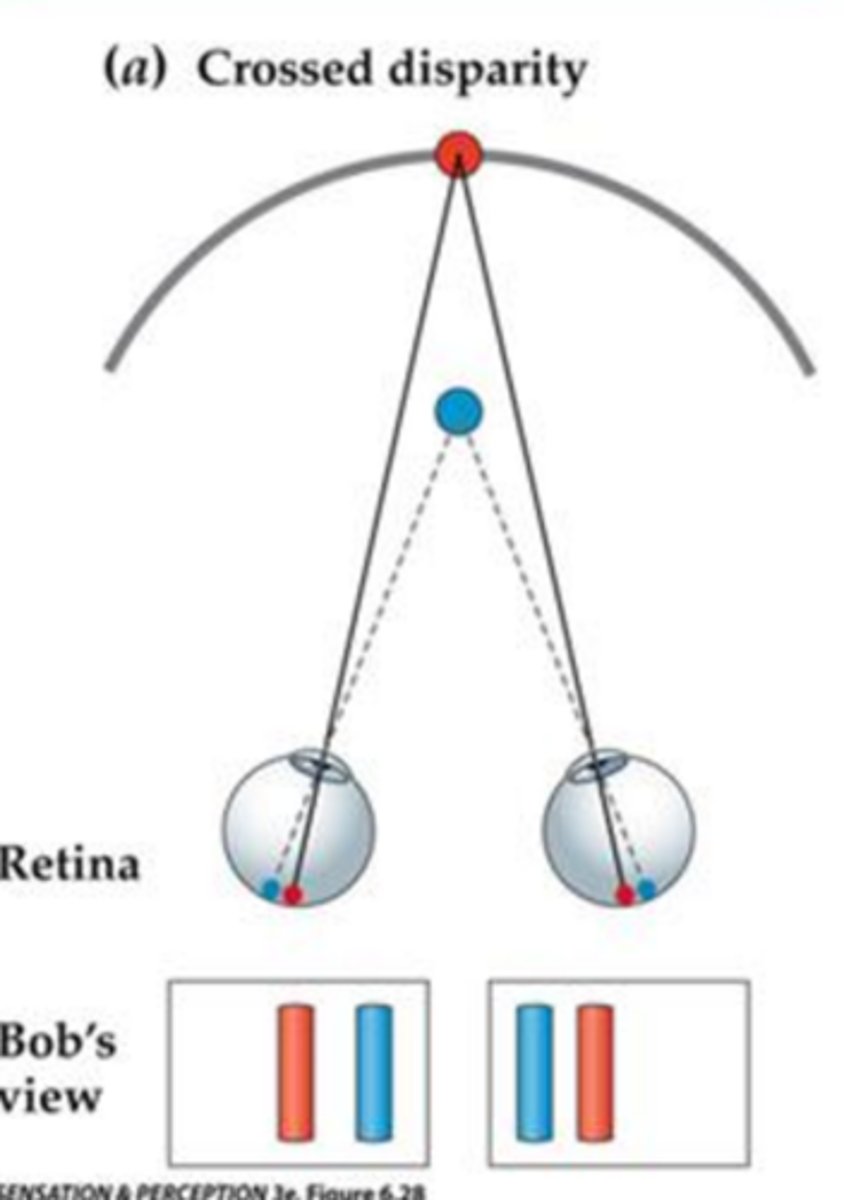
uncrossed disparity
The sign of disparity created by objects further than the horopter. image moves to nasal portion of eyes
3d glasses and depth perception