Motion - Chapter 2.1 - Spec 2.9 - 2.18
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Distance
the amount of ground the object has covered - scalar
Displacement
the overall distance travelled from the starting position - vector
Speed
the distance travelled per unit time - scalar
Velocity
rate of change of displacement - Δs/Δt
Acceleration
- rate of change of velocity - Δv/Δt - vector
Uniform acceleration
where the acceleration of an object stays constant
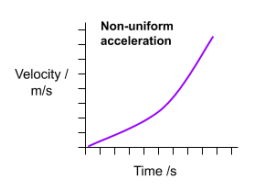
Acceleration time graphs
Represents the change in velocity over time.
The area under the graph is the change in velocity.
Displacement-time graphs
shows the change in displacement over time
gradient represents velocity
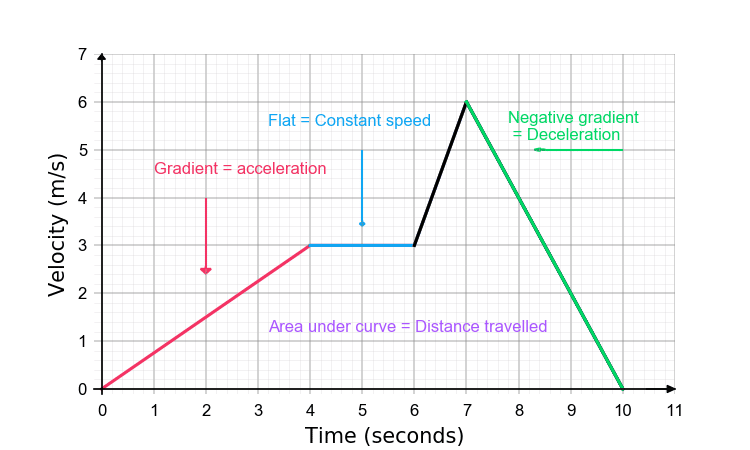
Velocity time graphs
represents the change in velocity over time.
The gradient of a velocity-time graph is acceleration
The area under the graph is displacement
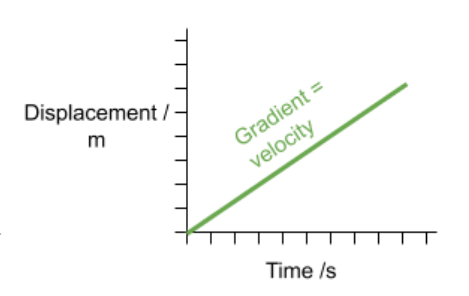
Displacement time graphs
show change in displacement over time
the gradient represents velocity.
Instantaneous velocity
velocity of an object at a specific moment in time
How to find Instantaneous velocity?
draw a tangent on the graph at the specific time then calculate the gradient
Average Velocity
the velocity of an object over a specified time frame.
How is average velocity found?
It can be found by dividing the final displacement by the time taken
Four Scalar quantities
Distance, Speed, Mass, Temperature
Four Vector Quantities
Displacement, velocity, force/weight, acceleration
Vector
magnitude and direction
Scalar
magnitude only
What is resolving a vector?
when you split a vector into two parts which are perpendicular to each other, these are its vertical and horizontal components
How do you resolve vectors using the calculation method
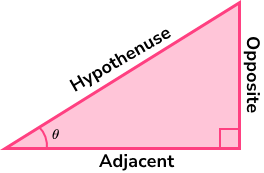
use trigonometry to split a vector V into its components x and y
When resolving he vector what is x equal to?
x = Vcosθ
When resolving the vector what is y equal to?
V sin θ
Steps for resolving a vector using the scale drawing method.
1. Choose an appropriate scale for your drawing and make note of this somewhere on your page. e.g 1cm = 2m/s
2. Using a ruler and a protractor, draw the vector V (as described by the question). Then, draw the vector’s horizontal and vertical components, making sure that they meet up at a right angle.
Finally, measure the length of the components (that you have drawn), and find their value using the scale you used to initially draw V.
When do you use the calculation method when adding vectors?
when the two vectors are perpendicular to each other. (meet at 90°)
How to add vectors using the calculation method
use Pythagoras’ theorem to find the magnitude of the vector and trigonometry to find its direction.
When do you use the scale drawing method when adding vectors?
When the vector is at any angle other than 90°
How do you use the scale drawing
draw a scale diagram using a ruler and a protractor, in order to find the resultant vector. Make sure to note the scale that you are using in your diagram
If two vectors are moving in the same direction, adding/subtracting them can be done by adding/subtracting their magnitudes.
Otherwise, they will have to be resolved into their horizontal and vertical components
Are vertical and horizontal components of a projectile’s motion are independent or codependent
Independent
How can the projectile’s horizontal and vertical motion be calculated.
They can be calculated separately using the uniform acceleration formula, where acceleration is constant.
What is a freebody diagram
A diagram which shows all the forces that act on an object
What does a Freebody diagram show?
shows how each of the forces act on the object compare with each other.
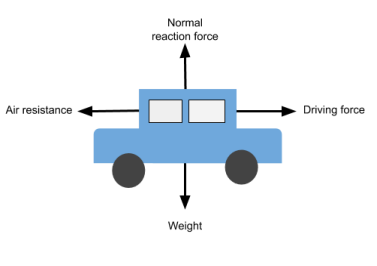
Newton’s 1st Law
An object will remain at rest or travel at a constant velocity, until it experiences a resultant force.
Newton’s 2nd Law
The acceleration of an object is proportional to the resultant force experienced by the object. (F = ma)
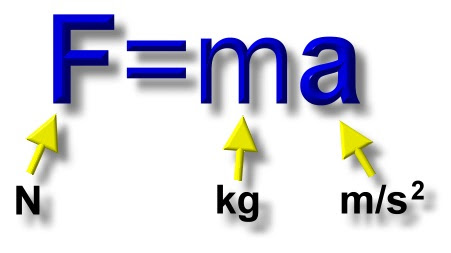
When can Newtons 2nd Law be used?
When two others are known
When the mass of the object is constant
How can you dervice Newtons 1st Law from Newtons 2nd Law.
if you substitute in a resultant force of 0N, you get an acceleration of 0 m/s2 , which shows that the object is either at rest or travelling at a constant velocity.
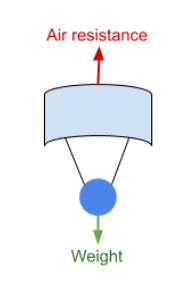
When does Terminal Velocity occur?
where the frictional forces acting on an object and driving forces are equal, therefore there is no resultant force and so no acceleration, so the object travels at a constant velocity
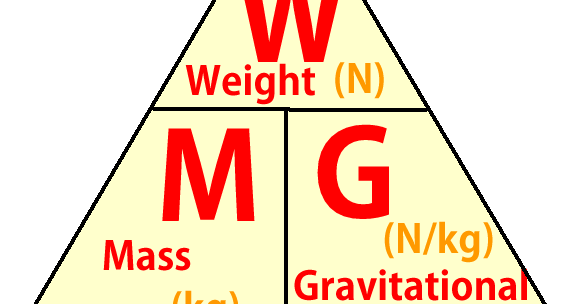
Gravitational Field strength (g)
The force per unit mass exerted by a gravitational field on an object. This can be calculated using the formula g = F/m
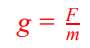
What is Weight?
the gravitational force that acts on an object due to its mass
How is Weight calculated
multiplying the objects mass and gravitational field strength. W=mg
What is Newtons 3rd Law
For each force experienced by an object, the object exerts an equal and opposite force.