Bacteria/Virus/Immune System Quiz
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/45
Last updated 11:07 PM on 3/14/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
1
New cards
What are useful things bacteria can do?
Aid in digestion, essential part of ecosystems, recycle nutrients
2
New cards
What is our best defense against bacteria?
Antibiotics
3
New cards
What is the issue with the overuse of antibiotics?
Bacteria becomes resistant to antibiotics
4
New cards
What is eubacteria?
These are bacteria that YOU are familiar with - they live in many places
5
New cards
What is Archaea?
These live in extreme environments (incredibly salty, incredibly hot, etc.). They are sometimes called “extremophiles”. They are no longer classified as bacteria.
6
New cards
What organelles would the two prokaryotes have?
Cell membrane, DNA floating in cytoplasm, Ribosomes (no membranes)
7
New cards
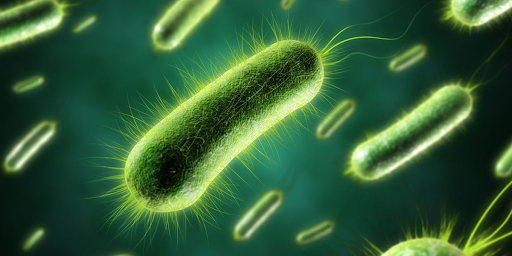
Cilia
Tiny hair-like structures that help the bacteria move around in a water-environment
8
New cards
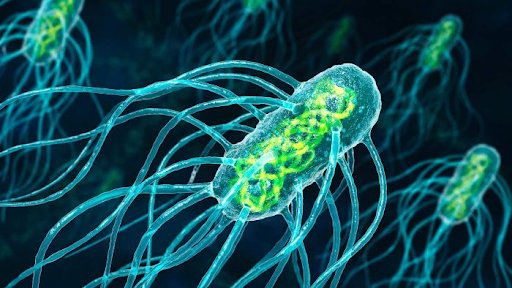
Flagella
Part of the cytoskeleton of the cell. A tail-like structure on the bacteria is made of lots of protein filaments that helps the bacteria move.
9
New cards
Binary fission
Vocab term that describes mitosis/asexual reproduction in bacteria
10
New cards
Conjugation
A method that some bacteria have of sexual reproduction where one bacteria can inject some genes into another bacteria
11
New cards
Obligate Aerobes
Obligated to live in an environment that is rich in oxygen
12
New cards
Obligate Anaerobes
Obligated to live in an environment that has NO oxygen such as thick layers of mud
13
New cards
Facultative Anaerobes
Can survive in an environment with or without oxygen. Oxygen is not required nor harmful to these bacteria.
14
New cards
Coccus
Sphere shape
15
New cards
Bacillus
Rod shape
16
New cards
Spirillum
spiral shape
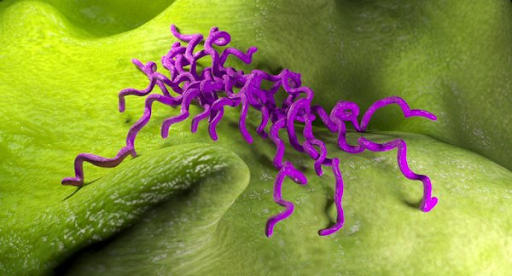
17
New cards
Diplo
in pairs
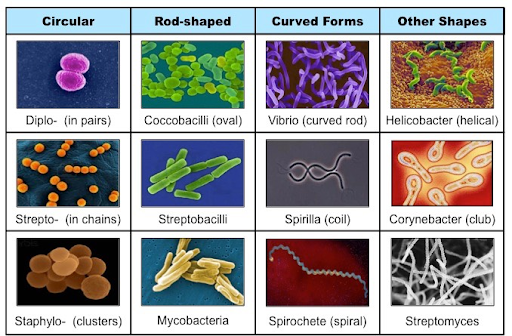
18
New cards
Staphylo
In clusters
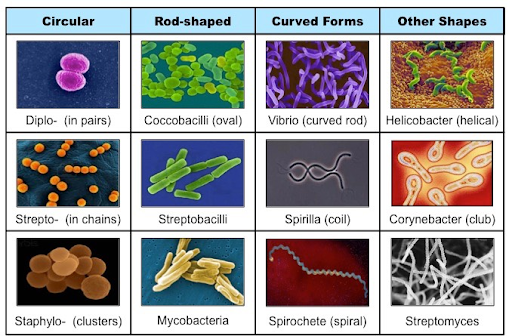
19
New cards
Strepto
In chains
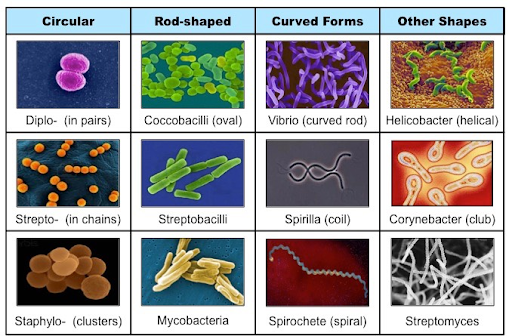
20
New cards
What is gram staining?
Gram staining is a common technique used to differentiate two large groups of bacteria based on the amount of **peptidoglycan** that is present in the cell wall of the bacteria.
21
New cards
What does bacteria staining purple mean?
The bacteria has a thick layer of peptidoglycan in its cell wall and it is gram positive
22
New cards
What does bacteria staining red mean?
The bacteria has a thin layer of peptidoglycan in its cell wall and it is gram negative
23
New cards
What part do all viruses have in common?
Capsids
24
New cards
What makes viruses different than retroviruses?
Viruses have DNA when retroviruses only have RNA
25
New cards
What are two reasons that we do not die quickly from a viral infection?
Because we have so many cells and because of your immune system
26
New cards
What body system attacks viruses?
Immune system
27
New cards
What is a prophage?
Viral information from the virus combined with the DNA in the cell
28
New cards
Which of the two cycles is where the virus is currently causing active harm to the host cells?
Lytic
29
New cards
Lytic cycle vs the lysogenic cycle
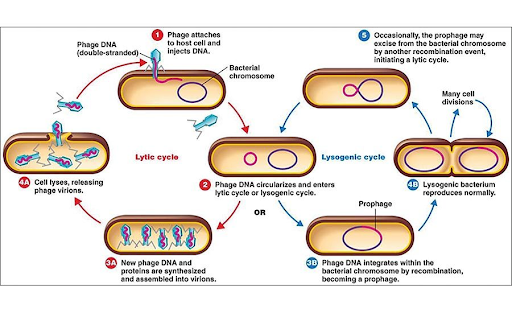
30
New cards
First line of defense in the immune system (in order) and what they do
* Macrophage (A type of White Blood Cell): Very large cells that kill bacteria
* Neutrophils (when they die they are PUSS): Cells that KILL everything--including good cells.
* Complement proteins: Will rip holes in bacteria to kill them
* Neutrophils (when they die they are PUSS): Cells that KILL everything--including good cells.
* Complement proteins: Will rip holes in bacteria to kill them
31
New cards
What happens at the site of an inflammatory wound?
Body temperature rises: This is due to the fact that the blood vessels are expanding to quickly bring more cells to defend your body. Also, it inhibits the growth of pathogens. As the blood vessels dilate, blood plasma leaks out into the impacted area to containing the invading pathogen. This fluid is seen as inflammation at the site.
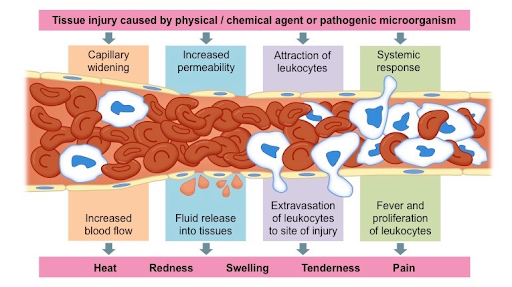
32
New cards
What is the second line of defense?
Specific immunity
* Dendrites: enters Lymphatic System and then activates the specific helper T cells
* Specific helper T cells: Split into groups and activate macrophages and b cells
* Dendrites: enters Lymphatic System and then activates the specific helper T cells
* Specific helper T cells: Split into groups and activate macrophages and b cells
33
New cards
What does a macrophage do when activated by a T cell?
Wakes up and begins to kill pathogens again
34
New cards
What do B cells do?
Pump out antibodies which stick to bacteria. The antibodies make the bacteria stick together for macrophages to kill.
35
New cards
What does a memory B cell do?
Will remain to guard tissue
36
New cards
What do memory B cells do?
Will continue to pump out low amounts of antibodies
37
New cards
What type of cells are responsible for allergies?
Lymphocytes
38
New cards
How many different antibodies do we have?
Almost 10 billion
39
New cards
What is the difference between mRNA vaccines and other vaccines?
mRNA vaccines contain RNA to help us get our antibodies, but other vaccines use an actual part of the virus (treated so that it doesn’t hurt you) to help us make antibodies.
40
New cards
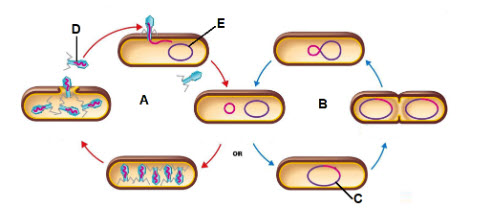
Letter A is showing what process?
lytic infection
41
New cards
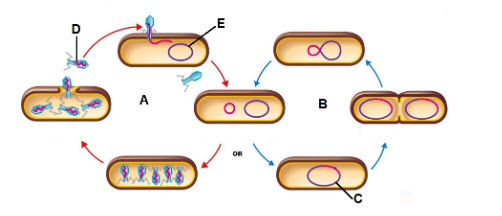
Letter B is showing what process?
lysogenic cycle
42
New cards
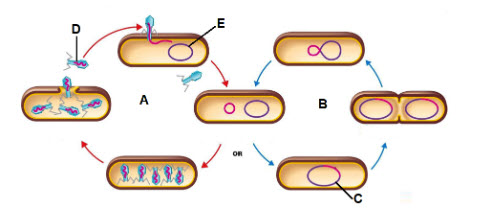
The piece of DNA shown by the letter C is called a ________
prophage
43
New cards
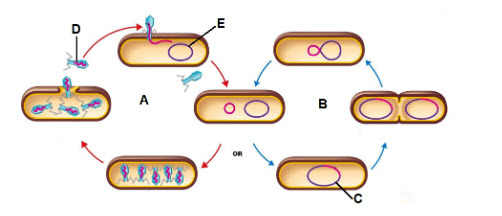
What is the virus that letter D is pointing to?
Bacteriophage
44
New cards
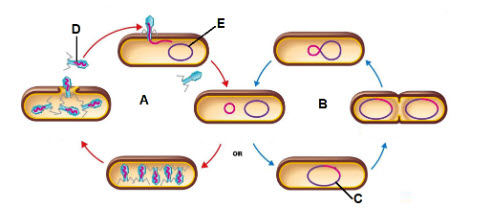
What is the letter E the pointing to?
Bacterial DNA
45
New cards
Viruses cannot be treated with antibiotics because:
Antibiotics block the growth of **bacteria**
46
New cards
Bacteriophages infect
Bacteria ONLY