Nurs 241 Patho Midterm
1/228
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
229 Terms
Homeostasis
The maintenance of a relatively stable internal environment regardless of external changes
What may develop if homeostasis is not internally maintained?
Disease
Medical interventions may be necessary to achieve homeostasis
Can be temporary—ex: fluids to correct hypovolemia (This is not DISEASE)
May need to be continuous—ex: daily medications for blood pressure control—This indicates DISEASE
Example of disease related to homeostasis
Daily med for blood pressure control
State of health
Physical, mental, and social well-being are considered and should be within individuals normal health status
Disease
Deviation from the normal state of homeostasis
Process with characteristic set of signs and symptoms
Disease develops when
The state of homeostasis cannot be maintained without an intervention
Concept and Scope of Pathophysiology
Functional (physiologic) changes in the body as a result from disease
Uses knowledge of basic anatomy and physiology.
Includes aspects of pathology, which describes structural changes in body tissues caused by disease.
Interruption of the normal functioning of one organ will
Affect other organ systems as well
Cause and effect relationships are defined by
Signs and symptoms which guide the study of a specific disease
What is pathophysiology?
The study of functional or physiologic changes in the body that result from disease processes
We study pathophysiology to increase understanding of
Complexity of disease processes
Diagnosis and treatment
Possible implications of signs and symptoms or a prognosis
Comprehension of the potential complications of a disease
Disease prevention!
Gross level
Organ or system level
Pathophysiology
Microscopic level
Cellular level
Pathology
Biopsy
Excision of small amounts of living tissue
Idiopathic
Cause of disease is unknown
Iatrogenic
Error/treatment/procedure may cause the disease
Predisposing factors
Age, gender, inherited factors, environment (tendencies that promote the development of disease)
Prophylaxis
Preserve health, prevent spread of disease
Prevention of disease
Vaccinations; Dietary/lifestyle modifications; Prevention of potentially harmful activities
Remission
Period which manifestations subside
Exacerbation
A worsening of severity
Precipitating factor
Condition that triggers an acute episode
Complications
New secondary or additional problems
Subclinical state
Pathologic changes, no obvious manifestations
Latent state
No symptoms or clinical signs evident
In infectious diseases: incubation period
Prodromal period
Early development of the disease
Signs are nonspecific or absent
Manifestations
Clinical evidence with signs and symptoms
Local: at site of the problem
Systemic: general indicators of illness, i.e. fever
Morbidity
Disease rates within a group
Mortality
Relative number of deaths resulting from the disease
Autopsy
Postmortem examination
Epidemiology
Tracking the pattern or occurrence of disease
Major data collection centers: WHO and CDC
Incidence
Number of new cases in a given population within a given time period
Prevalence
Number of new, old, or existing cases within a given population and time period
Epidemics
A higher number of expected cases of an infectious disease occur within an area
Pandemic
Involve a higher number of infectious diseases in many regions of the globe
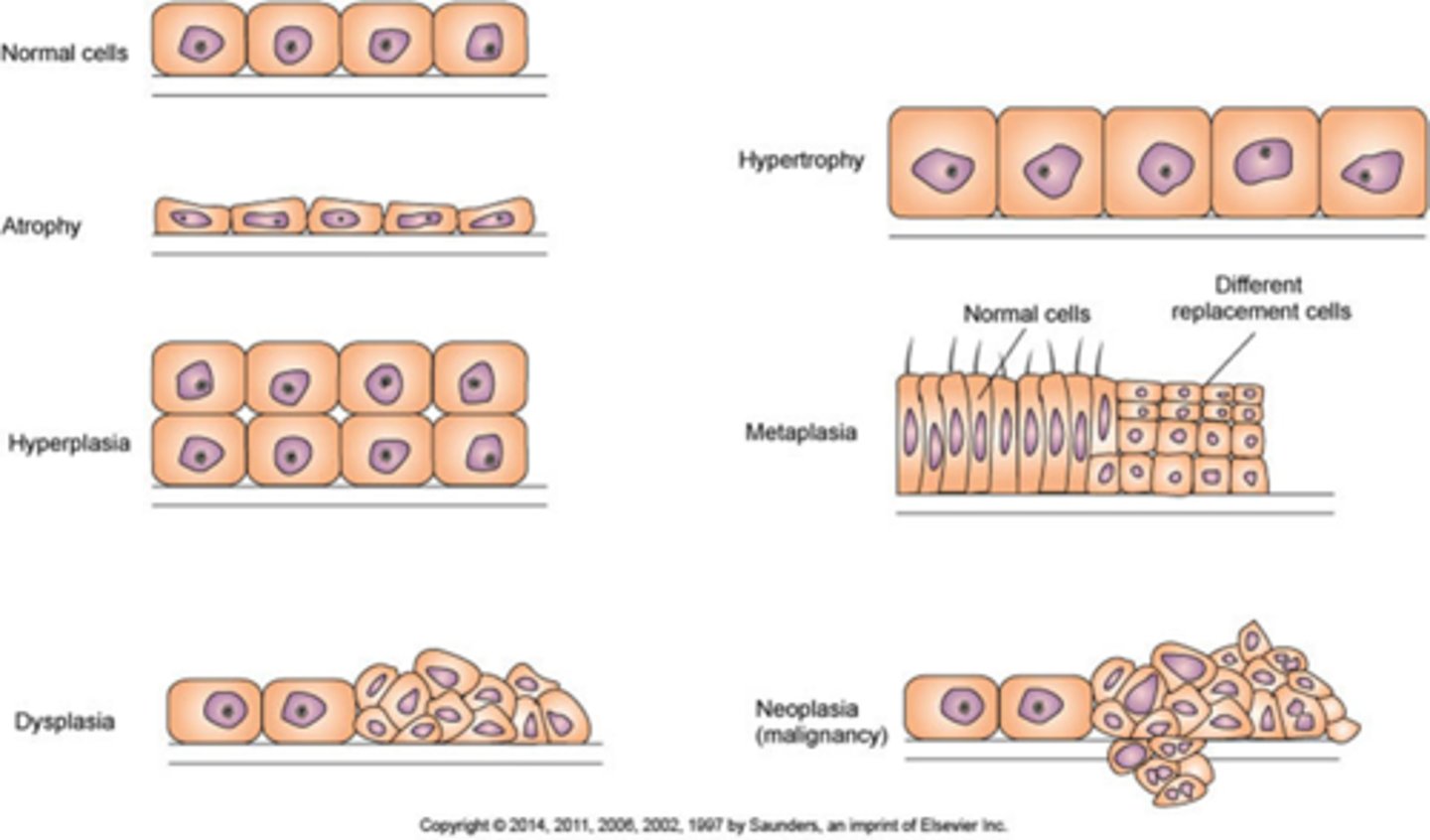
Atrophy
Decrease in size of cell
Decreases tissue mass
Hypertrophy
Increase size of cells
Increases tissue mass
Hyperplasia
Increase in number of cells
Increases tissue mass
Metaplasia
Mature cell type is replaced by a different mature cell type
Dysplasia
Cells vary in size and shape within a tissue
Neoplasia
“New growth” of cells—tumor
LOOK AT PIC FOR TEST
Hormones increasing blood pressure
Antidiuretic hormone (inc. BP)
Aldosterone (inc. bld volume, inc. BP)
Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone (vasoconstriction, inc. BP)
Meds for Hypertension
Diuretics
ACE inhibitors
Beta blockers
Calcium channel blockers Angiotensin Receptor Blockers Alpha adrenergic blockers
Cardiac Output (CO) =
HR x SV
Angina Pectoris
Occurs when there is a deficit of oxygen to meet myocardial needs
Dec. bld flow/ O2 supply to hrt
Heart works harder
Comb. of both
Chest pain may occur in diff. patterns
Classic or exertional
Variant
Variant Angina
Vasospasm occurs at rest
Unstable angina
Prolonged pain at rest, may precede to MI
Assessments seen in angina
Pallor, Diaphoresis (excessive sweating), Nausea, Chest pain or tightness in the chest, can radiate to neck or arm
Meds to give for angina
Coronary vasodilators
Nitroglycerin
Lab/Diagnostics for angina
12 lead EKG
Interventions for angina
Rest
Determine predisposing factors to attacks and minimize frequency
Emergency treatment for angina
Rest
Patient seated in upright position
Check pulse & respirations
Administer O2 if necessary
If patient has no history of angina give emergency aid after 2 min of pain
If pt. known to have angina give 2nd dose of NTG
Myocardial Infarction (MI)
Occurs when coronary artery is totally obstructed
Atherosclerosis most common cause
Thrombus from atheroma may obstruct artery
Vasospasm is caused in a small percentage
Size and location of the infarct determine severity of damage
(MI) If collateral circulation can develop before infarction
Size of the infarct can be reduced
(MI) Because lack of blood flow decreases contractility and conduction quickly; If blood flow is restored in 20-30 min
Irreversible damage can be prevented
Assessments for MI
Chest pain, pallor, diaphoresis, dizziness, dyspnea, marked anxiety and fear, hypotension, low-grade fever
Meds for MI pneumonic (M.O.N.O.B.A.S.H.)
•Morphine for pain relief
•Oxygen
•Nitrates --nitroglycerin
•Aspirin chew one and swallow one; use non-enteric coated
•Beta Blockers
•Ace Inhibitors
•Statin drugs
•Heparin
•Thrombolytic therapy
Labs/Diagnostics for MI
Serum Enzymes Troponin
Leukocytosis, elevated CRP and ESR
EKG
Congestive Heart Failure (CHF)
Heart is unable to pump out sufficient blood to meet metabolic demands of the body
Usually a complication of another cardiopulmonary condition
Can be the result of an infarction or valve defect
One side usually fails 1st depending on cause
Left-sided HF
Right-sided HF
Can progress to BOTH sides
Various compensation mechanisms maintain CO
Some aggravate condition
In congestive heart failure cardiac output or stroke volume decreases causing
Less blood reaches the various organs
Decreased cell function
Fatigue & lethargy
Mild acidosis develops
(CHF) Backup and congestion develop as coronary demands for oxygen and glucose are not met causing
Output from vent. is less than the inflow of bld
Congestion in venous circulation draining into the affected side
Left-sided CHF → Pulmonary congestion
Right-sided CHF → Systemic congestion, hepatomegaly, JVD, edema of legs and abdomen (ascites)
Nephrons
Functional units of the kidneys
Each kidney has over 1 million
Renal corpuscles
Glomerulus
Bowman capsule
Renal tubules
Proximal convoluted tubules
Loop of Henle
Distal convoluted tubules
Collecting duct
Filtration
In renal corpuscles
Large volume of fluid passes from glomerular capillaries into the tubule
Wastes, nutrients, electrolytes, other dissolved substances
Cells and protein remain in the blood
Reabsorption
Reabsorption of essential nutrients, water, and electrolytes into the peritubular capillaries
Control of pH and electrolytes
Proximal convoluted tubules
Most of water reabsorption
Glucose reabsorption
Nutrients and electrolytes to maintain homeostasis
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
Secreted by posterior pituitary
Reabsorption of water in distal convoluted tubules and collecting ducts
Aldosterone
Secreted by adrenal cortex
Sodium reabsorption in exchange for potassium or hydrogen
Dilation of AFFERENT arteriole
Increased pressure in glomerulus -increased filtrate
Vasoconstriction of AFFERENT arteriole
Decreased glomerular pressure -decreased filtrate
Vasoconstriction of EFFERENT arteriole
Increased glomerular pressure -increased filtrate
3 factors controlling arteriolar constriction
Autoregulation
Sympathetic Nervous System
Renin (R.A.A.S)
Autoregulation
Local adjustment in diameter of arterioles
Made in response to changes in blood flow in kidneys
Sympathetic nervous system
Increases vasoconstriction in both arterioles
Renin (R.A.A.S.)
Secreted by juxtaglomerular cells when blood flow to afferent arteriole is reduced
Renin-angiotensin mechanism
Pyelonephritis
Infection spreads from ureters to the kidney involving the renal pelvis and medullary tissue; one or both kidneys can be involved
Purulent exudate fills pelvis and calyces
Recurrent or chronic infection can lead to scar tissue formation.
Loss of tubule function
Obstruction and collection of filtrate → hydronephrosis
Eventual chronic renal failure if untreated
Assessment for pyelonephritis
Dysuria, dull aching pain in the lower back or flank area, fever, chills, N/V, malaise
Medications for pyelonephritis
Antibacterial drugs
Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (Bactrim, Septra, Cotrim)
Cephalosporins (Keflex)
Amoxicillin
Labs/Diagnostics test for pyelonephritis
Urinalysis
May show pyuria, bacteriuria, hematuria, and WBC’s
Urinary casts are present
Urinary casts
Indicate inflammation of renal tubules
Interventions for pyelonephritis
Increase water intake
Cranberry juice**tannin content appears to reduce the ability of E.Coli to adhere to mucosa
Urinary tract infections (UTIs)
Urine is an excellent growth medium; organisms grow in urine and can ascend to the urinary tract
Lower UTI causes
Cystitis
Urethritis
Upper UTI causes
Pyelonephritis- can occur from a blood stream infection
Common organism that causes a UTI
Escherichia coli
Who is at higher risk for a UTI?
Women, older adults, and children
Why are UTIs more common in women?
Shortness of urethra
Proximity to anus
Why are UTIs common in older men?
Prostatic hypertrophy
Urine retention
Why are UTIs common in children?
Congenital abnormalities
Common predisposing factors causing UTIs
Incontinence
Retention of urine
Decreased host resistance
Direct contamination with fecal material
Urolithiasis (Calculi)
Calculi (stones) can develop anywhere in urinary tract and lead to a decrease in flow of urine
Stones may be small or very large
Calculi tend to form with
Excessive amounts of solutes in filtrate
Insufficient fluid intake—major factor for calculi formation
Urinary tract infection-struvite stones
Calculi are composed of
Calcium salts
High urine calcium levels due to hypercalcemia
Form readily with highly alkaline urine
Uric acid
Hyperuricemia
Gout, high-purine diets, cancer chemotherapy
Especially with acidic urine
Assessment for urolithiasis
Manifestations only occur with obstruction of urine flow.
May lead to infection
Hydronephrosis with dilation of calyces
If located in kidney or ureter and atrophy of renal tissue
Stones in kidney or bladder often asymptomatic
Frequent infections may lead to investigation.
Flank pain possible caused by distention of renal capsule
Renal colic
Intense spasms of pain in flank area-distention of renal capsule
Radiating into groin area
Lasts until stone passes or is removed
Possible nausea and vomiting, cool moist skin, rapid pulse
Renal colic is caused by
obstruction of the ureter
Labs/Diagnostic tests for urolithiasis
CT Scan or ultrasound
Urinalysis-hematuria, crystalluria, urine pH, serum Ca+, uric acid, BUN, creat; 24 hour urine.
Treatment for urolithiasis
Strain urine to pass stones
Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL)
Laser lithotripsy
Drugs
Surgery
Increase fluid intake and changes to diet to adjust the urine pH
Treat underlying cause