AP Physics C Mechanics EXAM REVIEW
1/48
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
vectors
quantities with magnitude and direction; ex- velocity, displacement, acceleration, force, momentum
can be written in component form: v= ai +bj+ ck
scalar
quantities with only a magnitude; ex- distance, speed, mass, energy, temperature, time
Dot Product (vector multiplication)
method 1: A*B = |A||B|cosθ
method 2: A*B= AxBx + AyBy + AzBz
produces a scalar
Cross Product (vector multiplication)
method 1: |AxB| = |A||B| sinθ
method 2: if A= Axi + Ayj + Azk and B= Bxi + Byj + Bzk
then AxB= (AyBz - AzBy)i - (AxBz + AzBx)j + (AxBy - AyBx)j
produces a vector
average displacement, velocity, and acceleration
displacement: ∆x=(xf - xi) units: m
velocity: ∆v= ∆x/t units: m/s
acceleration: ∆a= ∆v/t units: m/s2
instantaneous displacement, velocity, and acceleration
displacement: x(t)= ∫v(t) dt
velocity: vinst= dx/dt; v(t)= ∫a(t) dt
acceleration: ainst=dv/dt OR ainst=d2x/dt2
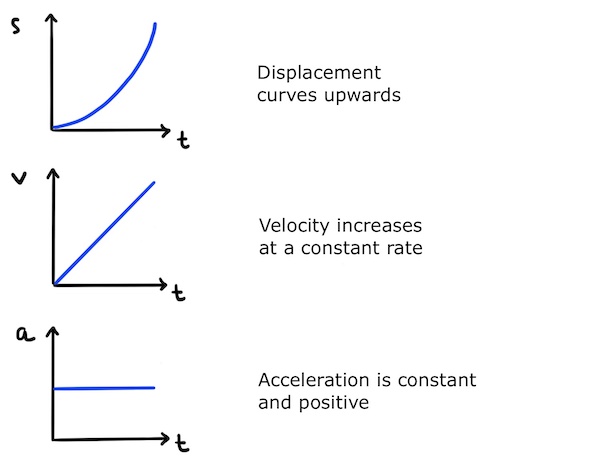
graphical representation of position, velocity, and acceleration
slope of x(t) = v(t)
slope of v(t) = a(t)
area under curve of a(t) = v(t)
area under curve of v(t) = x(t)
how to linearize data in desmos
steps
add table, insert values, and adjust window
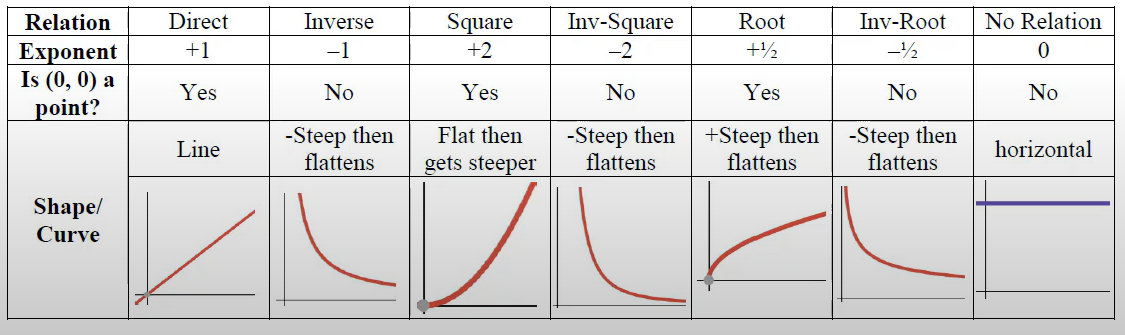
determine the type of non-linear relationship (ex: inverse, square, inv-square, root, inv-root, quadratic, log, exponential)
create new variables to represent the transformation
plot the new data points
draw a line of best fit
non-linear power function relationship examples (c is constant):
inverse: y= c/x
square: y= cx2
inv-square: y= c/x2
root: y= c√x
inv-root: y=c/√x
kinematic equations for constant acceleration
vf= vi + at
x= xi + vit + 1/2at2
vf2= vi2 + 2a(xf - xi)
x= 1/2(vi + vf)t
only when acceleration is constant!!
Reference frames
the velocity of an object depends on the location and motion of the observer.
EX1: Object A is moving left at 4m/s and Object B is moving is moving right at 6 m/s. the velocity of Object A from the reference frame of Object B is 10 m/s to the left.
EX2: an observer on land is watching a river. the velocity of the water relative to the observer is VWL, the velocity of the boat relative to the water is VBW, the boat moves perpendicular to VWL. what is the velocity of the boat relative to the land? VBL2 = VBW2 + VWL2
projectile motion
break down into horizontal and vertical components of d, v, and a. a faster horizontal velocity will result in a greater horizontal distance. horizontal motion of an object does not affect its vertical motion. the horizontal motion of a projectile is independent of its vertical motion and the vertical motion is independent of its horizontal motion.
the horizontal acceleration is zero and the vertical acceleration is constant. use kinematic equations in the vertical and horizontal directions separately. the time of the horizontal and vertical directions is the same.
launch angles in projectile motion
the greater the launch angle the greater the vertical distance of the projectile. the optimal angle for max range is 45 degrees.
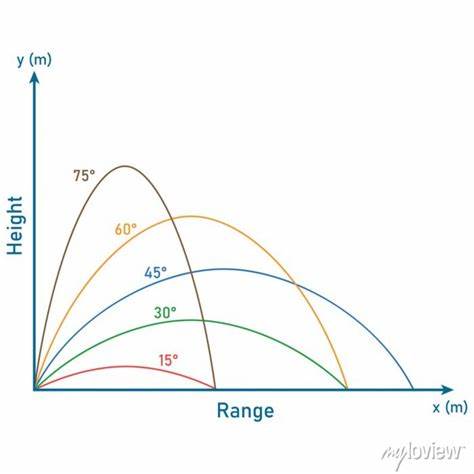
projectile motion equations
hmax= (vi2sin2θi)/(2g)
tmax h= (visinθi)/g
R= (vi2sin2θi)/g
Rmax=vi2/g
Uniform Circular Motion
ac= v2/r
v= rω
T= (2πr)/v
ω= (2π)/T
ac= rω2
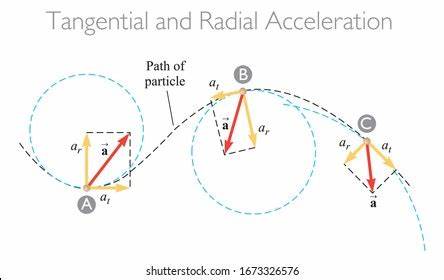
Tangential and Radial Acceleration
a= √(ar2+at2)
QUESTION: which of the following are accelerating?
a car slowing down
ball being swung in a circle
vibrating string
moon orbiting
skydiver at terminal speed
astronaut orbiting in space
ball rolling down a hill
person driving straight at a constant speed with their foot on the gas
objects changing direction or changing speed are accelerating. therefore 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 7 are accelerating while 5 and 8 are not
newtons first law
in the absence of external forces and when viewed from an inertial reference frame, an object at rest remains at rest and an object in motion will stay in motion with a straight-line velocity, unless acted on by an external force.
-condition 1: object can move but must be at a constant speed
-condition 2: object is a rest
constraint: forces must be balanced, sum of forces is zero
inertial frame of reference
a non-accelerating frame of reference
inertia vs weight
inertia- quantity of matter, aka mass (unit kg)
weight- mass effected by gravity; w=mg; (unit newton)
mass never changes; weight changes with gravity
facts about forces
unit: Newton (N)
a push or a pull
can exist during physical contact or without contact
equilibrium
when the sum of the forces acting on the object is zero; Fnet=0
newtons second law
the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force and inversely proportional to the mass;
a=Fnet/m
ΣF=ma
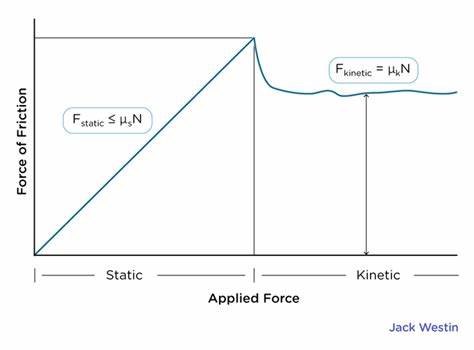
static vs kinetic friction
static- friction that keeps an object at rest and prevents it from moving
Ff=FNµs
kinetic- friction that acts during motion
Ff=FNµk
µ has no units
friction depends on the materials sliding against each other, NOT surface area!
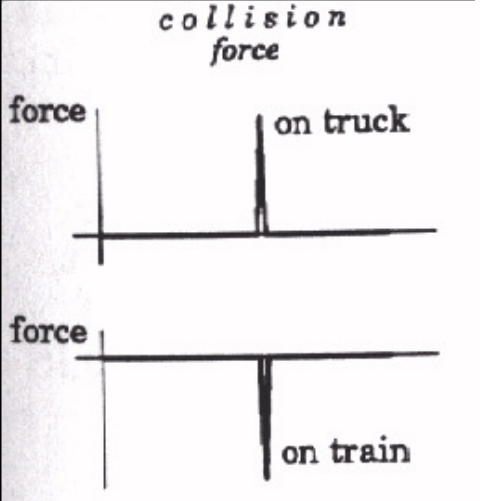
newtons third law
for every action force there is an equal and opposite reaction force
they NEVER cancel out
ie: a person exerts a force on a wall and the wall exerts a force on the person
ie: mcar Acar = Mtrain atrain
Air resistance
linear: R= -bv
b is a constant
velocity (v) is changing
m(dv/dt)=mg-bv
to find terminal 0=mg-bv therefore vT=mg/b
centripetal force
Fc=mv2/r
has to be supplied by another force
ie: a cart on a roller coaster at the top of a hill the Fc=Fg-FN while a cart at the bottom of the hill Fc=FN-Fg
centripetal force is the net force directed toward the center of a circular path, allowing an object to maintain circular motion. it can be provided by tension, gravity, friction, depending on the situation.
resistive forces
R=-bv
basics of energy
work- force applied through a distance; must be parallel; W=Fd
kinetic energy- energy of motion; KE= ½ mv2
potential energy- energy of position; 2 types: gravitational (U= mgh) and elastic (U= ½ kx2)
power- rate at which energy is transferred/consumed- P=W/t or P=E/t
work
W= F∆d → FdCosθ
work is found by multiplying the force times the displacement and result is energy.
units: joules (J)
F and d must be parallel
W= ∫ F(x)dx → work is the area under the force vs displacement graph
Wnet= ∆K → W=(mv2/2 - mv02/2)
W= -∆U → W= mgy - mgy0 → work equals the negative change in potential energy
energy conservation
∆K = -∆U
K-K0 = -(U-U0)
in a closed isolated system energy is conserved, meaning the initial energy equals the final energy.
Elastic Potential Energy
hooks law: Fs=-Kx
negative because it’s a restoring force that works in the opposite direction of the displacement
Us= ½ Kx2
power
Power = work/time
P= Energy/time
P= F v → P= F(d/t)
Momentum and Impulse
momentum: moving mass- inertia in motion
momentum = mass x velocty →(p= mv); units: kgm/s
Impulse: applying a force for a period of time to change momentum
Impulse= forceavg x time →(J= Favgt) or J= ∆p; units: Ns or Kgm/s
relationship: the area under the curve of a force vs time graph is the impulse/change in momentum.
increasing momentum: apply the greatest force for the longest period of time (ie: following through)
Decreasing momentum: extending the impact time (ie: air bags)
bouncing delivers a greater impulse (∆p= 2mv)
conservation of momentum
in a closed isolated system total momentum is conserved
collisions
elastic collisions: momentum AND kinetic energy are conserved (ie: billiard balls)
inelastic collisions: ONLY momentum is conserved (ie: car crashes)
perfectly inelastic collisions: objects stick together
imperfectly inelastic collisions: objects don’t stick together
pay attention to signs!
center of mass
use for elastic collisions only!
vcm= Σ mivi / mi
subtract Vcm from initial velocity to enter Center of mass reference frame; add Vcm to final velocity to leave the center of mass reference frame.
rotation of a rigid object a fixed axis
angular position: θ = S/r
S is arc length
r is radius of rotation
θ is the angle through which the object rotates
angular speed: ωavg = ∆θ/∆t or ω= dθ/dt or ω= 2π/T
ω is angular speed (units rad/sec)
T is the period
Angular acceleration: αavg= ∆ω/∆t or α= dω/dt
α is angular acceleration (units rad/sec2
rigid object under constant acceleration
ωf=ωi+αt
θf= θi+ωit+1/2 αt2
ωf2=ωi2+2α(θf-θi)
θf=θi+1/2(ωi+ωf)t
angular and translational quantities
v= rω
a= rα
ac = rω²
angular speed radius does not matter
linear/translational speed radius matters
Torque
T= rFsinθ
force should be perpendicular to the lever arm
units: Nm
ΣT= Iα
moment of inertia
I= Σ miri²
Hoop/Thin Cylindrical Shell: Icm= 1MR2
Solid Cylinder/disk: Icm= 1/2MR2
Hollow cylinder: Icm=1/2M(R12+R22)
Long thin rod with rotation axis through center: Icm=1/12ML2
Long thin rod with rotation axis through end: I=1/3ML2
Rectangular plate: Icm=1/12M(a2+b2)
Solid Sphere: Icm=2/5MR2
thin spherical shell: Icm= 2/3MR2
Parallel Axis Theorem
I= Icm+ MD2
D= distance between parallel lines
Rotational Kinetic Energy
KR=1/2 Iω2
energy considerations
dW= Fds = (F sinθ)rdθ
Power= dW/dt = tω
rolling motion of a rigid object
VT= ωR
VCM= Rω
acm= Rα
angular momentum
L= position cross linear momentum
L= mvr sinθ
L= Iω
angular momentum is conserved in an isolated system
∆L= 0 with no external torques
gravity
Fg= G(m1m2)/r²
don’t forget r is measured to the center of mass!!
Ug= Gm1m2/r
escape speed as the particle gets infinitely faraway velocity approaches 0
oscillatory motion
Fs= -kx
ax=-k/m x
ω=√(k/m)
x(t)= Acos(ωt+∅)
Vmax= ωA
a(max)= ω²A
spring constant (k)
in series: ktotal= (1/k)+(1/k)…
in parallel: ktotal= k+k+k…